Impact of Zinc, Vitamins C and D on Disease Prognosis among Patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A Cross-Sectional Study
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14235029, Nov 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
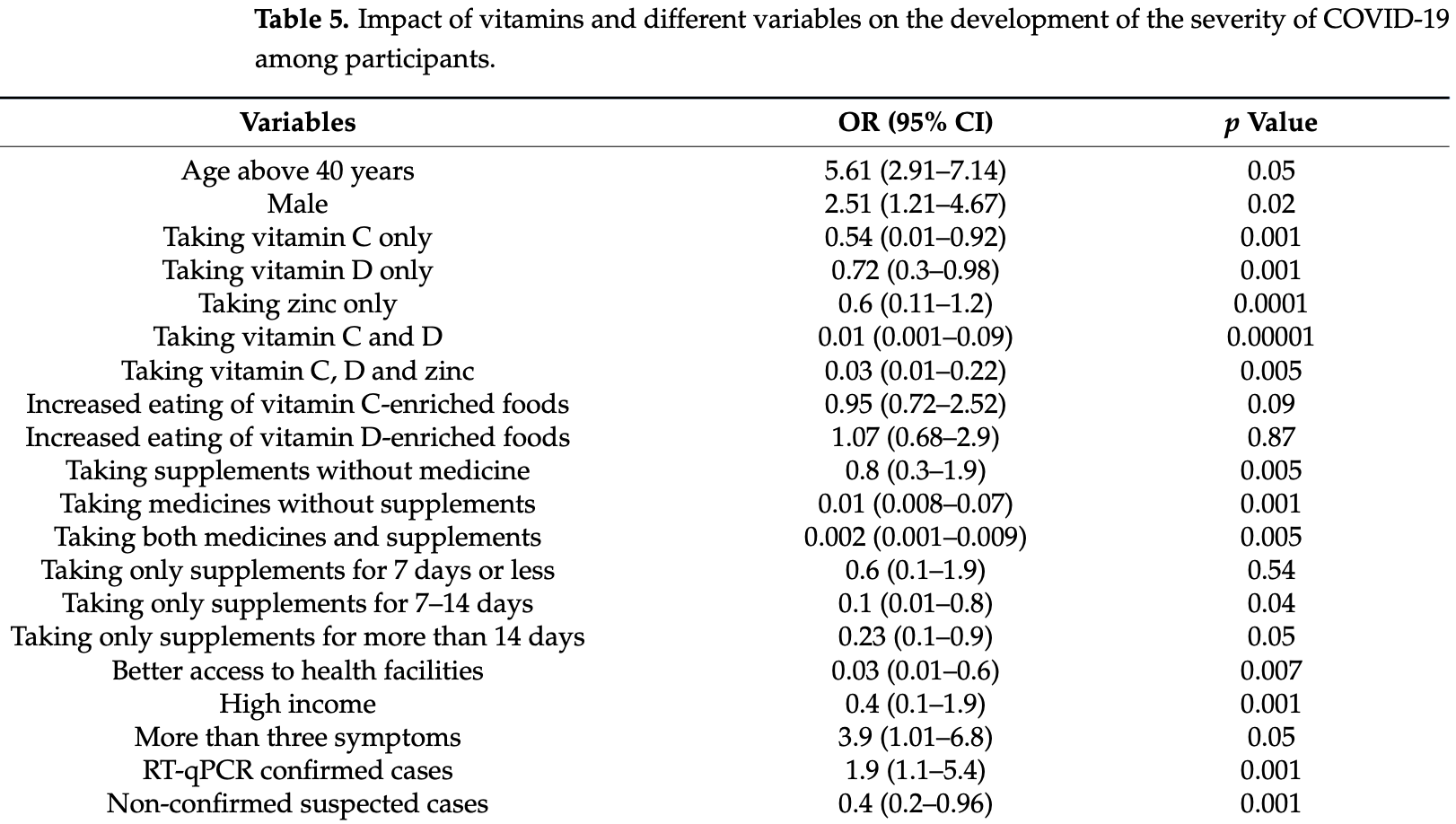
Retrospective 962 COVID-19 patients in Bangladesh, showing significantly lower severity with vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc supplementation, and improved results from the combination of all three.
This is the 109th of 136 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of severe case, 28.0% lower, OR 0.72, p = 0.001, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of severe case, 97.0% lower, OR 0.03, p = 0.005, adjusted per study, combined use of vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sharif et al., 26 Nov 2022, retrospective, Bangladesh, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, study period 13 December, 2020 - 4 February, 2021, dosage 2,000IU daily.
Impact of Zinc, Vitamins C and D on Disease Prognosis among Patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A Cross-Sectional Study
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14235029
Vitamin C, (ascorbic acid), vitamin D (cholecalciferol) and zinc (zinc sulfate monohydrate) supplements are important in immunity against coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). However, a limited number of studies have been conducted on the association of vitamins and supplements with the reduced risks of COVID-19 infection. This study aims to evaluate the association of vitamins and supplements as treatment options to reduce the severity of COVID-19. Data were collected from 962 participants from 13 December 2020 to 4 February 2021. The presence of COVID-19 was confirmed by qRT-PCR. The Chi-square test and multivariate regression analyses were conducted. The ratio of uptake of vitamin C:vitamin D:zinc was 1:1:0.95. Uptake of vitamin C, vitamin D and zinc were significantly associated with the reduced risk of infection and severity of COVID-19 (OR: 0.006 (95% CI: 0.03-0.11) (p = 0.004)) and (OR: 0.03 (95% CI: 0.01-0.22) (p = 0.005)). The tendency of taking supplements was associated with the presence of infection of COVID-19 (p = 0.001), age (p = 0.02), sex (p = 0.05) and residence (p = 0.04). The duration of supplementation and medication was significantly associated with reduced hospitalization (p = 0.0001). Vitamins C, D and zinc were not significantly (p = 0.9) associated with a reduced risk of severity when taken through the diet. Hospitalization (p = 0.000001) and access to health facilities (p = 0.0097) were significantly associated with the survival period of the participants. Participants with better access to health facilities recovered early (OR: 6.21, 95% CI 1.56-24.7). This study will add knowledge in the field of treatment of COVID-19 by using vitamins and zinc supplements.
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, N.S. and S.K.D.; methodology, N.S. and M.Z.; software, N.S. and M.Z.; validation, N.S., M.Z and S.K.D.; formal analysis, N.S., R.R.O., A.K., H.J.B., F.M.A., N.H., S.K., S.T.S., M.Z., H.H., X.S. and A.K.P.; investigation, N.S.; resources, A.K.P. and S.K.D.; data curation, R.R.O., N.H., S.K. and S.T.S.; writing-original draft preparation, N.S.; writing-review and editing, N.S., A.K., K.J.A., H.J.B., F.M.A., M.Z. and H.H.; visualization, N.S. and S.K.D; supervision,
References
Abobaker, Alzwi, Alraied, Overview of the possible role of vitamin C in management of COVID-19, Pharmacol Rep, doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00176-1
Ahmad, Vitamin C for COVID-19 Treatment: Have We Got Enough Evidence?, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.892561
Ahmed, Hasan, Akter, Sarkar, Rahman et al., Behavioral preventive measures and the use of medicines and herbal products among the public in response to Covid-19 in Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0243706
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021
Alruwaili, Jarrar, Effects of vitamin C and D on the mRNA expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor, cathepsin L, and transmembrane serine protease in the mouse lungs, Libyan. J. Med, doi:10.1080/19932820.2022.2054111
Alzaben, The Potential Influence of Vitamin A, C, and D and Zinc Supplements on the Severity of COVID-19 Symptoms and Clinical Outcomes: An Updated Review of Literature, Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci, doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.8.3.04
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubée, Legrand et al., Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID quasi-experimental study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Arvinte, Singh, Marik, Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients of a North American community hospital intensive care unit in May 2020: A pilot study, Med. Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064
Bae, Kim, The role of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in immune system against COVID-19, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules25225346
Bartley, Vitamin, innate immunity and upper respiratory tract infection, J. Laryngol. Otol, doi:10.1017/S0022215109992684
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-Preliminary report, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Beigmohammadi, Bitarafan, Hoseindokht, Abdollahi, Amoozadeh et al., The effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E on disease severity and inflammatory responses in patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4
Bendich, Machlin, Scandurra, Burton, Wayner, The antioxidant role of vitamin C. Free Radic, Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/S8755-9668(86)80021-7
Bonaventura, Benedetti, Albarède, Miossec, Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.008
Bourbour, Mirzaei Dahka, Gholamalizadeh, Akbari, Shadnoush et al., Nutrients in prevention, treatment, and management of viral infections; special focus on Coronavirus, Arch. Physiol. Biochem, doi:10.1080/13813455.2020.1791188
Carr, Maggini, Vitamin C and immune function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu9111211
Fath, Naderi, Hamzavi, Ganji, Shabani et al., Molecular Mechanisms and therapeutic effects of different vitamins and minerals in COVID-19 patients, J. Trace. Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.127044
Finzi, Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: A report on four patients, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.006
Funding Acquisition, All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Gao, Xu, Wang, Lv, Ma et al., The efficiency and safety of high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.202557
Gasmi, Tippairote, Mujawdiya, Peana, Menzel et al., Micronutrients as immunomodulatory tools for COVID-19 management, J. Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108545
Giacalone, Marin, Febbi, Tovani-Palone, Current Evidence on Vitamin C, D, and Zinc Supplementation for COVID-19 Prevention and/or Treatment, Electron. J. Gen. Med, doi:10.29333/ejgm/11099
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: A meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11040708
Hewison, An update on vitamin D and human immunity, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04261.x
Jaun, Boesing, Lüthi-Corridori, Abig, Makhdoomi et al., High-dose vitamin D substitution in patients with COVID-19: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center study-VitCov Trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-022-06016-2
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Ma, Zhou, Heianza, Qi, Habitual use of vitamin D supplements and risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: A prospective study in UK Biobank, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa381
Maares, Haase, Zinc and immunity: An essential interrelation, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1016/j.abb.2016.03.022
Mahjoub, Rodenstein, Jounieaux, Severe Covid-19 disease: Rather AVDS than ARDS?, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-02972-w
Malik, Properties of coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2, Malays J Pathol
Margolin, Luchins, Margolin, Margolin, Lefkowitz, 20-week study of clinical outcomes of over-the-counter COVID-19 prophylaxis and treatment, J. Evid.-Based Integr. Med, doi:10.1177/2515690X211026193
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Murdaca, Pioggia, Negrini, Vitamin D and Covid-19: An update on evidence and potential therapeutic implications, Clin. Mol. Allergy, doi:10.1186/s12948-020-00139-0
Nimer, Khabour, Swedan, Kofahi, The impact of vitamin and mineral supplements usage prior to COVID-19 infection on disease severity and hospitalization, Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci, doi:10.17305/bjbms.2021.7009
Prather, Wang, Schooley, Reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abc6197
Prietl, Treiber, Pieber, Amrein, Vitamin D and immune function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu5072502
Sharif, Ahmed, Opu, Tani, Dewan et al., Prevalence and impact of diabetes and cardiovascular disease on clinical outcome among patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.005
Sharif, Dey, Phylogenetic and whole genome analysis of first seven SARS-CoV-2 isolates in Bangladesh, Future Virol, doi:10.2217/fvl-2020-0201
Sharif, Opu, Ahmed, Sarkar, Jaheen et al., Prevalence and impact of comorbidities on disease prognosis among patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A nationwide study amid the second wave, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.021
Sharif, Sarkar, Ahmed, Ferdous, Nobel et al., Environmental correlation and epidemiologic analysis of COVID-19 pandemic in ten regions in five continents, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06576
Souza, Vasconcelos, Prado, Pereira, Zinc et al., Perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2020.606398
Speakman, Michienzi, Badowski, Vitamins, supplements and COVID-19: A review of currently available evidence, Drugs Context, doi:10.7573/dic.2021-6-2
Thomas, Holt, Vitamin C and immunity: An assessment of the evidence, Clin. Exp. Immunol
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Wolski, Wang et al., Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: The COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
Wei, Liu, Li, Zhang, Zhong et al., Evaluation of the nutritional status in patients with COVID-19, J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr, doi:10.3164/jcbn.20-91
Wong, Chan, Venkatakrishnan, Chiu, Shen et al., Impact of dietary nutrients (functional foods/nutraceuticals) and micronutrients on COVID-19: A review, J. Food Bioact, doi:10.31665/JFB.2021.15280
Yadav, Birdi, Tomo, Charan, Bhardwaj et al., Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 infection and mortality in the Asia Pacific region: A cross-sectional study, Indian J. Clin. Biochem, doi:10.1007/s12291-020-00950-1
Zhang, Rao, Li, Zhu, Liu et al., Pilot trial of high-dose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Ann. Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s13613-020-00792-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14235029",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu14235029",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Vitamin C, (ascorbic acid), vitamin D (cholecalciferol) and zinc (zinc sulfate monohydrate) supplements are important in immunity against coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). However, a limited number of studies have been conducted on the association of vitamins and supplements with the reduced risks of COVID-19 infection. This study aims to evaluate the association of vitamins and supplements as treatment options to reduce the severity of COVID-19. Data were collected from 962 participants from 13 December 2020 to 4 February 2021. The presence of COVID-19 was confirmed by qRT-PCR. The Chi-square test and multivariate regression analyses were conducted. The ratio of uptake of vitamin C:vitamin D:zinc was 1:1:0.95. Uptake of vitamin C, vitamin D and zinc were significantly associated with the reduced risk of infection and severity of COVID-19 (OR: 0.006 (95% CI: 0.03–0.11) (p = 0.004)) and (OR: 0.03 (95% CI: 0.01–0.22) (p = 0.005)). The tendency of taking supplements was associated with the presence of infection of COVID-19 (p = 0.001), age (p = 0.02), sex (p = 0.05) and residence (p = 0.04). The duration of supplementation and medication was significantly associated with reduced hospitalization (p = 0.0001). Vitamins C, D and zinc were not significantly (p = 0.9) associated with a reduced risk of severity when taken through the diet. Hospitalization (p = 0.000001) and access to health facilities (p = 0.0097) were significantly associated with the survival period of the participants. Participants with better access to health facilities recovered early (OR: 6.21, 95% CI 1.56–24.7). This study will add knowledge in the field of treatment of COVID-19 by using vitamins and zinc supplements.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu14235029"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2377-9726",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sharif",
"given": "Nadim",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0373-1509",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Opu",
"given": "Rubayet Rayhan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Afsana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6688-0106",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Alzahrani",
"given": "Khalid J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2841-5438",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Banjer",
"given": "Hamsa Jameel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6930-5214",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Alzahrani",
"given": "Fuad M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haque",
"given": "Nusaira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Shahriar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2595-2070",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Soumik",
"given": "Saimum Tahreef",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7461-4967",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Hanwen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Xiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0246-3872",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Parvez",
"given": "Anowar Khasru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2440-5673",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dey",
"given": "Shuvra Kanti",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-28T12:01:30Z",
"timestamp": 1669636890000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-28T12:46:30Z",
"timestamp": 1669639590000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"TURSP-2020/128"
],
"name": "Taif University Researchers Supporting Program"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-16T02:45:38Z",
"timestamp": 1700102738880
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issue": "23",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "23",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1669420800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/23/5029/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "5029",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "(2022, August 13). COVID-19 Map-Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html/2022."
},
{
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "(2022, August 13). WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int//2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06576",
"article-title": "Environmental correlation and epidemiologic analysis of COVID-19 pandemic in ten regions in five continents",
"author": "Sharif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e06576",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Properties of coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Malik",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Malays J Pathol.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2020-0201",
"article-title": "Phylogenetic and whole genome analysis of first seven SARS-CoV-2 isolates in Bangladesh",
"author": "Sharif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "735",
"journal-title": "Future Virol.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc6197",
"article-title": "Reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Prather",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1422",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.005",
"article-title": "Prevalence and impact of diabetes and cardiovascular disease on clinical outcome among patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh",
"author": "Sharif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1009",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.021",
"article-title": "Prevalence and impact of comorbidities on disease prognosis among patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A nationwide study amid the second wave",
"author": "Sharif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102148",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108545",
"article-title": "Micronutrients as immunomodulatory tools for COVID-19 management",
"author": "Gasmi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108545",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "220",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31665/JFB.2021.15280",
"article-title": "Impact of dietary nutrients (functional foods/nutraceuticals) and micronutrients on COVID-19: A review",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "J. Food Bioact.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25225346",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Bae, M., and Kim, H. (2020). The role of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in immune system against COVID-19. Molecules, 25."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-020-00176-1",
"article-title": "Overview of the possible role of vitamin C in management of COVID-19",
"author": "Abobaker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1517",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1373",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public Health",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc, Vitamin D and Vitamin C: Perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity",
"author": "Souza",
"first-page": "295",
"journal-title": "Front. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3164/jcbn.20-91",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the nutritional status in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9111211",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Carr, A.C., and Maggini, S. (2017). Vitamin C and immune function. Nutrients, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S8755-9668(86)80021-7",
"article-title": "The antioxidant role of vitamin C",
"author": "Bendich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "419",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1986"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.127044",
"article-title": "Molecular Mechanisms and therapeutic effects of different vitamins and minerals in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Fath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "127044",
"journal-title": "J. Trace. Elem. Med. Biol.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin C and immunity: An assessment of the evidence",
"author": "Thomas",
"first-page": "370",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "32",
"year": "1978"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04261.x",
"article-title": "An update on vitamin D and human immunity",
"author": "Hewison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "315",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5072502",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and immune function",
"author": "Prietl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2502",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0022215109992684",
"article-title": "Vitamin D, innate immunity and upper respiratory tract infection",
"author": "Bartley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "J. Laryngol. Otol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"key": "ref_23",
"unstructured": "Pierce, G.N., Rupp, H., Izumi, T., and Grynberg, A. (2013). Molecular and Cellular Effects of Nutrition on Disease Processes, Springer Science & Business Media."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2016.03.022",
"article-title": "Zinc and immunity: An essential interrelation",
"author": "Maares",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "611",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.008",
"article-title": "Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation",
"author": "Bonaventura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "277",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202003.0235.v2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Grant, W.B., Lahore, H., McDonnell, S.L., Baggerly, C.A., French, C.B., Aliano, J.L., and Bhattoa, H.P. (2020). Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13813455.2020.1791188",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "BourBour, F., Mirzaei Dahka, S., Gholamalizadeh, M., Akbari, M.E., Shadnoush, M., Haghighi, M., Taghvaye-Masoumi, H., Ashoori, N., and Doaei, S. (2020). Nutrients in prevention, treatment, and management of viral infections; special focus on Coronavirus. Arch. Physiol. Biochem., 1791188."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.202557",
"article-title": "The efficiency and safety of high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7020",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00792-3",
"article-title": "Pilot trial of high-dose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intensive Care.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12948-020-00139-0",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and Covid-19: An update on evidence and potential therapeutic implications",
"author": "Murdaca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Clin. Mol. Allergy.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064",
"article-title": "Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients of a North American community hospital intensive care unit in May 2020: A pilot study",
"author": "Arvinte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100064",
"journal-title": "Med. Drug Discov.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—Preliminary report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Annweiler, G., Corvaisier, M., Gautier, J., Dubée, V., Legrand, E., Sacco, G., and Annweiler, C. (2020). Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: The GERIA-COVID quasi-experimental study. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-02972-w",
"article-title": "Severe Covid-19 disease: Rather AVDS than ARDS?",
"author": "Mahjoub",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11040708",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "Hemilä, H., and Chalker, E. (2019). Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: A meta-analysis. Nutrients, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-020-00950-1",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 infection and mortality in the Asia Pacific region: A cross-sectional study",
"author": "Yadav",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "492",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Clin. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.006",
"article-title": "Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: A report on four patients",
"author": "Finzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "307",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12944/CRNFSJ.8.3.04",
"article-title": "The Potential Influence of Vitamin A, C, and D and Zinc Supplements on the Severity of COVID-19 Symptoms and Clinical Outcomes: An Updated Review of Literature",
"author": "Alzaben",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "703",
"journal-title": "Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency",
"author": "Jothimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.29333/ejgm/11099",
"article-title": "Current Evidence on Vitamin C, D, and Zinc Supplementation for COVID-19 Prevention and/or Treatment",
"author": "Giacalone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "em311",
"journal-title": "Electron. J. Gen. Med.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqaa381",
"article-title": "Habitual use of vitamin D supplements and risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: A prospective study in UK Biobank",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1275",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"article-title": "Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: The COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Thomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e210369",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.15.20175513",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_44",
"unstructured": "Ahmed, I., Hasan, M., Akter, R., Sarkar, B.K., Rahman, M., Sarker, M.S., and Samad, M.A. (2020). Behavioral preventive measures and the use of medicines and herbal products among the public in response to Covid-19 in Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE, 15."
},
{
"article-title": "The impact of vitamin and mineral supplements usage prior to COVID-19 infection on disease severity and hospitalization",
"author": "Nimer",
"first-page": "826",
"journal-title": "Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2515690X211026193",
"article-title": "20-week study of clinical outcomes of over-the-counter COVID-19 prophylaxis and treatment",
"author": "Margolin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2515690X211026193",
"journal-title": "J. Evid.-Based Integr. Med.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4",
"article-title": "The effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E on disease severity and inflammatory responses in patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Beigmohammadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "802",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-022-06016-2",
"article-title": "High-dose vitamin D substitution in patients with COVID-19: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center study—VitCov Trial",
"author": "Jaun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7573/dic.2021-6-2",
"article-title": "Vitamins, supplements and COVID-19: A review of currently available evidence",
"author": "Speakman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2021-6-2",
"journal-title": "Drugs Context",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2022.892561",
"article-title": "Vitamin C for COVID-19 Treatment: Have We Got Enough Evidence?",
"author": "Ahmad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "892561",
"journal-title": "Front. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19932820.2022.2054111",
"article-title": "Effects of vitamin C and D on the mRNA expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor, cathepsin L, and transmembrane serine protease in the mouse lungs",
"author": "Alruwaili",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2054111",
"journal-title": "Libyan. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 51,
"references-count": 51,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/23/5029"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of Zinc, Vitamins C and D on Disease Prognosis among Patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A Cross-Sectional Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}
