Fluoxetine use is associated with improved survival of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A retrospective case-control study
et al., Ideggyógyászati Szeml, doi:10.18071/ISZ.74.0389, Aug 2021 (preprint)
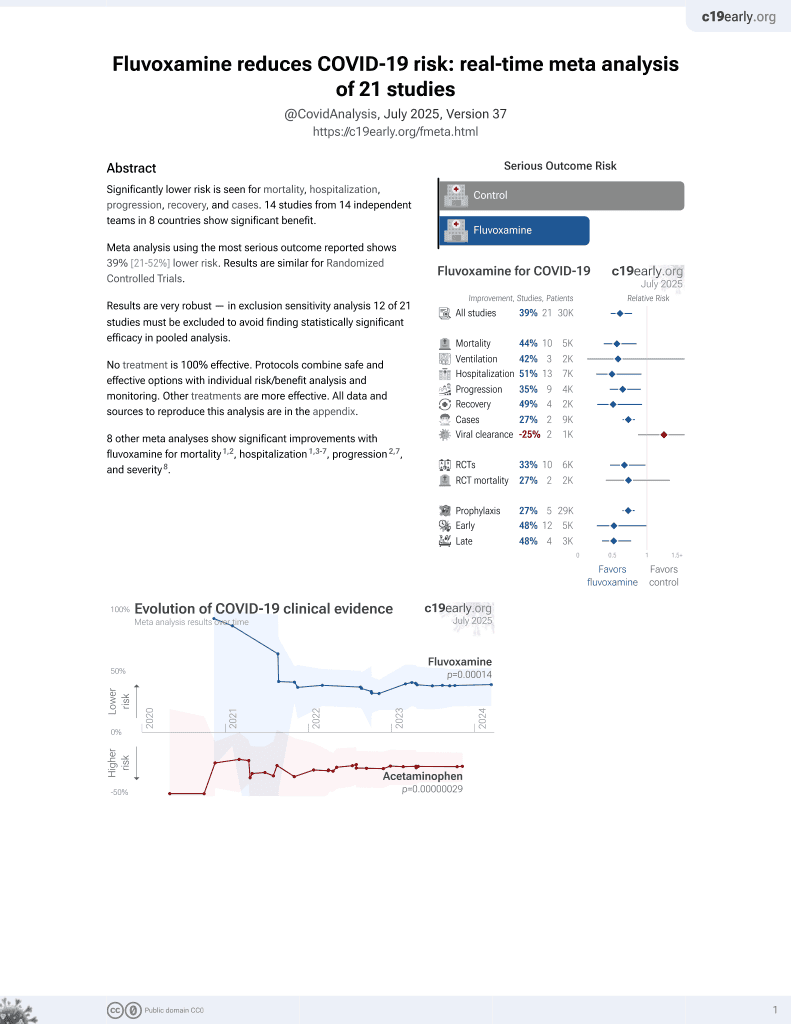
31st treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 269 hospitalized patients in Hungary, 110 treated with fluoxetine, showing lower mortality with treatment.
|
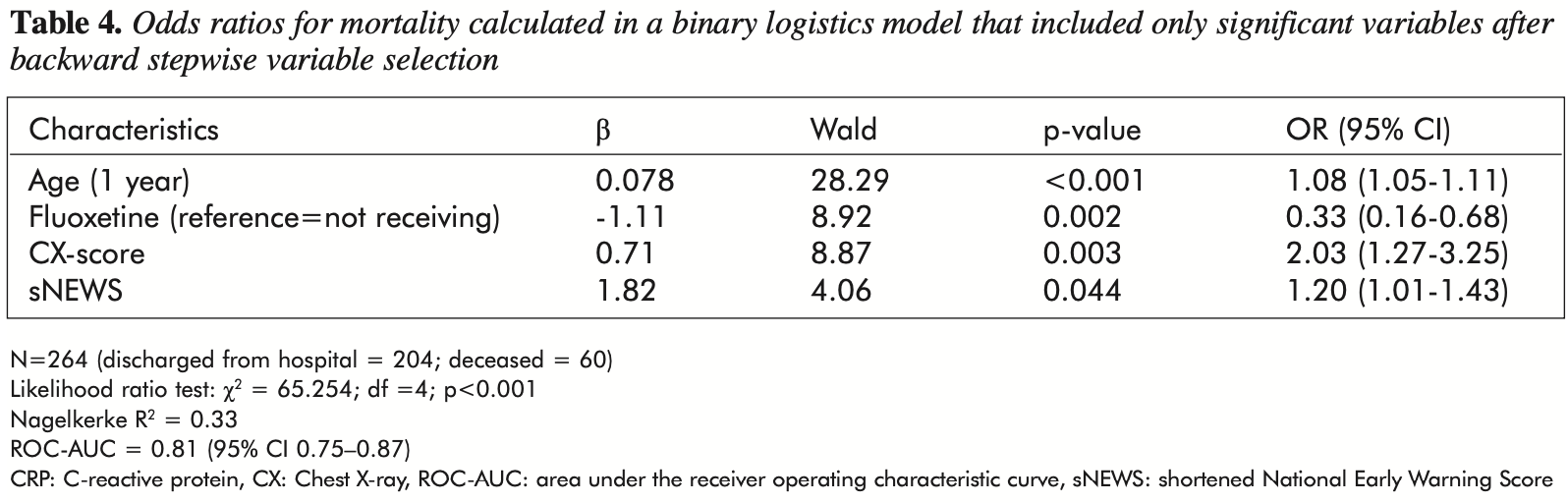
risk of death, 58.4% lower, RR 0.42, p = 0.002, treatment 15 of 110 (13.6%), control 49 of 159 (30.8%), NNT 5.8, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable logistic regression.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Németh et al., 12 Aug 2021, retrospective, Hungary, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Fluoxetine use is associated with improved survival of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia : A retrospective case-control study
Ideggyógyászati szemle, doi:10.18071/isz.74.0389
Az alábbi dokumentumot magáncélra töltötték le az eLitMed.hu webportálról. A dokumentum felhasználása a szerzôi jog szabályozása alá esik. Kulcsszavak: fluoxetin, COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, pneumonia, túlélés, mortalitás score did not show statistical difference between the fluoxetine and non-fluoxetine groups supporting the reliability of our finding. Conclusion -Provisional to confirmation in randomised controlled studies, fluoxetine may be a potent treatment increasing the survival for COVID-19 pneumonia.
References
Baldwin, Woods, Lawson, Taylor, Efficacy of drug treatments for generalised anxiety disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.d1199
Brambilla, Cipriani, Hotopf, Barbui, Side-effect profile of fluoxetine in comparison with other SSRIs, tricyclic and newer antidepressants: a meta-analysis of clinical trial data, Pharmacopsychiatry, doi:10.1055/s-2005-837806
Carpinteiro, Edwards, Hoffmann, Kochs, Gripp et al., Pharmacological inhibition of acid sphin gomyelinase prevents uptake of SARS-CoV-2 by epithelial cells, Cell Rep Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100142
Colombo, Colombo, Maves, Performance analysis of the national early warning score and modified early warning score in the adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial Cohort, Crit Care Explor
Coughlin, Anxiety and depression: linkages with viral diseases, Public Health Rev, doi:10.1007/BF03391675
Creeden, Imami, Eby, Gillman, Becker et al., Fluoxetine as an anti-inflammatory therapy in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111437
Dechaumes, Nekoua, Belouzard, Sane, En Gelmann I, Dubuisson, Fluoxetine can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms9020339
Doupnik, Mitra, Feudtner, Marcus, The Influence of Comorbid Mood and Anxiety Disorders on Outcomes of Pediatric Patients Hospitalized for Pneumonia, Hosp Pediatr, doi:10.1542/hpeds.2015-0177
Ely, Dittus, Girard, Point: should benzodiazepines be avoided in mechanically ventilated patients? Yes, Chest, doi:10.1378/chest.12-1189
Fred, Kuivanen, Ugurlu, Casarotto, Levanov et al., Antidepressant and antipsychotic drugs reduce viral infection by SARS-CoV-2 and fluoxetine show antiviral activity against the novel variants in vitro, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.22.436379
Glebov, Low-dose fluvoxamine modulates endocytic trafficking of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: a potential mechanism for anti-COVID-19 protection by antidepressants, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.06.15.448391
Gordon, Hiatt, Bouhaddou, Rezelj, Ulferts et al., Comparative host-coronavirus protein inter action networks reveal pan-viral disease mechanisms, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abe9403
Hashimoto, Repurposing of CNS drugs to treat COVID-19 infection: targeting the sigma-1 receptor, Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, doi:10.1007/s00406-020-01231-x
Hiles, Baker, De Malmanche, Attia, Interleukin-6, C-reactive protein and interleukin-10 after antidepressant treatment in people with depression: a meta-analysis, Psychol Med, doi:10.1017/S0033291712000128
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Vernet, Beeker, Jannot et al., Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4
Jakubovski, Johnson, Nasir, Müller-Vahl, Bloch, Systematic review and meta-analysis: Dose-response curve of SSRIs and SNRIs in anxiety disorders, Depress Anxiety, doi:10.1002/da.22854
Laporte, Chapelle, Caillet, Beyens, Bellet et al., Bleeding risk under selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants: A meta-analysis of observational studies, Pharmacol Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.08.017
Larici, Cicchetti, Marano, Bonomo, Storto, COVID-19 pneumonia: current evidence of chest imaging features, evolution and prognosis, Chin J Acad Radiol, doi:10.1007/s42058-021-00068-0
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
Lundström, Isaksson, Näsman, Wester, Mår Tensson et al., Safety and efficacy of fluoxetine on functional recovery after acute stroke (EFFECTS): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Neurol, doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30219-2
Obiora, Hubbard, Sanders, Myles, The impact of benzodiazepines on occurrence of pneumonia and mortality from pneumonia: a nested case-control and survival analysis in a population-based cohort, Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-202374
Pérez-Cano, Moreno-Murguía, Morales-López, Crow-Buchanan, English et al., Anxiety, depression, and stress in response to the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic, Cir, doi:10.24875/CIRU.20000561
Rosen, Seki, Fernández-Castañeda, Beiter, Eccles et al., Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aau5266
Safrany, Brimson, Are fluoxetine's effects due to sigma-1 receptor agonism, Pharmacol Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.05.031
Samuel, Seifert, Risk of bleeding in patients on fulldose enoxaparin with venous thromboembolism and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, Ann Pharmacother, doi:10.1177/1060028016677309
Schloer, Brunotte, Goretzko, Mecate-Zambrano, Korthals et al., Targeting the endolysosomal host-SARS-CoV-2 interface by clinically licensed functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase (FIASMA) including the antidepressant fluoxetine, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1829082
Schloer, Brunotte, Mecate-Zambrano, Zheng, Tang et al., Drug synergy of combinatory treatment with remdesivir and the repurposed drugs fluoxetine and itraconazole effectively impairs SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, Br J Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bph.15418
Sed, El-Khouly, Bar, Am, Ghorab, Fluoxetine hydrochloride loaded lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles showed possible efficiency against SARS-CoV-2 infection, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121023
Starke, Reissig, Petereit-Haack, Schmauder, Nienhaus et al., The isolated effect of age on the risk of COVID-19 severe outcomes: a systematic review with meta-analysis, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.05.27.21257909
Sukhatme, Reiersen, Vayttaden, Sukhatme, Flu voxamine: a review of its mechanism of action and its role in COVID-19, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.652688
Sultana, Crisafulli, Gabbay, Lynn, Shakir et al., Challenges for drug repurposing in the COVID-19 pandemic era, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.588654
Taylor, Freemantle, Geddes, Bhagwagar, Early onset of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressant action: systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch Gen Psychiatry, doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.11.1217
Vai, Mazza, Colli, Foiselle, Allen et al., Mental disorders and risk of COVID-19-related mortality, hospitalisation, and intensive care unit admission: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Psychiatry, doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00232-7
Viramontes, Truong, Linnebur, Antidepressantinduced hyponatremia in older adults, Consult Pharm, doi:10.4140/TCP.n.2016.139
Wang, Li, Shi, Que, Liu et al., Depression and anxiety in relation to cancer incidence and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-019-0595-x
Watkins, Koch, Sherwood, Blumenthal, Davidson et al., Association of anxiety and depression with all-cause mortality in individuals with coronary heart disease, J Am Heart Assoc, doi:10.1161/JAHA.112.000068
Yanez, Weiss, Romand, Treggiari, COVID-19 mortality risk for older men and women, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09826-8
Zimniak, Kirschner, Hilpert, Geiger, Danov et al., The serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluoxetine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung tissue, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-85049-0
Çağlar, Kaçer, Anxiety levels in patients admitted to the emergency department with myocardial infarction or COVID-19 pneumonia, Psychol Health Med, doi:10.1080/13548506.2021
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.18071/isz.74.0389",
"ISSN": [
"0019-1442",
"2498-6208"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.18071/isz.74.0389",
"abstract": "<jats:p>We aimed to investigate the association between fluoxetine use and the survival of hospitalised coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia patients. This retrospective case-control study used data extracted from the medical records of adult patients hospitalised with moderate or severe COVID-19 pneumonia at the Uzsoki Teaching Hospital of the Semmelweis University in Budapest, Hungary between 17 March and 22 April 2021. As a part of standard medical treatment, patients received anti-COVID-19 therapies as favipiravir, remdesivir, baricitinib or a combination of these drugs; and 110 of them received 20 mg fluoxetine capsules once daily as an adjuvant medication. Multivariable logistic regression was used to evaluate the association between fluoxetine use and mortality. For excluding a fluoxetine-selection bias potentially influencing our results, we compared baseline prognostic markers in the two groups treated versus not treated with fluoxetine. Out of the 269 participants, 205 (76.2%) survived and 64 (23.8%) died between days 2 and 28 after hospitalisation. Greater age (OR [95% CI] 1.08 [1.05–1.11], p<0.001), radiographic severity based on chest X-ray (OR [95% CI] 2.03 [1.27–3.25], p=0.003) and higher score of shortened National Early Warning Score (sNEWS) (OR [95% CI] 1.20 [1.01-1.43], p=0.04) were associated with higher mortality. Fluoxetine use was associated with an important (70%) decrease of mortality (OR [95% CI] 0.33 [0.16–0.68], p=0.002) compared to the non-fluoxetine group. Age, gender, LDH, CRP, and D-dimer levels, sNEWS, Chest X-ray score did not show statistical difference between the fluoxetine and non-fluoxetine groups supporting the reliability of our finding. Provisional to confirmation in randomised controlled studies, fluoxetine may be a potent treatment increasing the survival for COVID-19 pneumonia.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Németh",
"given": "Zsófia Klára",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szűcs",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vitrai",
"given": "József",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juhász",
"given": "Dóra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Németh",
"given": "János Pál",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8855-0469",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Holló",
"given": "András",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Ideggyógyászati szemle"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T11:12:43Z",
"timestamp": 1638357163000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T11:12:47Z",
"timestamp": 1638357167000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-02T11:42:23Z",
"timestamp": 1638445343842
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0019-1442"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2498-6208"
}
],
"issue": "11-12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11-12",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
}
},
"member": "7411",
"original-title": [],
"page": "389-396",
"prefix": "10.18071",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ideggyogyaszati Szemle Journal",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Ideggyogy Sz"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Clinical Neurology",
"Neurology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Fluoxetine use is associated with improved survival of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia : A retrospective case-control study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "74"
}