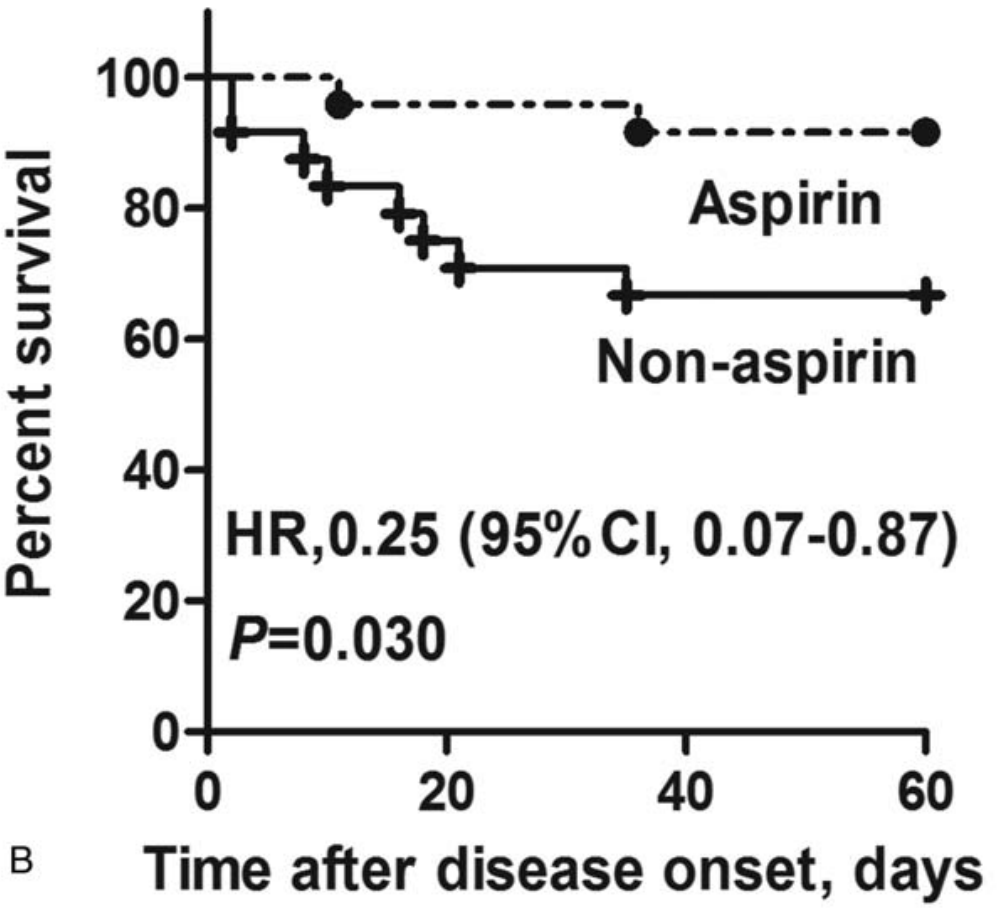
Effect of low-dose aspirin on mortality and viral duration of the hospitalized adults with COVID-19
et al., Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000024544, Feb 2021
Retrospective PSM analysis of 232 hospitalized patients, 28 treated with aspirin, showing lower mortality with treatment. There was no significant difference in viral clearance.
Viral load measured by PCR may not accurately reflect infectious virus measured by viral culture. Porter et al. show that viral load early in infection was correlated with infectious virus, but viral load late in infection could be high even with low or undetectable infectious virus. Assessing viral load later in infection may underestimate reductions in infectious virus with treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments2.
|
risk of death, 75.0% lower, HR 0.25, p = 0.03, treatment 2 of 28 (7.1%), control 11 of 204 (5.4%), adjusted per study, 60 days, KM, PSM.
|
|
risk of death, 81.0% lower, HR 0.19, p = 0.02, treatment 1 of 28 (3.6%), control 9 of 204 (4.4%), adjusted per study, 30 days, KM, PSM.
|
|
time to viral-, 1.9% higher, relative time 1.02, p = 0.94, treatment 24, control 24, PSM.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Liu et al., 12 Feb 2021, retrospective, propensity score matching, China, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/md.0000000000024544",
"ISSN": [
"0025-7974",
"1536-5964"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000024544",
"abstract": "<jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>To clarify the effect of aspirin on mortality and viral duration in adults infected with respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-Cov-2).</jats:p>\n <jats:p>After propensity score-matched (PSM) case-control analyses 24 pairs of patients were enrolled and followed up for 2 months. Both 30-day and 60-day mortality in the aspirin group were significantly lower than that in the non-aspirin group (<jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">P</jats:italic> = .021 and <jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">P</jats:italic> = .030, respectively). The viral duration time between the 2 groups was not significantly different (<jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">P</jats:italic> = .942).</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Among adults (with hypertension, cardiovascular diseases) infected with SARS-Cov-2, low-dose aspirin medication (100 mg/day) was associated with lower risk of mortality compared with non-aspirin users.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Yichang Central People's Hospital, The First College of Clinical Medical Science, China Three Gorges University, Yichang"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Qiang",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Yichang Central People's Hospital, The First College of Clinical Medical Science, China Three Gorges University, Yichang"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Na",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Yichang Central People's Hospital, The First College of Clinical Medical Science, China Three Gorges University, Yichang"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Anni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Yichang Central People's Hospital, The First College of Clinical Medical Science, China Three Gorges University, Yichang"
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Yuanhong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Yichang Central People's Hospital, The First College of Clinical Medical Science, China Three Gorges University, Yichang"
}
],
"family": "Liang",
"given": "Liang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Yichang Central People's Hospital, The First College of Clinical Medical Science, China Three Gorges University, Yichang"
}
],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Xinyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Virology, Institute of Medical Virology, School of Medicine, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China."
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Zhanqiu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9437-9896",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Yichang Central People's Hospital, The First College of Clinical Medical Science, China Three Gorges University, Yichang"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Xiaolin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-22T16:34:17Z",
"timestamp": 1614011657000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-16T03:08:29Z",
"timestamp": 1694833709000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"81402404"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "National Nature Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"81402404"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "National Nature Science Foundation of China"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-24T07:33:14Z",
"timestamp": 1711265594275
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 28,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1613088000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000024544",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e24544",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25748",
"article-title": "Unique epidemiological and clinical features of the emerging 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) implicate special control measures",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "568",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "R1-20230916",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 and treatment with NSAIDs and corticosteroids: should we be limiting their use in the clinical setting?",
"author": "Russell",
"first-page": "1023",
"journal-title": "E cancer medical science",
"key": "R2-20230916",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1534735406291499",
"article-title": "Preadministration of high-dose salicylates, suppressors of NF-kappaB activation, may increase the chemosensitivity of many cancers: an example of proapoptotic signal modulation therapy",
"author": "McCarty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Integrity Cancer Therapy",
"key": "R3-20230916",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.22215",
"article-title": "Acetylsalicylic acid inhibits hepatitis C virus RNA and protein expression through cyclooxygenase 2 signalling pathways",
"author": "Trujillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1462",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "R4-20230916",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25884",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 3,062 COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "R5-20230916",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3121/cmr.2007.698",
"article-title": "An evidence-based update on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs",
"author": "Ong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "Clin Med Res",
"key": "R6-20230916",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Goodman and Gilmans the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics",
"key": "R7-20230916",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1409",
"article-title": "Covid-19: NICE advises against using NSAIDs for fever in patients with suspected cases",
"author": "Torjesen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1409",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "R8-20230916",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/irv.12421",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of aspirin against RNA viruses of the respiratory tract-an in vitro study",
"author": "Glatthaar-Saalmüller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Influenza Other Respir Viruses",
"key": "R9-20230916",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of acetylsalicylic acid after intravenous and oral administration to healthy volunteers",
"author": "Nagelschmitz",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "R10-20230916",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 10,
"references-count": 10,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MD.0000000000024544"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of low-dose aspirin on mortality and viral duration of the hospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "100"
}