Higher-Dose Fluvoxamine and Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With COVID-19
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2023.23363, ACTIV-6, NCT04885530, Sep 2023 (preprint)
30th treatment shown to reduce risk in
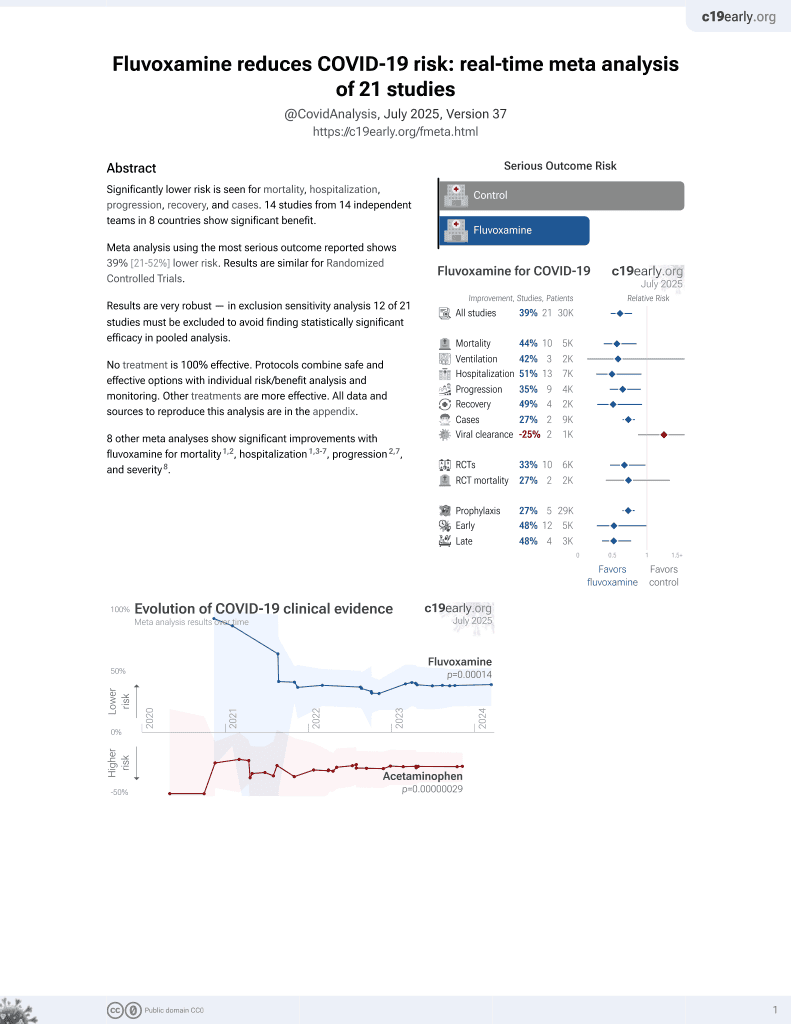
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Late treatment low risk population RCT showing lower progression to hospitalization or urgent care/ER visits with fluvoxamine, without statistical significance.
There was no mortality and only three hospitalizations. Authors provide no details on the cause of hospitalization, but they appear to be unrelated to COVID-19. eFigure 5 shows no COVID-19 clinical progression to hospitalization (note that a hospitalization can be seen in the equivalent plot for the low dose arm), and the text indicates that the "COVID clinical progression scale simplified into a self-reported evaluation of home levels (limited vs not)".
Note that the urgent care/ER visit outcome is also likely diluted due to inclusion of all-cause events, and could be statistically significant for only COVID-19 events.
The sustained recovery outcome, which shows no difference, was a post-hoc creation used to hide efficacy for ivermectin, and is not logical for evaluating efficacy in this trial. The definition includes any minor symptom within a three day period - e.g., any minor cough, headache, body ache, or fatigue that occurs in a three day period, regardless of cause, results in the treatment being considered a failure. For example, late treatment that is effective at minimizing progression, but has no improvement in resolution of cough, would not be detected. (Authors even use the end of the three day period to further minimize efficacy).
Late treatment - median 5 days, 75% 4+ days, 25% 7+ days, up to 12 days.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments3.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of progression, 31.0% lower, RR 0.69, p = 0.34, treatment 14 of 589 (2.4%), control 21 of 586 (3.6%), NNT 83, adjusted per study, urgent or emergency care visits, hospitalizations, or death.
|
|
clinical progression, 34.0% lower, OR 0.66, p = 0.32, treatment 589, control 586, mid-recovery, day 14, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
clinical progression, 15.0% higher, OR 1.15, p = 0.68, treatment 589, control 586, day 7, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
clinical progression, 6.0% lower, OR 0.94, p = 0.90, treatment 589, control 586, day 28, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
recovery time, 1.5% lower, relative time 0.99, treatment 589, control 586, mean time unwell.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 1.0% higher, HR 1.01, p = 0.86, treatment 589, control 586, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, post-hoc primary outcome.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 49.0% lower, RR 0.51, p = 0.59, treatment 1 of 589 (0.2%), control 2 of 586 (0.3%), NNT 583, non-COVID-19 hospitalization, day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Naggie et al., Effect of Ivermectin vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.18590.
Stewart et al., 13 Sep 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, 32 authors, study period 5 August, 2022 - 20 January, 2023, average treatment delay 5.0 days, trial NCT04885530 (history) (ACTIV-6).
Contact: susanna.naggie@duke.edu.
Higher-Dose Fluvoxamine and Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With COVID-19
JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2023.23363
IMPORTANCE The effect of higher-dose fluvoxamine in reducing symptom duration among outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19 remains uncertain. OBJECTIVE To assess the effectiveness of fluvoxamine, 100 mg twice daily, compared with placebo, for treating mild to moderate COVID-19.
DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS The ACTIV-6 platform randomized clinical trial aims to evaluate repurposed medications for mild to moderate COVID-19. Between August 25, 2022, and January 20, 2023, a total of 1175 participants were enrolled at 103 US sites for evaluating fluvoxamine; participants were 30 years or older with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and at least 2 acute COVID-19 symptoms for 7 days or less. INTERVENTIONS Participants were randomized to receive fluvoxamine, 50 mg twice daily on day 1 followed by 100 mg twice daily for 12 additional days (n = 601), or placebo (n = 607).
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary outcome was time to sustained recovery (defined as at least 3 consecutive days without symptoms). Secondary outcomes included time to death; time to hospitalization or death; a composite of hospitalization, urgent care visit, emergency department visit, or death; COVID-19 clinical progression scale score; and difference in mean time unwell. Follow-up occurred through day 28. RESULTS Among 1208 participants who were randomized and received the study drug, the median (IQR) age was 50 (40-60) years, 65.8% were women, 45.5% identified as Hispanic/Latino, and 76.8% reported receiving at least 2 doses of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Among 589 participants who received fluvoxamine and 586 who received placebo included in the primary analysis, differences in time to sustained recovery were not observed (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.99 [95% credible interval, 0.89-1.09]; P for efficacy = .40]). Additionally, unadjusted median time to sustained recovery was 10 (95% CI, 10-11) days in both the intervention and placebo groups. No deaths were reported. Thirty-five participants reported health care use events (a priori defined as death, hospitalization, or emergency department/urgent care visit): 14 in the fluvoxamine group compared with 21 in the placebo group (HR, 0.69 [95% credible interval, 0.27-1.21]; P for efficacy = .86) There were 7 serious adverse events in 6 participants (2 with fluvoxamine and 4 with placebo) but no deaths. CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE Among outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19, treatment with fluvoxamine does not reduce duration of COVID-19 symptoms.
References
Acosta, Garg, Pham, Racial and ethnic disparities in rates of COVID-19-associated hospitalization, intensive care unit admission, and in-hospital death in the united states from March 2020 to February 2021, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.30479?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.23363
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2201662
Brilleman, Elci, Novik, Wolfe, Bayesian survival analysis using the rstanarm R package, doi:10.48550/arxiv.2002.09633
Core, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing
Goodrich, Gabry, Ali, Brilleman, Bayesian Applied Regression Modeling via Stan [R Package Rstanarm
Guan, Puenpatom, Johnson, Impact of molnupiravir treatment on patient-reported coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) symptoms in the phase 3 MOVe-OUT trial: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad409
Harrell, Bayesian Regression Modeling Strategies [R Package Rmsb
Hashimoto, Suzuki, Hashimoto, Mechanisms of action of fluvoxamine for COVID-19: a historical review, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01432-3
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.23363
Lopez, Iii, Hart, Iii, Katz, Racial and ethnic health disparities related to COVID-19, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26443?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.23363
Mccarthy, Naggie, Boulware, Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators. Effect of fluvoxamine vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.24100?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.23363
Naggie, Boulware, Lindsell, Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV-6) Study Group and Investigators. Effect of ivermectin vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.18590?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.23363
Reis, Santos Moreira-Silva, Silva, Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
Reis, Santos, Silva, Silva, Oral fluvoxamine with inhaled budesonide for treatment of early-onset COVID-19: a randomized platform trial, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M22-3305
Sukhatme, Reiersen, Vayttaden, Sukhatme, Fluvoxamine: a review of its mechanism of action and its role in COVID-19, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.652688
Therneau, Survival Analysis [R Package Survival
Venkatesan, Repurposing drugs for treatment of COVID-19, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00270-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2023.23363",
"ISSN": [
"0098-7484"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2023.23363",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Importance</jats:title><jats:p>The effect of higher-dose fluvoxamine in reducing symptom duration among outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19 remains uncertain.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To assess the effectiveness of fluvoxamine, 100 mg twice daily, compared with placebo, for treating mild to moderate COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design, Setting, and Participants</jats:title><jats:p>The ACTIV-6 platform randomized clinical trial aims to evaluate repurposed medications for mild to moderate COVID-19. Between August 25, 2022, and January 20, 2023, a total of 1175 participants were enrolled at 103 US sites for evaluating fluvoxamine; participants were 30 years or older with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and at least 2 acute COVID-19 symptoms for 7 days or less.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Interventions</jats:title><jats:p>Participants were randomized to receive fluvoxamine, 50 mg twice daily on day 1 followed by 100 mg twice daily for 12 additional days (n = 601), or placebo (n = 607).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Main Outcomes and Measures</jats:title><jats:p>The primary outcome was time to sustained recovery (defined as at least 3 consecutive days without symptoms). Secondary outcomes included time to death; time to hospitalization or death; a composite of hospitalization, urgent care visit, emergency department visit, or death; COVID-19 clinical progression scale score; and difference in mean time unwell. Follow-up occurred through day 28.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Among 1208 participants who were randomized and received the study drug, the median (IQR) age was 50 (40-60) years, 65.8% were women, 45.5% identified as Hispanic/Latino, and 76.8% reported receiving at least 2 doses of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Among 589 participants who received fluvoxamine and 586 who received placebo included in the primary analysis, differences in time to sustained recovery were not observed (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.99 [95% credible interval, 0.89-1.09]; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> for efficacy = .40]). Additionally, unadjusted median time to sustained recovery was 10 (95% CI, 10-11) days in both the intervention and placebo groups. No deaths were reported. Thirty-five participants reported health care use events (a priori defined as death, hospitalization, or emergency department/urgent care visit): 14 in the fluvoxamine group compared with 21 in the placebo group (HR, 0.69 [95% credible interval, 0.27-1.21]; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> for efficacy = .86) There were 7 serious adverse events in 6 participants (2 with fluvoxamine and 4 with placebo) but no deaths.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions and Relevance</jats:title><jats:p>Among outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19, treatment with fluvoxamine does not reduce duration of COVID-19 symptoms.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Trial Registration</jats:title><jats:p>ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04885530\">NCT04885530</jats:ext-link></jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Data Science, University of Virginia, Charlottesville"
}
],
"family": "Stewart",
"given": "Thomas G.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Global Health, Division of Infectious Diseases, Emory University School of Medicine and Rollins School of Public Health, Atlanta, Georgia"
}
],
"family": "Rebolledo",
"given": "Paulina A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Mourad",
"given": "Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Lindsell",
"given": "Christopher J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Minnesota Medical School, General Internal Medicine, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Boulware",
"given": "David R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, New York"
}
],
"family": "McCarthy",
"given": "Matthew W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stakeholder Advisory Committee, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Thicklin",
"given": "Florence",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "L&A Morales Healthcare, Inc, Hialeah, Florida"
}
],
"family": "Garcia del Sol",
"given": "Idania T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Minnesota Medical School, General Internal Medicine, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Bramante",
"given": "Carolyn T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston"
}
],
"family": "Lenert",
"given": "Leslie A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center New Orleans, University Medical Center New Orleans, New Orleans"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Section on Infectious Diseases, Winston-Salem, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "John C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford University School of Medicine, Department of Medicine, Infectious Diseases and Geographic Medicine Division, Stanford, California"
}
],
"family": "Cardona",
"given": "Orlando Quintero",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford University School of Medicine, Department of Medicine, Infectious Diseases and Geographic Medicine Division, Stanford, California"
}
],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "Jake",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Kansas School of Medicine-Wichita, Center for Clinical Research, Wichita"
}
],
"family": "Schwasinger-Schmidt",
"given": "Tiffany",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora"
}
],
"family": "Ginde",
"given": "Adit A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City"
}
],
"family": "Castro",
"given": "Mario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, Miami, Florida"
}
],
"family": "Jayaweera",
"given": "Dushyantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland"
}
],
"family": "Sulkowski",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Gentile",
"given": "Nina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "McTigue",
"given": "Kathleen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Felker",
"given": "G. Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "DeLong",
"given": "Allison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Wilder",
"given": "Rhonda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
}
],
"family": "Rothman",
"given": "Russell L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
},
{
"name": "Veterans Affairs Tennessee Valley Healthcare System, Geriatric Research, Education and Clinical Center (GRECC), Nashville"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Sean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, Bethesda, Maryland"
}
],
"family": "Dunsmore",
"given": "Sarah E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland"
}
],
"family": "Adam",
"given": "Stacey J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, Washington, DC"
}
],
"family": "Hanna",
"given": "George J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Outcomes & Biomedical Informatics, College of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville"
}
],
"family": "Shenkman",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Hernandez",
"given": "Adrian F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Naggie",
"given": "Susanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fraser",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gamboa Jackman",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McAdams",
"given": "M. Patricia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vail",
"given": "Julia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Korzekwinski",
"given": "Kayla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oyelakin",
"given": "Martina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chopp",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Randle",
"given": "Desmon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dockery",
"given": "Samantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adkins",
"given": "Rodney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Crow",
"given": "Mathew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nowell",
"given": "Erin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wells",
"given": "Kadie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Herbert",
"given": "Alicia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stone",
"given": "Allegra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Heavlin",
"given": "Heather",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Linley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harding",
"given": "Tina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrington",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beauchaine",
"given": "Meaghan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lindblom",
"given": "Kelly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burns",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aamodt",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Jess",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dixon",
"given": "Sheri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Yue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Graves",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grindstaff",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrell",
"given": "Frank",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lai",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Liao",
"given": "Vicky",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lopez",
"given": "Itzel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Manis",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mankowski",
"given": "Kalley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marlin",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Merkel",
"given": "Alyssa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nwosu",
"given": "Sam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Obregon",
"given": "Savannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Orozco",
"given": "Dirk",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prato",
"given": "Nelson",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rohde",
"given": "Max",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shirey-Rice",
"given": "Jana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vermillion",
"given": "Krista",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Jacob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Hsi-nien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vance",
"given": "Meghan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Weir",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vincent",
"given": "William (Kelly)",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vincent",
"given": "Raina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bianchi",
"given": "Ray",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Premas",
"given": "Jen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cordero-Loperena",
"given": "Diana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rivera",
"given": "Evelyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Madhu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Karawan",
"given": "Greg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arena",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "DeAlmeida",
"given": "Sonaly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramin",
"given": "Soroush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nataraj",
"given": "Jaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dedier",
"given": "Julien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramirez",
"given": "Ana Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Waite",
"given": "Katherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Okulicz",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marcus",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Southwell",
"given": "Alexis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jacques",
"given": "Genice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sexton",
"given": "Cedar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brounce",
"given": "Ginger",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "George-Adebayo",
"given": "Constance",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adebayo",
"given": "Adeolu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zapatero",
"given": "Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clement",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ronan",
"given": "Theresa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Woods",
"given": "Ashley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gallegos",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Flys",
"given": "Tamara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sloan",
"given": "Olivia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Olofintuyi",
"given": "Anthony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Samraj",
"given": "Joshua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Samraj",
"given": "Jackelyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vasbinder",
"given": "Alma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Averett",
"given": "Amaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Slandzicki",
"given": "Alex",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Milstone",
"given": "Aaron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wallan",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robbs",
"given": "Lindsey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vogel",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Munoz",
"given": "Sebastian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kavtaradze",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "Casandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Singleton",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sevier",
"given": "Marcus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rivon",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Del Pilar",
"given": "Arnold",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spangler",
"given": "Amber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rao",
"given": "Sohail",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cantu",
"given": "Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Krishna",
"given": "Arvind",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Daugherty",
"given": "Heidi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kerr",
"given": "Brandi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "Kathy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spees",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marta",
"given": "Mailyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dolor",
"given": "Rowena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vergara",
"given": "Lorraine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jordan",
"given": "Jackie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burruss",
"given": "Valencia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hurst",
"given": "Terri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ofotokun",
"given": "Igho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rebolledo",
"given": "Paulina A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Cecilia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Veronica E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prabhu",
"given": "Rajesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Klicka",
"given": "Krystal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lightfeather",
"given": "Amber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "James",
"given": "Vickie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "Marcella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parihar",
"given": "Pradeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Torress",
"given": "De'Ambra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oragwu",
"given": "Chukwuemeka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oguego",
"given": "Ngozi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pillai",
"given": "Rajesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Juma",
"given": "Mustafa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gabriel",
"given": "Ahab",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ghaly",
"given": "Emad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Michal",
"given": "Marian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vasquez",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mamon",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sheets",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hassanien",
"given": "Gammal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "Samah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Samir",
"given": "Yehia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Meltzer",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shahamatdar",
"given": "Soroush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Heidish",
"given": "Ryan S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brehaut",
"given": "Scott",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roche",
"given": "Angelina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "Manisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Koppinger",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baez",
"given": "Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pagan",
"given": "Ivone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdelsayed",
"given": "Dallal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aziz",
"given": "Mina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Philip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lozinski",
"given": "Grace",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Griffin",
"given": "Alvin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Love",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mattox",
"given": "Bonnie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Raykel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pardue",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rowland",
"given": "Teddy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ruiz-Unger",
"given": "Juan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reyes",
"given": "Lionel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zamora",
"given": "Yadira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bacallao",
"given": "Navila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cienki",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jenny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Szeto",
"given": "Jeremy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sulkowski",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stelmash",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garcia del Sol",
"given": "Idania",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morales Castillo",
"given": "Ledular",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gutierrez",
"given": "Anya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prieto",
"given": "Sabrina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Amon",
"given": "Arch",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barbera",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bugajski",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wills",
"given": "Walter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jacklin",
"given": "Kellcee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lamb",
"given": "Deryl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harper",
"given": "Amron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stout",
"given": "Elmer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Weeks",
"given": "Katherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Griffin",
"given": "Merischia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pyram-Bernard",
"given": "Nancy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quintero",
"given": "Arlen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adhami",
"given": "Eftim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carrillo",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maria",
"given": "Josette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Paudel",
"given": "Diksha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Raymond",
"given": "Oksana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Summers",
"given": "Jeffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "Tammy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Panaccione",
"given": "Ebony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Szwast",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdulghani",
"given": "Ahsan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vasoya",
"given": "Pravin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Conrad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wiley",
"given": "Hawa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Austin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khizer",
"given": "Saadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Nirav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adeyemi",
"given": "Oluwadamilola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chi",
"given": "Wei Ning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "July",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morton-Jost",
"given": "Melissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Castex",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Feliciano",
"given": "Phillip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Olivo",
"given": "Jacqueline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maldonado",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vecchiarelli",
"given": "Anthony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gaytan-Alvarez",
"given": "Diana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cherukuri",
"given": "Vijaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lima",
"given": "Santia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alicic",
"given": "Radica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lambert",
"given": "Allison A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Urbat",
"given": "Carissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baxter",
"given": "Joni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "Ann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Linn",
"given": "Dawn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fisher",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Vijay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Yuti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Talati",
"given": "Roshan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Priti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ellison",
"given": "Leonard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roman",
"given": "Angee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "Jeffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moy",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Naquiallah",
"given": "Dina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Binod",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Upinder",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jazayeri",
"given": "Yasmin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Donnell",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quintero",
"given": "Orlando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pathak",
"given": "Divya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Anita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chandrasekar",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Curtis",
"given": "Clifford",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "White",
"given": "Briana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dockery",
"given": "Martha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hicks",
"given": "Maya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fortt",
"given": "Tabitha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fortt",
"given": "Anisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones-Ince",
"given": "Ingrid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McKee",
"given": "Alix",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Farlow",
"given": "Brenda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gentile",
"given": "Nina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grady",
"given": "Casey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Richwine",
"given": "Randall",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Tearani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pazier",
"given": "Penny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Michelson",
"given": "Edward",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Watts",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kariyawasam",
"given": "Diluma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rodriguez",
"given": "Leann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Luis Garcia",
"given": "Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Manresa",
"given": "Ismarys",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Achong",
"given": "Angel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garcia",
"given": "Mari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khetpal",
"given": "Sangeeta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Posey",
"given": "Faith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mahadevan",
"given": "Arvind",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gnoni",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "VandeWeerd",
"given": "Carla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sappington",
"given": "Erica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "Mitchell",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "Melissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ding",
"given": "Xinyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "D'Andrea",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Swink",
"given": "Wayne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bozant",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Powers-Fletcher",
"given": "Margaret",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Delia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mukunzi",
"given": "Sylvere",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Manning",
"given": "Brittney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Isache",
"given": "Carmen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bowman",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Callaghan-Brown",
"given": "Angelique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Debra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ast",
"given": "Ashley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duran",
"given": "Brent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cornejo",
"given": "Ashlie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Archer",
"given": "Allie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jayaweera",
"given": "Dushyantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Almanzar",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Motel",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bhat",
"given": "Neeta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parra",
"given": "Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pullen",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campora",
"given": "Paula",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seithel",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sekikawa",
"given": "Akira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Klawson",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arnold",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ostrosky-Zeichner",
"given": "Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Umana",
"given": "Virginia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nielsen",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grimes",
"given": "Carolyn Z.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patterson",
"given": "Thomas F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tragus",
"given": "Robin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Soileau",
"given": "Bridgette T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "Patrick E.H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hallowell",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haughey",
"given": "Heather M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vaidya-Tank",
"given": "Bhavna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gould",
"given": "Cameron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Goyal",
"given": "Parul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sommers",
"given": "Sue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pangburn",
"given": "Haley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Carly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abbott",
"given": "Rica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seagle",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "DeComarmond",
"given": "Mathias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pickell",
"given": "Nicholas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Umana",
"given": "Unwana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alleyne",
"given": "Candace",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Armas",
"given": "Eddie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Perez Landabur",
"given": "Ramon O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "De La Cruz",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ballmajo",
"given": "Martha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA",
"container-title-short": "JAMA",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-17T16:31:12Z",
"timestamp": 1700238672000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-17T16:31:17Z",
"timestamp": 1700238677000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-18T00:39:48Z",
"timestamp": 1700267988727
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/articlepdf/2812204/jama_stewart_2023_oi_230138_1700012803.18294.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00270-8",
"article-title": "Repurposing drugs for treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Venkatesan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "joi230138r1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2201662",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for Covid-19.",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "599",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi230138r2",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.652688",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine: a review of its mechanism of action and its role in COVID-19.",
"author": "Sukhatme",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "joi230138r3",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2292",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi230138r5",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4",
"article-title": "Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial.",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e42",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Lancet Glob Health",
"key": "joi230138r6",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.24100",
"article-title": "Effect of fluvoxamine vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "McCarthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "296",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi230138r7",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-3305",
"article-title": "Oral fluvoxamine with inhaled budesonide for treatment of early-onset COVID-19: a randomized platform trial.",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "667",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "joi230138r8",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.18590",
"article-title": "Effect of ivermectin vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Naggie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1595",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi230138r9",
"volume": "328",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Bayesian survival analysis using the rstanarm R package.",
"author": "Brilleman",
"journal-title": "arXiv",
"key": "joi230138r12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad409",
"article-title": "Impact of molnupiravir treatment on patient-reported coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) symptoms in the phase 3 MOVe-OUT trial: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial.",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "joi230138r15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01432-3",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of action of fluvoxamine for COVID-19: a historical review.",
"author": "Hashimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1898",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Mol Psychiatry",
"key": "joi230138r16",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26443",
"article-title": "Racial and ethnic health disparities related to COVID-19.",
"author": "Lopez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "719",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi230138r18",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.30479",
"article-title": "Racial and ethnic disparities in rates of COVID-19-associated hospitalization, intensive care unit admission, and in-hospital death in the united states from March 2020 to February 2021.",
"author": "Acosta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "joi230138r19",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "R Core Team",
"key": "joi230138r10",
"volume-title": "R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"author": "Goodrich",
"key": "joi230138r11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"author": "Harrell",
"key": "joi230138r13",
"volume-title": "Bayesian Regression Modeling Strategies [R Package Rmsb]",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "Therneau",
"key": "joi230138r14",
"volume-title": "Survival Analysis [R Package Survival]",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "joi230138r4",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Accessed September 5, 2023. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/"
},
{
"key": "joi230138r17",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 provisional counts: health disparities. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed September 5, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/covid19/health_disparities.htm"
}
],
"reference-count": 19,
"references-count": 19,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2812204"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [
"The ACTIV-6 Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Higher-Dose Fluvoxamine and Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article"
}