The efficacy and safety of fluvoxamine in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis from randomized controlled trials
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0300512, May 2024
30th treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
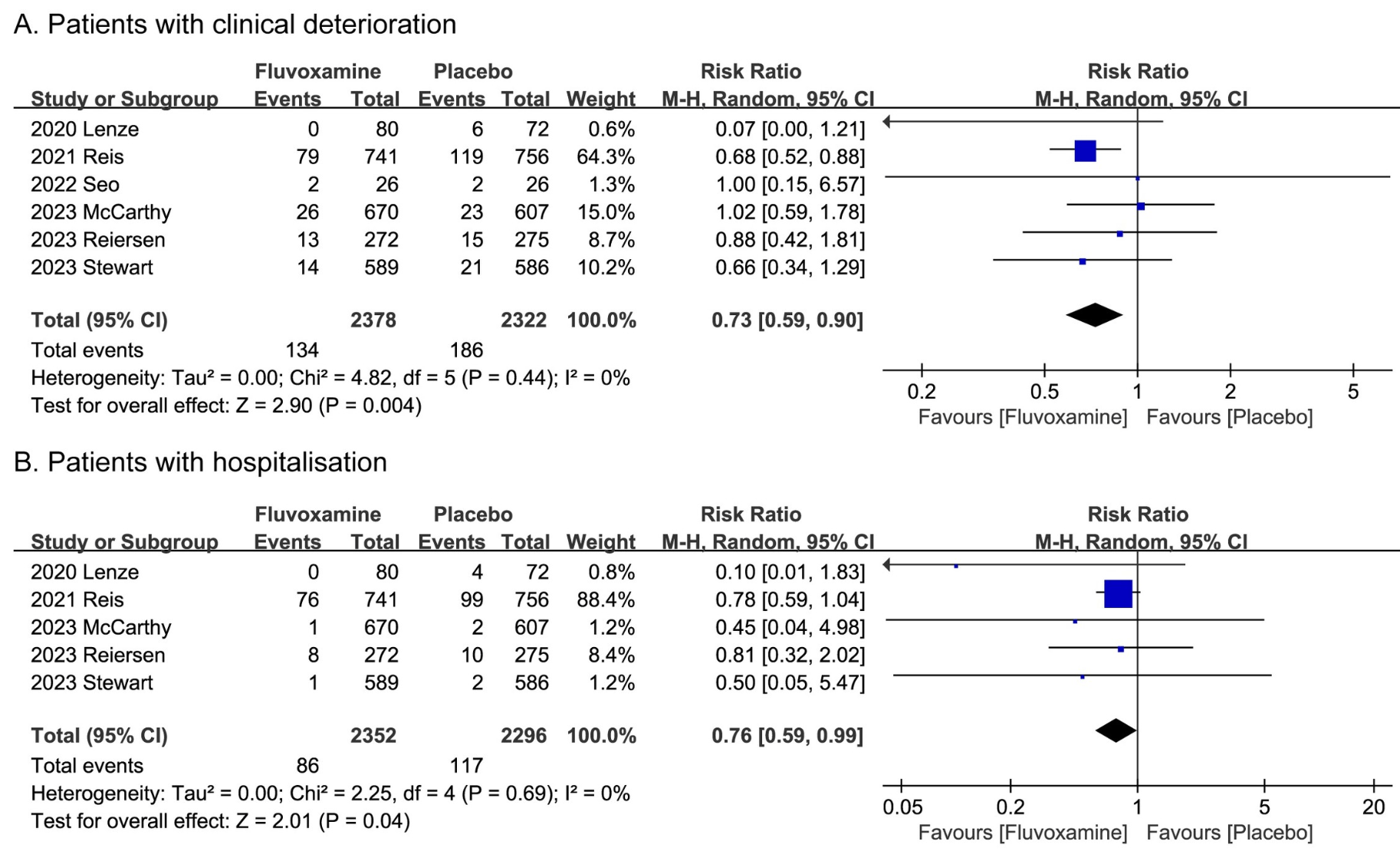
Meta analysis of 6 RCTs with 4,711 total participants showing significantly lower clinical deterioration and hospitalization with fluvoxamine treatment for COVID-19. Fluvoxamine doses ≥200mg daily were more effective than lower doses. There was no significant difference in adverse events or serious adverse events compared to placebo.
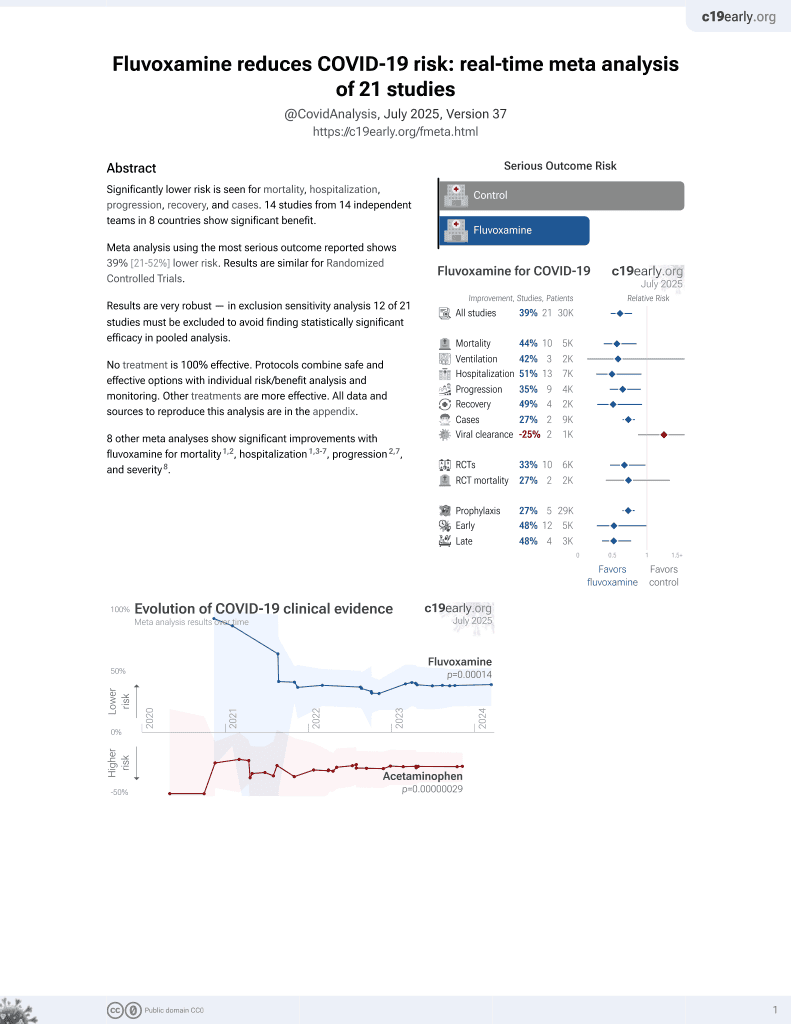
9 meta-analyses show significant improvements with fluvoxamine for mortality1-3,
hospitalization1,4-8 ,
progression2,8, and
severity9.
Currently there are 21 fluvoxamine for COVID-19 studies, showing 44% lower mortality [15‑63%], 42% lower ventilation [-151‑86%], 10% higher ICU admission [-72‑326%], 51% lower hospitalization [8‑73%], and 27% fewer cases [18‑35%].
1.
Deng et al., Efficacy and safety of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in COVID-19 management: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2023.01.010.
2.
Prasanth et al., A systematic review and meta-analysis, investigating dose and time of fluvoxamine treatment efficacy for COVID-19 clinical deterioration, death, and Long-COVID complications, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-64260-9.
3.
Fico et al., Psychotropic drug repurposing for COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, European Neuropsychopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2022.10.004.
4.
Lee et al., Fluvoxamine for Outpatient Management of COVID-19 to Prevent Hospitalization: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.6269.
5.
Lu et al., Effect of fluvoxamine on outcomes of nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Journal of Infection and Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2022.10.010.
6.
Marcec et al., A meta-analysis regarding fluvoxamine and hospitalization risk of COVID-19 patients: TOGETHER making a difference, Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2022.11.011.
7.
Deng (B) et al., Evaluating fluvoxamine for the outpatient treatment of COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2501.
Zhou et al., 16 May 2024, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: niyuehua1982@163.com.
The efficacy and safety of fluvoxamine in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis from randomized controlled trials
PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0300512
Background Recently, several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of fluvoxamine have been successfully conducted for the treatment of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 . This systematic review and meta-analysis was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of fluvoxamine in patients with COVID-19.
Methods MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library and clinicaltrials.gov were searched for RCTs which were performed to evaluate fluvoxamine and placebo up to January 31, 2024. Review Manager 5.3 was used to perform meta-analysis. The risk ratio (RR) and mean difference (MD) was analyzed and calculated with a random effect model.
Results We pooled 4,711 participants from six RCTs (2,382 in the fluvoxamine group and 2,329 in the placebo group). Compared to the placebo group, the fluvoxamine group had a significantly lower rate of clinical deterioration (RR, 0.73; P = 0.004; 95% CI, 0.59 to 0.90; I 2 = 0%) and hospitalization (RR, 0.76; P = 0.04; 95% CI, 0.59 to 0.99; I 2 = 0%). In the meantime, compared with the placebo group, fluvoxamine group did not show any higher risk of AEs (P = 0.13 and 0.91, respectively) in safety outcomes analysis. The subgroup analysis showed that fluvoxamine treatment performed more than 200 mg daily appears to be more effective than those performed less than 200 mg daily in reducing clinical deterioration and hospitalization risks, while not exhibiting higher AE and SAE risks than placebo group.
Conclusion Fluvoxamine for patients with COVID-19, especially those who take 200 mg or more daily, is superior to the placebo group in reducing clinical deterioration and hospitalization, and did
Supporting information S1
References
Bhuta, Khokher, Kesireddy, Iftikhar, Beran et al., Fluvoxamine in Nonhospitalized Patients With Acute COVID-19 Infection and the Lack of Efficacy in Reducing Rates of Hospitalization, Mechanical Ventilation, and Mortality in Placebo-Controlled Trials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, American journal of therapeutics, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001496
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Buse, Liebovitz et al., Randomized Trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2201662
Cheema, Jafar, Elrashedy, Shahid, Awan et al., Efficacy and safety of fluvoxamine for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2022.10.012
Higgins, Altman, Gotzsche, Juni, Moher et al., The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ (Clinical research, doi:10.1136/bmj.d5928
Hillary, Ceasar, An update on COVID-19: SARS-CoV-2 variants, antiviral drugs, and vaccines, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13952
Hoertel, Sanchez-Rico, Cougoule, Gulbins, Kornhuber et al., Repurposing antidepressants inhibiting the sphingomyelinase acid/ceramide system against COVID-19: current evidence and potential mechanisms, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01254-3
Ishima, Fujita, Hashimoto, Interaction of new antidepressants with sigma-1 receptor chaperones and their potentiation of neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.064
Lee, Vigod, Bortolussi-Courval, Hanula, Boulware et al., Fluvoxamine for Outpatient Management of COVID-19 to Prevent Hospitalization: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, JAMA network open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.6269
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients With Symptomatic COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
Liberati, Altman, Tetzlaff, Mulrow, Gotzsche et al., The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration, BMJ (Clinical research
Marcec, Dodig, Likic, A meta-analysis regarding fluvoxamine and hospitalization risk of COVID-19 patients: TOGETHER making a difference, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2022.11.011
Mccarthy, Naggie, Boulware, Lindsell, Stewart et al., Effect of Fluvoxamine vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.24100
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Nicol, Karp, Reiersen, Zorumski, Lenze, What Were You Before the War?" Repurposing Psychiatry During the COVID-19 Pandemic, The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, doi:10.4088/JCP.20com13373
Reiersen, Mattar, Bender Ignacio, Boulware, Lee et al., The STOP COVID 2 Study: Fluvoxamine vs Placebo for Outpatients With Symptomatic COVID-19, a Fully Remote Randomized Controlled Trial, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofad419
Reis, Santos Moreira-Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
Reis, Santos, Silva, Silva, Thabane et al., Oral Fluvoxamine With Inhaled Budesonide for Treatment of Early-Onset COVID-19: A Randomized Platform Trial, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M22-3305
Seo, Kim, Bae, Park, Chung et al., Fluvoxamine Treatment of Patients with Symptomatic COVID-19 in a Community Treatment Center: A Preliminary Result of Randomized Controlled Trial, Infect Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2021.0142
Stewart, Rebolledo, Mourad, Lindsell, Boulware et al., Higher-Dose Fluvoxamine and Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With COVID-19: The ACTIV-6 Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2023.23363
Sukhatme, Reiersen, Vayttaden, Sukhatme, Fluvoxamine: A Review of Its Mechanism of Action and Its Role in COVID-19, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.652688
Yu, Carvalho, Thompson, Tsai, Tseng et al., Trial Sequential Analysis and Updated Meta-Analysis of Fluvoxamine on Clinical Deterioration in Adult Patients with Symptomatic COVID-19 Infection, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph20054088
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0300512",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300512",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"sec001\">\n<jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Recently, several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of fluvoxamine have been successfully conducted for the treatment of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This systematic review and meta-analysis was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of fluvoxamine in patients with COVID-19.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec002\">\n<jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n<jats:p>MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library and clinicaltrials.gov were searched for RCTs which were performed to evaluate fluvoxamine and placebo up to January 31, 2024. Review Manager 5.3 was used to perform meta-analysis. The risk ratio (RR) and mean difference (MD) was analyzed and calculated with a random effect model.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec003\">\n<jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n<jats:p>We pooled 4,711 participants from six RCTs (2,382 in the fluvoxamine group and 2,329 in the placebo group). Compared to the placebo group, the fluvoxamine group had a significantly lower rate of clinical deterioration (RR, 0.73; P = 0.004; 95% CI, 0.59 to 0.90; I<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0%) and hospitalization (RR, 0.76; P = 0.04; 95% CI, 0.59 to 0.99; I<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0%). In the meantime, compared with the placebo group, fluvoxamine group did not show any higher risk of AEs (P = 0.13 and 0.91, respectively) in safety outcomes analysis. The subgroup analysis showed that fluvoxamine treatment performed more than 200 mg daily appears to be more effective than those performed less than 200 mg daily in reducing clinical deterioration and hospitalization risks, while not exhibiting higher AE and SAE risks than placebo group.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec004\">\n<jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Fluvoxamine for patients with COVID-19, especially those who take 200 mg or more daily, is superior to the placebo group in reducing clinical deterioration and hospitalization, and did not show any higher risk of AEs and SAEs in safety concerns, which might be a promising intervention for COVID-19.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Qiufeng",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Guozheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0007-9514-0653",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ni",
"given": "Yuehua",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS ONE",
"container-title-short": "PLoS ONE",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-16T17:57:54Z",
"timestamp": 1715882274000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-16T17:58:15Z",
"timestamp": 1715882295000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sehgal",
"given": "Sheikh Arslan",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"WWK202112"
],
"name": "Wujiang Science, Education and Health Project"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-17T00:36:23Z",
"timestamp": 1715906183377
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
16
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1715817600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300512",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0300512",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"key": "pone.0300512.ref001",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard [https://covid19.who.int]"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "N Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref002",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13952",
"article-title": "An update on COVID-19: SARS-CoV-2 variants, antiviral drugs, and vaccines",
"author": "VE Hillary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref003",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "P Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref004",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4088/JCP.20com13373",
"article-title": "What Were You Before the War?” Repurposing Psychiatry During the COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "GE Nicol",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref005",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.652688",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine: A Review of Its Mechanism of Action and Its Role in COVID-19",
"author": "VP Sukhatme",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref006",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.064",
"article-title": "Interaction of new antidepressants with sigma-1 receptor chaperones and their potentiation of neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells",
"author": "T Ishima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref007",
"volume": "727",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01254-3",
"article-title": "Repurposing antidepressants inhibiting the sphingomyelinase acid/ceramide system against COVID-19: current evidence and potential mechanisms",
"author": "N Hoertel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7098",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Mol Psychiatry",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref008",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients With Symptomatic COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "EJ Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2292",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref009",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4",
"article-title": "Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial",
"author": "G Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Lancet Glob Health",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref010",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2021.0142",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine Treatment of Patients with Symptomatic COVID-19 in a Community Treatment Center: A Preliminary Result of Randomized Controlled Trial",
"author": "H Seo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Infect Chemother",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref011",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.24100",
"article-title": "Effect of Fluvoxamine vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "MW McCarthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "296",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref012",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofad419",
"article-title": "The STOP COVID 2 Study: Fluvoxamine vs Placebo for Outpatients With Symptomatic COVID-19, a Fully Remote Randomized Controlled Trial",
"author": "AM Reiersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref013",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2023.23363",
"article-title": "Higher-Dose Fluvoxamine and Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With COVID-19: The ACTIV-6 Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "TG Stewart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2354",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref014",
"volume": "330",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.b2700",
"article-title": "The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration",
"author": "A Liberati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ (Clinical research ed)",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref015",
"volume": "339",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.d5928",
"article-title": "The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials",
"author": "JP Higgins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ (Clinical research ed)",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref016",
"volume": "343",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001496",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine in Nonhospitalized Patients With Acute COVID-19 Infection and the Lack of Efficacy in Reducing Rates of Hospitalization, Mechanical Ventilation, and Mortality in Placebo-Controlled Trials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "S Bhuta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e298",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "American journal of therapeutics",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref017",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.10.012",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of fluvoxamine for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "HA Cheema",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "702",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref018",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.11.011",
"article-title": "A meta-analysis regarding fluvoxamine and hospitalization risk of COVID-19 patients: TOGETHER making a difference",
"author": "R Marcec",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref019",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine for Outpatient Management of COVID-19 to Prevent Hospitalization: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis",
"author": "TC Lee",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA network open",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref020",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Trial Sequential Analysis and Updated Meta-Analysis of Fluvoxamine on Clinical Deterioration in Adult Patients with Symptomatic COVID-19 Infection",
"author": "CL Yu",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref021",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2201662",
"article-title": "Randomized Trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19",
"author": "CT Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "599",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref022",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-3305",
"article-title": "Oral Fluvoxamine With Inhaled Budesonide for Treatment of Early-Onset COVID-19: A Randomized Platform Trial",
"author": "G Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "667",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "pone.0300512.ref023",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 23,
"references-count": 23,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300512"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The efficacy and safety of fluvoxamine in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis from randomized controlled trials",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "19"
}