Effect of Fluvoxamine vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.24100, ACTIV-6, NCT04885530, Oct 2022 (preprint)
30th treatment shown to reduce risk in
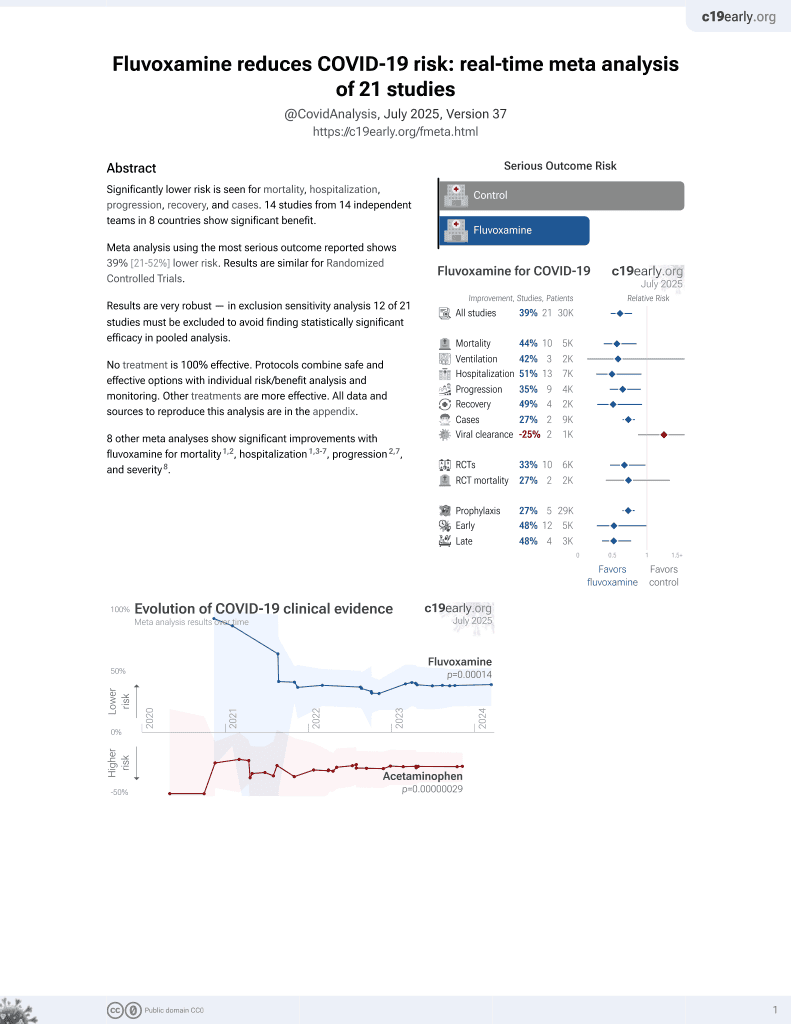
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT low-risk outpatients with very late treatment (median 5
days, 20% ≥8 days) in the USA, showing no significant differences with
low-dose fluvoxamine treatment.
Many of the issues noted for the ivermectin arm1 also apply to this arm, for example none of the
pre-specified outcomes have been reported2.
In the ivermectin paper the abstract refers to the main post-hoc outcome as
the "main outcome", this wording has been updated to "primary outcome" for
fluvoxamine.
eFigure 4 shows efficacy continuously declining over time,
which may be due to lower severity as the virus evolves. Treatment delay was
up to 13 days (eFigure 1). Severe dyspnea at baseline was more common for
fluvoxamine (6/586 vs. 3/533, eTable 1).
Authors state that the median treatment delay (5 days) is at
the upper limit of the "recommend (sic) start of antiviral medicines (≤5
days)". There is no reference and it's unclear who recommends such late
treatment.
Fluvoxamine 50mg twice daily.
ACTIV trial authors have reported a number of issues that may affect
the reliability of the results in ACTIV trials including
participant fraud3,
biased participant demographics4,
resource issues that may have led to protocol deviations4,
differences in trial design including inconsistent inclusion/exclusion
criteria4,
participant self-selection bias3,4,
underrepresentation of older patients due to web-based recruitment4,
changes in treatment and public health policies during trials4,
treatment delay determination from shipping logs and delivery that may not be directly
to the patient3,
variable placebo responses (e.g., oral vs. inhaled)5,
logistical challenges maintaining blinding5,
errors from complex data collection systems5,
unplanned design changes including endpoint changes5, and
inconsistent SoC across trial sites and time periods5.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments6.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
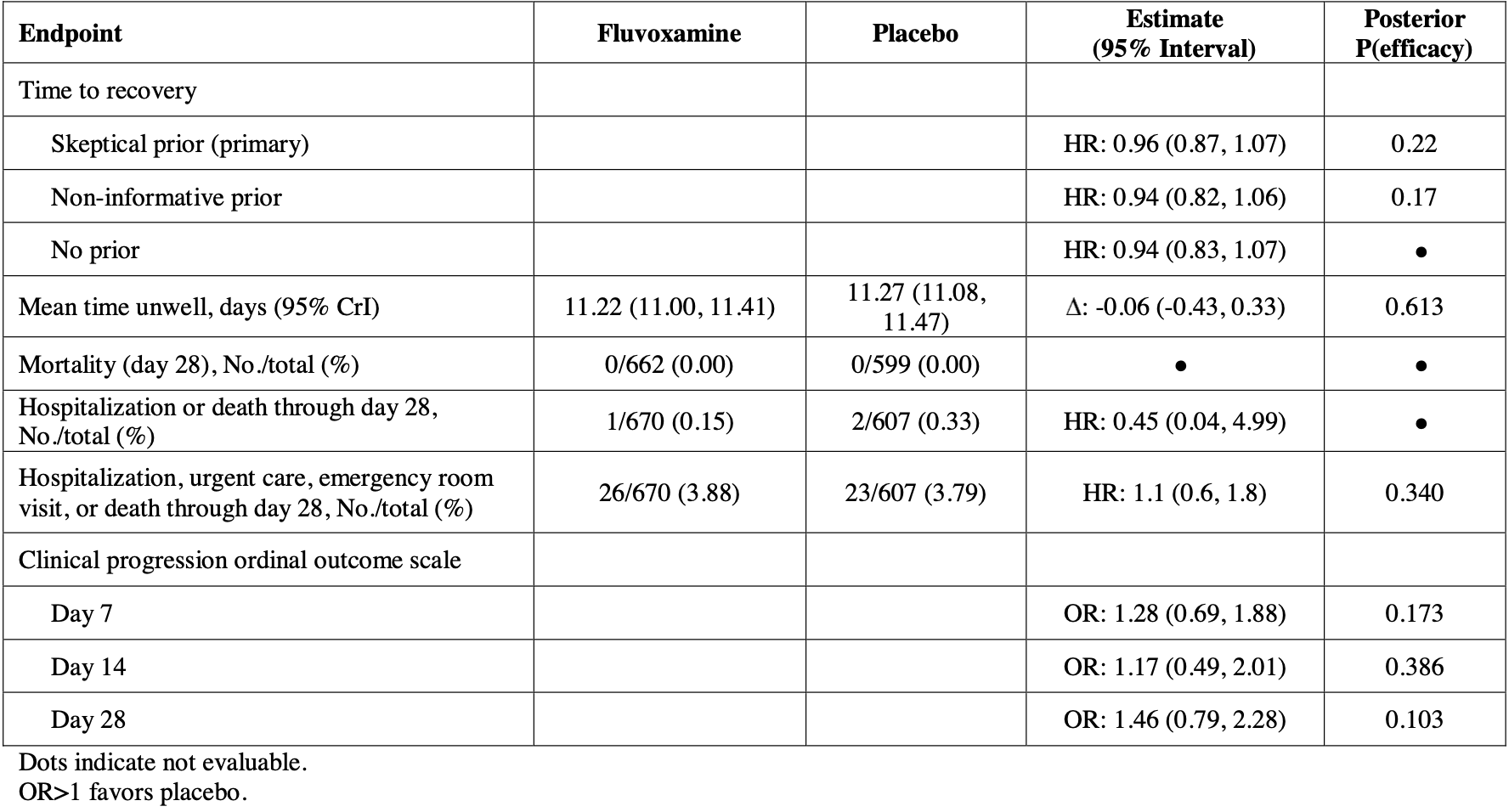
risk of hospitalization, 55.0% lower, RR 0.45, p = 0.51, treatment 1 of 670 (0.1%), control 2 of 607 (0.3%), NNT 555, day 28.
|
|
C19 pneumonia, 67.6% lower, RR 0.32, p = 0.48, treatment 0 of 615 (0.0%), control 1 of 565 (0.2%), NNT 565, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), C19 pneumonia, eTable 2.
|
|
risk of progression, 10.0% higher, RR 1.10, p = 0.78, treatment 26 of 670 (3.9%), control 23 of 607 (3.8%), adjusted per study, urgent or emergency care visits, hospitalizations, or death.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 4.2% higher, HR 1.04, p = 0.45, treatment 674, control 614, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, post-hoc primary outcome.
|
|
clinical progression, 28.0% higher, OR 1.28, p = 0.33, treatment 670, control 607, mid-recovery, day 7, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
clinical progression, 17.0% higher, OR 1.17, p = 0.68, treatment 670, control 607, day 14, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
clinical progression, 47.0% higher, OR 1.47, p = 0.16, treatment 670, control 607, day 28, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Naggie et al., Effect of Ivermectin vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.18590.
3.
Lindsell et al., ACTIV-6: Operationalizing a decentralized, outpatient randomized platform trial to evaluate efficacy of repurposed medicines for COVID-19, Journal of Clinical and Translational Science, doi:10.1017/cts.2023.644.
4.
Wohl et al., Engaging communities in therapeutics clinical research during pandemics: Experiences and lessons from the ACTIV COVID-19 therapeutics research initiative, Journal of Clinical and Translational Science, doi:10.1017/cts.2024.561.
McCarthy et al., 18 Oct 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, mean age 48.5, 243 authors, study period 6 August, 2021 - 27 May, 2022, average treatment delay 5.0 days, trial NCT04885530 (history) (ACTIV-6).
Contact: naggie@duke.edu.
Effect of Fluvoxamine vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19
JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.24100
for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators IMPORTANCE The effectiveness of fluvoxamine to shorten symptom duration or prevent hospitalization among outpatients with mild to moderate symptomatic COVID-19 is unclear. OBJECTIVE To evaluate the efficacy of low-dose fluvoxamine (50 mg twice daily) for 10 days compared with placebo for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in the US. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS The ongoing Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV-6) platform randomized clinical trial was designed to test repurposed medications in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19. A total of 1288 participants aged 30 years or older with test-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and experiencing 2 or more symptoms of acute COVID-19 for 7 days or less were enrolled between August 6, 2021, and May 27, 2022, at 91 sites in the US. INTERVENTIONS Participants were randomized to receive 50 mg of fluvoxamine twice daily for 10 days or placebo.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary outcome was time to sustained recovery (defined as the third day of 3 consecutive days without symptoms). There were 7 secondary outcomes, including a composite outcome of hospitalization, urgent care visit, emergency department visit, or death through day 28. RESULTS Among 1331 participants who were randomized (median age, 47 years [IQR, 38-57 years]; 57% were women; and 67% reported receiving Ն2 doses of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine), 1288 completed the trial (674 in the fluvoxamine group and 614 in the placebo group). The median time to sustained recovery was 12 days (IQR, 11-14 days) in the fluvoxamine group and 13 days (IQR, 12-13 days) in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.96 [95% credible interval, 0.86-1.06], posterior P = .21 for the probability of benefit [determined by an HR >1]). For the composite outcome, 26 participants (3.9%) in the fluvoxamine group were hospitalized, had an urgent care visit, had an emergency department visit, or died compared with 23 participants (3.8%) in the placebo group (HR, 1.1 [95% credible interval, 0.5-1.8], posterior P = .35 for the probability of benefit [determined by an HR <1]). One participant in the fluvoxamine group and 2 participants in the placebo group were hospitalized; no deaths occurred in either group. Adverse events were uncommon in both groups. CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE Among outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19, treatment with 50 mg of fluvoxamine twice daily for 10 days, compared with placebo, did not improve time to sustained recovery. These findings do not support the use of fluvoxamine at this dose and duration in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.
References
Acquisition, Naggie, Boulware, Lindsell, Stewart et al., Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content
Administrative, Mccarthy, Naggie, Boulware, Singh et al., Supervision: Naggie
Ahmad, Cisewski, Anderson, Provisional mortality data-United States, 2021, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7117e1
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Group. Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Boulware, Pullen, Bangdiwala, A randomized trial of hydroxychloroquine as postexposure prophylaxis for Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2016638
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2201662
Core, R: A language and environment for statistical computing
Guy, Dipaola, Romanelli, Dutch, Rapid repurposing of drugs for COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb9332
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19
Lee, Vigod, Bortolussi-Courval, Fluvoxamine for outpatient management of COVID-19 to prevent hospitalization: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.6269?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2022.24100
Lenze, Fluvoxamine for Early Treatment of Covid-19 (STOP COVID 2)
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2022.24100
Reis, Santos Moreira-Silva, Silva, Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
Rosen, Seki, Fernández-Castañeda, Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aau5266
Seftel, Boulware, Prospective cohort of fluvoxamine for early treatment of coronavirus disease 19, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab050
Skipper, Pastick, Engen, Hydroxychloroquine in nonhospitalized adults with early COVID-19: a randomized trial, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M20-4207
Sukhatme, Reiersen, Vayttaden, Sukhatme, Fluvoxamine: a review of its mechanism of action and its role in COVID-19, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.652688
Wiltz, Feehan, Molinari, Racial and ethnic disparities in receipt of medications for treatment of COVID-19-United States, March 2020, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7103e1
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.24100",
"ISSN": [
"0098-7484"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2022.24100",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Importance</jats:title><jats:p>The effectiveness of fluvoxamine to shorten symptom duration or prevent hospitalization among outpatients with mild to moderate symptomatic COVID-19 is unclear.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To evaluate the efficacy of low-dose fluvoxamine (50 mg twice daily) for 10 days compared with placebo for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in the US.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design, Setting, and Participants</jats:title><jats:p>The ongoing Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV-6) platform randomized clinical trial was designed to test repurposed medications in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19. A total of 1288 participants aged 30 years or older with test-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and experiencing 2 or more symptoms of acute COVID-19 for 7 days or less were enrolled between August 6, 2021, and May 27, 2022, at 91 sites in the US.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Interventions</jats:title><jats:p>Participants were randomized to receive 50 mg of fluvoxamine twice daily for 10 days or placebo.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Main Outcomes and Measures</jats:title><jats:p>The primary outcome was time to sustained recovery (defined as the third day of 3 consecutive days without symptoms). There were 7 secondary outcomes, including a composite outcome of hospitalization, urgent care visit, emergency department visit, or death through day 28.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Among 1331 participants who were randomized (median age, 47 years [IQR, 38-57 years]; 57% were women; and 67% reported receiving ≥2 doses of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine), 1288 completed the trial (674 in the fluvoxamine group and 614 in the placebo group). The median time to sustained recovery was 12 days (IQR, 11-14 days) in the fluvoxamine group and 13 days (IQR, 12-13 days) in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.96 [95% credible interval, 0.86-1.06], posterior <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .21 for the probability of benefit [determined by an HR &amp;gt;1]). For the composite outcome, 26 participants (3.9%) in the fluvoxamine group were hospitalized, had an urgent care visit, had an emergency department visit, or died compared with 23 participants (3.8%) in the placebo group (HR, 1.1 [95% credible interval, 0.5-1.8], posterior <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .35 for the probability of benefit [determined by an HR &amp;lt;1]). One participant in the fluvoxamine group and 2 participants in the placebo group were hospitalized; no deaths occurred in either group. Adverse events were uncommon in both groups.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions and Relevance</jats:title><jats:p>Among outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19, treatment with 50 mg of fluvoxamine twice daily for 10 days, compared with placebo, did not improve time to sustained recovery. These findings do not support the use of fluvoxamine at this dose and duration in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Trial Registration</jats:title><jats:p>ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04885530?id=NCT04885530&amp;amp;draw=2&amp;amp;rank=1\">NCT04885530</jats:ext-link></jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, New York"
}
],
"family": "McCarthy",
"given": "Matthew W.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Naggie",
"given": "Susanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and International Medicine, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Boulware",
"given": "David R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biostatistics, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
}
],
"family": "Lindsell",
"given": "Christopher J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biostatistics, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
},
{
"name": "Now with School of Data Science, University of Virginia, Charlottesville"
}
],
"family": "Stewart",
"given": "Thomas G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Felker",
"given": "G. Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, Miami, Florida"
}
],
"family": "Jayaweera",
"given": "Dushyantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland"
}
],
"family": "Sulkowski",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, Temple University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Gentile",
"given": "Nina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and International Medicine, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis"
}
],
"family": "Bramante",
"given": "Carolyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departments of Internal Medicine and Microbiology and Immunology, School of Medicine, Stanford University, Stanford, California"
}
],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Upinder",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Dolor",
"given": "Rowena J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Innovation Medical Research Center, Kendall, Florida"
}
],
"family": "Ruiz-Unger",
"given": "Juan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Sybil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "DeLong",
"given": "Allison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Remaly",
"given": "April",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Wilder",
"given": "Rhonda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biostatistics, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Sean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, Bethesda, Maryland"
}
],
"family": "Dunsmore",
"given": "Sarah E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland"
}
],
"family": "Adam",
"given": "Stacey J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stakeholder Advisory Committee, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Thicklin",
"given": "Florence",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, Washington, DC"
}
],
"family": "Hanna",
"given": "George",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Colorado, Denver"
}
],
"family": "Ginde",
"given": "Adit A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Missouri, Kansas City, Kansas"
}
],
"family": "Castro",
"given": "Mario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "McTigue",
"given": "Kathleen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Outcomes and Biomedical Informatics, College of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville"
}
],
"family": "Shenkman",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Clinical Research Institute, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Hernandez",
"given": "Adrian F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vincent",
"given": "William (Kelly)",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vincent",
"given": "Raina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bianchi",
"given": "Ray",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Premas",
"given": "Jen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evelyn Rivera",
"given": "Diana Cordero-Loperena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Madhu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Karawan",
"given": "Greg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ziomek",
"given": "Carey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arena",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "DeAlmeida",
"given": "Sonaly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramin",
"given": "Soroush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nataraj",
"given": "Jaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Paasche-Orlow",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Henault",
"given": "Lori",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Waite",
"given": "Katie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brounce",
"given": "Ginger",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "George-Adebayo",
"given": "Constance",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adebayo",
"given": "Adeolu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wallan",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vogel",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Munoz",
"given": "Sebastian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kavtaradze",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "Cassandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Singleton",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rivon",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sevier",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Del Pilar",
"given": "Arnold",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spangler",
"given": "Amber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rao",
"given": "Sohail",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cantu",
"given": "Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Krishna",
"given": "Arvind",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "Kathy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Falkner",
"given": "Tylene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kerr",
"given": "Brandi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spees",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marta",
"given": "Mailyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrington",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Frazier",
"given": "Madison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vergara",
"given": "Lorraine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burruss",
"given": "Valencia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hurst",
"given": "Terri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ofotokun",
"given": "Igho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bristow",
"given": "Laurel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prabhu",
"given": "Rajesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Klicka",
"given": "Krystal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lightfeather",
"given": "Amber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "James",
"given": "Vicki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "Marcella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parihar",
"given": "Pradeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Torress",
"given": "De'Ambra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oragwu",
"given": "Chukwuemeka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oguego",
"given": "Ngozi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pillai",
"given": "Rajesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Juma",
"given": "Mustafa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ghaly",
"given": "Emad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Al-Haddadin",
"given": "Dafer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramirez",
"given": "Courtney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hassanien",
"given": "Gammal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "Samah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Meltzer",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moran",
"given": "Seamus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brehaut",
"given": "Scott",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roche",
"given": "Angelina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "Manisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Koppinger",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baez",
"given": "Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pagan",
"given": "Ivone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdelsayed",
"given": "Dallal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aziz",
"given": "Mina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Philip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pardue",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hammons",
"given": "Llisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gonzalez",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reyes",
"given": "Lionel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cienki",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jimenez",
"given": "Gisselle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Szeto",
"given": "Jeremy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stelmash",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Amon",
"given": "Arch",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haight",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lamb",
"given": "Deryl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harper",
"given": "Amron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pyram-Bernard",
"given": "Nancy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quintero",
"given": "Arlen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adhami",
"given": "Eftim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maria",
"given": "Josette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Paudel",
"given": "Diksha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Raymond",
"given": "Oksana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Summers",
"given": "Jeffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "Tammy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gallegos",
"given": "Sam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Szwast",
"given": "Elizabeth Ann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdulghani",
"given": "Ahsan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vasoya",
"given": "Pravin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Conrad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wiley",
"given": "Hawa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Klein",
"given": "Tovah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Castex",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Feliciano",
"given": "Phillip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Olivo",
"given": "Jacqueline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ghaly",
"given": "Marian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Javed",
"given": "Zainub",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nawrocki",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vecchiarelli",
"given": "Anthony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vigil",
"given": "Nikki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cherukuri",
"given": "Vijaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burden",
"given": "Erica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Linn",
"given": "Dawn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fisher",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Vijay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Praksha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Yuti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ellison",
"given": "Leonard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "Jeffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Binod",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Sugata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Upinder",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Donahue",
"given": "Julia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jazayeri",
"given": "Yasmin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Anita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chandrasekar",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moritz",
"given": "Beth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fortt",
"given": "Tabitha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fortt",
"given": "Anisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones-Ince",
"given": "Ingrid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McKee",
"given": "Alix",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schattinger",
"given": "Christy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Farlow",
"given": "Brenda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Finlaw",
"given": "Lillian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Richwine",
"given": "Randall",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Tearani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Paizer",
"given": "Penny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carson",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Michelson",
"given": "Edward",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Austin",
"given": "Danielle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khetpal",
"given": "Sangeeta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cantrell",
"given": "Tiffany",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Franklin",
"given": "Drew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "Karissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mahadevan",
"given": "Arvind",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rosequist",
"given": "Madelyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gnoni",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Daffner",
"given": "Crystal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "VandeWeerd",
"given": "Carla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "Mitchell",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "D'Andrea",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Swink",
"given": "Wayne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Powers-Fletcher",
"given": "Margaret",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mukunzi",
"given": "Sylvere",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hensley",
"given": "Jamie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Manning",
"given": "Brittney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Isache",
"given": "Carmen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bowman",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Callaghan-Brown",
"given": "Angelique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "Taylor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schwasinger-Schmidt",
"given": "Tiffany",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cornejo",
"given": "Ashlie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Almanzar",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ginsburg",
"given": "Letty",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hajaz",
"given": "Americo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seithel",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sekikawa",
"given": "Akira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Klawson",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ostrosky",
"given": "Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Umana",
"given": "Virginia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patterson",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tragus",
"given": "Robin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hallowell",
"given": "Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haughey",
"given": "Heather",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vaidya-Tank",
"given": "Bhavna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gould",
"given": "Cameron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Goyal",
"given": "Parul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gatewood",
"given": "Carly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seagle",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Salsgiver",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Armas",
"given": "Eddie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Jhonsai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Huerta",
"given": "Priscilla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garcia-Diaz",
"given": "Julia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aamodt",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ayers",
"given": "JaMario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Jess",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Graves",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grindstaff",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lai",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lopez",
"given": "Itzel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marlin",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Merkel",
"given": "Alyssa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nwosu",
"given": "Sam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Obregon",
"given": "Savannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Orozco",
"given": "Dirk",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Perez-Torres",
"given": "Yoli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prato",
"given": "Nelson",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ratcliff",
"given": "Colleen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rhode",
"given": "Max",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rothman",
"given": "Russell",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shirey-Rice",
"given": "Jana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vermillion",
"given": "Krista",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Hsi-Nien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tregoning",
"given": "Seibert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vance",
"given": "Meghan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vongsamphanh",
"given": "Amber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Weir",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zaleski",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV)-6 Study Group and Investigators",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA",
"container-title-short": "JAMA",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-12T16:30:51Z",
"timestamp": 1673541051000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-12T16:31:02Z",
"timestamp": 1673541062000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-13T06:40:01Z",
"timestamp": 1673592001505
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
12
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/articlepdf/2800448/jama_mccarthy_2023_oi_220148_1672949734.65382.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7117e1",
"article-title": "Provisional mortality data—United States, 2021.",
"author": "Ahmad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "597",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "joi220148r1",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19.",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi220148r2",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients.",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi220148r3",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb9332",
"article-title": "Rapid repurposing of drugs for COVID-19.",
"author": "Guy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "829",
"issue": "6493",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "joi220148r4",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7103e1",
"article-title": "Racial and ethnic disparities in receipt of medications for treatment of COVID-19—United States, March 2020-August 2021.",
"author": "Wiltz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "96",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "joi220148r5",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.652688",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine: a review of its mechanism of action and its role in COVID-19.",
"author": "Sukhatme",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "joi220148r6",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.6269",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine for outpatient management of COVID-19 to prevent hospitalization: a systematic review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "joi220148r7",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2292",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi220148r8",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aau5266",
"article-title": "Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis.",
"author": "Rosen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "478",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "joi220148r9",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4",
"article-title": "Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial.",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e42",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Lancet Glob Health",
"key": "joi220148r10",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab050",
"article-title": "Prospective cohort of fluvoxamine for early treatment of coronavirus disease 19.",
"author": "Seftel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "joi220148r12",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2016638",
"article-title": "A randomized trial of hydroxychloroquine as postexposure prophylaxis for Covid-19.",
"author": "Boulware",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "517",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi220148r13",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-4207",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine in nonhospitalized adults with early COVID-19: a randomized trial.",
"author": "Skipper",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "623",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "joi220148r14",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2201662",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for Covid-19.",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "599",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi220148r16",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "joi220148r11",
"unstructured": "Lenze? E. Fluvoxamine for Early Treatment of Covid-19 (STOP COVID 2). Accessed December 29, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04668950"
},
{
"key": "joi220148r15",
"unstructured": "R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Accessed October 25, 2022. http://www.R-project.org/"
}
],
"reference-count": 16,
"references-count": 16,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2800448"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [
"A Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Effect of Fluvoxamine vs Placebo on Time to Sustained Recovery in Outpatients With Mild to Moderate COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article"
}