Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients With Symptomatic COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760, STOP COVID, NCT04342663, Nov 2020
30th treatment shown to reduce risk in
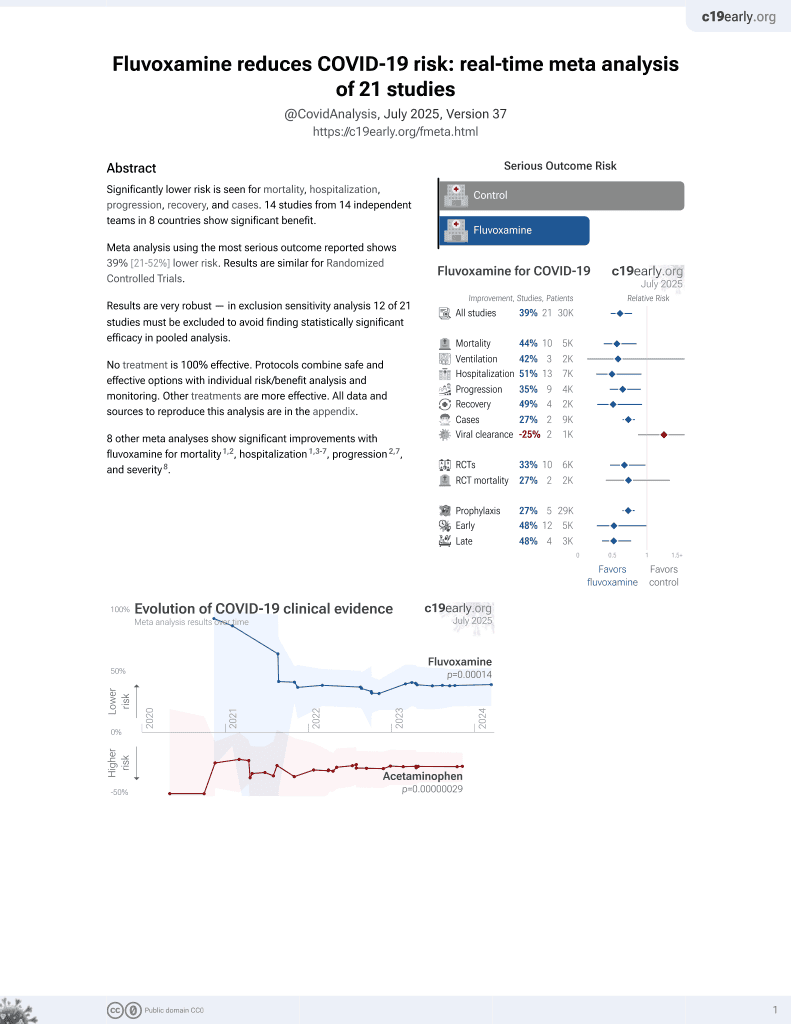
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
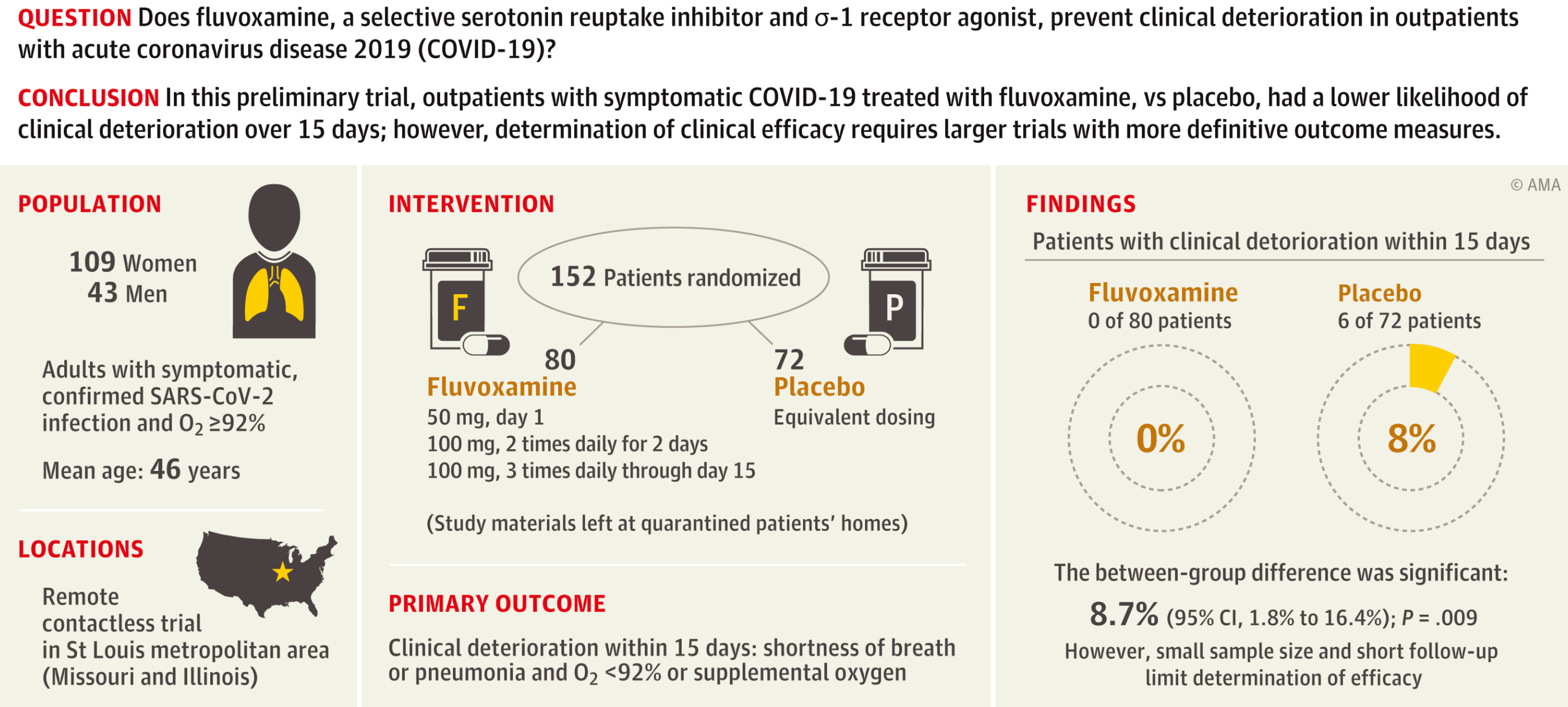
RCT 152 outpatients, 80 treated with fluvoxamine showing lower progression with treatment (0 of 80 versus 6 of 72 control).
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of progression, 92.7% lower, RR 0.07, p = 0.009, treatment 0 of 80 (0.0%), control 6 of 72 (8.3%), NNT 12, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), clinical deterioration over 15 days.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 82.0% lower, RR 0.18, p = 0.009, treatment 1 of 80 (1.2%), control 5 of 72 (6.9%), NNT 18, COVID-19 hospitalization within 15 days, see supplemental appendix for details.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Lenze et al., 12 Nov 2020, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 10 April, 2020 - 5 August, 2020, average treatment delay 4.0 days, trial NCT04342663 (history) (STOP COVID).
Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients With Symptomatic COVID-19
JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
IMPORTANCE Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) may lead to serious illness as a result of an excessive immune response. Fluvoxamine may prevent clinical deterioration by stimulating the σ-1 receptor, which regulates cytokine production. OBJECTIVE To determine whether fluvoxamine, given during mild COVID-19 illness, prevents clinical deterioration and decreases the severity of disease. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS Double-blind, randomized, fully remote (contactless) clinical trial of fluvoxamine vs placebo. Participants were community-living, nonhospitalized adults with confirmed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection, with COVID-19 symptom onset within 7 days and oxygen saturation of 92% or greater. One hundred fifty-two participants were enrolled from the St Louis metropolitan area (Missouri and Illinois) from April 10, 2020, to August 5, 2020. The final date of follow-up was September 19, 2020. INTERVENTIONS Participants were randomly assigned to receive 100 mg of fluvoxamine (n = 80) or placebo (n = 72) 3 times daily for 15 days.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary outcome was clinical deterioration within 15 days of randomization defined by meeting both criteria of (1) shortness of breath or hospitalization for shortness of breath or pneumonia and (2) oxygen saturation less than 92% on room air or need for supplemental oxygen to achieve oxygen saturation of 92% or greater.
RESULTS Of 152 patients who were randomized (mean [SD] age, 46 [13] years; 109 [72%] women), 115 (76%) completed the trial. Clinical deterioration occurred in 0 of 80 patients in the fluvoxamine group and in 6 of 72 patients in the placebo group (absolute difference, 8.7% [95% CI, 1.8%-16.4%] from survival analysis; log-rank P = .009). The fluvoxamine group had 1 serious adverse event and 11 other adverse events, whereas the placebo group had 6 serious adverse events and 12 other adverse events.
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE In this preliminary study of adult outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19, patients treated with fluvoxamine, compared with placebo, had a lower likelihood of clinical deterioration over 15 days. However, the study is limited by a small sample size and short follow-up duration, and determination of clinical efficacy would require larger randomized trials with more definitive outcome measures.
Adverse Events The fluvoxamine group had 1 serious adverse event and 11 other adverse events, whereas the placebo group had 6 serious adverse events and 12 other adverse events (Table 3 and eResults 1 in Supplement 2). Pneumonia and gastrointestinal symptoms (such as nausea and vomiting) occurred more often in the placebo group compared with those who received fluvoxamine.
Missing Data In terms of missing data, 517 of 3943 follow-up surveys (13%) were not filled out by participants. The mean score for those Body mass index category, No. (%) c Underweight (<18.5) 1 Normal (18.5-24.9) 14 (18) 7 (10) Overweight (25-29. ). For primary prevention, traditional public health approaches include wearing masks, physical distancing, contact tracing, and quarantine. These steps are the current standard of care as the world awaits the results of randomized trials of vaccines and monoclonal antibodies. For the treatment of patients with serious illness in the hospital, corticosteroids have emerged as the standard of care. 1, 2 But what about treatments for patients with COVID-19 who are neither hospitalized nor severely ill? The pilot study by Lenze and colleagues 3 addresses a critically important question during the pandemic of how to prevent individuals who acquire COVID-19 from deteriorating to serious illness. 4 If an effective treatment is found for this key gap in treatment, it will affect the health of millions of people worldwide. This study has important..
References
Cdc Covid-, 19 Response Team. Severe outcomes among patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Morbid Mortal Weekly Rep
Chastain, Osae, Henao-Martínez, Racial disproportionality in Covid clinical trials, N Engl J Med
Cobos, Entrena, Nieto, Pharmacology and therapeutic potential of sigma(1) receptor ligands, Curr Neuropharmacol
Gillings, Koch, The application of the principle of intention-to-treat to the analysis of clinical trials, Drug Information J, doi:10.1177/009286159102500311
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Hallifax, Houston, Saturable uptake of lipophilic amine drugs into isolated hepatocytes, Drug Metab Dispos
Hashimoto, Activation of sigma-1 receptor chaperone in the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases and its clinical implication, J Pharmacol Sci
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Ishikawa, Ishiwata, Ishii, High occupancy of sigma-1 receptors in the human brain after single oral administration of fluvoxamine, Biol Psychiatry
Ishima, Fujita, Hashimoto, Interaction of new antidepressants with sigma-1 receptor chaperones and their potentiation of neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells, Eur J Pharmacol
Lescure, Bouadma, Nguyen, Clinical and virological data of the first cases of COVID-19 in Europe, Lancet Infect Dis
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Mofsen, Rodebaugh, Nicol, When all else fails, listen to the patient, JMIR Ment Health
Nicol, Karp, Reiersen, What were you before the war?, J Clin Psychiatry, doi:10.4088/JCP.20com13373
Nicol, Piccirillo, Mulsant, Lenze, Action at a distance, J Am Geriatr Soc
Prasad, Prasad, Single virus targeting multiple organs, Front Med
Rosen, Seki, Fernández-Castañeda, Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis, Sci Transl Med
Wiersinga, Rhodes, Cheng, Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), JAMA
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"ISSN": [
"0098-7484"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Lenze",
"given": "Eric J.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Mattar",
"given": "Caline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Zorumski",
"given": "Charles F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Stevens",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Schweiger",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Nicol",
"given": "Ginger E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Biostatistics, Informatics Institute, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "J. Philip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Yingling",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Avidan",
"given": "Michael S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, Missouri"
}
],
"family": "Reiersen",
"given": "Angela M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA",
"container-title-short": "JAMA",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-12T16:46:46Z",
"timestamp": 1605199606000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-09T22:52:11Z",
"timestamp": 1607554331000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T11:09:27Z",
"timestamp": 1712228967556
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 404,
"issue": "22",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "22",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/articlepdf/2773108/jama_lenze_2020_pc_200006_1607119471.77989.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2292",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12839",
"article-title": "Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).",
"author": "Wiersinga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "782",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "jpc200006r1",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China.",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1708",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "jpc200006r2",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China.",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "jpc200006r3",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30200-0",
"article-title": "Clinical and virological data of the first cases of COVID-19 in Europe.",
"author": "Lescure",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "697",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "jpc200006r4",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression.",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "jpc200006r5",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00370",
"article-title": "Single virus targeting multiple organs.",
"author": "Prasad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "370",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "jpc200006r6",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "“What were you before the war?”",
"author": "Nicol",
"journal-title": "J Clin Psychiatry",
"key": "jpc200006r7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.064",
"article-title": "Interaction of new antidepressants with sigma-1 receptor chaperones and their potentiation of neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells.",
"author": "Ishima",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "jpc200006r8",
"volume": "727",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aau5266",
"article-title": "Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis.",
"author": "Rosen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "478",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "jpc200006r9",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jphs.2014.11.010",
"article-title": "Activation of sigma-1 receptor chaperone in the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases and its clinical implication.",
"author": "Hashimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "jpc200006r10",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/157015908787386113",
"article-title": "Pharmacology and therapeutic potential of sigma(1) receptor ligands.",
"author": "Cobos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "344",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Curr Neuropharmacol",
"key": "jpc200006r11",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/dmd.107.015131",
"article-title": "Saturable uptake of lipophilic amine drugs into isolated hepatocytes.",
"author": "Hallifax",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1325",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab Dispos",
"key": "jpc200006r12",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2013.281053",
"article-title": "World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki.",
"author": "World Medical Association",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2191",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "jpc200006r13",
"volume": "310",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgs.v68.5",
"article-title": "Action at a distance.",
"author": "Nicol",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "922",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Am Geriatr Soc",
"key": "jpc200006r14",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/11845",
"article-title": "When all else fails, listen to the patient.",
"author": "Mofsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JMIR Ment Health",
"key": "jpc200006r15",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6912e2",
"article-title": "Severe outcomes among patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).",
"author": "CDC COVID-19 Response Team",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "343",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Morbid Mortal Weekly Rep",
"key": "jpc200006r16",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.04.001",
"article-title": "High occupancy of sigma-1 receptors in the human brain after single oral administration of fluvoxamine.",
"author": "Ishikawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "878",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Biol Psychiatry",
"key": "jpc200006r17",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/009286159102500311",
"article-title": "The application of the principle of intention-to-treat to the analysis of clinical trials.",
"author": "Gillings",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "411",
"journal-title": "Drug Information J",
"key": "jpc200006r19",
"volume": "25",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMp2021971",
"article-title": "Racial disproportionality in Covid clinical trials.",
"author": "Chastain",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "jpc200006r20",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136",
"article-title": "Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019.",
"author": "Deftereos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2013136",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "jpc200006r21",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"article-title": "Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Sterne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1330",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "jpc200006r22",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17052",
"article-title": "Cytokine levels in critically ill patients with COVID-19 and other conditions.",
"author": "Kox",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1565",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "jpc200006r23",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106044",
"article-title": "Widely available lysosome targeting agents should be considered as potential therapy for COVID-19.",
"author": "Homolak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "jpc200006r24",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2019.05.002",
"article-title": "The ER stress sensor IRE1 and MAP kinase ERK modulate autophagy induction in cells infected with coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus.",
"author": "Fung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "34",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "jpc200006r25",
"volume": "533",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00129784-200303030-00001",
"article-title": "Effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on platelet activation.",
"author": "Schlienger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "149",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am J Cardiovasc Drugs",
"key": "jpc200006r26",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0269881108089876",
"article-title": "Efficacy, tolerability and side-effect profile of fluvoxamine for major depression.",
"author": "Omori",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "539",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Psychopharmacol",
"key": "jpc200006r27",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1681/ASN.2018101032",
"article-title": "Comparative cardiac safety of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors among individuals receiving maintenance hemodialysis.",
"author": "Assimon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "611",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Am Soc Nephrol",
"key": "jpc200006r28",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1067/mcp.2002.121788",
"article-title": "Low daily 10-mg and 20-mg doses of fluvoxamine inhibit the metabolism of both caffeine (cytochrome P4501A2) and omeprazole (cytochrome P4502C19).",
"author": "Christensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "141",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "jpc200006r29",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcad.2020.03.001",
"article-title": "Cardiac troponin I in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).",
"author": "Lippi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "390",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Prog Cardiovasc Dis",
"key": "jpc200006r30",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Outcomes of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in patients recently recovered from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).",
"author": "Puntmann",
"journal-title": "JAMA Cardiol",
"key": "jpc200006r31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.09.001",
"article-title": "Sigma-1 receptor chaperone and brain-derived neurotrophic factor.",
"author": "Hashimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Prog Neurobiol",
"key": "jpc200006r32",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1681/ASN.2015070772",
"article-title": "s1-receptor agonism protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.",
"author": "Hosszu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "152",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Am Soc Nephrol",
"key": "jpc200006r33",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "jpc200006r18",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Novel coronavirus. Accessed November 2, 2020. https://www.who.int/blueprint/priority-diseases/key-action/COVID-19_Treatment_Trial_Design_Master_Protocol_synopsis_Final_18022020.pdf?"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2773108"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [
"A Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients With Symptomatic COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "324"
}