Fluvoxamine Treatment of Patients with Symptomatic COVID-19 in a Community Treatment Center: A Preliminary Result of Randomized Controlled Trial
et al., Infection & Chemotherapy, doi:10.3947/ic.2021.0142, Mar 2022
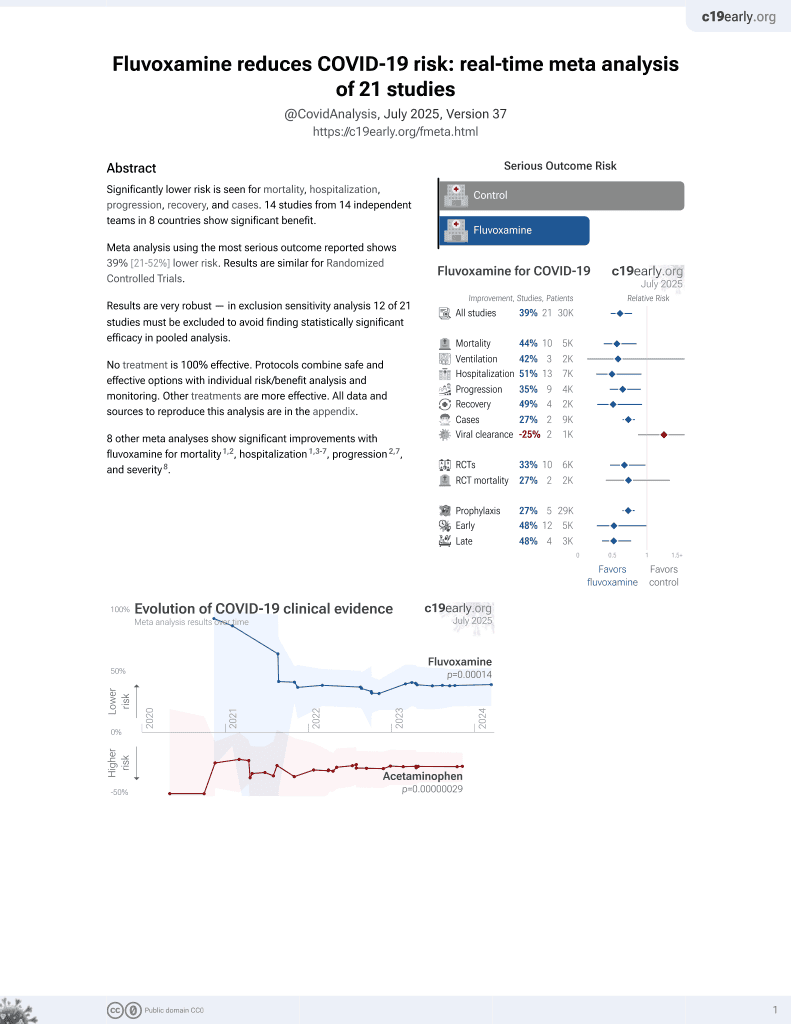
30th treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Early terminated RCT with 52 COVID+ patients in South Korea, showing no significant difference in progression with fluvoxamine treatment. There were only 2 events in each arm, and only one event for fluvoxamine in PP analysis. The trial was terminated early because the treatment center closed. 100mg fluvoxamine bid for 10 days.
|
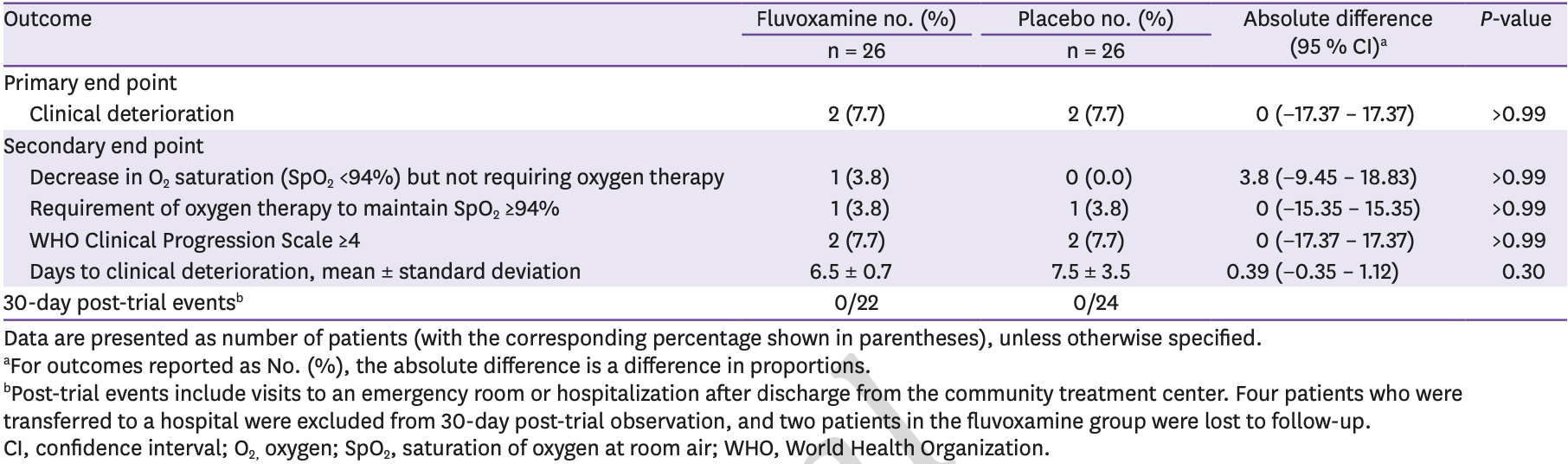
risk of progression, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 26 (7.7%), control 2 of 26 (7.7%).
|
|
risk of progression, 34.2% lower, RR 0.66, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 19 (5.3%), control 2 of 25 (8.0%), NNT 37, PP.
|
|
time to progression, 13.3% lower, relative time 0.87, p = 0.16, treatment mean 6.5 (±0.7) n=26, control mean 7.5 (±3.5) n=26.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Seo et al., 3 Mar 2022, Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, South Korea, peer-reviewed, median age 53.5, 14 authors, study period 15 January, 2021 - 19 February, 2021.
Fluvoxamine Treatment of Patients with Symptomatic COVID-19 in a Community Treatment Center: A Preliminary Result of Randomized Controlled Trial
Infection & Chemotherapy, doi:10.3947/ic.2021.0142
Background: This study aimed to evaluate whether fluvoxamine reduces clinical deterioration in adult patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), and to identify risk factors for clinical deterioration in patients admitted to a community treatment center (CTC). Materials and Methods: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted in a CTC, in Seoul, Korea from January 15, 2021, to February 19, 2021. Symptomatic adult patients with positive results of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 real timepolymerase chain reaction within 3 days of randomization were assigned at random to receive 100 mg of fluvoxamine or placebo twice daily for 10 days. The primary outcome was clinical deterioration defined by any of the following criteria: oxygen requirement to keep oxygen saturation over 94.0%, aggravation of pneumonia with dyspnea, or World Health Organization clinical progression scale 4 or greater. Results: Of 52 randomized participants [median (interquartile range) age, 53.5 (43.3 -60.0) years; 31 (60.0%) men], 44 (85.0%) completed the trial. Clinical deterioration occurred in 2 of 26 patients in each group (P >0.99). There were no serious adverse events in either group. Clinical deterioration occurred in 15 (6.0%) of 271 patients admitted to the CTC, and all of them were transferred to a hospital. In multivariate analysis, age between 55 and 64, fever and pneumonia at admission were independent risk factors for clinical deterioration.
Conclusion: In this study of adult patients with symptomatic COVID-19 who were admitted to the CTC, there was no significant differences in clinical deterioration between patients treated with fluvoxamine and placebo.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary document 1
Supplementary Table 1 Primary and secondary outcomes in the per-protocol analysis
Click here to view
Supplementary Table 2 Baseline and clinical characteristics of patients admitted to CTC according to the outcome Click here to view Supplementary Table 3 Results of analyses of risk factors for transfer to hospital due to clinical deterioration Click here to view
References
Ahmad, Cisewski, Miniño, Anderson, Provisional mortality data -United States, 2020, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7014e1
Almási, Török, Valkusz, Tajti, Csonka et al., Sigma-1 receptor engages an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant feedback loop mediated by peroxiredoxin in experimental colitis, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox9111081
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., ACTT-1 Study Group Members. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 -Final Report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Feng, Yu, Yao, Luo, Zhou et al., Early prediction of disease progression in COVID-19 pneumonia patients with chest CT and clinical characteristics, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-18786-x
Gandhi, Lynch, Rio, Mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMcp2009249
Hashimoto, Repurposing of CNS drugs to treat COVID-19 infection: targeting the sigma-1 receptor, Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, doi:10.1007/s00406-020-01231-x
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Vernet, Beeker, Jannot et al., Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4
Kang, Lee, Jung, Kim, Cho et al., Operating protocols of a community treatment center for isolation of patients with coronavirus disease, South Korea, Emerg Infect Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2610.201460
Kim, Kim, Lee, Lee, Discovering spatiotemporal patterns of COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-03487-2
Kim, Yoo, Heo, Lee, Oh, Clinical characteristics and risk factors for severe disease of coronavirus disease 2019 in a low case fatality rate region in Korea, Infect Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2021.0104
Lee, Hong, Kim, Lee, Lee, Clinical course of asymptomatic and mildly symptomatic patients with coronavirus disease admitted to community treatment centers, South Korea, Emerg Infect Dis
Lee, Song, Lim, Kim, Chai et al., Operation and management of Seoul metropolitan city community treatment center for mild condition COVID-19 patients, J Korean Med Sci, doi:10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e367
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
Medical, World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2013.281053
Park, Kim, Heo, Kim, Park et al., Out-of-hospital cohort treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 patients with mild symptoms in Korea: an experience from a single community treatment center, J Korean Med Sci, doi:10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e140
Park, Lee, Lim, Lim, Hong et al., Presenting characteristics and clinical outcome of patients with COVID-19 in South Korea: A nationwide retrospective observational study, Lancet Reg Health West Pac, doi:10.1016/j.lanwpc.2020.100061
Peck, Collaborative response to COVID-19 pandemic, and development of treatment guidelines, Infect Chemother
Pubmed | Crossref, None, doi:10.3201/eid2610.201620
Pubmed | Crossref, None, doi:10.3947/ic.2021.0301
Recovery Collaborative Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Reis, Santos Moreira-Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
Salama, Han, Yau, Reiss, Kramer et al., Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2030340
Seftel, Boulware, Prospective cohort of fluvoxamine for early treatment of coronavirus disease 19, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab050
Undurraga, Chowell, Mizumoto, COVID-19 case fatality risk by age and gender in a high testing setting in Latin America: Chile, March-August 2020, Infect Dis Poverty, doi:10.1186/s40249-020-00785-1
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Zarandi, Zinatizadeh, Zinatizadeh, Yousefi, Rezaei, SARS-CoV-2: From the pathogenesis to potential anti-viral treatments, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111352
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2021.0142",
"ISSN": [
"2093-2340",
"2092-6448"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3947/ic.2021.0142",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6659-6853",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
},
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Seo",
"given": "Hyeonji",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2002-1098",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Haein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6375-3657",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bae",
"given": "Seongman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2902-8341",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Park",
"given": "Seonghee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4447-975X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chung",
"given": "Hyemin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6062-4451",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Laboratory Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sung",
"given": "Heung-sup",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4333-3270",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jung",
"given": "Jiwon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5489-8608",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Min Jae",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6596-8253",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Sung-Han",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1381-8787",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Sang-Oh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4972-4531",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Sang-Ho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6785-8824",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Yang Soo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5592-7458",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Son",
"given": "Ki Young",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1672-3185",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chong",
"given": "Yong Pil",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Infection & Chemotherapy"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-10T07:51:52Z",
"timestamp": 1646898712000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-10T07:51:52Z",
"timestamp": 1646898712000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-10T08:15:41Z",
"timestamp": 1646900141005
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2093-2340"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2092-6448"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1640995200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://icjournal.org/pdf/10.3947/ic.2021.0142",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://icjournal.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3947/ic.2021.0142",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://icjournal.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3947/ic.2021.0142",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2343",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3947",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
},
"publisher": "Korean Society of Infectious Diseases and Korean Society for Chemotherapy",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://icjournal.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3947/ic.2021.0142"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Infect Chemother"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Infectious Diseases"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Fluvoxamine Treatment of Patients with Symptomatic COVID-19 in a Community Treatment Center: A Preliminary Result of Randomized Controlled Trial"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "54"
}