Impact of Zinc, Vitamins C and D on Disease Prognosis among Patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A Cross-Sectional Study
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14235029, Nov 2022
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
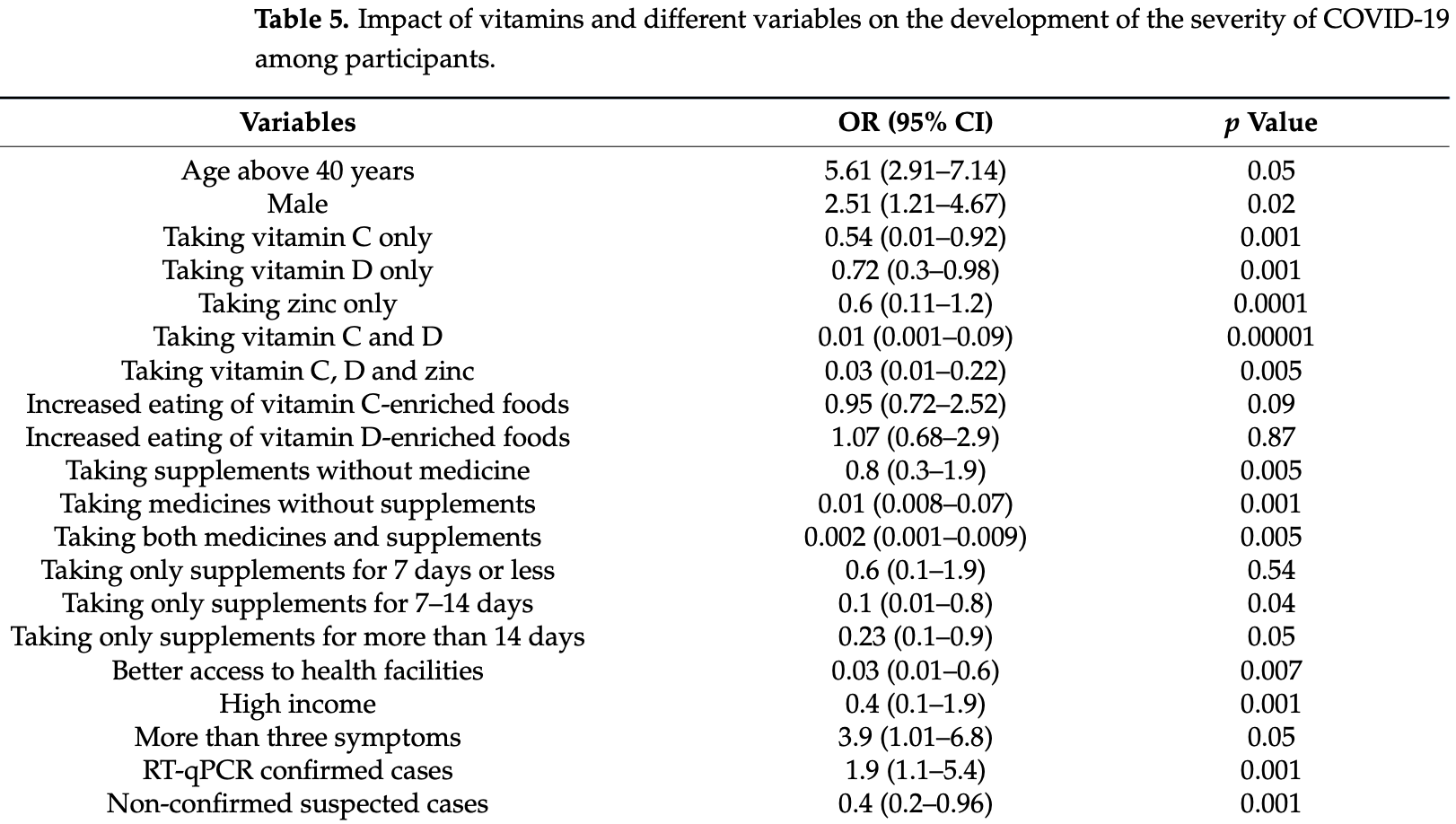
Retrospective 962 COVID-19 patients in Bangladesh, showing significantly lower severity with vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc supplementation, and improved results from the combination of all three.
Table 2 has a typographical error where the columns for Vitamin C and Vitamin D are duplicates. The OR for "Taking vitamin C, D and zinc as medication" in Table 4 is likely a typo, with the point estimate outside the CI.
The study aims to evaluate the risk of infection by comparing COVID-19 PCR-positive patients to a control group of suspected patients who had close contact and symptoms but were PCR-negative, however this introduces selection bias. These estimates are likely to be less reliable and are excluded in our analysis.
This is the 54th of 73 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000076.
20 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0016.
|
risk of severe case, 46.0% lower, OR 0.54, p = 0.001, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sharif et al., 26 Nov 2022, retrospective, Bangladesh, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, study period 13 December, 2020 - 4 February, 2021.
Impact of Zinc, Vitamins C and D on Disease Prognosis among Patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A Cross-Sectional Study
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14235029
Vitamin C, (ascorbic acid), vitamin D (cholecalciferol) and zinc (zinc sulfate monohydrate) supplements are important in immunity against coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). However, a limited number of studies have been conducted on the association of vitamins and supplements with the reduced risks of COVID-19 infection. This study aims to evaluate the association of vitamins and supplements as treatment options to reduce the severity of COVID-19. Data were collected from 962 participants from 13 December 2020 to 4 February 2021. The presence of COVID-19 was confirmed by qRT-PCR. The Chi-square test and multivariate regression analyses were conducted. The ratio of uptake of vitamin C:vitamin D:zinc was 1:1:0.95. Uptake of vitamin C, vitamin D and zinc were significantly associated with the reduced risk of infection and severity of COVID-19 (OR: 0.006 (95% CI: 0.03-0.11) (p = 0.004)) and (OR: 0.03 (95% CI: 0.01-0.22) (p = 0.005)). The tendency of taking supplements was associated with the presence of infection of COVID-19 (p = 0.001), age (p = 0.02), sex (p = 0.05) and residence (p = 0.04). The duration of supplementation and medication was significantly associated with reduced hospitalization (p = 0.0001). Vitamins C, D and zinc were not significantly (p = 0.9) associated with a reduced risk of severity when taken through the diet. Hospitalization (p = 0.000001) and access to health facilities (p = 0.0097) were significantly associated with the survival period of the participants. Participants with better access to health facilities recovered early (OR: 6.21, 95% CI 1.56-24.7). This study will add knowledge in the field of treatment of COVID-19 by using vitamins and zinc supplements.
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, N.S. and S.K.D.; methodology, N.S. and M.Z.; software, N.S. and M.Z.; validation, N.S., M.Z and S.K.D.; formal analysis, N.S., R.R.O., A.K., H.J.B., F.M.A., N.H., S.K., S.T.S., M.Z., H.H., X.S. and A.K.P.; investigation, N.S.; resources, A.K.P. and S.K.D.; data curation, R.R.O., N.H., S.K. and S.T.S.; writing-original draft preparation, N.S.; writing-review and editing, N.S., A.K., K.J.A., H.J.B., F.M.A., M.Z. and H.H.; visualization, N.S. and S.K.D; supervision,
References
Abobaker, Alzwi, Alraied, Overview of the possible role of vitamin C in management of COVID-19, Pharmacol Rep, doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00176-1
Ahmad, Vitamin C for COVID-19 Treatment: Have We Got Enough Evidence?, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.892561
Ahmed, Hasan, Akter, Sarkar, Rahman et al., Behavioral preventive measures and the use of medicines and herbal products among the public in response to Covid-19 in Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0243706
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021
Alruwaili, Jarrar, Effects of vitamin C and D on the mRNA expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor, cathepsin L, and transmembrane serine protease in the mouse lungs, Libyan. J. Med, doi:10.1080/19932820.2022.2054111
Alzaben, The Potential Influence of Vitamin A, C, and D and Zinc Supplements on the Severity of COVID-19 Symptoms and Clinical Outcomes: An Updated Review of Literature, Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci, doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.8.3.04
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubée, Legrand et al., Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID quasi-experimental study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Arvinte, Singh, Marik, Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients of a North American community hospital intensive care unit in May 2020: A pilot study, Med. Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064
Bae, Kim, The role of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in immune system against COVID-19, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules25225346
Bartley, Vitamin, innate immunity and upper respiratory tract infection, J. Laryngol. Otol, doi:10.1017/S0022215109992684
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-Preliminary report, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Beigmohammadi, Bitarafan, Hoseindokht, Abdollahi, Amoozadeh et al., The effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E on disease severity and inflammatory responses in patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4
Bendich, Machlin, Scandurra, Burton, Wayner, The antioxidant role of vitamin C. Free Radic, Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/S8755-9668(86)80021-7
Bonaventura, Benedetti, Albarède, Miossec, Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.008
Bourbour, Mirzaei Dahka, Gholamalizadeh, Akbari, Shadnoush et al., Nutrients in prevention, treatment, and management of viral infections; special focus on Coronavirus, Arch. Physiol. Biochem, doi:10.1080/13813455.2020.1791188
Carr, Maggini, Vitamin C and immune function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu9111211
Fath, Naderi, Hamzavi, Ganji, Shabani et al., Molecular Mechanisms and therapeutic effects of different vitamins and minerals in COVID-19 patients, J. Trace. Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.127044
Finzi, Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: A report on four patients, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.006
Funding Acquisition, All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Gao, Xu, Wang, Lv, Ma et al., The efficiency and safety of high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.202557
Gasmi, Tippairote, Mujawdiya, Peana, Menzel et al., Micronutrients as immunomodulatory tools for COVID-19 management, J. Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108545
Giacalone, Marin, Febbi, Tovani-Palone, Current Evidence on Vitamin C, D, and Zinc Supplementation for COVID-19 Prevention and/or Treatment, Electron. J. Gen. Med, doi:10.29333/ejgm/11099
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: A meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11040708
Hewison, An update on vitamin D and human immunity, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04261.x
Jaun, Boesing, Lüthi-Corridori, Abig, Makhdoomi et al., High-dose vitamin D substitution in patients with COVID-19: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center study-VitCov Trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-022-06016-2
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Ma, Zhou, Heianza, Qi, Habitual use of vitamin D supplements and risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: A prospective study in UK Biobank, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa381
Maares, Haase, Zinc and immunity: An essential interrelation, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1016/j.abb.2016.03.022
Mahjoub, Rodenstein, Jounieaux, Severe Covid-19 disease: Rather AVDS than ARDS?, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-02972-w
Malik, Properties of coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2, Malays J Pathol
Margolin, Luchins, Margolin, Margolin, Lefkowitz, 20-week study of clinical outcomes of over-the-counter COVID-19 prophylaxis and treatment, J. Evid.-Based Integr. Med, doi:10.1177/2515690X211026193
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Murdaca, Pioggia, Negrini, Vitamin D and Covid-19: An update on evidence and potential therapeutic implications, Clin. Mol. Allergy, doi:10.1186/s12948-020-00139-0
Nimer, Khabour, Swedan, Kofahi, The impact of vitamin and mineral supplements usage prior to COVID-19 infection on disease severity and hospitalization, Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci, doi:10.17305/bjbms.2021.7009
Prather, Wang, Schooley, Reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abc6197
Prietl, Treiber, Pieber, Amrein, Vitamin D and immune function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu5072502
Sharif, Ahmed, Opu, Tani, Dewan et al., Prevalence and impact of diabetes and cardiovascular disease on clinical outcome among patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.005
Sharif, Dey, Phylogenetic and whole genome analysis of first seven SARS-CoV-2 isolates in Bangladesh, Future Virol, doi:10.2217/fvl-2020-0201
Sharif, Opu, Ahmed, Sarkar, Jaheen et al., Prevalence and impact of comorbidities on disease prognosis among patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A nationwide study amid the second wave, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.021
Sharif, Sarkar, Ahmed, Ferdous, Nobel et al., Environmental correlation and epidemiologic analysis of COVID-19 pandemic in ten regions in five continents, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06576
Souza, Vasconcelos, Prado, Pereira, Zinc et al., Perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2020.606398
Speakman, Michienzi, Badowski, Vitamins, supplements and COVID-19: A review of currently available evidence, Drugs Context, doi:10.7573/dic.2021-6-2
Thomas, Holt, Vitamin C and immunity: An assessment of the evidence, Clin. Exp. Immunol
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Wolski, Wang et al., Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: The COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
Wei, Liu, Li, Zhang, Zhong et al., Evaluation of the nutritional status in patients with COVID-19, J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr, doi:10.3164/jcbn.20-91
Wong, Chan, Venkatakrishnan, Chiu, Shen et al., Impact of dietary nutrients (functional foods/nutraceuticals) and micronutrients on COVID-19: A review, J. Food Bioact, doi:10.31665/JFB.2021.15280
Yadav, Birdi, Tomo, Charan, Bhardwaj et al., Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 infection and mortality in the Asia Pacific region: A cross-sectional study, Indian J. Clin. Biochem, doi:10.1007/s12291-020-00950-1
Zhang, Rao, Li, Zhu, Liu et al., Pilot trial of high-dose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Ann. Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s13613-020-00792-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14235029",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu14235029",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Vitamin C, (ascorbic acid), vitamin D (cholecalciferol) and zinc (zinc sulfate monohydrate) supplements are important in immunity against coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). However, a limited number of studies have been conducted on the association of vitamins and supplements with the reduced risks of COVID-19 infection. This study aims to evaluate the association of vitamins and supplements as treatment options to reduce the severity of COVID-19. Data were collected from 962 participants from 13 December 2020 to 4 February 2021. The presence of COVID-19 was confirmed by qRT-PCR. The Chi-square test and multivariate regression analyses were conducted. The ratio of uptake of vitamin C:vitamin D:zinc was 1:1:0.95. Uptake of vitamin C, vitamin D and zinc were significantly associated with the reduced risk of infection and severity of COVID-19 (OR: 0.006 (95% CI: 0.03–0.11) (p = 0.004)) and (OR: 0.03 (95% CI: 0.01–0.22) (p = 0.005)). The tendency of taking supplements was associated with the presence of infection of COVID-19 (p = 0.001), age (p = 0.02), sex (p = 0.05) and residence (p = 0.04). The duration of supplementation and medication was significantly associated with reduced hospitalization (p = 0.0001). Vitamins C, D and zinc were not significantly (p = 0.9) associated with a reduced risk of severity when taken through the diet. Hospitalization (p = 0.000001) and access to health facilities (p = 0.0097) were significantly associated with the survival period of the participants. Participants with better access to health facilities recovered early (OR: 6.21, 95% CI 1.56–24.7). This study will add knowledge in the field of treatment of COVID-19 by using vitamins and zinc supplements.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu14235029"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2377-9726",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sharif",
"given": "Nadim",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0373-1509",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Opu",
"given": "Rubayet Rayhan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Afsana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6688-0106",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Alzahrani",
"given": "Khalid J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2841-5438",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Banjer",
"given": "Hamsa Jameel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6930-5214",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Alzahrani",
"given": "Fuad M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haque",
"given": "Nusaira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Shahriar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2595-2070",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Soumik",
"given": "Saimum Tahreef",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7461-4967",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Hanwen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Xiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0246-3872",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Parvez",
"given": "Anowar Khasru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2440-5673",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dey",
"given": "Shuvra Kanti",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-28T12:01:30Z",
"timestamp": 1669636890000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-28T12:46:30Z",
"timestamp": 1669639590000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"TURSP-2020/128"
],
"name": "Taif University Researchers Supporting Program"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-16T02:45:38Z",
"timestamp": 1700102738880
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issue": "23",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "23",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1669420800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/23/5029/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "5029",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "(2022, August 13). COVID-19 Map-Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html/2022."
},
{
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "(2022, August 13). WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int//2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06576",
"article-title": "Environmental correlation and epidemiologic analysis of COVID-19 pandemic in ten regions in five continents",
"author": "Sharif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e06576",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Properties of coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Malik",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Malays J Pathol.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2020-0201",
"article-title": "Phylogenetic and whole genome analysis of first seven SARS-CoV-2 isolates in Bangladesh",
"author": "Sharif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "735",
"journal-title": "Future Virol.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc6197",
"article-title": "Reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Prather",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1422",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.005",
"article-title": "Prevalence and impact of diabetes and cardiovascular disease on clinical outcome among patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh",
"author": "Sharif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1009",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.021",
"article-title": "Prevalence and impact of comorbidities on disease prognosis among patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A nationwide study amid the second wave",
"author": "Sharif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102148",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108545",
"article-title": "Micronutrients as immunomodulatory tools for COVID-19 management",
"author": "Gasmi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108545",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "220",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31665/JFB.2021.15280",
"article-title": "Impact of dietary nutrients (functional foods/nutraceuticals) and micronutrients on COVID-19: A review",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "J. Food Bioact.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25225346",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Bae, M., and Kim, H. (2020). The role of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in immune system against COVID-19. Molecules, 25."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-020-00176-1",
"article-title": "Overview of the possible role of vitamin C in management of COVID-19",
"author": "Abobaker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1517",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1373",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public Health",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc, Vitamin D and Vitamin C: Perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity",
"author": "Souza",
"first-page": "295",
"journal-title": "Front. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3164/jcbn.20-91",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the nutritional status in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9111211",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Carr, A.C., and Maggini, S. (2017). Vitamin C and immune function. Nutrients, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S8755-9668(86)80021-7",
"article-title": "The antioxidant role of vitamin C",
"author": "Bendich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "419",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.127044",
"article-title": "Molecular Mechanisms and therapeutic effects of different vitamins and minerals in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Fath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "127044",
"journal-title": "J. Trace. Elem. Med. Biol.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin C and immunity: An assessment of the evidence",
"author": "Thomas",
"first-page": "370",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "32",
"year": "1978"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04261.x",
"article-title": "An update on vitamin D and human immunity",
"author": "Hewison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "315",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5072502",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and immune function",
"author": "Prietl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2502",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0022215109992684",
"article-title": "Vitamin D, innate immunity and upper respiratory tract infection",
"author": "Bartley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "J. Laryngol. Otol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"key": "ref_23",
"unstructured": "Pierce, G.N., Rupp, H., Izumi, T., and Grynberg, A. (2013). Molecular and Cellular Effects of Nutrition on Disease Processes, Springer Science & Business Media."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2016.03.022",
"article-title": "Zinc and immunity: An essential interrelation",
"author": "Maares",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "611",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.008",
"article-title": "Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation",
"author": "Bonaventura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "277",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202003.0235.v2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Grant, W.B., Lahore, H., McDonnell, S.L., Baggerly, C.A., French, C.B., Aliano, J.L., and Bhattoa, H.P. (2020). Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13813455.2020.1791188",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "BourBour, F., Mirzaei Dahka, S., Gholamalizadeh, M., Akbari, M.E., Shadnoush, M., Haghighi, M., Taghvaye-Masoumi, H., Ashoori, N., and Doaei, S. (2020). Nutrients in prevention, treatment, and management of viral infections; special focus on Coronavirus. Arch. Physiol. Biochem., 1791188."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.202557",
"article-title": "The efficiency and safety of high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7020",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00792-3",
"article-title": "Pilot trial of high-dose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intensive Care.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12948-020-00139-0",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and Covid-19: An update on evidence and potential therapeutic implications",
"author": "Murdaca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Clin. Mol. Allergy.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064",
"article-title": "Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients of a North American community hospital intensive care unit in May 2020: A pilot study",
"author": "Arvinte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100064",
"journal-title": "Med. Drug Discov.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—Preliminary report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Annweiler, G., Corvaisier, M., Gautier, J., Dubée, V., Legrand, E., Sacco, G., and Annweiler, C. (2020). Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID quasi-experimental study. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-02972-w",
"article-title": "Severe Covid-19 disease: Rather AVDS than ARDS?",
"author": "Mahjoub",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11040708",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "Hemilä, H., and Chalker, E. (2019). Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: A meta-analysis. Nutrients, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-020-00950-1",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 infection and mortality in the Asia Pacific region: A cross-sectional study",
"author": "Yadav",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "492",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Clin. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.006",
"article-title": "Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: A report on four patients",
"author": "Finzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "307",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12944/CRNFSJ.8.3.04",
"article-title": "The Potential Influence of Vitamin A, C, and D and Zinc Supplements on the Severity of COVID-19 Symptoms and Clinical Outcomes: An Updated Review of Literature",
"author": "Alzaben",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "703",
"journal-title": "Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency",
"author": "Jothimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.29333/ejgm/11099",
"article-title": "Current Evidence on Vitamin C, D, and Zinc Supplementation for COVID-19 Prevention and/or Treatment",
"author": "Giacalone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "em311",
"journal-title": "Electron. J. Gen. Med.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqaa381",
"article-title": "Habitual use of vitamin D supplements and risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: A prospective study in UK Biobank",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1275",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"article-title": "Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: The COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Thomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e210369",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.15.20175513",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_44",
"unstructured": "Ahmed, I., Hasan, M., Akter, R., Sarkar, B.K., Rahman, M., Sarker, M.S., and Samad, M.A. (2020). Behavioral preventive measures and the use of medicines and herbal products among the public in response to Covid-19 in Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE, 15."
},
{
"article-title": "The impact of vitamin and mineral supplements usage prior to COVID-19 infection on disease severity and hospitalization",
"author": "Nimer",
"first-page": "826",
"journal-title": "Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2515690X211026193",
"article-title": "20-week study of clinical outcomes of over-the-counter COVID-19 prophylaxis and treatment",
"author": "Margolin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2515690X211026193",
"journal-title": "J. Evid.-Based Integr. Med.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4",
"article-title": "The effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E on disease severity and inflammatory responses in patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Beigmohammadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "802",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-022-06016-2",
"article-title": "High-dose vitamin D substitution in patients with COVID-19: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center study—VitCov Trial",
"author": "Jaun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7573/dic.2021-6-2",
"article-title": "Vitamins, supplements and COVID-19: A review of currently available evidence",
"author": "Speakman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2021-6-2",
"journal-title": "Drugs Context",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2022.892561",
"article-title": "Vitamin C for COVID-19 Treatment: Have We Got Enough Evidence?",
"author": "Ahmad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "892561",
"journal-title": "Front. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19932820.2022.2054111",
"article-title": "Effects of vitamin C and D on the mRNA expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor, cathepsin L, and transmembrane serine protease in the mouse lungs",
"author": "Alruwaili",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2054111",
"journal-title": "Libyan. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 51,
"references-count": 51,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/23/5029"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of Zinc, Vitamins C and D on Disease Prognosis among Patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A Cross-Sectional Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}
sharif
