Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Positivity in Lebanon Among Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study in South Lebanon
et al., COVID, doi:10.3390/covid5070097, Jun 2025
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Cross-sectional study of 384 adults showing no significant association between vitamin D levels and test positivity.
This is the 221st of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
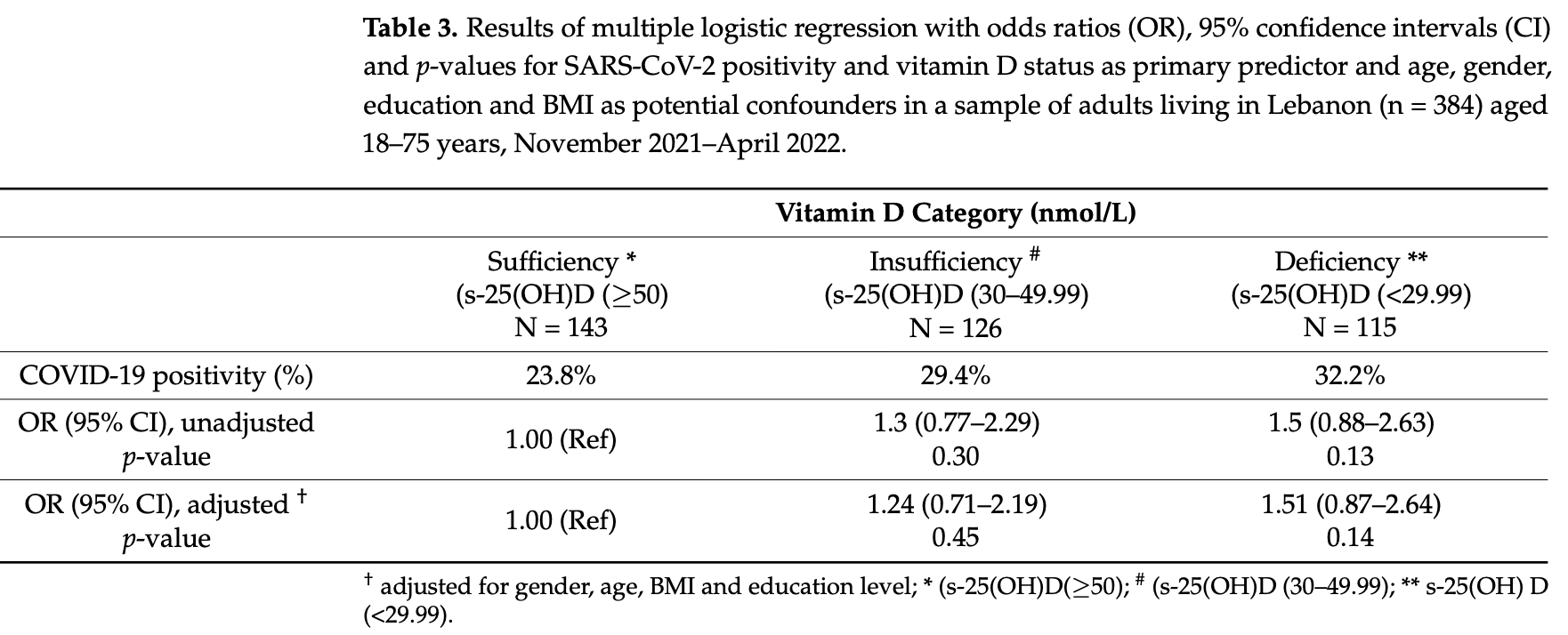
risk of case, 33.8% lower, OR 0.66, p = 0.15, high D levels (≥50 ng/mL) 143, low D levels (<30 ng/mL) 114, adjusted per study, inverted to make OR<1 favor high D levels (≥50 ng/mL), RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Madar et al., 27 Jun 2025, retrospective, Lebanon, peer-reviewed, mean age 38.8, 4 authors, study period 23 November, 2021 - 30 April, 2022.
Contact: a.a.madar@medisin.uio.no.
Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Positivity in Lebanon Among Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study in South Lebanon
COVID, doi:10.3390/covid5070097
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has affected countries globally, causing significant respiratory tract symptoms, including shortness of breath, coughing, chest tightness, and wheezing. Vitamin D has been proposed to play a key role, especially in upper respiratory tract infections. Recently, numerous studies and reports associating low serum 25hydroxyvitamin D levels (s-25-(OH)D) and adverse outcomes in COVID-19 have emerged. We aimed to assess the association between vitamin D status and SARS-CoV-2 positivity among adults in Lebanon. Method: A cross-sectional study was conducted, recruiting 384 participants aged 18-75 years from a university hospital in South Lebanon. Background variables were collected through structured questionnaires. Serum 25(OH)D levels were measured using electrochemiluminescence immunoassay, and SARS-CoV-2 positivity was assessed through PCR testing. Results: The mean s-25(OH)D level was 46.8 nmol/L (SD 28.1), and 30% of the participants had vitamin D deficiency (s-25-(OH)D level <30 nmol/L). SARS-CoV-2 positivity was reported in 28% of participants. However, no significant association was found between s-25(OH)D levels and SARS-CoV-2 positivity. This study had several limitations, including potential selection bias due to recruiting participants from a hospital for PCR testing, the collection of data across different seasons, and the refusal of several eligible individuals to participate. Additionally, the lack of data on participants' immunization status and assay variability may impact the generalizability and interpretation of the findings. Conclusion: There was a high prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency among adults participating in COVID-19 tests in Lebanon, but it was not associated with SARS-CoV-2 positivity.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at https: //www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/covid5070097/s1 , Table S1 : SARS-CoV-2 positivity and BMI gender, age, and education level with vitamin D levels.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021
Alquaiz, Kazi, Fouda, Alyousefi, Age and gender differences in the prevalence and correlates of vitamin D deficiency, Arch. Osteoporos, doi:10.1007/s11657-018-0461-5
Arabi, Chamoun, Nasrallah, Tamim, Vitamin D Deficiency in Lebanese Adults: Prevalence and Predictors from a Cross-Sectional Community-Based Study, Int. J. Endocrinol, doi:10.1155/2021/3170129
Bae, Choe, Holick, Lim, Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 and its severity: Vitamin D and COVID-19: A narrative review, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-021-09705-6
Baktash, Hosack, Patel, Shah, Kandiah et al., Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19, Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138712
Bergman, The link between vitamin D and COVID-19: Distinguishing facts from fiction, J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13158
Boulkrane, Ilina, Melchakov, Fedotova, Drago et al., COVID-19 Disease and Vitamin D: A Mini-Review, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.604579
Brunvoll, Nygaard, Ellingjord-Dale, Holland, Istre et al., Prevention of COVID-19 and other acute respiratory infections with cod liver oil supplementation, a low dose vitamin D supplement: Quadruple blinded, randomised placebo-controlled trial, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-071245
Chang, Understanding the COVID-19 pandemic from a gender perspective, Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol, doi:10.1016/j.tjog.2020.09.004
Chen, Klein, Garibaldi, Li, Wu et al., Aging in COVID-19: Vulnerability, immunity and intervention, Ageing Res. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.arr.2020.101205
Chiodini, Gatti, Soranna, Merlotti, Mingiano et al., Vitamin D Status and SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes, Front. Public Heal, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.736665
Delle Monache, Di Fulvio, Iannetti, Valerii, Capone et al., Body mass index represents a good predictor of vitamin D status in women independently from age, Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2018.02.024
Dissanayake, De Silva, Sumanatilleke, De Silva, Gamage et al., Prognostic and Therapeutic Role of Vitamin D in COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab892
Farha, Abi Jaoude, Lebanese Healthcare System: How Will the Aftermath Look? Cureus 2020, doi:10.7759/cureus.10270
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Huang, Lu, Huang, Wang, Ling et al., Obesity in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154378
Jakovac, COVID-19 and vitamin D-Is there a link and an opportunity for intervention?, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00138.2020
Jolliffe, Holt, Greenig, Talaei, Perdek et al., Effect of a test-and-treat approach to vitamin D supplementation on risk of all cause acute respiratory tract infection and COVID-19: Phase 3 randomised controlled trial (CORONAVIT), BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-071230
Lupu, Tiganasu, Does education influence COVID-19 vaccination? A global view, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24709
Malaguarnera, Vitamin D3 as Potential Treatment Adjuncts for COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113512
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics with COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Mitchell, Vitamin-D and COVID-19: Do deficient risk a poorer outcome?, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30183-2
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients with Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger et al., Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092757
Verdoia, Schaffer, Barbieri, Di Giovine, Marino et al., (NAS). Impact of gender difference on vitamin D status and its relationship with the extent of coronary artery disease, Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2015.01.009
Vieth, Holick, Chapter 57B-The IOM-Endocrine Society Controversy on Recommended Vitamin D Targets: In Support of the Endocrine Society Position
Wang, Joshi, Leopold, Jackson, Christensen et al., Association of vitamin D deficiency with COVID-19 infection severity: Systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/cen.14540
Whittemore, COVID-19 fatalities, latitude, sunlight, and vitamin D, Am. J. Infect. Control, doi:10.1016/j.ajic.2020.06.193
Who, Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard
Who, Director-General's Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19-11
Xu, Yang, Yang, Zou, Wang et al., Clinical course and predictors of 60-day mortality in 239 critically ill patients with COVID-19: A multicenter retrospective study from Wuhan, China, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03098-9
Yisak, Ewunetei, Kefale, Mamuye, Teshome et al., Effects of Vitamin D on COVID-19 Infection and Prognosis: A Systematic Review, Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy, doi:10.2147/RMHP.S291584
Yoshikawa, Asaba, Educational Attainment Decreases the Risk of COVID-19 Severity in the European Population: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.673451
Zhao, Cao, Chong, Gao, Lou et al., COVID-19 and genderspecific difference: Analysis of public surveillance data in Hong Kong and Shenzhen, China, Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol, doi:10.1017/ice.2020.64
