Repurposing antidepressants inhibiting the sphingomyelinase acid/ceramide system against COVID-19: current evidence and potential mechanisms
et al., Molecular Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01254-3, Aug 2021
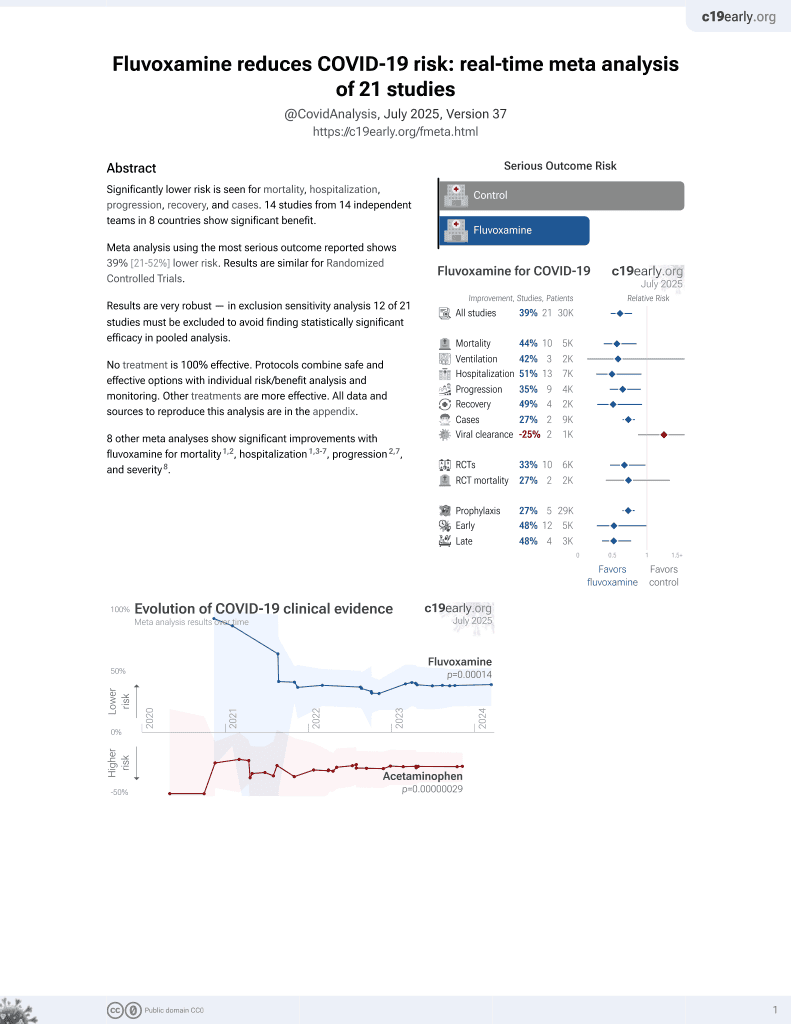
30th treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the mechanisms of action and clinical studies for the treatment of COVID-19 with FIASMA antidepressants such as fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, escitalopram, or amitriptyline.
1.
Scheim et al., Back to the Basics of SARS-CoV-2 Biochemistry: Microvascular Occlusive Glycan Bindings Govern Its Morbidities and Inform Therapeutic Responses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16040647.
2.
Hashimoto, K., Overview of the potential use of fluvoxamine for COVID-19 and long COVID, Discover Mental Health, doi:10.1007/s44192-023-00036-3.
3.
Hashimoto (B) et al., Mechanisms of action of fluvoxamine for COVID-19: a historical review, Molecular Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01432-3.
4.
Hashimoto (C) et al., Old drug fluvoxamine, new hope for COVID-19, European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, doi:10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z.
5.
Hoertel et al., Repurposing antidepressants inhibiting the sphingomyelinase acid/ceramide system against COVID-19: current evidence and potential mechanisms, Molecular Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01254-3.
Hoertel et al., 12 Aug 2021, peer-reviewed, 12 authors.
Repurposing antidepressants inhibiting the sphingomyelinase acid/ceramide system against COVID-19: current evidence and potential mechanisms
Molecular Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01254-3
Molecular Psychiatry might collectively lead to anti-SARS-COV-2 effects while diminishing coagulopathy and cytokine storm consequences, which are known hallmarks of severe COVID-19. Following these preclinical, observational and clinical converging findings, and as stated by Salles et al. [1] and Stip et al. [2], large-scale double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials of FIASMA antidepressants for COVID-19 at different stages of the disease, either alone or combined with medications that have shown preliminary evidence of potential efficacy and good tolerability, are urgently needed. Fluoxetine and fluvoxamine, which display high in vitro inhibition effect on ASM, showed potential positive effects at usual antidepressant doses, and are easy to use, including high safety margins, good tolerability, widespread availability and low cost, should be considered compelling treatments to prioritize for phase 3 trials against .
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Writing-original draft: NH; Writing-review & editing: MS-R, CG, EG, JK, AC, KAB, AMR, EJL, DS, CL, FL.
COMPETING INTERESTS
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to N.H. Reprints and permission information is available at http://www.nature.com/ reprints Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Carpinteiro, Edwards, Hoffmann, Kochs, Gripp et al., Pharmacological inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase prevents uptake of SARS-CoV-2 by epithelial cells, Cell Rep Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100142
Carpinteiro, Gripp, Hoffmann, Pöhlmann, Hoertel et al., Inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase by ambroxol prevents SARS-CoV-2 entry into epithelial cells, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100701
Darquennes, Corre, Moine, Loas, Association between functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase (Fiasmas) and reduced risk of death in covid-19 patients: a retrospective cohort study, Pharmaceuticals
Fred, Kuivanen, Ugurlu, Casarotto, Levanov et al., Antidepressant and antipsychotic drugs reduce viral infection by SARS-CoV-2 and fluoxetine show antiviral activity against the novel variants in vitro, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.22.436379
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Gulbins, Kornhuber, Carpinteiro et al., Association between FIASMAs and Reduced Risk of Intubation or Death in Individuals Hospitalized for Severe COVID-19: an observational multicenter study, Clin Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1002/cpt.2317
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Gulbins, Kornhuber, Carpinteiro et al., Association between Psychotropic Medications Functionally Inhibiting Acid Sphingomyelinase and reduced risk of Intubation or Death among Individuals with Mental Disorder and Severe COVID-19: an Observational Study, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.02.18.21251997
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Vernet, Beeker, Jannot et al., Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Vernet, Beeker, Jannot et al., SSRIs and SNRIs and Risk of Death or Intubation in COVID-19: Results from an Observational Study, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.07.09.20143339
Kornhuber, Tripal, Reichel, Mühle, Rhein et al., Functional Inhibitors of Acid Sphingomyelinase (FIASMAs): a novel pharmacological group of drugs with broad clinical applications, Cell Physiol Biochem
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients With Symptomatic COVID-19: a Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA
Marín-Corral, Rodríguez-Morató, Gomez-Gomez, Pascual-Guardia, Muñoz-Bermúdez et al., Metabolic Signatures Associated with Severity in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients, Int J Mol Sci
Salles, Briand-Mésange, Trudel, Ausseil, Salles et al., Can antidepressants unlock prescription of rimonabant in the fight against COVID-19?, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01221-y
Schloer, Brunotte, Goretzko, Mecate-Zambrano, Korthals et al., Targeting the endolysosomal host-SARS-CoV-2 interface by clinically licensed functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase (FIASMA) including the antidepressant fluoxetine, Emerg Microbes Infect
Seftel, Boulware, Prospective Cohort of Fluvoxamine for Early Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 19, Open Forum Infect Dis
Stip, Arnone, Aziz, Javaid, Diversity of mechanism of action of psychotropic drugs in their anti-COVID-19 properties, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01222-x
Sukhatme, Reiersen, Vayttaden, Sukhatme, Fluvoxamine: a Review of Its Mechanism of Action and Its Role in COVID-19, Molecular Psychiatry
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01254-3",
"ISSN": [
"1359-4184",
"1476-5578"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01254-3",
"alternative-id": [
"1254"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "30 June 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 2,
"value": "26 July 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 3,
"value": "29 July 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 4,
"value": "12 August 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "NH, MS-R, EG, JK, AC, and FL are inventors on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, filled by Assistance Publique —Hopitaux de Paris in France. NH has received personal fees and nonfinancial support from Lundbeck, outside the submitted work. AMR and EJL are inventors on a patent application related to methods of treating COVID-19, which was filed by Washington University in St. Louis. EJL has received consulting fees from Johnson and Johnson, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. AMR has received grant or research support from the McDonnell Center for Systems Neuroscience, the McDonnell Center for Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, and the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research. DS is the Chief Medical Officer and CEO of Enable Biosciences, a CLIA certified Federal clinical reference laboratory that performs COVID-19 antibody testing. CL reports personal fees and nonfinancial support from Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, and Boehringer Ingelheim, outside the submitted work. FL has received speaker and consulting fees from Janssen-Cilag, Euthérapie-Servier, and Lundbeck, outside the submitted work. Other authors declare no competing interests related to this work."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7890-1349",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hoertel",
"given": "Nicolas",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1121-8641",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sánchez-Rico",
"given": "Marina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cougoule",
"given": "Céline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gulbins",
"given": "Erich",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8096-3987",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kornhuber",
"given": "Johannes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carpinteiro",
"given": "Alexander",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Becker",
"given": "Katrin Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3203-4590",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Reiersen",
"given": "Angela M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lenze",
"given": "Eric J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seftel",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3487-4721",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lemogne",
"given": "Cédric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Limosin",
"given": "Frédéric",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Molecular Psychiatry"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-12T14:03:15Z",
"timestamp": 1628776995000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-12T15:05:41Z",
"timestamp": 1628780741000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-03T11:09:55Z",
"timestamp": 1638529795013
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1359-4184"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1476-5578"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1628726400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1628726400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-021-01254-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-021-01254-3",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-021-01254-3.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01221-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1254_CR1",
"unstructured": "Salles J, Briand-Mésange F, Trudel S, Ausseil J, Salles J-P, Chap H. Can antidepressants unlock prescription of rimonabant in the fight against COVID-19? Mol Psychiatry. 2021:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01221-y. Epub ahead of print."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01222-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1254_CR2",
"unstructured": "Stip E, Arnone D, Abdel Aziz K, Javaid S. Diversity of mechanism of action of psychotropic drugs in their anti-COVID-19 properties. Mol Psychiatry. 2021:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01222-x. Epub ahead of print."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1254_CR3",
"unstructured": "Hoertel N, Sánchez-Rico M, Vernet R, Beeker N, Jannot A-S, Neuraz A, et al. Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4 Epub ahead of print."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.09.20143339",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1254_CR4",
"unstructured": "Hoertel N, Sánchez-Rico M, Vernet R, Beeker N, Jannot A-S, Neuraz A, et al. SSRIs and SNRIs and Risk of Death or Intubation in COVID-19: Results from an Observational Study. medRxiv 2020.07.09.20143339; https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.09.20143339."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000315101",
"author": "J Kornhuber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Cell Physiol Biochem",
"key": "1254_CR5",
"unstructured": "Kornhuber J, Tripal P, Reichel M, Mühle C, Rhein C, Muehlbacher M, et al. Functional Inhibitors of Acid Sphingomyelinase (FIASMAs): a novel pharmacological group of drugs with broad clinical applications. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010;26:9–20.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100142",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1254_CR6",
"unstructured": "Carpinteiro A, Edwards MJ, Hoffmann M, Kochs G, Gripp B, Weigang S, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase prevents uptake of SARS-CoV-2 by epithelial cells. Cell Rep Med. 2020;1:100142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100142. Epub 2020 Oct 29."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100701",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1254_CR7",
"unstructured": "Carpinteiro A, Gripp B, Hoffmann M, Pöhlmann S, Hoertel N, Edwards MJ, et al. Inhibition of acid sphingomyelinase by ambroxol prevents SARS-CoV-2 entry into epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100701. Epub 2021 Apr 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1829082",
"author": "S Schloer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2245",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "1254_CR8",
"unstructured": "Schloer S, Brunotte L, Goretzko J, Mecate-Zambrano A, Korthals N, Gerke V, et al. Targeting the endolysosomal host-SARS-CoV-2 interface by clinically licensed functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase (FIASMA) including the antidepressant fluoxetine. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:2245–55.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2317",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1254_CR9",
"unstructured": "Hoertel N, Sánchez‐Rico M, Gulbins E, Kornhuber J, Carpinteiro A, Lenze EJ, et al. Association between FIASMAs and Reduced Risk of Intubation or Death in Individuals Hospitalized for Severe COVID‐19: an observational multicenter study. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2021:10.1002/cpt.2317. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.2317. Epub ahead of print."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.02.18.21251997",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1254_CR10",
"unstructured": "Hoertel N, Sánchez-Rico M, Gulbins E, Kornhuber J, Carpinteiro A, Abellán M, et al. Association between Psychotropic Medications Functionally Inhibiting Acid Sphingomyelinase and reduced risk of Intubation or Death among Individuals with Mental Disorder and Severe COVID-19: an Observational Study. medRxiv 2021.02.18.21251997; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.18.21251997."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph14030226",
"author": "G Darquennes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "226",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceuticals.",
"key": "1254_CR11",
"unstructured": "Darquennes G, Le Corre P, Le Moine O, Loas G. Association between functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase (Fiasmas) and reduced risk of death in covid-19 patients: a retrospective cohort study. Pharmaceuticals. 2021;14:226.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"author": "EJ Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2292",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "1254_CR12",
"unstructured": "Lenze EJ, Mattar C, Zorumski CF, Stevens A, Schweiger J, Nicol GE, et al. Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients With Symptomatic COVID-19: a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2020;324:2292–2300.",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab050",
"author": "D Seftel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "ofab050",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "1254_CR13",
"unstructured": "Seftel D, Boulware DR. Prospective Cohort of Fluvoxamine for Early Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 19. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021;8:ofab050.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22094794",
"author": "J Marín-Corral",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4794",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "1254_CR14",
"unstructured": "Marín-Corral J, Rodríguez-Morató J, Gomez-Gomez A, Pascual-Guardia S, Muñoz-Bermúdez R, Salazar-Degracia A, et al. Metabolic Signatures Associated with Severity in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:4794.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.22.436379",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1254_CR15",
"unstructured": "Fred SM, Kuivanen S, Ugurlu H, Casarotto PC, Levanov L, Saksela K, et al. Antidepressant and antipsychotic drugs reduce viral infection by SARS-CoV-2 and fluoxetine show antiviral activity against the novel variants in vitro. bioRxiv 2021.03.22.436379; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.22.436379."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.652688",
"author": "VP Sukhatme",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "652688",
"journal-title": "Front Pharm",
"key": "1254_CR16",
"unstructured": "Sukhatme VP, Reiersen AM, Vayttaden SJ, Sukhatme VV. Fluvoxamine: a Review of Its Mechanism of Action and Its Role in COVID-19. Front Pharm. 2021;12:652688.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 16,
"references-count": 16,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Mol Psychiatry"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cellular and Molecular Neuroscience",
"Psychiatry and Mental health",
"Molecular Biology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Repurposing antidepressants inhibiting the sphingomyelinase acid/ceramide system against COVID-19: current evidence and potential mechanisms"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}