Old drug fluvoxamine, new hope for COVID-19
et al., European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, doi:10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z, Sep 2021
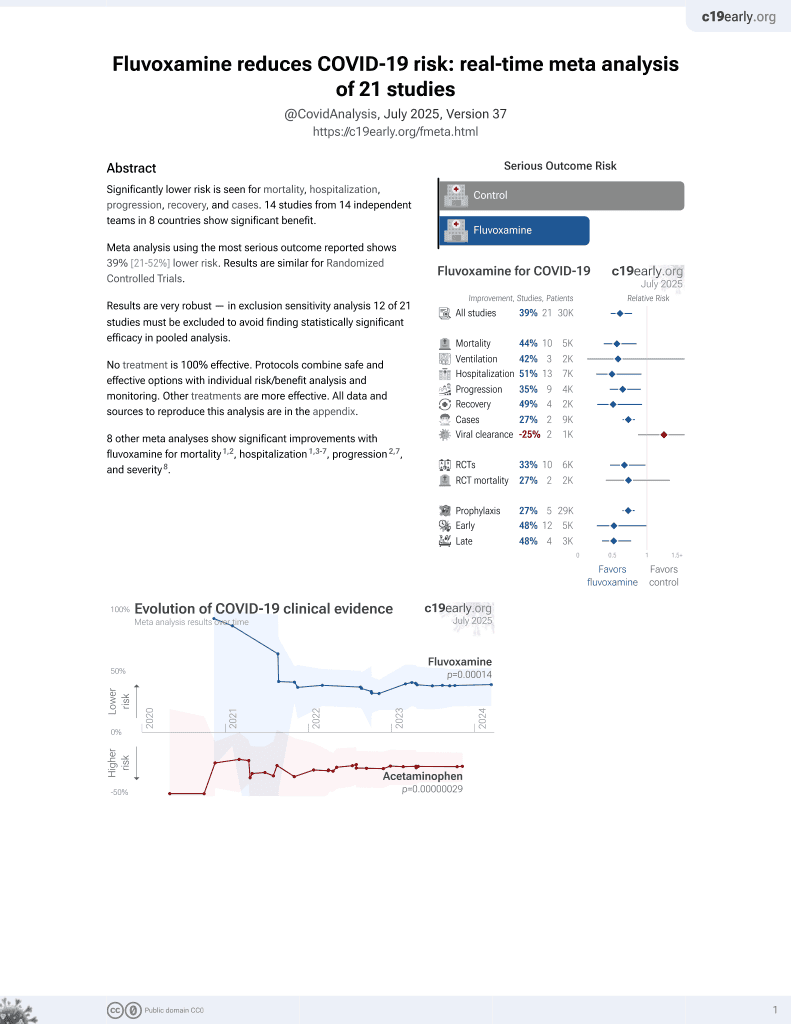
30th treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of research supporting the use of fluvoxamine for COVID-19. Authors note the favorable safety profiles, widespread availability, very low cost, and oral administration.
1.
Scheim et al., Back to the Basics of SARS-CoV-2 Biochemistry: Microvascular Occlusive Glycan Bindings Govern Its Morbidities and Inform Therapeutic Responses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16040647.
2.
Hashimoto, K., Overview of the potential use of fluvoxamine for COVID-19 and long COVID, Discover Mental Health, doi:10.1007/s44192-023-00036-3.
3.
Hashimoto (B) et al., Mechanisms of action of fluvoxamine for COVID-19: a historical review, Molecular Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01432-3.
4.
Hashimoto (C) et al., Old drug fluvoxamine, new hope for COVID-19, European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, doi:10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z.
5.
Hoertel et al., Repurposing antidepressants inhibiting the sphingomyelinase acid/ceramide system against COVID-19: current evidence and potential mechanisms, Molecular Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01254-3.
Hashimoto et al., 2 Sep 2021, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Abstract: European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Old drug fluvoxamine, new hope for COVID‑19
Yaeko Hashimoto1,2 · Takuji Suzuki1 · Kenji Hashimoto2
Received: 24 August 2021 / Accepted: 27 August 2021
© Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an acute respiratory disease caused by the novel coronavirus SARSCoV-2. Despite the second vaccination for SARS-CoV-2,
the number of individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants (i.e., delta and lambda) has markedly increased worldwide. Although approximately 80% of individuals infected
with SARS-CoV-2 is mild to moderate, a part of them may
convert to severe clinical stages in about 1 week, ultimately
resulting in the intubation or death. Using drug repurposing,
it is, therefore, necessary to discover drugs that can prevent
clinical deterioration [1]. Here, we discuss the emergent use
of the old antidepressant fluvoxamine which may block clinical deterioration in mild to moderate patients infected with
SARS-CoV-2.
In November 2020, Dr. Lenze and his colleagues reported
that fluvoxamine could prevent clinical deterioration in adult
outpatients infected with SARS-CoV-2. In the study, clinical
deterioration occurred in 0 of the fluvoxamine group (n = 80)
and in 6 of placebo group (n = 72) [2]. Although sample
size of this study was small, this study strongly encouraged further trials using a large sample size. In February
2021, Dr. Seftel and his colleague reported a prospective,
non-randomized observational cohort study of fluvoxamine
in outpatients (n = 113) infected with SARS-CoV-2 at the
Golden Gate Fields horse racing track in Berkeley, California [3]. Incidence of hospitalization was 0 of the fluvoxamine-treated group (n = 65) and 6 of the observation alone
group (n = 48). Two patients required intensive care unit stay
with mechanical ventilation, one of them died. On April 23,
2021, fluvoxamine was added in the US National Institutes
of Health (NIH) COVID-19 Guidelines Panel although there
is insufficient evidence for the efficacy of fluvoxamine.
* Kenji Hashimoto
hashimoto@faculty.chiba-u.jp
1
Department of Respirology, Chiba University Graduate
School of Medicine, Chiba 260‑8670, Japan
2
Division of Clinical Neuroscience, Chiba University Center
for Forensic Mental Health, 1‑8‑1 Inohana, Chiba 260‑8670,
Japan
On August 6, 2021, the interim results of TOGETHER
trial (NCT04727424) by a multinational group in Canada
and Brazil were presented at the NIH symposium. They
compared three compounds, fluvoxamine, the antidiabetic
drug metformin, and the antiparasitic drug ivermectin.
Although metformin and ivermectin did not show beneficial
effects, fluvoxamine was much more promising. Among the
randomized participants (n = 1,480), fluvoxamine significantly reduced the risk of disease progression by 29% (95%
confidence interval 0.54–0.93) [4].
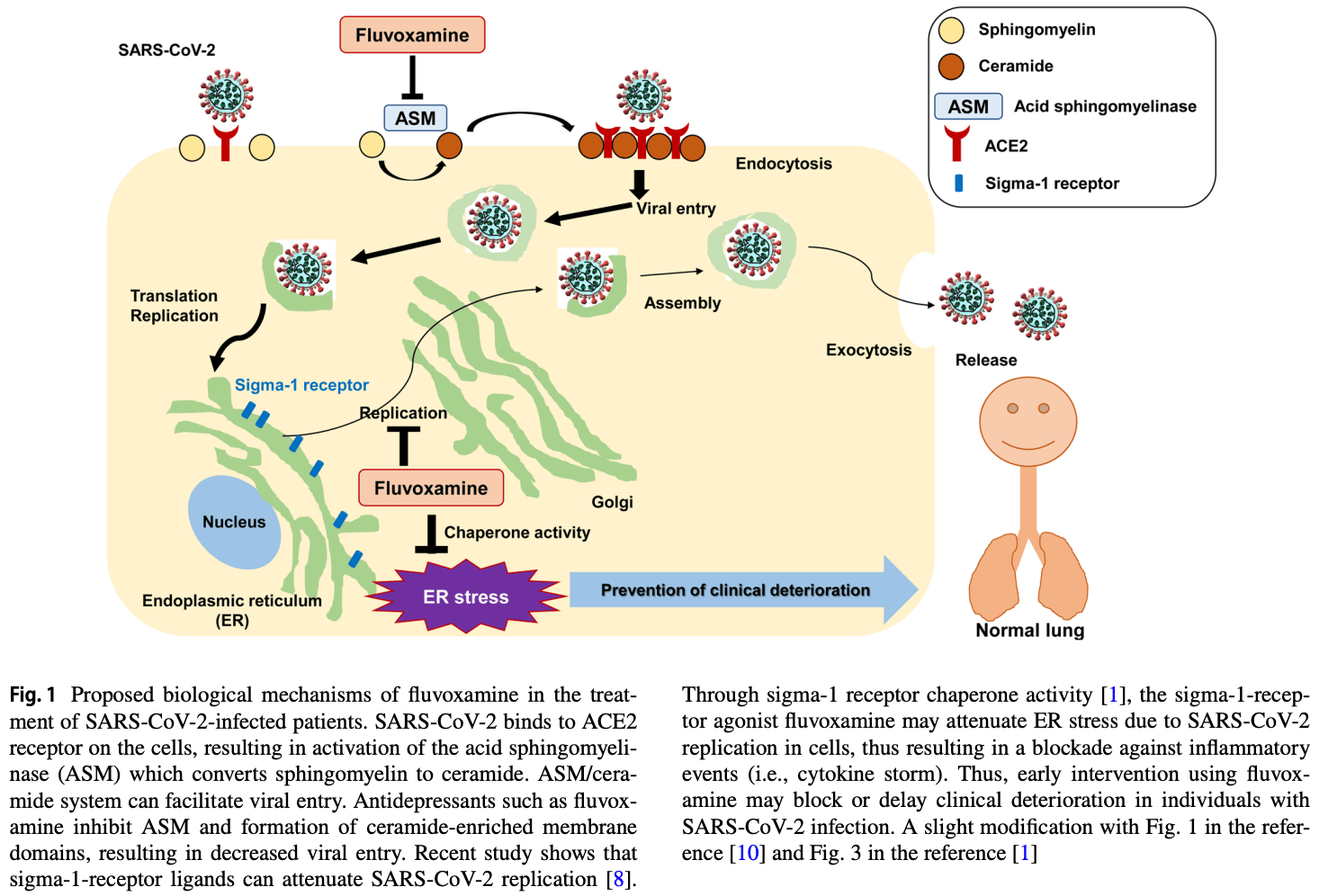
Detailed mechanisms of action of fluvoxamine for
COVID-19 are currently unknown. In 1996, we reported
that fluvoxamine binds to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) protein sigma-1 receptor with high affinity, suggesting a role of
sigma-1 receptor in the mechanisms of its action [5]. Subsequent studies suggest that fluvoxamine is a potent agonist
at sigma-1 receptor which plays a key role in inflammation
[1, 5, 6]. Among the antidepressants, fluvoxamine was the
most potent at sigma-1 receptor [1, 5, 6]. Furthermore, fluvoxamine has..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z",
"ISSN": [
"0940-1334",
"1433-8491"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z",
"alternative-id": [
"1326"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "24 August 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "27 August 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "2 September 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Dr. Y. Hashimoto and Dr. Suzuki have no conflict of interest. Dr. K. Hashimoto has received speakers’ honoraria from Abbott and Meiji Seika."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hashimoto",
"given": "Yaeko",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suzuki",
"given": "Takuji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8892-0439",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hashimoto",
"given": "Kenji",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience",
"container-title-short": "Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-03T22:22:38Z",
"timestamp": 1630707758000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-31T16:11:23Z",
"timestamp": 1643645483000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-30T00:20:35Z",
"timestamp": 1706574035553
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 17,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1630540800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1630540800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "161-163",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00406-020-01231-x",
"author": "K Hashimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "249",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur Arch psychiatry Clin Neurosci",
"key": "1326_CR1",
"unstructured": "Hashimoto K (2021) Repurposing of CNS drugs to treat COVID-19 infection: targeting the sigma-1 receptor. Eur Arch psychiatry Clin Neurosci 271(1):249–258",
"volume": "271",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"author": "E Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2292",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1326_CR2",
"unstructured": "Lenze E, Mattar C, Zorumski CF, Stevens A, Schweiger J, Nicol GE, Miller JP, Yang L, Yingling M, Avidan MS, Reiersen AM (2020) Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19. A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 324(22):2292–2300",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab050",
"author": "D Seftel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "1326_CR3",
"unstructured": "Seftel D, Boulware DR (2021) Prospective cohort of fluvoxamine for early treatment of coronavirus disease 19. Open Forum Infect Dis 8(2):ofab050",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "1326_CR4",
"unstructured": "Sax PE (2021) Could this be our first effective, inexpensive, widely available outpatient treatment for COVID-19? NEJM J Watch. https://blogs.jwatch.org/hiv-id-observations/index.php/could-this-be-our-first-effective-inexpensive-widely-available-outpatient-treatment-for-covid-19/2021/08/12/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0014-2999(96)00254-3",
"author": "N Narita",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "117",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "1326_CR5",
"unstructured": "Narita N, Hashimoto K, Tomitaka S, Minabe Y (1996) Interaction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors with subtypes of sigma receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 307(1):117–119",
"volume": "307",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jphs.2014.11.010",
"author": "K Hashimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "1326_CR6",
"unstructured": "Hashimoto K (2015) Activation of sigma-1 receptor chaperone in the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases and its clinical implication. J Pharmacol Sci 127(1):6–9",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.652688",
"author": "VP Sukhatme",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "652688",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "1326_CR7",
"unstructured": "Sukhatme VP, Reiersen AM, Vayttaden SJ, Sukhatme V (2021) Fluvoxamine: a review of its mechanisms of actions and its role in COVID-19. Front Pharmacol 12:652688",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe9403",
"author": "DE Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "6521",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "1326_CR8",
"unstructured": "Gordon DE, Hiatt J, Bouhaddou M, Rezelj VV, Ulferts S, Braberg H, Jureka AS, Obernier K, Guo JZ, Batra J, Kaake RM, Weckstein AR, Owens TW, Gupta M, Pourmal S, Titus EW, Cakir M, Soucheray M, McGregor M, Cakir Z, Jang G, O’Meara MJ, Tummino TA, Zhang Z, Foussard H, Rojc A, Zhou Y, Kuchenov D, Hüttenhain R, Xu J, Eckhardt M, Swaney DL, Fabius JM, Ummadi M, Tutuncuoglu B, Rathore U, Modak M, Haas P, Haas KM, Naing ZZC, Pulido EH, Shi Y, Barrio-Hernandez I, Memon D, Petsalaki E, Dunham A, Marrero MC, Burke D, Koh C, Vallet T, Silvas JA, Azumaya CM, Billesbølle C, Brilot AF, Campbell MG, Diallo A, Dickinson MS, Diwanji D, Herrera N, Hoppe N, Kratochvil HT, Liu Y, Merz GE, Moritz M, Nguyen HC, Nowotny C, Puchades C, Rizo AN, Schulze-Gahmen U, Smith AM, Sun M, Young ID, Zhao J, Asarnow D, Biel J, Bowen A, Braxton JR, Chen J, Chio CM, Chio US, Deshpande I, Doan L, Faust B, Flores S, Jin M, Kim K, Lam VL, Li F, Li J, Li YL, Li Y, Liu X, Lo M, Lopez KE, Melo AA, Moss FR 3rd, Nguyen P, Paulino J, Pawar KI, Peters JK, Pospiech TH Jr, Safari M, Sangwan S, Schaefer K, Thomas PV, Thwin AC, Trenker R, Tse E, Tsui TKM, Wang F, Whitis N, Yu Z, Zhang K, Zhang Y, Zhou F, Saltzberg D, QCRG Structural Biology Consortium, Hodder AJ, Shun-Shion AS, Williams DM, White KM, Rosales R, Kehrer T, Miorin L, Moreno E, Patel AH, Rihn S, Khalid MM, Vallejo-Gracia A, Fozouni P, Simoneau CR, Roth TL, Wu D, Karim MA, Ghoussaini M, Dunham I, Berardi F, Weigang S, Chazal M, Park J, Logue J, McGrath M, Weston S, Haupt R, Hastie CJ, Elliott M, Brown F, Burness KA, Reid E, Dorward M, Johnson C, Wilkinson SG, Geyer A, Giesel DM, Baillie C, Raggett S, Leech H, Toth R, Goodman N, Keough KC, Lind AL, Zoonomia Consortium, Klesh RJ, Hemphill KR, Carlson-Stevermer J, Oki J, Holden K, Maures T, Pollard KS, Sali A, Agard DA, Cheng Y, Fraser JS, Frost A, Jura N, Kortemme T, Manglik A, Southworth DR, Stroud RM, Alessi DR, Davies P, Frieman MB, Ideker T, Abate C, Jouvenet N, Kochs G, Shoichet B, Ott M, Palmarini M, Shokat KM, García-Sastre A, Rassen JA, Grosse R, Rosenberg OS, Verba KA, Basler CF, Vignuzzi M, Peden AA, Beltrao P, Krogan NJ (2020) Comparative host-coronavirus protein interaction networks reveal pan-viral disease mechanisms. Science 370(6521):eabe9403",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aau5266",
"author": "DA Rosen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "478",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "1326_CR9",
"unstructured": "Rosen DA, Seki SM, Fernández-Castañeda A, Beiter RM, Eccles JD, Woodfolk JA, Gaultier A (2019) Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis. Sci Transl Med 11(478):eaau5266",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2317.10.1002/cpt.2317",
"author": "N Hoertel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "1326_CR10",
"unstructured": "Hoertel N, Sánchez-Rico M, Gulbins E, Kornhuber J, Carpinteiro A, Lenze EJ, Reiersen AM, Abellán M, de la Muela P, Vernet R, Blanco C, Cougoule C, Beeker N, Neuraz A, Gorwood P, Alvarado JM, Meneton P, Limosin F (2021) AP-HP / Université de Paris / INSERM COVID-19 research collaboration, AP-HP COVID CDR Initiative, “Entrepôt de Données de Santé” AP-HP Consortium (in press) Association between FIASMAs and reduced risk of intubation or death in individuals hospitalized for severe COVID-19: an observational multicenter study. Clin Pharmacol Ther. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.2317.10.1002/cpt.2317",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 10,
"references-count": 10,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Old drug fluvoxamine, new hope for COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "272"
}