Safety and efficacy of fluvoxamine in COVID-19 ICU patients: an open label, prospective cohort trial with matched controls
et al., British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15126, Nov 2021
30th treatment shown to reduce risk in
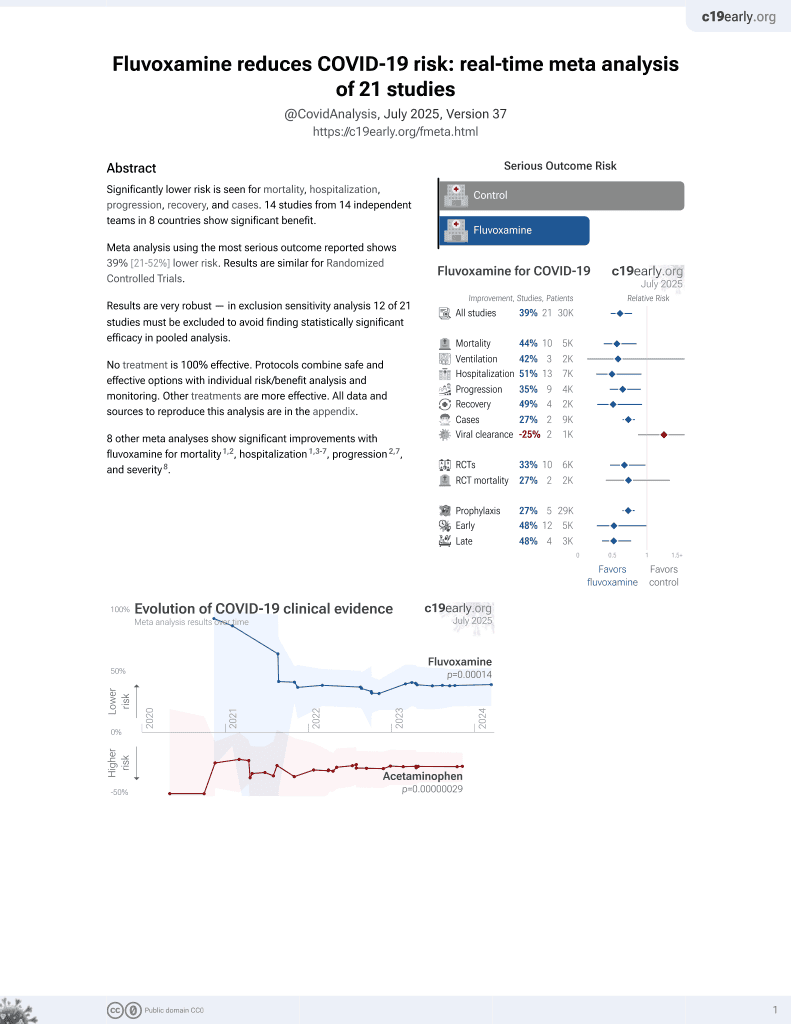
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
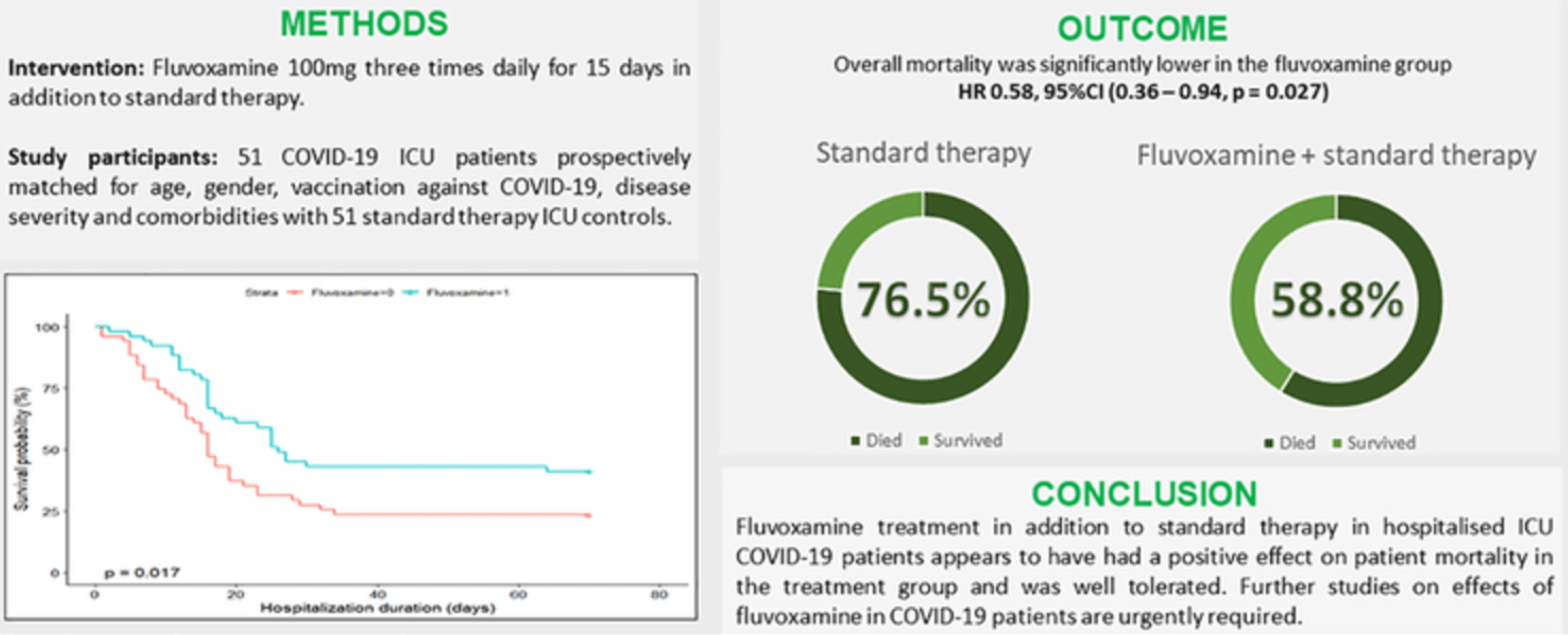
Prospective PSM study of 51 COVID-19 ICU patients in Croatia and 51 matched controls, showing significantly lower mortality with treatment.
|
risk of death, 42.0% lower, HR 0.58, p = 0.03, treatment 30 of 51 (58.8%), control 39 of 51 (76.5%), NNT 5.7, adjusted per study, propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Calusic et al., 1 Nov 2021, prospective, propensity score matching, Croatia, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 1 April, 2021 - 31 May, 2021.
Safety and efficacy of fluvoxamine in COVID‐19 ICU patients: An open label, prospective cohort trial with matched controls
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15126
Background: Fluvoxamine, an SSRI and sigma-1 receptor agonist, has so far shown promise in the prevention of COVID-19 progression as an early treatment option in 3 conducted trials. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of fluvoxamine in COVID-19 patients if administered later in the disease's course. Methods: The study was designed as an open label, prospective cohort trial with matched controls. In April and May 2021, 51 ICU COVID-19 patients hospitalised in the
References
Anderson, Fluvoxamine , melatonin and COVID
Asakura, Koyama, Hosokai, Kawano, Kajii, Post-Marketing Surveillance of Fluvoxamine Maleate Used Long-Term in Patients with Social Anxiety Disorder in Japan, Drugs -Real World Outcomes, doi:10.1007/s40801-014-0005-2
Buchberger, Wagner, Fluvoxamine: Safety profile in extensive post-marketing surveillance, Pharmacopsychiatry, doi:10.1055/s-2002-31522
Carpinteiro, Edwards, Hoffmann, Pharmacological Inhibition of Acid Sphingomyelinase Prevents Uptake of SARS-CoV-2 by Epithelial Cells, Cell Reports Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100142
Elbahlawan, Bissler, Morrison, Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy: A Review of Use and Application in Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients, Front Oncol, doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.632263
Esfahani, Rafiee, Javanmard, Evaluation of the Effect of Antidepressant Drug, Fluvoxamine, on Cyclooxygenase-2 Protein Expression in Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated Macrophages, Adv Biomed Res, doi:10.4103/abr.abr_141_18
Hashimoto, Repurposing of CNS drugs to treat COVID-19 infection: targeting the sigma-1 receptor, Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, doi:10.1007/s00406-020-01231-x
Hashimoto, Suzuki, Hashimoto, Old drug fluvoxamine, new hope for COVID-19, Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, doi:10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z
Hassanipour, Arab-Zozani, Amani, Heidarzad, Fathalipour et al., The efficacy and safety of Favipiravir in treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-90551-6
Hinks, Cureton, Knight, Azithromycin versus standard care in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 (ATOMIC2): an open-label, randomised trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(21)00263-0
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Cougoule, Repurposing antidepressants inhibiting the sphingomyelinase acid/ceramide system against COVID-19: current evidence and potential mechanisms, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01254-3
Homolak, Kodvanj, Widely available lysosome targeting agents should be considered as potential therapy for COVID-19
Hospitalization, AMONG PATIENTS WITH COVID-19: THE TOGETHER RANDOMIZED PLATFORM CLINICAL TRIAL, doi:10.1101/2021.08.19.21262323
Hägg, Spigset, Dahlqvist, Influence of gender and oral contraceptives on CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 activity in healthy volunteers, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2001.01328
Israel, Shenhar, Green, Large-scale study of antibody titer decay following BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine or SARS-CoV-2 infection, doi:10.1101/2021.08.19.21262111v1%0Ahttps://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.08.19.21262111v1.abstract
Kornhuber, Muehlbacher, Trapp, Identification of novel functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023852
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients with Symptomatic COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA -J Am Med Assoc, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
Marcec, Majta, Likic, Will vaccination refusal prolong the war on SARS-CoV-2?, Postgrad Med J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138903
Marčec, Likić, Could fluvoxamine keep COVID-19 patients out of hospitals and intensive care units?, Croat Med J, doi:10.3325/CMJ.2021.62.95
Moiseev, Brovko, Tao, Bulanov, Akulkina et al., Sex differences in mortality in the intensive care unit patients with severe COVID-19, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.09.031
Ou-Yang, Huang, Phenotypic polymorphism and gender-related differences of CYP1A2 activity in a Chinese population, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2000.00128.x
Planas, Veyer, Baidaliuk, Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9
Reardon, Flawed ivermectin preprint highlights challenges of COVID drug studies, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-021-02081-w
Rosen, Seki, Fernández-Castañeda, Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aau5266
Saha, Tanmoy, Tanni, New waves, new variants, old inequity: A continuing COVID-19 crisis, BMJ Glob Heal, doi:10.1136/bmjgh-2021-007031
Schloer, Brunotte, Goretzko, Targeting the endolysosomal host-SARS-CoV-2 interface by clinically licensed functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase (FIASMA) including the antidepressant fluoxetine, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1829082
Seftel, Boulware, Prospective Cohort of Fluvoxamine for Early Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 19, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab050
Servillo, Vargas, Pastore, Immunomodulatory effect of continuous venovenous hemofiltration during sepsis: Preliminary data, Biomed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2013/108951
Shrotri, Navaratnam, Nguyen, Spike-antibody waning after second dose of BNT162b2 or ChAdOx1, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01642-1
Soldin, Mattison, Sex differences in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, Clin Pharmacokinet, doi:10.2165/00003088-200948030-00001
Sukhatme, Reiersen, Vayttaden, Sukhatme, Fluvoxamine: A Review of Its Mechanism of Action and Its Role in COVID-19, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.652688
Who, COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update 55
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.15126",
"ISSN": [
"0306-5251",
"1365-2125"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bcp.15126",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Aims</jats:title><jats:p>Fluvoxamine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) and sigma‐1 receptor agonist, has so far shown promise in the prevention of COVID‐19 progression as an early treatment option in three trials. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of fluvoxamine in COVID‐19 patients if administered later in the course of the disease.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>The study was designed as an open‐label, prospective cohort trial with matched controls. In April and May 2021, 51 ICU COVID‐19 patients hospitalised in the University Hospital Dubrava and University Hospital Centre Zagreb, Croatia, were treated with fluvoxamine 100 mg three times daily for 15 days in addition to standard therapy and they were prospectively matched for age, gender, vaccination against COVID‐19, disease severity and comorbidities with 51 ICU controls.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>No statistically significant differences between groups were observed regarding the number of days on ventilator support, duration of ICU or total hospital stay. However, overall mortality was lower in the fluvoxamine group, 58.8% (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 30/51), than in the control group, 76.5% (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 39/51), HR 0.58, 95% CI (0.36–0.94, <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .027).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Fluvoxamine treatment in addition to the standard therapy in hospitalised ICU COVID‐19 patients could have a positive impact on patient survival. Further studies on the effects of fluvoxamine in COVID‐19 patients are urgently required.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/bcp.15126"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anaesthesiology, Resuscitation and Intensive Care University Hospital Centre Zagreb Zagreb Croatia"
}
],
"family": "Calusic",
"given": "Martina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8750-2083",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine University of Zagreb Zagreb Croatia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Marcec",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anaesthesiology, Resuscitation and Intensive Care University Hospital Centre Zagreb Zagreb Croatia"
}
],
"family": "Luksa",
"given": "Lea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anaesthesiology, Resuscitation and Intensive Care University Hospital Centre Zagreb Zagreb Croatia"
}
],
"family": "Jurkovic",
"given": "Ivan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anaesthesiology, Resuscitation and Intensive Care University Hospital Centre Zagreb Zagreb Croatia"
}
],
"family": "Kovac",
"given": "Natasa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anaesthesiology, Resuscitation and Intensive Care University Hospital Centre Zagreb Zagreb Croatia"
},
{
"name": "School of Medicine University of Zagreb Zagreb Croatia"
}
],
"family": "Mihaljevic",
"given": "Slobodan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1413-4862",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine University of Zagreb Zagreb Croatia"
},
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Unit of Clinical Pharmacology University Hospital Centre Zagreb Zagreb Croatia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Likic",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Brit J Clinical Pharma",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-01T08:28:50Z",
"timestamp": 1635755330000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-25T22:29:19Z",
"timestamp": 1693002559000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-02T05:16:37Z",
"timestamp": 1712034997817
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 49,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638316800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/bcp.15126",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1111/bcp.15126",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/bcp.15126",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2065-2073",
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_2_1",
"unstructured": "WHO.COVID‐19 Weekly Epidemiological Update 55.2021.https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---31-august-2021. Published August 31 2021. Accessed November 5 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138903",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjgh-2021-007031",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01642-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.08.19.21262111",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_11_7_1",
"unstructured": "IsraelA ShenharY&GreenIet al. Large‐scale study of antibody titer decay following BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine or SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. medRxiv. 2021:2021.08.19.21262111.https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.19.21262111v1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2023184",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-2600(21)00263-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_9_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_10_1",
"unstructured": "Effect of Early Treatment with Metformin on Risk of Emergency Care and Hospitalization Among Patients with COVID‐19: The TOGETHER Randomized Platform Clinical Trial.https://www.togethertrial.com/results"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-90551-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-02081-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab050",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2214-109x(21)00448-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.652688",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3325/CMJ.2021.62.95",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00406-020-01231-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aau5266",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/abr.abr_141_18",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0023852",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01254-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1829082",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100142",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00213-020-05753-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15537",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.09.031",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00003088-200948030-00001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2125.2001.01328.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2125.2000.00128.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-2002-31522",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40801-014-0005-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2013/108951",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fonc.2021.632263",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_36_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bcp.15126"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Safety and efficacy of fluvoxamine in COVID‐19 ICU patients: An open label, prospective cohort trial with matched controls",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "88"
}