Efficacy and safety of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in COVID-19 management: A systematic review and meta-analysis
et al., Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2023.01.010, Jan 2023
31st treatment shown to reduce risk in
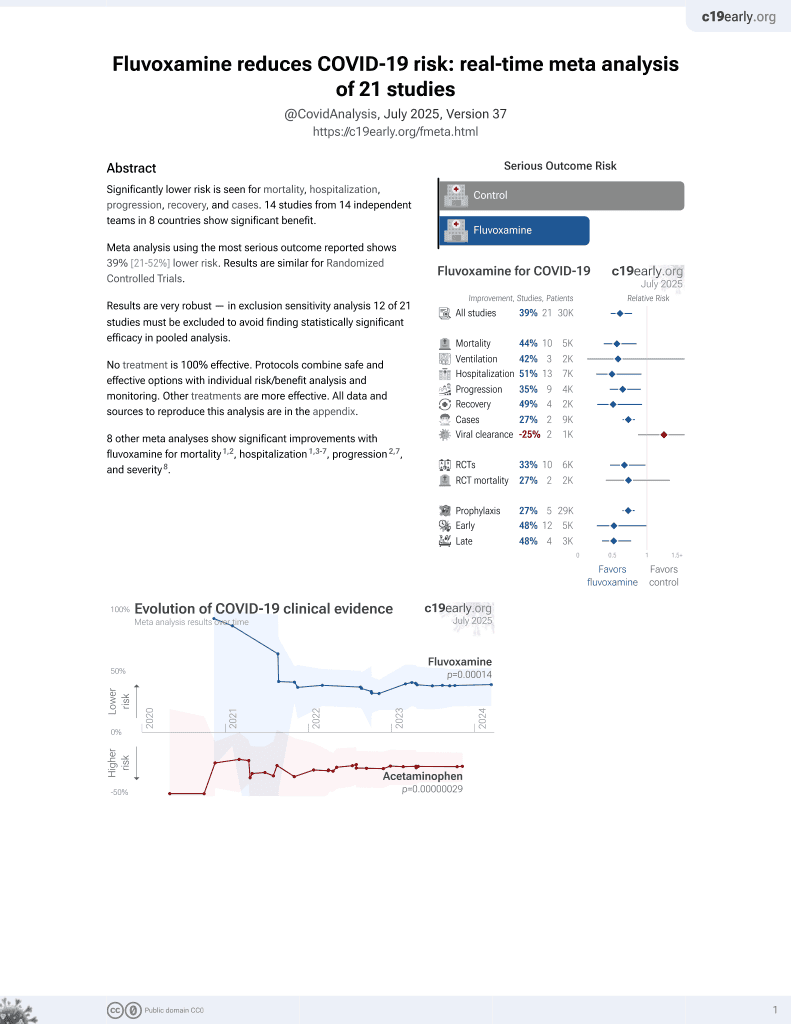
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
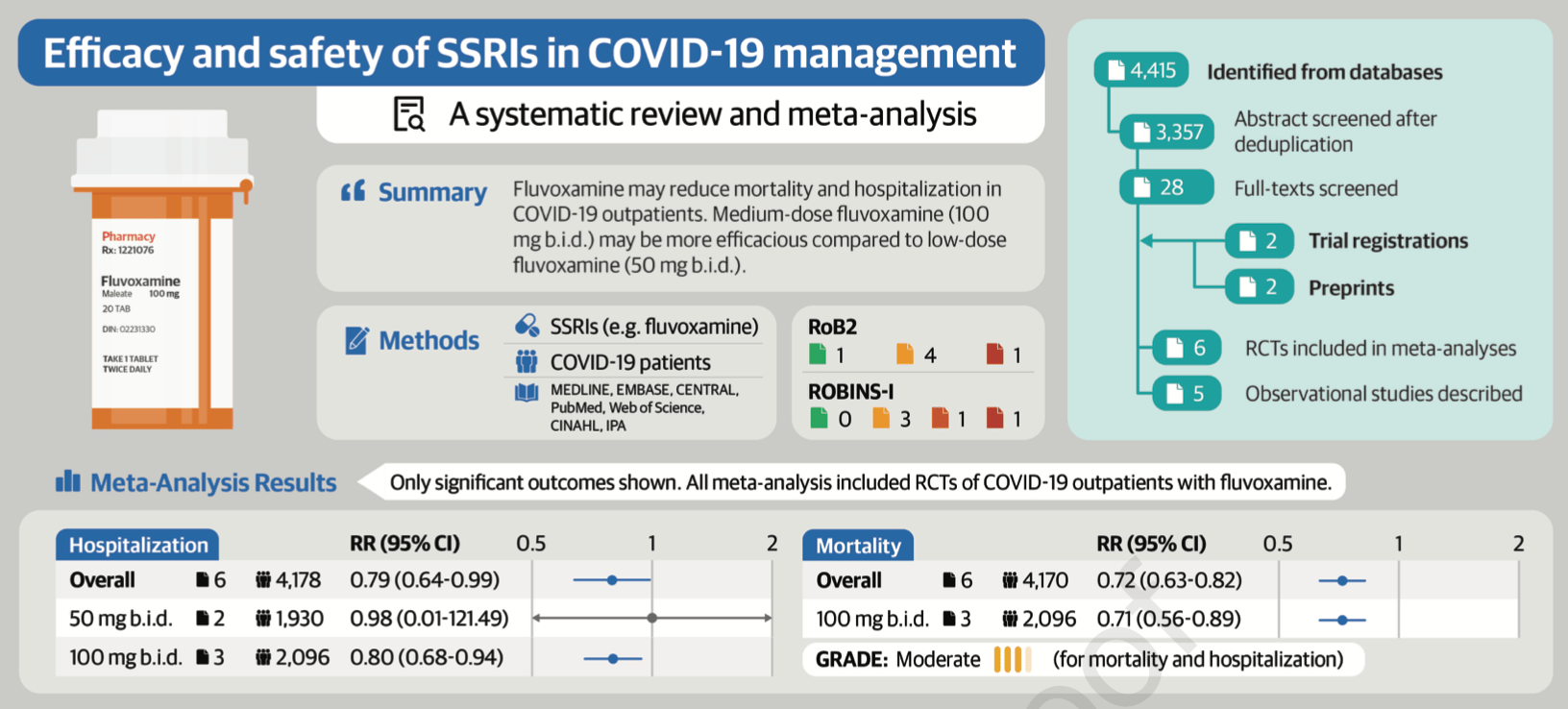
Meta analysis of 6 fluvoxamine RCTs showing fluvoxamine associated with lower mortality and hospitalization. 100mg bid showed lower mortality and hospitalization, but 50mg bid did not.
Authors use the Hartung-Knapp adjustment and they include trials reporting zero events in both arms - 5 of 6 trials for mortality. This narrows the confidence interval from the Together Trial so that it becomes significant, but this is not logical - zero mortality in both arms does not provide information on the mortality benefit of fluvoxamine.
Bias evaluation is not accurate. For example, authors rate the Together Trial as low risk of bias except for some concerns for deviations from the intended interventions. However, this trial not only shows a very high theoretical risk of bias, but also has very high actual bias, randomization failure, blinding failure, and reports conflicting data that is impossible to be correct1.
9 meta-analyses show significant improvements with fluvoxamine for mortality2-4,
hospitalization2,5-9 ,
progression3,9, and
severity10.
Currently there are 21 fluvoxamine for COVID-19 studies, showing 44% lower mortality [15‑63%], 42% lower ventilation [-151‑86%], 10% higher ICU admission [-72‑326%], 51% lower hospitalization [8‑73%], and 27% fewer cases [18‑35%].
|
risk of death, 28.0% lower, RR 0.72, p < 0.001.
|
|
risk of death, 29.0% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.004, 100mg bid.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 21.0% lower, RR 0.79, p = 0.03.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 20.0% lower, RR 0.80, p = 0.007, 100mg bid.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 2.0% lower, RR 0.98, p = 0.99, 50mg bid.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Reis et al., Effect of Early Treatment with Ivermectin among Patients with Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2115869.
2.
Deng et al., Efficacy and safety of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in COVID-19 management: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2023.01.010.
3.
Prasanth et al., A systematic review and meta-analysis, investigating dose and time of fluvoxamine treatment efficacy for COVID-19 clinical deterioration, death, and Long-COVID complications, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-64260-9.
4.
Fico et al., Psychotropic drug repurposing for COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, European Neuropsychopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2022.10.004.
5.
Lee et al., Fluvoxamine for Outpatient Management of COVID-19 to Prevent Hospitalization: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.6269.
6.
Lu et al., Effect of fluvoxamine on outcomes of nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Journal of Infection and Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2022.10.010.
7.
Marcec et al., A meta-analysis regarding fluvoxamine and hospitalization risk of COVID-19 patients: TOGETHER making a difference, Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2022.11.011.
8.
Deng (B) et al., Evaluating fluvoxamine for the outpatient treatment of COVID‐19: A systematic review and meta‐analysis, Reviews in Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/rmv.2501.
Deng et al., 14 Jan 2023, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
Efficacy and safety of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in COVID-19 management: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2023.01.010
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Lastly, we found that fluvoxamine was not associated with reduced hospitalization once we excluded one study with a high risk of bias rating. This was likely due to loss of precision from a reduced sample size given the small number of studies and patients included in this review. The incorporation of larger, betterdesigned RCTs in future meta-analyses can help confirm our findings relating to hospitalization.
CONCLUSION This systematic review and meta-analysis of 6 RCTs and 5 observational studies found that fluvoxamine may reduce mortality and hospitalization based on moderate quality of evidence. Medium
J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
GRADE Working Group quality of evidence rating [28] High quality: We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect Moderate quality: We are moderately confident in the effect estimate; the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different Low quality: Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited; the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect Very low quality: We have very little confidence in the effect estimate; the true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect a The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% CI) is based on the assumed risk in..
References
Bhimraj, Morgan, Shumaker, Baden, Cheng et al., IDSA Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19, doi:10.1101/2022.09.27.22280428
Bloch, Mcguire, Landeros-Weisenberger, Leckman, Pittenger, Meta-analysis of the dose-response relationship of SSRI in obsessive-compulsive disorder, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/mp.2009.50
Bollini, Pampallona, Tibaldi, Kupelnick, Munizza, Effectiveness of antidepressants. Meta-analysis of dose-effect relationships in randomised clinical trials, Br J Psychiatry, doi:10.1192/bjp.174.4.297
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Buse, Liebovitz et al., Randomized Trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2201662
Calusic, Marcec, Luksa, Jurkovic, Kovac et al., Safety and efficacy of fluvoxamine in COVID-19 ICU patients: An open label, prospective cohort trial with matched controls, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bcp.15126
Cheng, Pullenayegum, Marshall, Iorio, Thabane, Impact of including or excluding botharmed zero-event studies on using standard meta-analysis methods for rare event outcome: a simulation study, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010983
Guo, Harari, Chernecki, Thorlund, Forrest, Fluvoxamine for the Early Treatment of COVID-19: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.21-1310
Guyatt, Oxman, Santesso, Helfand, Vist et al., GRADE guidelines: 12. J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f Preparing summary of findings tables-binary outcomes, J Clin Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.01.012
Guyatt, Oxman, Vist, Kunz, Falck-Ytter et al., GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD
Hashimoto, Activation of sigma-1 receptor chaperone in the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases and its clinical implication, J Pharmacol Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2014.11.010
Hashimoto, Repurposing of CNS drugs to treat COVID-19 infection: targeting the sigma-1 receptor, Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, doi:10.1007/s00406-020-01231-x
Hashimoto, Suzuki, Hashimoto, Mechanisms of action of fluvoxamine for COVID-19: a historical review, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01432-3
Higgins, Green, Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, doi:10.1056/NEJMe2209017
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Kornhuber, Gulbins, Reiersen et al., Antidepressant Use and Its Association with 28-Day Mortality in Inpatients with SARS-CoV-2: Support for the FIASMA Model against COVID-19, J Clin Med Res, doi:10.3390/jcm11195882
Ishikawa, Ishiwata, Ishii, Kimura, Sakata et al., High occupancy of sigma-1 receptors in the human brain after single oral administration of fluvoxamine: a positron emission tomography study using [11C]SA4503, Biol Psychiatry, doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.04.001
Karim, Devnarain, Time to Stop Using Ineffective Covid-19 Drugs, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMe2209017
Khan, Schwartz, Kolts, Brown, BMI, sex, and antidepressant response, J Affect Disord, doi:10.1016/j.jad.2006.08.027
Lee, Vigod, Bortolussi-Courval, Hanula, Boulware et al., Fluvoxamine for Outpatient Management of COVID-19 to Prevent Hospitalization: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.6269
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients With Symptomatic COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
Marzolini, Marra, Boyle, Khoo, Back, Fluvoxamine for the treatment of COVID-19, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00592-1
Mccarthy, Naggie, Boulware, Lindsell, Stewart et al., Fluvoxamine for Outpatient Treatment of COVID-19: A Decentralized, Placebo-controlled, Randomized, Platform Clinical Trial, doi:10.1101/2022.10.17.22281178v2
Min, Kim, Oh, Kim, Lee, COVID-19 Prognosis in Association with Antidepressant Use, Pharmacopsychiatry, doi:10.1055/a-1842-7859
Nawas, Zeidan, Edwards, El-Desoky, Barriers to COVID-19 Vaccines and Strategies to Improve Acceptability and Uptake, J Pharm Pract, doi:10.1177/08971900221081621
Németh, Szûcs, Vitrai, Juhász, Németh et al., Fluoxetine use is associated with improved survival of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A retrospective case-control study, Ideggyogy Sz, doi:10.18071/isz.74.0389
Oskotsky, Maric, Tang, Oskotsky, Wong et al., Mortality Risk Among Patients With COVID-19 Prescribed Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.33090
Ouzzani, Hammady, Fedorowicz, Elmagarmid, Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews, Syst Rev, doi:10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Pepperrell, Ellis, Wang, Hill, Barriers to Worldwide Access for Paxlovid, a New Treatment for COVID-19, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac174
Pineda, Singh, Pineda, Umanzor, Baires et al., Impact of Fluvoxamine on outpatient treatment of COVID-19 in Honduras, doi:10.1101/2022.09.27.22280428
Puzhko, Aboushawareb, Kudrina, Schuster, Barnett et al., Excess body weight as a predictor of response to treatment with antidepressants in patients with depressive disorder, J Affect Disord, doi:10.1016/j.jad.2020.01.113
Reis, Santos Moreira-Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., r n a l P r e -p r o o f Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
Ren, Lin, Lian, Zou, Chu, Real-world Performance of Meta-analysis Methods for Double-Zero-Event Studies with Dichotomous Outcomes Using the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, J Gen Intern Med, doi:10.1007/s11606-019-04925-8
Sattar, Valabhji, Obesity as a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19: Summary of the Best Evidence and Implications for Health Care, Curr Obes Rep, doi:10.1007/s13679-021-00448-8
Schiavo, PROSPERO: An International Register of Systematic Review Protocols, Med Ref Serv Q, doi:10.1080/02763869.2019.1588072
Schwarzer, Carpenter, Rucker, Meta-Analysis with R, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-21416-0
Seftel, Boulware, Prospective Cohort of Fluvoxamine for Early Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 19, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab050
Seo, Kim, Bae, Park, Chung et al., Fluvoxamine Treatment of Patients with Symptomatic COVID-19 in a Community Treatment Center: A Preliminary Result of Randomized Controlled Trial, Infect Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2021.0142
Sterne, Hernán, Reeves, Savović, Berkman et al., ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i4919
Sterne, Savović, Page, Elbers, Blencowe et al., RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.l4898
Sweeting, Sutton, Lambert, What to add to nothing? Use and avoidance of continuity corrections in meta-analysis of sparse data, Stat Med, doi:10.1002/sim.1761
Vela, Repurposing Sigma-1 Receptor Ligands for COVID-19 Therapy?, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.582310