Diverse roles of SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Nucleocapsid proteins in EndMT stimulation through the TGF-β-MRTF axis inhibited by aspirin
et al., Cell Communication and Signaling, doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01665-z, May 2024
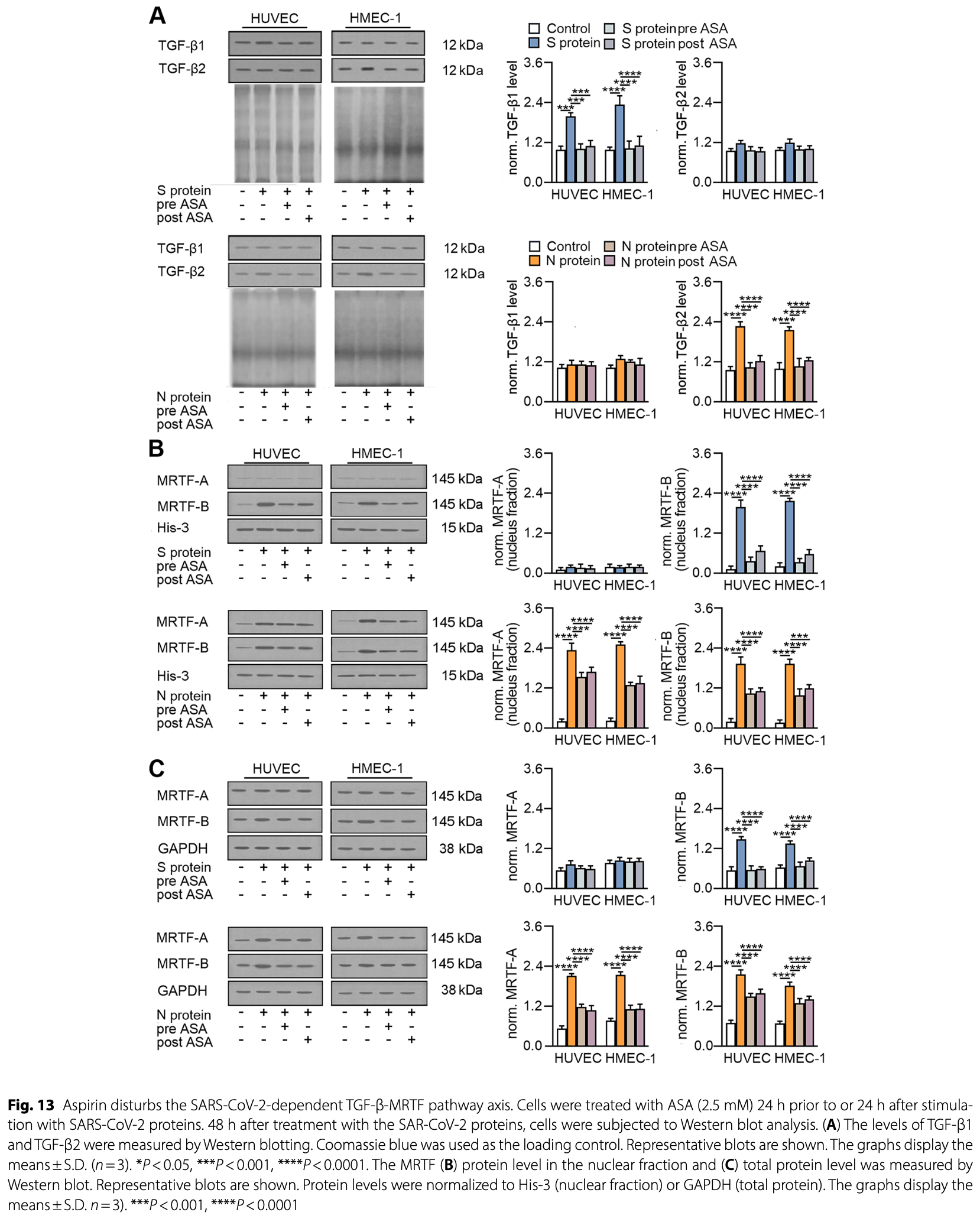
In vitro study showing that SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins induce endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) in endothelial cells, with the nucleocapsid protein having a more potent effect. The spike protein stimulates TGF-β1 secretion through ACE2 downregulation, while the nucleocapsid protein stimulates TGF-β2 secretion through the TLR4-ROS pathway. TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 then induce EndMT through MRTF-B and MRTF-A/B nuclear translocation, respectively. Authors find that aspirin inhibits and reverses the SARS-CoV-2 protein-induced EndMT by blocking TGF-β secretion and MRTF nuclear translocation. The results suggest that aspirin may reduce the risk of COVID-19-associated fibrosis.
4 preclinical studies support the efficacy of aspirin for COVID-19:
1.
Eissa et al., Identification of Potential FDA-Approved Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Helicase Through a Multistep In Silico Approach: A Promising Prospect for COVID-19 Treatment, Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.2174/0115734064318640241112071225.
2.
Perico et al., Acetylsalicylic acid disrupts SARS-CoV-2 spike protein glycosylation and selectively impairs binding to ACE2, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2025.1706997.
Ciszewski et al., 28 May 2024, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: katarzyna.sobierajska@umed.lodz.pl.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Diverse roles of SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Nucleocapsid proteins in EndMT stimulation through the TGF-β-MRTF axis inhibited by aspirin
Cell Communication and Signaling, doi:10.1186/s12964-024-01665-z
Background The SARS-CoV-2 virus causes severe COVID-19 in one-fifth of patients. In addition to high mortality, infection may induce respiratory failure and cardiovascular complications associated with inflammation. Acute or prolonged inflammation results in organ fibrosis, the cause of which might be endothelial disorders arising during the endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT). Methods HUVECs and HMEC-1 cells were stimulated with SARS-CoV-2 S (Spike) and N (Nucleocapsid) proteins, and EndMT induction was evaluated by studying specific protein markers via Western blotting. Wound healing and tube formation assays were employed to assess the potential of SARS-CoV-2 to stimulate changes in cell behaviour. MRTF nuclear translocation, ROS generation, TLR4 inhibitors, TGF-β-neutralizing antibodies, and inhibitors of the TGF-βdependent pathway were used to investigate the role of the TGF-β-MRTF signalling axis in SARS-CoV-2-dependent EndMT stimulation.
Results Both viral proteins stimulate myofibroblast trans-differentiation. However, the N protein is more effective at EndMT induction. The TGF-β-MRTF pathway plays a critical role in this process. The N protein preferentially favours action through TGF-β2, whose secretion is induced through TLR4-ROS action. TGF-β2 stimulates MRTF-A and MRTF-B nuclear translocation and strongly regulates EndMT. In contrast, the Spike protein stimulates TGF-β1 secretion as a result of ACE2 downregulation. TGF-β1 induces only MRTF-B, which, in turn, weakly regulates EndMT. Furthermore, aspirin, a common nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, might prevent and reverse SARS-CoV-2-dependent EndMT induction through TGF-β-MRTF pathway deregulation.
Conclusion The reported study revealed that SARS-CoV-2 infection induces EndMT. Moreover, it was demonstrated for the first time at the molecular level that the intensity of the EndMT triggered by SARS-CoV-2 infection may vary and depend on the viral protein involved. The N protein acts through TLR4-ROS-TGF-β2-MRTF-A/B, whereas the S protein acts through ACE2-TGF-β1-MRTF-B. Furthermore, we identified aspirin as a potential anti-fibrotic drug for treating patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi. org/10.1186/s12964-024-01665-z.
Supplementary Material 1 Author contributions WMC conducted the research, analysed and interpreted the data, and wrote the original manuscript. LAW analysed and interpreted the data, and made corrections to the original manuscript. KS designed the research, designed the experiments, analysed and interpreted the data, and contributed to writing the original manuscript.
Declarations Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Aboudounya, Heads, COVID-19 and Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4): SARS-CoV-2 May Bind and Activate TLR4 to Increase ACE2 Expression, Facilitating Entry and Causing Hyperinflammation, Mediators Inflamm
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Haverich, Welte et al., Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Ali, Ibrahim, Burzangi, Ghoneim, Aljohani et al., Scoping insight on antiviral drugs against COVID-19, Arab J Chem
Bai, Cao, Liu, Li, The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and its role in viral structure, Biological functions, and a potential target for drug or vaccine mitigation, Viruses
Batra, Tian, Zhang, Sacher, Miranda et al., Role of IgG against N-protein of SARS-CoV2 in COVID19 clinical outcomes, Sci Rep
Beyerstedt, Casaro, Rangel, COVID-19: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis
Bhattacharya, Sharma, Mallick, Sharma, Lee et al., Immunoinformatics approach to understand molecular interaction between multi-epitopic regions of SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein with TLR4/MD-2 complex, Infect Genet Evol
Castelli, Cimini, Ferri, Cytokine storm in COVID-19: when you come out of the storm, you won't be the same person who walked in, Front Immunol
Chen, Guan, Qiu, Xu, Bai et al., SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein triggers hyperinflammation via protein-protein interaction-mediated intracellular Cl(-) accumulation in respiratory epithelium, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Chou, Chuang, Lu, Guh, Interaction between TGF-beta and ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas pathway in high glucose-cultured NRK-52E cells, Mol Cell Endocrinol
Ciszewski, Chmielewska-Kassassir, Wozniak, Sobierajska, Thymidylate synthase overexpression drives the invasive phenotype in Colon cancer cells, Biomedicines
Ciszewski, Wawro, Sacewicz-Hofman, Sobierajska, Cytoskeleton reorganization in EndMT-The role in Cancer and Fibrotic diseases, Int J Mol Sci
Ciszewski, Wozniak, Sobierajska, SARS-CoV-2 S and N protein peptides drive invasion abilities of colon cancer cells through TGF-beta1 regulation, Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res
Clere, Renault, Corre, Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in Cancer, Front Cell Dev Biol
Cocconcelli, Bernardinello, Giraudo, Castelli, Giorgino et al., Characteristics and prognostic factors of Pulmonary Fibrosis after COVID-19 Pneumonia, Front Med
Dejana, Hirschi, Simons, The molecular basis of endothelial cell plasticity, Nat Commun
Eapen, Lu, Gaikwad, Bhattarai, Chia et al., Endothelial to mesenchymal transition: a precursor to post-COVID-19 interstitial pulmonary fibrosis and vascular obliteration?, Eur Respir J
El-Shabasy, Nayel, Taher, Abdelmonem, Shoueir et al., Three waves changes, new variant strains, and vaccination effect against COVID-19 pandemic, Int J Biol Macromol
Fathizadeh, Afshar, Masoudi, Gholizadeh, Asgharzadeh et al., SARS-CoV-2 (Covid-19) vaccines structure, mechanisms and effectiveness: a review, Int J Biol Macromol
Ferreira-Gomes, Kruglov, Durek, Heinrich, Tizian et al., SARS-CoV-2 in severe COVID-19 induces a TGF-beta-dominated chronic immune response that does not target itself, Nat Commun
Gal, Brabek, Holub, Jakubek, Sedo et al., Autoimmunity, cancer and COVID-19 abnormally activate wound healing pathways: critical role of inflammation, Histochem Cell Biol
George, Wells, Jenkins, Pulmonary fibrosis and COVID-19: the potential role for antifibrotic therapy, Lancet Respir Med
Hamming, Timens, Bulthuis, Lely, Navis et al., Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis, J Pathol
Henderson, Rieder, Wynn, Fibrosis: from mechanisms to medicines, Nature
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Kruger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Huang, Yang, Xu, Xu, Liu, Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19, Acta Pharmacol Sin
Imig, SARS-CoV-2 spike protein causes cardiovascular disease independent of viral infection, Clin Sci (Lond)
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol
Jansen, Reimer, Nagai, Varghese, Overheul et al., SARS-CoV-2 infects the human kidney and drives fibrosis in kidney organoids, Cell Stem Cell
Khan, Shafiei, Longoria, Schoggins, Savani et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-kappaB pathway, Elife
Khanmohammadi, Rezaei, Role of toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of COVID-19, J Med Virol
Kolesova, Vanaga, Laivacuma, Derovs, Kolesovs et al., Intriguing findings of liver fibrosis following COVID-19, BMC Gastroenterol
Kow, Hasan, Use of antiplatelet drugs and the risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, J Thromb Thrombolysis
Kushner, Mccarberg, Grange, Kolosov, Haveric et al., The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in COVID-19, NPJ Prim Care Respir Med
Lee, Ko, Sy, Differential expression patterns of toll-like receptors in COVID-19 patients, Front Biosci
Lei, Zhang, Schiavon, He, Chen et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein impairs endothelial function via downregulation of ACE 2, Circ Res
Li, Wang, Wang, Li, Zhang et al., Serum SARS-COV-2 nucleocapsid protein: a sensitivity and specificity early diagnostic marker for SARS-COV-2 infection, Front Cell Infect Microbiol
Liu, Huang, Chen, Penninger, Lan, Loss of angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 enhances TGF-beta/Smad-mediated renal fibrosis and NF-kappaB-driven renal inflammation in a mouse model of obstructive nephropathy, Lab Invest
Ma, Sanchez-Duffhues, Goumans, Dijke, TGF-beta-Induced endothelial to mesenchymal transition in Disease and tissue Engineering, Front Cell Dev Biol
Merad, Blish, Sallusto, Iwasaki, The immunology and immunopathology of COVID-19, Science
Montazersaheb, Khatibi, Hejazi, Tarhriz, Farjami et al., COVID-19 infection: an overview on cytokine storm and related interventions, Virol J
Moretti, Stalfort, Barker, Abebayehu, The interplay of fibroblasts, the extracellular matrix, and inflammation in scar formation, J Biol Chem
Mothes, Pascual-Reguant, Koehler, Liebeskind, Liebheit et al., Distinct tissue niches direct lung immunopathology via CCL18 and CCL21 in severe COVID-19, Nat Commun
Mustroph, Hupf, Baier, Evert, Brochhausen et al., Cardiac Fibrosis is a risk factor for severe COVID-19, Front Immunol
Osborne, Veigulis, Arreola, Mahajan, Roosli et al., Association of mortality and aspirin prescription for COVID-19 patients at the Veterans Health Administration, PLoS ONE
Pardali, Sanchez-Duffhues, Mc, Dijke, TGF-beta-Induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition in Fibrotic diseases, Int J Mol Sci
Park, Epidemiology, virology, and clinical features of severe acute respiratory syndrome -coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus Disease-19), Clin Exp Pediatr
Perna, Bruzzaniti, Piemonte, Maddaloni, Atripaldi et al., Serum levels of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen associate with inflammatory status and disease severity in COVID-19 patients, Clin Immunol
Pi, Zhang, Li, Guo, Cao et al., Inhibition of reactive oxygen species generation attenuates TLR4-mediated proinflammatory and proliferative phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells, Lab Invest
Piera-Velazquez, Jimenez, Endothelial to mesenchymal transition: role in physiology and in the Pathogenesis of Human diseases, Physiol Rev
Poloni, Moretti, Medici, Turturici, Belli et al., COVID-19 Pathology in the Lung, Kidney, Heart and Brain: The Different Roles of T-Cells, Macrophages, and Microthrombosis, Cells
Qian, Lei, Patel, Lee, Monaghan-Nichols et al., Direct activation of endothelial cells by SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is blocked by Simvastatin, J Virol
Robb, Goepp, Rossi, Yao, Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins, and COVID-19, Br J Pharmacol
Russell, Moss, Rigg, Van Hemelrijck, COVID-19 and treatment with NSAIDs and corticosteroids: should we be limiting their use in the clinical setting?, Ecancermedicalscience
Shen, Luo, Wang, Chen, Features of Cytokine Storm identified by distinguishing clinical manifestations in COVID-19, Front Public Health
Smadja, Mentzer, Fontenay, Laffan, Ackermann et al., COVID-19 is a systemic vascular hemopathy: insight for mechanistic and clinical aspects, Angiogenesis
Sobierajska, Ciszewski, Macierzynska-Piotrowska, Klopocka, Przygodzka et al., The New Model of snail expression regulation: the role of MRTFs in fast and slow endothelialmesenchymal transition, Int J Mol Sci
Sobierajska, Wawro, Ciszewski, Niewiarowska, Transforming growth factor-beta receptor internalization via Caveolae is regulated by Tubulin-beta2 and Tubulin-beta3 during endothelial-mesenchymal transition, Am J Pathol
Sobierajska, Wawro, Niewiarowska, Oxidative stress enhances the TGF-beta2-RhoA-MRTF-A/B Axis in cells entering endothelial-mesenchymal transition, Int J Mol Sci
Sun, Liu, Xie, Jiang, Xiao et al., Aspirin attenuates liver fibrosis by suppressing TGF-beta1/Smad signaling, Mol Med Rep
Takamatsu, Oshiro, Mizutani, Tada, Tabe et al., Correlation of COVID-19 Severity and Immunoglobulin Presence against Spike and Nucleocapsid Proteins in SARS-CoV-2, Viral Immunol
Tang, Lk, Lee, Gao, Xia et al., Smad3 initiates oxidative stress and proteolysis that underlies diaphragm dysfunction during mechanical ventilation, Sci Rep
Tawadros, Powers, Ailenberg, Birch, Marshall et al., Oxidative stress increases Surface Toll-Like receptor 4 expression in Murine macrophages Via Ceramide Generation, Shock
Varga, Flammer, Steiger, Haberecker, Andermatt et al., Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19, Lancet
Wawro, Sobierajska, Ciszewski, Niewiarowska, Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs prevent Vincristine-Dependent Cancer-Associated fibroblasts formation, Int J Mol Sci
Wu, Cheng, Zhou, Sun, Zhang, The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein: its role in the viral life cycle, structure and functions, and use as a potential target in the development of vaccines and diagnostics, Virol J
Yadav, Chowdhury, Effectivity of repurposed drugs against SARS-CoV-2 infections, a hope for COVID 19: inhibitor modelling studies docking and molecular dynamics, Heliyon
Yu, Nie, Wang, Yin, Huang et al., Toll-like receptor 4-mediated ROS signaling pathway involved in Ganoderma Atrum polysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion during macrophage activation, Food Chem Toxicol
Zhang, Li, Deng, Yang, Xiang et al., Aspirin inhibits endometrial fibrosis by suppressing the TGF-beta1-Smad2/Smad3 pathway in intrauterine adhesions, Int J Mol Med
Zhang, Ong, Yun, Mo, Whitman et al., Diagnostic Value of Nucleocapsid Protein in blood for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Clin Chem
Zhang, Tang, Zhang, Tong, Xie et al., Single cell meta-analysis of EndMT and EMT state in COVID-19, Front Immunol
Zhao, Kuang, Li, Zhu, Jia et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interacts with and activates TLR41, Cell Res
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12964-024-01665-z",
"ISSN": [
"1478-811X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12964-024-01665-z",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The SARS-CoV-2 virus causes severe COVID-19 in one-fifth of patients. In addition to high mortality, infection may induce respiratory failure and cardiovascular complications associated with inflammation. Acute or prolonged inflammation results in organ fibrosis, the cause of which might be endothelial disorders arising during the endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>HUVECs and HMEC-1 cells were stimulated with SARS-CoV-2 S (Spike) and N (Nucleocapsid) proteins, and EndMT induction was evaluated by studying specific protein markers via Western blotting. Wound healing and tube formation assays were employed to assess the potential of SARS-CoV-2 to stimulate changes in cell behaviour. MRTF nuclear translocation, ROS generation, TLR4 inhibitors, TGF-β-neutralizing antibodies, and inhibitors of the TGF-β-dependent pathway were used to investigate the role of the TGF-β-MRTF signalling axis in SARS-CoV-2-dependent EndMT stimulation.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Both viral proteins stimulate myofibroblast trans-differentiation. However, the N protein is more effective at EndMT induction. The TGF-β-MRTF pathway plays a critical role in this process. The N protein preferentially favours action through TGF-β2, whose secretion is induced through TLR4-ROS action. TGF-β2 stimulates MRTF-A and MRTF-B nuclear translocation and strongly regulates EndMT. In contrast, the Spike protein stimulates TGF-β1 secretion as a result of ACE2 downregulation. TGF-β1 induces only MRTF-B, which, in turn, weakly regulates EndMT. Furthermore, aspirin, a common nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, might prevent and reverse SARS-CoV-2-dependent EndMT induction through TGF-β-MRTF pathway deregulation.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The reported study revealed that SARS-CoV-2 infection induces EndMT. Moreover, it was demonstrated for the first time at the molecular level that the intensity of the EndMT triggered by SARS-CoV-2 infection may vary and depend on the viral protein involved. The N protein acts through TLR4-ROS-TGF-β2-MRTF-A/B, whereas the S protein acts through ACE2-TGF-β1-MRTF-B. Furthermore, we identified aspirin as a potential anti-fibrotic drug for treating patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"1665"
],
"article-number": "296",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "11 March 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "15 May 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "28 May 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ciszewski",
"given": "Wojciech M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woźniak",
"given": "Lucyna A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sobierajska",
"given": "Katarzyna",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cell Communication and Signaling",
"container-title-short": "Cell Commun Signal",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-28T15:08:55Z",
"timestamp": 1716908935000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-28T15:09:37Z",
"timestamp": 1716908977000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004281",
"award": [
"2017/01/X/NZ7/00499",
"2017/01/X/NZ7/00499"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Narodowe Centrum Nauki"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-28T17:40:18Z",
"timestamp": 1716918018065
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
28
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1716854400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1716854400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12964-024-01665-z.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12964-024-01665-z/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12964-024-01665-z.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
28
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
28
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3345/cep.2020.00493",
"author": "SE Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Pediatr",
"key": "1665_CR1",
"unstructured": "Park SE. Epidemiology, virology, and clinical features of severe acute respiratory syndrome -coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus Disease-19). Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63:119–24.",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "1665_CR2",
"unstructured": "WorldHealthOrganization. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV): situation report, 22. World Health Organization. 2022, https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/330991."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.076",
"author": "H Fathizadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "740",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Macromol",
"key": "1665_CR3",
"unstructured": "Fathizadeh H, Afshar S, Masoudi MR, Gholizadeh P, Asgharzadeh M, Ganbarov K, Kose S, Yousefi M, Kafil HS. SARS-CoV-2 (Covid-19) vaccines structure, mechanisms and effectiveness: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;188:740–50.",
"volume": "188",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.118",
"author": "RM El-Shabasy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "161",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Macromol",
"key": "1665_CR4",
"unstructured": "El-Shabasy RM, Nayel MA, Taher MM, Abdelmonem R, Shoueir KR, Kenawy ER. Three waves changes, new variant strains, and vaccination effect against COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;204:161–8.",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abm8108",
"author": "M Merad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1122",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "1665_CR5",
"unstructured": "Merad M, Blish CA, Sallusto F, Iwasaki A. The immunology and immunopathology of COVID-19. Science. 2022;375:1122–7.",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-022-01814-1",
"author": "S Montazersaheb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "92",
"journal-title": "Virol J",
"key": "1665_CR6",
"unstructured": "Montazersaheb S, Hosseiniyan Khatibi SM, Hejazi MS, Tarhriz V, Farjami A, Ghasemian Sorbeni F, Farahzadi R, Ghasemnejad T. COVID-19 infection: an overview on cytokine storm and related interventions. Virol J. 2022;19:92.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.823600",
"author": "E Cocconcelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "823600",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "1665_CR7",
"unstructured": "Cocconcelli E, Bernardinello N, Giraudo C, Castelli G, Giorgino A, Leoni D, Petrarulo S, Ferrari A, Saetta M, Cattelan A, et al. Characteristics and prognostic factors of Pulmonary Fibrosis after COVID-19 Pneumonia. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:823600.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11193124",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR8",
"unstructured": "Poloni TE, Moretti M, Medici V, Turturici E, Belli G, Cavriani E, Visona SD, Rossi M, Fantini V, Ferrari RR et al. COVID-19 Pathology in the Lung, Kidney, Heart and Brain: The Different Roles of T-Cells, Macrophages, and Microthrombosis. Cells 2022, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10456-021-09805-6",
"author": "DM Smadja",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "755",
"journal-title": "Angiogenesis",
"key": "1665_CR9",
"unstructured": "Smadja DM, Mentzer SJ, Fontenay M, Laffan MA, Ackermann M, Helms J, Jonigk D, Chocron R, Pier GB, Gendron N, et al. COVID-19 is a systemic vascular hemopathy: insight for mechanistic and clinical aspects. Angiogenesis. 2021;24:755–88.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms14361",
"author": "E Dejana",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14361",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "1665_CR10",
"unstructured": "Dejana E, Hirschi KK, Simons M. The molecular basis of endothelial cell plasticity. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14361.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00021.2018",
"author": "S Piera-Velazquez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1281",
"journal-title": "Physiol Rev",
"key": "1665_CR11",
"unstructured": "Piera-Velazquez S, Jimenez SA. Endothelial to mesenchymal transition: role in physiology and in the Pathogenesis of Human diseases. Physiol Rev. 2019;99:1281–324.",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101530",
"author": "L Moretti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101530",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "1665_CR12",
"unstructured": "Moretti L, Stalfort J, Barker TH, Abebayehu D. The interplay of fibroblasts, the extracellular matrix, and inflammation in scar formation. J Biol Chem. 2022;298:101530.",
"volume": "298",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2020.00747",
"author": "N Clere",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "747",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Dev Biol",
"key": "1665_CR13",
"unstructured": "Clere N, Renault S, Corre I. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in Cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:747.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.03167-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR14",
"unstructured": "Eapen MS, Lu W, Gaikwad AV, Bhattarai P, Chia C, Hardikar A, Haug G, Sohal SS. Endothelial to mesenchymal transition: a precursor to post-COVID-19 interstitial pulmonary fibrosis and vascular obliteration? Eur Respir J 2020, 56."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00418-022-02140-x",
"author": "P Gal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "415",
"journal-title": "Histochem Cell Biol",
"key": "1665_CR15",
"unstructured": "Gal P, Brabek J, Holub M, Jakubek M, Sedo A, Lacina L, Strnadova K, Dubovy P, Hornychova H, Ryska A, Smetana K Jr. Autoimmunity, cancer and COVID-19 abnormally activate wound healing pathways: critical role of inflammation. Histochem Cell Biol. 2022;158:415–34.",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.976512",
"author": "L Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "976512",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "1665_CR16",
"unstructured": "Zhang L, Tang C, Zhang M, Tong X, Xie Y, Yan R, Wang X, Zhang X, Liu D, Li S. Single cell meta-analysis of EndMT and EMT state in COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2022;13:976512.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6",
"author": "S Beyerstedt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis",
"key": "1665_CR17",
"unstructured": "Beyerstedt S, Casaro EB, Rangel EB. COVID-19: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021;40:905–19.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"author": "CB Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol",
"key": "1665_CR18",
"unstructured": "Jackson CB, Farzan M, Chen B, Choe H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23:3–20.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms18102157",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR19",
"unstructured": "Pardali E, Sanchez-Duffhues G, Gomez-Puerto MC, Ten Dijke P. TGF-beta-Induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition in Fibrotic diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2020.00260",
"author": "J Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "260",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Dev Biol",
"key": "1665_CR20",
"unstructured": "Ma J, Sanchez-Duffhues G, Goumans MJ, Ten Dijke P. TGF-beta-Induced endothelial to mesenchymal transition in Disease and tissue Engineering. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:260.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12327",
"author": "P Yadav",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e12327",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "1665_CR21",
"unstructured": "Yadav P, Chowdhury P. Effectivity of repurposed drugs against SARS-CoV-2 infections, a hope for COVID 19: inhibitor modelling studies by docking and molecular dynamics. Heliyon. 2022;8:e12327.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103385",
"author": "AS Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103385",
"journal-title": "Arab J Chem",
"key": "1665_CR22",
"unstructured": "Ali AS, Ibrahim IM, Burzangi AS, Ghoneim RH, Aljohani HS, Alsamhan HA, Barakat J. Scoping insight on antiviral drugs against COVID-19. Arab J Chem. 2021;14:103385.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.08.004",
"author": "K Sobierajska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2531",
"journal-title": "Am J Pathol",
"key": "1665_CR23",
"unstructured": "Sobierajska K, Wawro ME, Ciszewski WM, Niewiarowska J. Transforming growth factor-beta receptor internalization via Caveolae is regulated by Tubulin-beta2 and Tubulin-beta3 during endothelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Pathol. 2019;189:2531–46.",
"volume": "189",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21165875",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR24",
"unstructured": "Sobierajska K, Ciszewski WM, Macierzynska-Piotrowska E, Klopocka W, Przygodzka P, Karakula M, Pestka K, Wawro ME, Niewiarowska J. The New Model of snail expression regulation: the role of MRTFs in fast and slow endothelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10061267",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR25",
"unstructured": "Ciszewski WM, Chmielewska-Kassassir M, Wozniak LA, Sobierajska K. Thymidylate synthase overexpression drives the invasive phenotype in Colon cancer cells. Biomedicines 2022, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/8874339",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR26",
"unstructured": "Aboudounya MM, Heads RJ. COVID-19 and Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4): SARS-CoV-2 May Bind and Activate TLR4 to Increase ACE2 Expression, Facilitating Entry and Causing Hyperinflammation. Mediators Inflamm 2021, 2021:8874339."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fct.2014.01.018",
"author": "Q Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Food Chem Toxicol",
"key": "1665_CR27",
"unstructured": "Yu Q, Nie SP, Wang JQ, Yin PF, Huang DF, Li WJ, Xie MY. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated ROS signaling pathway involved in Ganoderma Atrum polysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion during macrophage activation. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014;66:14–22.",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms222111607",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR28",
"unstructured": "Ciszewski WM, Wawro ME, Sacewicz-Hofman I, Sobierajska K. Cytoskeleton reorganization in EndMT-The role in Cancer and Fibrotic diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20081941",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR29",
"unstructured": "Wawro ME, Sobierajska K, Ciszewski WM, Niewiarowska J. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs prevent Vincristine-Dependent Cancer-Associated fibroblasts formation. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.02132",
"author": "V Castelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2132",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "1665_CR30",
"unstructured": "Castelli V, Cimini A, Ferri C. Cytokine storm in COVID-19: when you come out of the storm, you won’t be the same person who walked in. Front Immunol. 2020;11:2132.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30225-3",
"author": "PM George",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "807",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "1665_CR31",
"unstructured": "George PM, Wells AU, Jenkins RG. Pulmonary fibrosis and COVID-19: the potential role for antifibrotic therapy. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:807–15.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2021.12.010",
"author": "J Jansen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "217",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "1665_CR32",
"unstructured": "Jansen J, Reimer KC, Nagai JS, Varghese FS, Overheul GJ, de Beer M, Roverts R, Daviran D, Fermin LAS, Willemsen B, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects the human kidney and drives fibrosis in kidney organoids. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29:217–e231218.",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.740260",
"author": "J Mustroph",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "740260",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "1665_CR33",
"unstructured": "Mustroph J, Hupf J, Baier MJ, Evert K, Brochhausen C, Broeker K, Meindl C, Seither B, Jungbauer C, Evert M, et al. Cardiac Fibrosis is a risk factor for severe COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2021;12:740260.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12876-021-01939-7",
"author": "O Kolesova",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "370",
"journal-title": "BMC Gastroenterol",
"key": "1665_CR34",
"unstructured": "Kolesova O, Vanaga I, Laivacuma S, Derovs A, Kolesovs A, Radzina M, Platkajis A, Eglite J, Hagina E, Arutjunana S, et al. Intriguing findings of liver fibrosis following COVID-19. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021;21:370.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2938-9",
"author": "NC Henderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "555",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "1665_CR35",
"unstructured": "Henderson NC, Rieder F, Wynn TA. Fibrosis: from mechanisms to medicines. Nature. 2020;587:555–66.",
"volume": "587",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"author": "M Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "1665_CR36",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Kruger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH, Nitsche A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–e280278.",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41401-020-0485-4",
"author": "Y Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1141",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmacol Sin",
"key": "1665_CR37",
"unstructured": "Huang Y, Yang C, Xu XF, Xu W, Liu SW. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41:1141–9.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-023-01968-6",
"author": "W Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "Virol J",
"key": "1665_CR38",
"unstructured": "Wu W, Cheng Y, Zhou H, Sun C, Zhang S. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein: its role in the viral life cycle, structure and functions, and use as a potential target in the development of vaccines and diagnostics. Virol J. 2023;20:6.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.68563",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR39",
"unstructured": "Khan S, Shafiei MS, Longoria C, Schoggins JW, Savani RC, Zaki H. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-kappaB pathway. Elife 2021, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20220028",
"author": "JD Imig",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "431",
"journal-title": "Clin Sci (Lond)",
"key": "1665_CR40",
"unstructured": "Imig JD. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein causes cardiovascular disease independent of viral infection. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022;136:431–4.",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/clinchem/hvab148",
"author": "Y Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "240",
"journal-title": "Clin Chem",
"key": "1665_CR41",
"unstructured": "Zhang Y, Ong CM, Yun C, Mo W, Whitman JD, Lynch KL, Wu AHB. Diagnostic Value of Nucleocapsid Protein in blood for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin Chem. 2021;68:240–8.",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-36333-2",
"author": "R Mothes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "791",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "1665_CR42",
"unstructured": "Mothes R, Pascual-Reguant A, Koehler R, Liebeskind J, Liebheit A, Bauherr S, Philipsen L, Dittmayer C, Laue M, von Manitius R, et al. Distinct tissue niches direct lung immunopathology via CCL18 and CCL21 in severe COVID-19. Nat Commun. 2023;14:791.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015432",
"author": "M Ackermann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "120",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1665_CR43",
"unstructured": "Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, Haverich A, Welte T, Laenger F, Vanstapel A, Werlein C, Stark H, Tzankov A, et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:120–8.",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30937-5",
"author": "Z Varga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1417",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "1665_CR44",
"unstructured": "Varga Z, Flammer AJ, Steiger P, Haberecker M, Andermatt R, Zinkernagel AS, Mehra MR, Schuepbach RA, Ruschitzka F, Moch H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet. 2020;395:1417–8.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13061115",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR45",
"unstructured": "Bai Z, Cao Y, Liu W, Li J. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and its role in viral structure, Biological functions, and a potential target for drug or vaccine mitigation. Viruses 2021, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22210-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR46",
"unstructured": "Ferreira-Gomes M, Kruglov A, Durek P, Heinrich F, Tizian C, Heinz GA, Pascual-Reguant A, Du W, Mothes R, Fan C et al. SARS-CoV-2 in severe COVID-19 induces a TGF-beta-dominated chronic immune response that does not target itself. Nat Commun 2021, 12:1961."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.671788",
"author": "WX Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "671788",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "1665_CR47",
"unstructured": "Shen WX, Luo RC, Wang JQ, Chen ZS. Features of Cytokine Storm identified by distinguishing clinical manifestations in COVID-19. Front Public Health. 2021;9:671788.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2023.119541",
"author": "WM Ciszewski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119541",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res",
"key": "1665_CR48",
"unstructured": "Ciszewski WM, Wozniak LA, Sobierajska K. SARS-CoV-2 S and N protein peptides drive invasion abilities of colon cancer cells through TGF-beta1 regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2023;1870:119541.",
"volume": "1870",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.1570",
"author": "I Hamming",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "631",
"journal-title": "J Pathol",
"key": "1665_CR49",
"unstructured": "Hamming I, Timens W, Bulthuis ML, Lely AT, Navis G, van Goor H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J Pathol. 2004;203:631–7.",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318902",
"author": "Y Lei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1323",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "1665_CR50",
"unstructured": "Lei Y, Zhang J, Schiavon CR, He M, Chen L, Shen H, Zhang Y, Yin Q, Cho Y, Andrade L, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein impairs endothelial function via downregulation of ACE 2. Circ Res. 2021;128:1323–6.",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/labinvest.2012.2",
"author": "Z Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "650",
"journal-title": "Lab Invest",
"key": "1665_CR51",
"unstructured": "Liu Z, Huang XR, Chen HY, Penninger JM, Lan HY. Loss of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 enhances TGF-beta/Smad-mediated renal fibrosis and NF-kappaB-driven renal inflammation in a mouse model of obstructive nephropathy. Lab Invest. 2012;92:650–61.",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2012.11.004",
"author": "CH Chou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell Endocrinol",
"key": "1665_CR52",
"unstructured": "Chou CH, Chuang LY, Lu CY, Guh JY. Interaction between TGF-beta and ACE2-Ang-(1–7)-Mas pathway in high glucose-cultured NRK-52E cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013;366:21–30.",
"volume": "366",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26826",
"author": "S Khanmohammadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2735",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "1665_CR53",
"unstructured": "Khanmohammadi S, Rezaei N. Role of toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. J Med Virol. 2021;93:2735–9.",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31083/j.fbl2811307",
"author": "N Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "307",
"journal-title": "Front Biosci (Landmark Ed)",
"key": "1665_CR54",
"unstructured": "Lee N, Ko R, Lee SY. Differential expression patterns of toll-like receptors in COVID-19 patients. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023;28:307.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/labinvest.2013.79",
"author": "Y Pi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "880",
"journal-title": "Lab Invest",
"key": "1665_CR55",
"unstructured": "Pi Y, Zhang LL, Li BH, Guo L, Cao XJ, Gao CY, Li JC. Inhibition of reactive oxygen species generation attenuates TLR4-mediated proinflammatory and proliferative phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells. Lab Invest. 2013;93:880–7.",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104587",
"author": "M Bhattacharya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104587",
"journal-title": "Infect Genet Evol",
"key": "1665_CR56",
"unstructured": "Bhattacharya M, Sharma AR, Mallick B, Sharma G, Lee SS, Chakraborty C. Immunoinformatics approach to understand molecular interaction between multi-epitopic regions of SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein with TLR4/MD-2 complex. Infect Genet Evol. 2020;85:104587.",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-021-00495-9",
"author": "Y Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "818",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "1665_CR57",
"unstructured": "Zhao Y, Kuang M, Li J, Zhu L, Jia Z, Guo X, Hu Y, Kong J, Yin H, Wang X, You F. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interacts with and activates TLR41. Cell Res. 2021;31:818–20.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01396-21",
"author": "Y Qian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0139621",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "1665_CR58",
"unstructured": "Qian Y, Lei T, Patel PS, Lee CH, Monaghan-Nichols P, Xin HB, Qiu J, Fu M. Direct activation of endothelial cells by SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is blocked by Simvastatin. J Virol. 2021;95:e0139621.",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/SHK.0000000000000392",
"author": "PS Tawadros",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "Shock",
"key": "1665_CR59",
"unstructured": "Tawadros PS, Powers KA, Ailenberg M, Birch SE, Marshall JC, Szaszi K, Kapus A, Rotstein OD. Oxidative stress increases Surface Toll-Like receptor 4 expression in Murine macrophages Via Ceramide Generation. Shock. 2015;44:157–65.",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-01048-1",
"author": "L Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "255",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "1665_CR60",
"unstructured": "Chen L, Guan WJ, Qiu ZE, Xu JB, Bai X, Hou XC, Sun J, Qu S, Huang ZX, Lei TL, et al. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein triggers hyperinflammation via protein-protein interaction-mediated intracellular Cl(-) accumulation in respiratory epithelium. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7:255.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-017-11978-4",
"author": "H Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14530",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "1665_CR61",
"unstructured": "Tang H, C LK, Lee M, Gao Y, Xia H, Olguin F, Fraga DA, Ayers K, Choi S, Kim M, et al. Smad3 initiates oxidative stress and proteolysis that underlies diaphragm dysfunction during mechanical ventilation. Sci Rep. 2017;7:14530.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23042062",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR62",
"unstructured": "Sobierajska K, Wawro ME, Niewiarowska J. Oxidative stress enhances the TGF-beta2-RhoA-MRTF-A/B Axis in cells entering endothelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.00470",
"author": "T Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "470",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "1665_CR63",
"unstructured": "Li T, Wang L, Wang H, Li X, Zhang S, Xu Y, Wei W. Serum SARS-COV-2 nucleocapsid protein: a sensitivity and specificity early diagnostic marker for SARS-COV-2 infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:470.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-83108-0",
"author": "M Batra",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3455",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "1665_CR64",
"unstructured": "Batra M, Tian R, Zhang C, Clarence E, Sacher CS, Miranda JN, De La Fuente JRO, Mathew M, Green D, Patel S, et al. Role of IgG against N-protein of SARS-CoV2 in COVID19 clinical outcomes. Sci Rep. 2021;11:3455.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2021.108720",
"author": "F Perna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108720",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "1665_CR65",
"unstructured": "Perna F, Bruzzaniti S, Piemonte E, Maddaloni V, Atripaldi L, Sale S, Sanduzzi A, Nicastro C, Pepe N, Bifulco M, et al. Serum levels of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen associate with inflammatory status and disease severity in COVID-19 patients. Clin Immunol. 2021;226:108720.",
"volume": "226",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/vim.2021.0168",
"author": "A Takamatsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "254",
"journal-title": "Viral Immunol",
"key": "1665_CR66",
"unstructured": "Takamatsu A, Oshiro S, Mizutani N, Tada T, Tabe Y, Miida T, Kirikae T, Tagashira Y. Correlation of COVID-19 Severity and Immunoglobulin Presence against Spike and Nucleocapsid Proteins in SARS-CoV-2. Viral Immunol. 2022;35:254–8.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41533-022-00300-z",
"author": "P Kushner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "NPJ Prim Care Respir Med",
"key": "1665_CR67",
"unstructured": "Kushner P, McCarberg BH, Grange L, Kolosov A, Haveric AL, Zucal V, Petruschke R, Bissonnette S. The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in COVID-19. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2022;32:35.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15206",
"author": "CT Robb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4899",
"journal-title": "Br J Pharmacol",
"key": "1665_CR68",
"unstructured": "Robb CT, Goepp M, Rossi AG, Yao C. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins, and COVID-19. Br J Pharmacol. 2020;177:4899–920.",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0246825",
"author": "TF Osborne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0246825",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "1665_CR69",
"unstructured": "Osborne TF, Veigulis ZP, Arreola DM, Mahajan SM, Roosli E, Curtin CM. Association of mortality and aspirin prescription for COVID-19 patients at the Veterans Health Administration. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0246825.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11239-021-02436-0",
"author": "CS Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "124",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Thrombolysis",
"key": "1665_CR70",
"unstructured": "Kow CS, Hasan SS. Use of antiplatelet drugs and the risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021;52:124–9.",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3332/ecancer.2020.1023",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR71",
"unstructured": "Russell B, Moss C, Rigg A, Van Hemelrijck M. COVID-19 and treatment with NSAIDs and corticosteroids: should we be limiting their use in the clinical setting? Ecancermedicalscience 2020, 14:1023."
},
{
"author": "Z Zhang",
"first-page": "1351",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Med",
"key": "1665_CR72",
"unstructured": "Zhang Z, Li S, Deng J, Yang S, Xiang Z, Guo H, Xi H, Sang M, Zhang W. Aspirin inhibits endometrial fibrosis by suppressing the TGF–beta1–Smad2/Smad3 pathway in intrauterine adhesions. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45:1351–60.",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2022.12697",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1665_CR73",
"unstructured": "Sun Y, Liu B, Xie J, Jiang X, Xiao B, Hu X, Xiang J. Aspirin attenuates liver fibrosis by suppressing TGF–beta1/Smad signaling. Mol Med Rep 2022, 25."
}
],
"reference-count": 73,
"references-count": 73,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://biosignaling.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12964-024-01665-z"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Diverse roles of SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Nucleocapsid proteins in EndMT stimulation through the TGF-β-MRTF axis inhibited by aspirin",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "22"
}