The Association Between COVID-19 Infection Severity and Micronutrient Deficiencies in Children
et al., Journal of Comprehensive Pediatrics, doi:10.5812/jcp-149127, Nov 2024
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
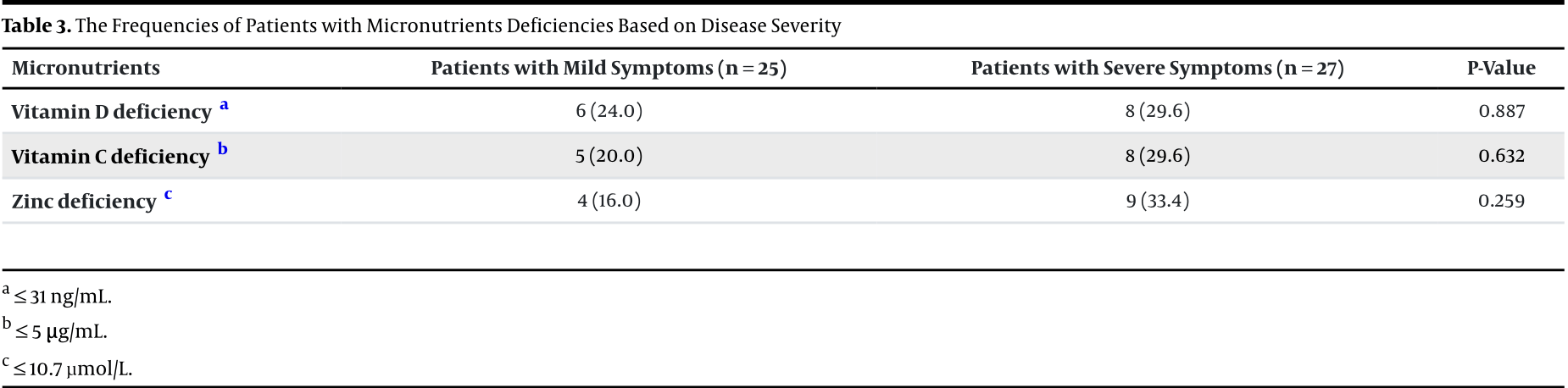
Analysis of 85 pediatric patients (33 healthy controls, 25 mild COVID-19, 27 severe COVID-19), showing significantly lower serum zinc levels in severe COVID-19 patients compared to healthy controls. Severe cases had higher prevalence of zinc, vitamin D, and vitamin C deficiency, without statistical significance.
|
risk of severe case, 20.8% lower, RR 0.79, p = 0.53, high vitamin C levels (≥5 μg/mL) 19 of 39 (48.7%), low vitamin C levels (<5 μg/mL) 8 of 13 (61.5%), NNT 7.8.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pashaei et al., 18 Nov 2024, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: zsadr801212@gmail.com.
The Association Between COVID-19 Infection Severity and Micronutrient Deficiencies in Children
Journal of Comprehensive Pediatrics, doi:10.5812/jcp-149127
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can cause pulmonary and systemic inflammation in both children and adults. Investigating the potential impact of micronutrient deficiencies on COVID-19 infection is of great importance. Objectives: This case-control study was designed to compare the serum levels of vitamins D and C and zinc between healthy children and children with mild or severe COVID-19 infection, as well as to investigate the impact of micronutrient deficiencies on the clinical symptoms of patients. Methods: This case-control study was conducted at a teaching hospital in Tehran, Iran. Control subjects were recruited from healthy children, and cases were included from children with mild and severe symptoms of COVID-19. Blood samples were obtained from participants to measure the levels of micronutrients and were analyzed using statistical software. Results: A total of 85 subjects were included (33 controls, 25 cases with mild symptoms, and 27 cases with severe symptoms). We found no differences in the means of serum vitamin D and vitamin C levels between the studied groups. However, the mean serum zinc level was significantly lower in severe patients compared to the controls (P < 0.01). Moreover, no significant difference was observed in the frequency of patients with micronutrient deficiencies based on their clinical conditions. Conclusions: Our findings revealed zinc deficiency in children with severe COVID-19 infection, while no significant differences were found in the mean serum levels of vitamins D and C between healthy children and patients. More studies are necessary to provide more robust evidence.
References
Arroyo-Diaz, Julve, Vlacho, Corcoy, Ponte et al., Previous Vitamin D Supplementation and Morbidity and Mortality Outcomes in People Hospitalised for COVID19: A Cross-Sectional Study, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.758347
Azadeh, Hedayatizadeh-Omran, Saeedi, Vahedi-Larijani, Mehravaran et al., Serum Vitamin D Concentrations in CoVID19 Patients, J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci
Bayramoglu, Akkoc, Agbas, Akgun, Yurdakul et al., The association between vitamin D levels and the clinical severity and inflammation markers in pediatric COVID-19 patients: single-center experience from a pandemic hospital, Eur J Pediatr, doi:10.1007/s00431-021-04030-1
Beran, Mhanna, Srour, Ayesh, Stewart et al., Clinical significance of micronutrient supplements in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Nutr ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.12.033
Carr, Vitamin C in Pneumonia and Sepsis, doi:10.1201/9780429442025-7
Cole, Grant, Swaby-Ellis, Smith, Jacques et al., Zinc and iron deficiency and their interrelations in low-income African American and Hispanic children in Atlanta, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28089
Esteghamati, Badamchi, Naghdalipoor, Faramarzi, Hasanabadi et al., Prevalence of Mycoplasma genitalium and Ureaplasma urealyticum in pregnant women, Tehran Univ Med J
Gao, Xu, Wang, Lv, Ma et al., The efficiency and safety of high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, J Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.202557
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System-Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12010236
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Guo, Wei, Zhang, Wu, Li et al., Clinical Features Predicting Mortality Risk in Patients With Viral Pneumonia: The MuLBSTA Score, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2019.02752
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050
Kakodkar, Kaka, Baig, A Comprehensive Literature Review on the Clinical Presentation, and Management of the Pandemic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.7560
Karimian, Tahami, Sayyahfar, Delavar, Association of vitamin D and severity of COVID-19 in children, Eur J Transl Myol, doi:10.4081/ejtm.2022.10453
Maggini, Pierre, Calder, Immune Function and Micronutrient Requirements Change over the Life Course, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10101531
Noorbakhsh, Ehsanipour, Sobouti, Aski, Faranoush et al., Comparison of Antiphospholipid Antibody Levels in Children with and Without COVID-19, J Arch Pediatr Infect Dis, doi:10.5812/apid-133851
Noorbakhsh, Farhadi, Haghighi, Minaeian, Hasanabad, Neonatal screening for congenital cytomegalovirus infection in Tehran, Iran, using Guthrie cards, Iran J Microbiol
Ramezaninejad, Sohrabi, Alikhani, Badabi, Kasgari, Relationship between Vitamin D, Vitamin C, and Selenium Intake and Disease Severity and Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19: A Retrospective Study, J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci
Rastegar, Hosseini Teshnizi, Khaleghinia, Seddighi, Rajaei, Vitamin D and Zinc Deficiency in Children with Congenital Heart Defects, J Comprehens Pediatr, doi:10.5812/jcp-145841
Razzaque, COVID-19 Pandemic: Can Maintaining Optimal Zinc Balance Enhance Host Resistance?, Tohoku J Exp Med, doi:10.1620/tjem.251.175
Sheikhi, Shirzadfar, Sheikhi, A Review on Novel Coronavirus (Covid-19): Symptoms, Transmission and Diagnosis Tests, Res Infect Dis Trop Med, doi:10.33702/ridtm.2020.2.1.1
Singhal, A Review of Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19), Indian J Pediatr, doi:10.1007/s12098-020-03263-6
Soldevila, Puig-Domingo, Marazuela, Basic mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. What endocrine systems could be implicated?, Rev Endocr Metab Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-021-09678-6
Teng, Pourmand, Mazer-Amirshahi, Vitamin C: The next step in sepsis management?, J Crit Care, doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.09.031
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Wolski, Wang et al., Effect of High-Dose Zinc and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation vs Usual Care on Symptom Length and Reduction Among Ambulatory Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The COVID A to Z Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369
Wintergerst, Maggini, Hornig, Immune-enhancing role of vitamin C and zinc and effect on clinical conditions, Ann Nutr Metab, doi:10.1159/000090495
Yao, Paguio, Dee, Tan, Moulick et al., The Minimal Effect of Zinc on the Survival of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: An Observational Study, J Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082
Yilmaz, Sen, Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for COVID-19 in children?, Pediatr Pulmonol, doi:10.1002/ppul.25106
Zheng, Gao, Wang, Song, Liu et al., Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients, Cell Mol Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.5812/jcp-149127",
"ISSN": [
"2251-8150",
"2251-8177"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.5812/jcp-149127",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can cause pulmonary and systemic inflammation in both children and adults. Investigating the potential impact of micronutrient deficiencies on COVID-19 infection is of great importance. Objectives: This case-control study was designed to compare the serum levels of vitamins D and C and zinc between healthy children and children with mild or severe COVID-19 infection, as well as to investigate the impact of micronutrient deficiencies on the clinical symptoms of patients. Methods: This case-control study was conducted at a teaching hospital in Tehran, Iran. Control subjects were recruited from healthy children, and cases were included from children with mild and severe symptoms of COVID-19. Blood samples were obtained from participants to measure the levels of micronutrients and were analyzed using statistical software. Results: A total of 85 subjects were included (33 controls, 25 cases with mild symptoms, and 27 cases with severe symptoms). We found no differences in the means of serum vitamin D and vitamin C levels between the studied groups. However, the mean serum zinc level was significantly lower in severe patients compared to the controls (P < 0.01). Moreover, no significant difference was observed in the frequency of patients with micronutrient deficiencies based on their clinical conditions. Conclusions: Our findings revealed zinc deficiency in children with severe COVID-19 infection, while no significant differences were found in the mean serum levels of vitamins D and C between healthy children and patients. More studies are necessary to provide more robust evidence.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"258346eaa9a5d70ba11ba3ec94f79f37b2600b30"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pashaei",
"given": "Haleh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ehsanipour",
"given": "Fahimeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noorbakhsh",
"given": "Samileh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sobouti",
"given": "Behnam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8787-5971",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Minaeian",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7426-9892",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Haghighi Hasanabad",
"given": "Morteza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sadr",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Comprehensive Pediatrics",
"container-title-short": "J Compr Ped",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"brieflands.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-18T11:30:04Z",
"timestamp": 1731929404000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-18T11:30:07Z",
"timestamp": 1731929407000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-18T12:10:08Z",
"timestamp": 1731931808477,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
18
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1728518400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://brieflands.com/articles/jcp-149127",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://brieflands.com/articles/jcp-149127",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "3819",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.5812",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "Brieflands",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12098-020-03263-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF1-1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.33702/ridtm.2020.2.1.1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF2-2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12010236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF3-3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10101531",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF4-4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.7560",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF5-5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF6-6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4081/ejtm.2022.10453",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF7-7"
},
{
"author": "Azadeh H",
"first-page": "30",
"issue": "195",
"journal-title": "J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci.",
"key": "key-A149127REF8-8",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1201/9780429442025-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF9-9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.09.031",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF10-10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000090495",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF11-11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1620/tjem.251.175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF12-12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2019.02752",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF13-13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-021-04030-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF14-14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5812/jcp-145841",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF15-15"
},
{
"author": "Esteghamati A",
"first-page": "568",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Tehran Univ Med J.",
"key": "key-A149127REF16-16",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "Noorbakhsh S",
"first-page": "198",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Iran J Microbiol.",
"key": "key-A149127REF17-17",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-021-09678-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF18-18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF19-19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.758347",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF20-20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF21-21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.25106",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF22-22"
},
{
"author": "Ramezaninejad S",
"first-page": "73",
"issue": "213",
"journal-title": "J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci.",
"key": "key-A149127REF23-23",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.12.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF24-24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.202557",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF25-25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5812/apid-133851",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF26-26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF27-27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF28-28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.2009.28089",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "key-A149127REF29-29"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://brieflands.com/articles/jcp-149127"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Association Between COVID-19 Infection Severity and Micronutrient Deficiencies in Children",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.5812/crossmark_update_policy",
"volume": "15"
}
pashaei
