The effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E on disease severity and inflammatory responses in patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial
et al., Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4, IRCT20200319046819N1, Nov 2021
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
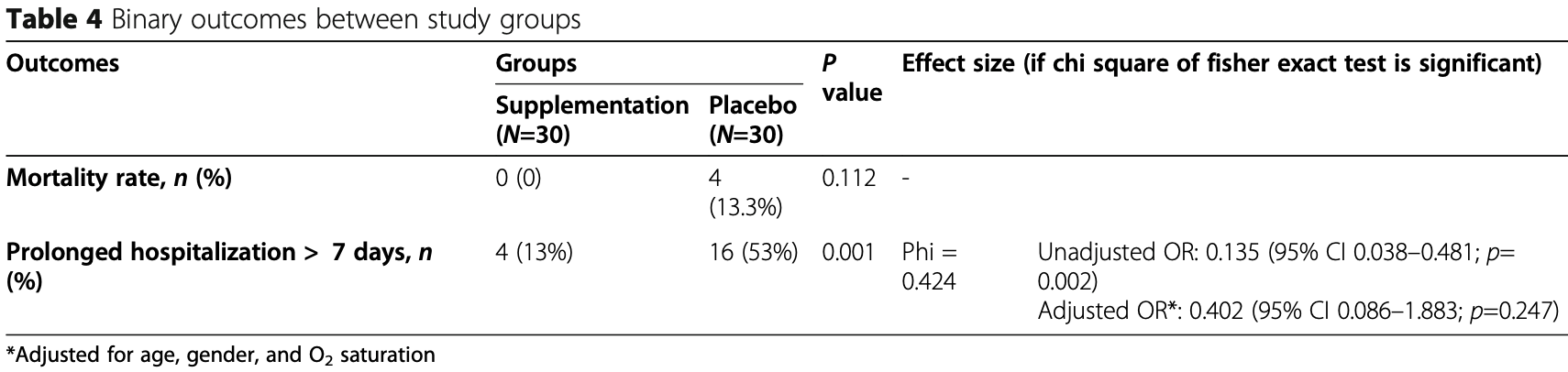
Small RCT 60 ICU patients in Iran, 30 treated with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E, showing significant improvement in SOFA score and several inflammatory markers at day 7 with treatment.
5,000 IU vitamin A daily, 600,000 IU vitamin D once, 300 IU of vitamin E twice a day, 500 mg vitamin C four times a day, and one ampule daily of B vitamins [thiamine nitrate 3.1 mg, sodium riboflavin phosphate 4.9 mg (corresponding to vitamin B2 3.6 mg), nicotinamide 40 mg, pyridoxine hydrochloride 4.9 mg (corresponding to vitamin B6 4.0 mg), sodium pantothenate 16.5 mg (corresponding to pantothenic acid 15 mg), sodium ascorbate 113 mg (corresponding to vitamin C 100 mg), biotin 60 μg, folic acid 400 μg, and cyanocobalamin 5 μg].
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
combined treatments may contribute more to the effect seen; very late stage, ICU patients.
|
risk of death, 88.9% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.11, treatment 0 of 30 (0.0%), control 4 of 30 (13.3%), NNT 7.5, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of hospitalization >7 days, 41.0% lower, RR 0.59, p = 0.25, treatment 4 of 30 (13.3%), control 16 of 30 (53.3%), NNT 2.5, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
relative SOFA score @day 7, 45.5% better, RR 0.55, p < 0.001, treatment 30, control 30.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Beigmohammadi et al., 14 Nov 2021, Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period April 2020 - July 2020, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with vitamins A, B, D, E) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial IRCT20200319046819N1.
Contact: bitarafans@gmail.com.
The effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E on disease severity and inflammatory responses in patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial
Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4
Background and objective: Because of the effect of vitamins on modulating the immune system function, we have evaluated the effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E in ICU-admitted patients with COVID-19. Methods: This study was a randomized and single-blinded clinical trial in which 60 subjects were randomly assigned to two groups. The intervention group (n=30) received vitamins, and the control group did not receive any vitamin or placebo. The intervention was included 25,000 IU daily of vitamins A, 600,000 IU once during the study of D, 300 IU twice daily of E, 500 mg four times daily of C, and one amp daily of B complex for 7 days. At baseline and after the 7-day intervention, the serum levels of inflammatory markers, vitamins, and the SOFA score were assessed. In addition, the mortality rate and duration of hospitalization were evaluated after the intervention (IRCT registration number: IRCT20200319046819N1/registration date: 2020-04-04, https://www.irct.ir/trial/46838). Results: Significant changes were detected in serum levels of vitamins (p < 0.001 for all vitamins), ESR (p < 0.001), CRP (p = 0.001), IL6 (p = 0.003), TNF-a (p = 0.001), and SOFA score (p < 0.001) after intervention compared with the control group. The effect of vitamins on the mortality rate was not statistically significant (p=0.112). The prolonged hospitalization rate to more than 7 days was significantly lower in the intervention group than the control group (p=0.001). Regarding the effect size, there was a significant and inverse association between receiving the intervention and prolonged hospitalization (OR = 0.135, 95% CI 0.038-0.481; p=0.002); however, after adjusting for confounders, it was not significant (OR=0.402, 95% CI 0.086-1.883; p=0.247).
Authors' contributions The authors are required to identify their contributions to the work described in the manuscript in the author page. SB presented the conception and design of the study, with contributions from MTB. LA and AH collected the data. AA managed and supervised the laboratory tests. DS and SB analyzed and interpreted the data. DS wrote the first draft. SB edited the manuscript. All authors reviewed the first draft and commented on that. MTB generated the random allocation sequence, enrolled participants, and assigned participants to interventions. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate The project has been approved by the ethical committee with the code of IR.TUMS.VCR.REC.1399.090 in Iran.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Anderson, Oosthuizen, Maritz, Van Rensburg, The effects of increasing weekly doses of ascorbate on certain cellular and humoral immune functions in normal volunteers, The American journal of clinical nutrition, doi:10.1093/ajcn/33.1.71
Annweiler, Corvaisier, Gautier, Dubée, Legrand et al., Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: the GERIA-COVID quasi-experimental study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113377
Arvinte, Singh, Marik, Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients of a north American community hospital intensive care unit in May 2020: A pilot study, Medicine in drug discovery, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064
Bouch, Thompson, Severity scoring systems in the critically ill. Continuing education in anaesthesia, critical care & pain, doi:10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkn033
Cannell, Vieth, Umhau, Epidemic influenza and vitamin D, Epidemiology & Infection, doi:10.1017/S0950268806007175
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study, The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Cheng, Chang, Lee, Lin, Huang, Vitamin B 6 supplementation increases immune responses in critically ill patients, European journal of clinical nutrition, doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602439
De La Fuente, Hernanz, Guayerbas, Victor, Arnalich, Vitamin E ingestion improves several immune functions in elderly men and women, Free radical research, doi:10.1080/10715760801898838
Erickson, Medina, Hubbard, Micronutrients and innate immunity, The Journal of infectious diseases, doi:10.1086/315922
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A review of micronutrients and the immune System-Working in harmony to reduce the risk of infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12010236
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: a meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11040708
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Singh, Mahor et al., Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers, Scientific reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z
Kotrlik, Williams, Jabor, Reporting and interpreting effect size in quantitative agricultural education research, Journal of Agricultural Education, doi:10.5032/jae.2011.01132
Long, Montoya, Hertzmark, Santos, Rosado, A double-blind, randomized, clinical trial of the effect of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on diarrheal disease and respiratory tract infections in children in Mexico City, Mexico. The American journal of clinical nutrition, doi:10.1093/ajcn.83.3.693
Maggini, Beveridge, Sorbara, Senatore, Feeding the immune system: the role of micronutrients in restoring resistance to infections, CAB Reviews: Perspectives in Agriculture, Veterinary Science, Nutrition and Natural Resources, doi:10.1079/PAVSNNR20083098
Maggini, Wintergerst, Beveridge, Hornig, Selected vitamins and trace elements support immune function by strengthening epithelial barriers and cellular and humoral immune responses, British Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S0007114507832971
Ong, Pérusse, Impact of nutritional epigenomics on disease risk and prevention: introduction, Lifestyle Genomics, doi:10.1159/000334859
Pecora, Persico, Argentiero, Neglia, Esposito, The role of micronutrients in support of the immune response against viral infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12103198
Pereira, Damascena, Azevedo, De Almeida, Da et al., Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Critical reviews in, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Schulz, Altman, Moher, Group, CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials, Trials, doi:10.1186/1741-7015-8-18
Vincent, Mendonça, Cantraine, Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study, Critical care medicine, doi:10.1097/00003246-199811000-00016
Vincent, Moreno, Takala, The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure, doi:10.1007/BF01709751
Wishart, Increased micronutrient requirements during physiologically demanding situations: Review of the current evidence, Vitamin Miner, doi:10.4172/2376-1318.1000166
Wong, Lam, Wu, Plasma inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in severe acute respiratory syndrome, Clinical & Experimental Immunology, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02415.x
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Xu, Yang, Yang, Zou, Wang et al., Clinical course and predictors of 60-day mortality in 239 critically ill patients with COVID-19: a multicenter retrospective study from Wuhan. China, Critical Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03098-9
Zaim, Chong, Sankaranarayanan, Harky, COVID-19 and multi-organ response, Current Problems in Cardiology, doi:10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2020.100618
Zhang, Zhou, Qiu, Song, Feng et al., Clinical characteristics of 82 death cases with COVID-19, MedRxiv, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0235458
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4",
"ISSN": [
"1745-6215"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background and objective</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Because of the effect of vitamins on modulating the immune system function, we have evaluated the effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E in ICU-admitted patients with COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This study was a randomized and single-blinded clinical trial in which 60 subjects were randomly assigned to two groups. The intervention group (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic>=30) received vitamins, and the control group did not receive any vitamin or placebo. The intervention was included 25,000 IU daily of vitamins A, 600,000 IU once during the study of D, 300 IU twice daily of E, 500 mg four times daily of C, and one amp daily of B complex for 7 days. At baseline and after the 7-day intervention, the serum levels of inflammatory markers, vitamins, and the SOFA score were assessed. In addition, the mortality rate and duration of hospitalization were evaluated after the intervention (IRCT registration number: IRCT20200319046819N1/registration date: 2020-04-04, <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://www.irct.ir/trial/46838\">https://www.irct.ir/trial/46838</jats:ext-link>).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Significant changes were detected in serum levels of vitamins (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.001 for all vitamins), ESR (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.001), CRP (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.001), IL6 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.003), TNF-a (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.001), and SOFA score (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.001) after intervention compared with the control group. The effect of vitamins on the mortality rate was not statistically significant (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic>=0.112). The prolonged hospitalization rate to more than 7 days was significantly lower in the intervention group than the control group (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic>=0.001). Regarding the effect size, there was a significant and inverse association between receiving the intervention and prolonged hospitalization (OR = 0.135, 95% CI 0.038–0.481; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic>=0.002); however, after adjusting for confounders, it was not significant (OR=0.402, 95% CI 0.086–1.883; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic>=0.247).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E could improve the inflammatory response and decrease the severity of disease in ICU-admitted patients with COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"5795"
],
"article-number": "802",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "12 June 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "3 November 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "14 November 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The project has been approved by the ethical committee with the code of IR.TUMS.VCR.REC.1399.090 in Iran."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beigmohammadi",
"given": "Mohammad Taghi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1451-7900",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bitarafan",
"given": "Sama",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hoseindokht",
"given": "Azin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdollahi",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amoozadeh",
"given": "Laya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soltani",
"given": "Danesh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Trials"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-14T19:02:32Z",
"timestamp": 1636916552000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-14T19:05:33Z",
"timestamp": 1636916733000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004484",
"award": [
"99-1-101-47104"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Health Services"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-15T08:12:44Z",
"timestamp": 1636963964628
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1745-6215"
}
],
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
14
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1636848000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1636848000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"author": "Z Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "5795_CR1",
"unstructured": "Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239–42. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.2648.",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03098-9",
"author": "J Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "China. Critical Care.",
"key": "5795_CR2",
"unstructured": "Xu J, Yang X, Yang L, Zou X, Wang Y, Wu Y, et al. Clinical course and predictors of 60-day mortality in 239 critically ill patients with COVID-19: a multicenter retrospective study from Wuhan. China. Critical Care. 2020;24(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-03098-9.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"author": "N Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "507",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "The Lancet.",
"key": "5795_CR3",
"unstructured": "Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. The Lancet. 2020;395(10223):507–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02415.x",
"author": "C Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "95",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Clinical & Experimental Immunology.",
"key": "5795_CR4",
"unstructured": "Wong C, Lam C, Wu A, et al. Plasma inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in severe acute respiratory syndrome. Clinical & Experimental Immunology. 2004;136(1):95–103. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02415.x.",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0235458",
"author": "B Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0235458",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv.",
"key": "5795_CR5",
"unstructured": "Zhang B, Zhou X, Qiu Y, Song Y, Feng F, Feng J, et al. Clinical characteristics of 82 death cases with COVID-19. MedRxiv. 2020;15(7):e0235458. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0235458.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2020.100618",
"author": "S Zaim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100618",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Current Problems in Cardiology.",
"key": "5795_CR6",
"unstructured": "Zaim S, Chong JH, Sankaranarayanan V, Harky A. COVID-19 and multi-organ response. Current Problems in Cardiology. 2020;100618(8):100618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2020.100618.",
"volume": "100618",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12010236",
"author": "AF Gombart",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "236",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "5795_CR7",
"unstructured": "Gombart AF, Pierre A, Maggini S. A review of micronutrients and the immune System–Working in harmony to reduce the risk of infection. Nutrients. 2020;12(1):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010236.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000334859",
"author": "TP Ong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "245",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lifestyle Genomics.",
"key": "5795_CR8",
"unstructured": "Ong TP, Pérusse L. Impact of nutritional epigenomics on disease risk and prevention: introduction. Lifestyle Genomics. 2011;4(5):245–7. https://doi.org/10.1159/000334859.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12103198",
"author": "F Pecora",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3198",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "5795_CR9",
"unstructured": "Pecora F, Persico F, Argentiero A, Neglia C, Esposito S. The role of micronutrients in support of the immune response against viral infections. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):3198. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103198.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z",
"author": "A Jain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Scientific reports.",
"key": "5795_CR10",
"unstructured": "Jain A, Chaurasia R, Sengar NS, Singh M, Mahor S, Narain S. Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers. Scientific reports. 2020;10(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn.83.3.693",
"author": "KZ Long",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "The American journal of clinical nutrition.",
"key": "5795_CR11",
"unstructured": "Long KZ, Montoya Y, Hertzmark E, Santos JI, Rosado JL. A double-blind, randomized, clinical trial of the effect of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on diarrheal disease and respiratory tract infections in children in Mexico City, Mexico. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 2006;83(3):693–700. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn.83.3.693.",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113377",
"author": "G Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3377",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "5795_CR12",
"unstructured": "Annweiler G, Corvaisier M, Gautier J, Dubée V, Legrand E, Sacco G, et al. Vitamin D supplementation associated to better survival in hospitalized frail elderly COVID-19 patients: the GERIA-COVID quasi-experimental study. Nutrients. 2020;12(11):3377. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113377.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1741-7015-8-18",
"author": "KF Schulz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "32",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trials.",
"key": "5795_CR13",
"unstructured": "Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D, Group C. CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Trials. 2010;11(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-8-18.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00003246-199811000-00016",
"author": "J-L Vincent",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1793",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Critical care medicine.",
"key": "5795_CR14",
"unstructured": "Vincent J-L, De Mendonça A, Cantraine F, et al. Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study. Critical care medicine. 1998;26(11):1793–800. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199811000-00016.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF01709751",
"author": "J-L Vincent",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "707",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "In: Springer-Verlag",
"key": "5795_CR15",
"unstructured": "Vincent J-L, Moreno R, Takala J, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. In: Springer-Verlag. 1996;22(7):707–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01709751.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkn033",
"author": "DC Bouch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "181",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Continuing education in anaesthesia, critical care & pain.",
"key": "5795_CR16",
"unstructured": "Bouch DC, Thompson JP. Severity scoring systems in the critically ill. Continuing education in anaesthesia, critical care & pain. 2008;8(5):181–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkn033.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5032/jae.2011.01132",
"author": "JW Kotrlik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "132",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Agricultural Education.",
"key": "5795_CR17",
"unstructured": "Kotrlik JW, Williams HA, Jabor MK. Reporting and interpreting effect size in quantitative agricultural education research. Journal of Agricultural Education. 2011;52(1):132–42. https://doi.org/10.5032/jae.2011.01132.",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"author": "ME Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105751",
"journal-title": "The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology.",
"key": "5795_CR18",
"unstructured": "Castillo ME, Costa LME, Barrios JMV, et al. Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study. The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology. 2020;203:105751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751.",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1079/PAVSNNR20083098",
"author": "S Maggini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "098",
"journal-title": "CAB Reviews: Perspectives in Agriculture, Veterinary Science, Nutrition and Natural Resources.",
"key": "5795_CR19",
"unstructured": "Maggini S, Beveridge S, Sorbara P, Senatore G. Feeding the immune system: the role of micronutrients in restoring resistance to infections. CAB Reviews: Perspectives in Agriculture, Veterinary Science, Nutrition and Natural Resources. 2008;3(098):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1079/PAVSNNR20083098.",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268806007175",
"author": "J Cannell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1129",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Epidemiology & Infection.",
"key": "5795_CR20",
"unstructured": "Cannell J, Vieth R, Umhau J, et al. Epidemic influenza and vitamin D. Epidemiology & Infection. 2006;134(6):1129–40. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268806007175.",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10715760801898838",
"author": "M De la Fuente",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "272",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Free radical research.",
"key": "5795_CR21",
"unstructured": "De la Fuente M, Hernanz A, Guayerbas N, Manuel Victor V, Arnalich F. Vitamin E ingestion improves several immune functions in elderly men and women. Free radical research. 2008;42(3):272–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760801898838.",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "5795_CR22",
"unstructured": "Pereira M, Dantas Damascena A, Galvão Azevedo LM, de Almeida OT, da Mota Santana J. Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. 2020:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064",
"author": "C Arvinte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100064",
"journal-title": "Medicine in drug discovery.",
"key": "5795_CR23",
"unstructured": "Arvinte C, Singh M, Marik PE. Serum levels of vitamin C and vitamin D in a cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients of a north American community hospital intensive care unit in May 2020: A pilot study. Medicine in drug discovery. 2020;8:100064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100064.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114507832971",
"author": "S Maggini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S29",
"issue": "S1",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Nutrition.",
"key": "5795_CR24",
"unstructured": "Maggini S, Wintergerst ES, Beveridge S, Hornig DH. Selected vitamins and trace elements support immune function by strengthening epithelial barriers and cellular and humoral immune responses. British Journal of Nutrition. 2007;98(S1):S29–35. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114507832971.",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4172/2376-1318.1000166",
"author": "K Wishart",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "03",
"journal-title": "Vitamin Miner.",
"key": "5795_CR25",
"unstructured": "Wishart K. Increased micronutrient requirements during physiologically demanding situations: Review of the current evidence. Vitamin Miner. 2017;6(03):1–16. https://doi.org/10.4172/2376-1318.1000166.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602439",
"author": "C Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1207",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "European journal of clinical nutrition.",
"key": "5795_CR26",
"unstructured": "Cheng C, Chang S-J, Lee B, Lin K, Huang Y. Vitamin B 6 supplementation increases immune responses in critically ill patients. European journal of clinical nutrition. 2006;60(10):1207–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602439.",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/33.1.71",
"author": "R Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "71",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "The American journal of clinical nutrition.",
"key": "5795_CR27",
"unstructured": "Anderson R, Oosthuizen R, Maritz R, Theron A, Van Rensburg A. The effects of increasing weekly doses of ascorbate on certain cellular and humoral immune functions in normal volunteers. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 1980;33(1):71–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/33.1.71.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "1980"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11040708",
"author": "H Hemilä",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "708",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "5795_CR28",
"unstructured": "Hemilä H, Chalker E. Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: a meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2019;11(4):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040708.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/315922",
"author": "KL Erickson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S5",
"issue": "Supplement_1",
"journal-title": "The Journal of infectious diseases",
"key": "5795_CR29",
"unstructured": "Erickson KL, Medina EA, Hubbard NE. Micronutrients and innate immunity. The Journal of infectious diseases. 2000;182(Supplement_1):S5–S10 https://doi.org/10.1086/315922.",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2000"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Trials"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"The effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E on disease severity and inflammatory responses in patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "22"
}
beigmohammadi2
