Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy
et al., Thrombosis Research, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024, Jul 2020
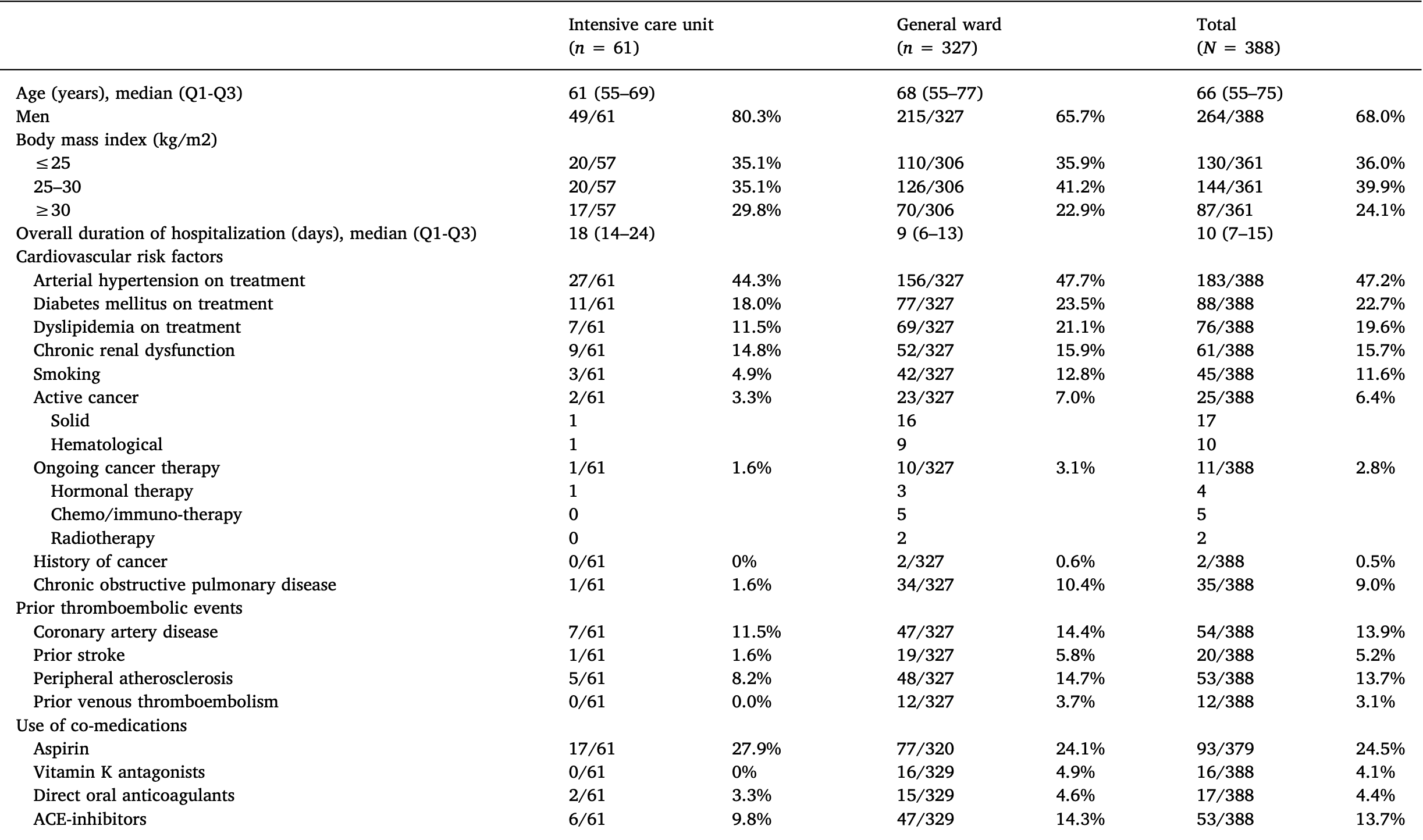
Retrospective 388 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Italy showing higher use of aspirin in ICU patients, without statistical significance.
|
risk of ICU admission, 20.8% higher, RR 1.21, p = 0.52, treatment 17 of 94 (18.1%), control 44 of 294 (15.0%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Lodigiani et al., 31 Jul 2020, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, median age 66.0, 12 authors, study period 13 February, 2020 - 10 April, 2020.
Contact: corrado.lodigiani@humanitas.it.
Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy
Thrombosis Research, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024
Background: Few data are available on the rate and characteristics of thromboembolic complications in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Methods: We studied consecutive symptomatic patients with laboratory-proven COVID-19 admitted to a university hospital in Milan, Italy (13.02.2020Italy (13.02. -10.04.2020)). The primary outcome was any thromboembolic complication, including venous thromboembolism (VTE), ischemic stroke, and acute coronary syndrome (ACS)/ myocardial infarction (MI). Secondary outcome was overt disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Results: We included 388 patients (median age 66 years, 68% men, 16% requiring intensive care [ICU]). Thromboprophylaxis was used in 100% of ICU patients and 75% of those on the general ward. Thromboembolic events occurred in 28 (7.7% of closed cases; 95%CI 5.4%-11.0%), corresponding to a cumulative rate of 21% (27.6% ICU, 6.6% general ward). Half of the thromboembolic events were diagnosed within 24 h of hospital admission. Forty-four patients underwent VTE imaging tests and VTE was confirmed in 16 (36%). Computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) was performed in 30 patients, corresponding to 7.7% of total, and pulmonary embolism was confirmed in 10 (33% of CTPA). The rate of ischemic stroke and ACS/MI was 2.5% and 1.1%, respectively. Overt DIC was present in 8 (2.2%) patients. Conclusions: The high number of arterial and, in particular, venous thromboembolic events diagnosed within 24 h of admission and the high rate of positive VTE imaging tests among the few COVID-19 patients tested suggest that there is an urgent need to improve specific VTE diagnostic strategies and investigate the efficacy and safety of thromboprophylaxis in ambulatory COVID-19 patients.
The analysis was restricted to closed cases. D-dimer levels are presented as median (Q1-Q3) and expressed in ng/mL. ICU, intensive care unit.
Table 3 Venous and arterial thromboembolic events in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
References
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Clerkin, Fried, Raikhelkar, Sayer, Griffin et al., Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and cardiovascular disease, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046941
Connors, Levy, Thromboinflammation and the hypercoagulability of COVID-19, J. Thromb. Haemost
Cui, Chen, Li, Liu, Wang, Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia, J. Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14830
Han, Yang, Liu, Liu, Wu et al., Prominent changes in blood coagulation of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Clin. Chem. Lab. Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2020-0188
Helms, Tacquard, Severac, Leonard-Lorant, Ohana et al., High risk of thrombosis in patients in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter prospective cohort study, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06062-x
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Kaplan, Casper, Elliott, Men, Pendleton et al., VTE incidence and risk factors in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock, Chest
Klok, Kruip, Van Der Meer, Arbous, Gommers et al., Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19, Thromb. Res, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013
Lang, Yang, Deng, Liu, Yang et al., Inhibition of SARS pseudovirus cell entry by lactoferrin binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans, PLoS One
Mycroft-West, The 2019 coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) surface protein (Spike) S1 Receptor Binding Domain undergoes conformational change upon heparin binding, doi:10.1101/2020.02.29.97109
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Med
Samama, Cohen, Darmon, Desjardins, Eldor et al., A comparison of enoxaparin with placebo for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in acutely ill medical patients. Prophylaxis in Medical Patients with Enoxaparin Study Group, N. Engl. J. Med
Schunemann, Cushman, Burnett, Kahn, Beyer-Westendorf et al., American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: prophylaxis for hospitalized and nonhospitalized medical patients, Blood Adv
Tang, Bai, Chen, Gong, Li et al., Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy, J. Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14817
Thachil, The versatile heparin in COVID-19, J. Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14821
Toh, Hoots, Sscodicot, The scoring system of the Scientific and Standardisation Committee on Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis: a 5-year overview, J. Thromb. Haemost
Varga, Flammer, Steiger, Haberecker, Andermatt et al., Endothelial Cell Infection and Endotheliitis in COVID-19
Zhang, Zhang, Mi, Wang, Zou et al., The cumulative venous thromboembolism incidence and risk factors in intensive care patients receiving the guideline-recommended thromboprophylaxis, Medicine (Baltimore)
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024",
"ISSN": [
"0049-3848"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024",
"alternative-id": [
"S0049384820301407"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Thrombosis Research"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lodigiani",
"given": "Corrado",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iapichino",
"given": "Giacomo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4646-2660",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Carenzo",
"given": "Luca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cecconi",
"given": "Maurizio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferrazzi",
"given": "Paola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0446-2862",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sebastian",
"given": "Tim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kucher",
"given": "Nils",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Studt",
"given": "Jan-Dirk",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sacco",
"given": "Clara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bertuzzi",
"given": "Alexia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sandri",
"given": "Maria Teresa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barco",
"given": "Stefano",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Thrombosis Research",
"container-title-short": "Thrombosis Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"thrombosisresearch.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
4,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2020-04-23T06:19:29Z",
"timestamp": 1587622769000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-25T09:38:34Z",
"timestamp": 1656149914000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002347",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100002347",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002347",
"award": [
"01EO1503",
"01EO1003"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100002347",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-22T02:13:28Z",
"timestamp": 1724292808278
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1570,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1593561600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0049384820301407?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0049384820301407?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "9-14",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0010",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China",
"author": "Ruan",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0015",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0188",
"article-title": "Prominent changes in blood coagulation of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin. Chem. Lab. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0025",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0030",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy",
"author": "Tang",
"journal-title": "J. Thromb. Haemost.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0035",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Varga",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0040",
"series-title": "Endothelial Cell Infection and Endotheliitis in COVID-19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and cardiovascular disease",
"author": "Clerkin",
"journal-title": "Circulation.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0045",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Klok",
"journal-title": "Thromb. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0050",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14830",
"article-title": "Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia",
"author": "Cui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Thromb. Haemost.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0055",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02313.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0060",
"unstructured": "Toh CH, Hoots WK, ISTH SSCoDICot. The scoring system of the Scientific and Standardisation Committee on Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis: a 5-year overview. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007;5(3):604–6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM199909093411103",
"article-title": "A comparison of enoxaparin with placebo for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in acutely ill medical patients. Prophylaxis in Medical Patients with Enoxaparin Study Group",
"author": "Samama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "793",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0065",
"volume": "341",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.15-0287",
"article-title": "VTE incidence and risk factors in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock",
"author": "Kaplan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1224",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Chest.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0070",
"volume": "148",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000015833",
"article-title": "The cumulative venous thromboembolism incidence and risk factors in intensive care patients receiving the guideline-recommended thromboprophylaxis",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltimore)",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0075",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06062-x",
"article-title": "High risk of thrombosis in patients in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter prospective cohort study",
"author": "Helms",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0080",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0085",
"unstructured": "Connors JM, Levy JH. Thromboinflammation and the hypercoagulability of COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/bloodadvances.2018022954",
"article-title": "American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: prophylaxis for hospitalized and nonhospitalized medical patients",
"author": "Schunemann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3198",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Blood Adv.",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0090",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0023710",
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS pseudovirus cell entry by lactoferrin binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans",
"author": "Lang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0095",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0100",
"unstructured": "Mycroft-West C et al. The 2019 coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) surface protein (Spike) S1 Receptor Binding Domain undergoes conformational change upon heparin binding. bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.29.97109."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14821",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024_bb0105",
"unstructured": "Thachil J. The versatile heparin in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.14821."
}
],
"reference-count": 20,
"references-count": 20,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0049384820301407"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"special_numbering": "C",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "191"
}