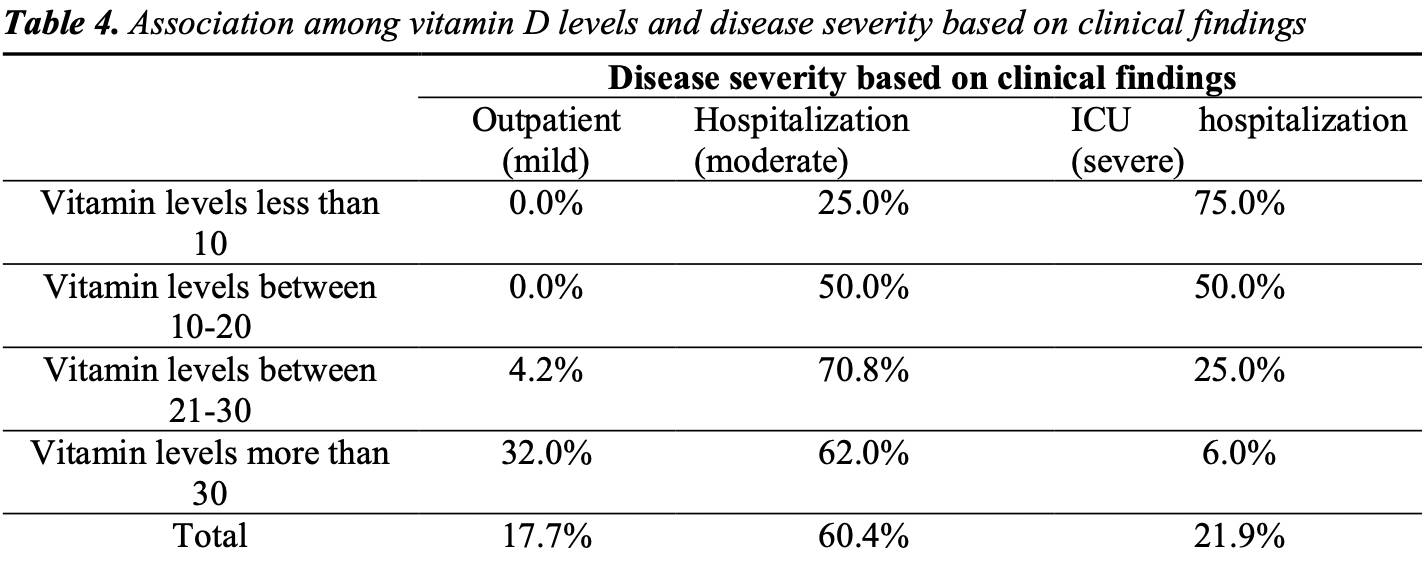
Association of vitamin D and severity of COVID-19 in children
et al., European Journal of Translational Myology, doi:10.4081/ejtm.2022.10453, Apr 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Analysis of 99 pediatric COVID-19 cases in Iran, mean age 2.9, showing severity associated with vitamin D levels.
Karimian et al., 20 Apr 2022, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, mean age 2.9, 4 authors.
Association of vitamin D and severity of COVID-19 in children
European Journal of Translational Myology, doi:10.4081/ejtm.2022.10453
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (CC BY-NC 4.0) which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Funding The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Ethical Publication Statement The author confirms that he has read the Journal's position on the issues involved in ethical publication and states that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
References
Afeketea, Vlacha, Bocsan, Corina, Vitamin D in Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Related Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:=10.3389/fimmu.2021.64854
Azadeh, Hedayatizadeh-Omran, Saeedi, Vahedi-Larijani, Mehravaran et al., Serum Vitamin D Concentrations in CoVID19 Patients, J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci
Camargo Ca, Ganmaa, Frazier, Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation and risk of acute respiratory infection in Mongolia, Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.2011-3029
Cascella, Rajnik, Cuomo, Dulebohn, Napoli, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19
Chen, Wu, Guo, Cao, Huang et al., Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI137244
Cruz, Zeichner, COVID-19 in children: initial characterization of the pediatric disease, Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.2020-0834
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System-Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12010236
Güven, Gültekin, The effect of high-dose parenteral vitamin D3 on COVID-19-related inhospital mortality in critical COVID-19 patients during intensive care unit admission: an observational cohort study, Eur J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-021-00984-5
Hastie, Pell, Sattar, Vitamin D and COVID-19 infection and mortality in UK Biobank, Eur J Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-020-02372-4
Holick, Vitamin D deficiency, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra070553
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Jafari, Cegolon, Torkaman, Kashaki, Dehghanpoor et al., A 6 months old infant with fever, dyspnea and poor feeding, diagnosed with COVID-19, Travel Med Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101789
Laaksi, Vitamin D and respiratory infection in adults, Proc Nutr Soc, doi:10.1017/S0029665111003351
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Pazoki, Kafan et al., Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Cohen et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Munshi, Hussein, Toraih, Elshazli, Jardak et al., Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26360
Nadiger, Hassor, Totapally, Vitamin d levels in children with COVID-19 admitted to the PICU, Critical Care Medicine
Panfili, Roversi, Argenio, Rossi, Cappa et al., Possible role of vitamin D in Covid-19 infection in pediatric population, J Endocrinol Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01327-0
Peiris, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2003.08.005
Rondanelli, Miccono, Lamburghini, Avanzato, Riva et al., Self-Care for Common Colds: The Pivotal Role of Vitamin D, Vitamin C, Zinc, and Echinacea in Three Main Immune Interactive Clusters (Physical Barriers, Innate and Adaptive Immunity) Involved during an Episode of Common Colds-Practical Advice on Dosages and on the Time to Take These Nutrients/Botanicals in order to Prevent or Treat Common Colds, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Rossi, Fanous, Colin, Viral strategies predisposing to respiratory bacterial superinfections, Pediatr Pulmonol
Schwalfenberg, A review of the critical role of vitamin D in the functioning of the immune system and the clinical implications of vitamin D deficiency, Mol Nutr Food Res, doi:10.1002/mnfr.201000174
Shafiee, Cegolon, Khafaei, Gholami, Zhao et al., Gastrointestinal cancers, ACE-2/TMPRSS2 expression and susceptibility to COVID-19, Cancer Cell Int, doi:10.1186/s12935-021-02129-x
Sharifi, Vahedi, Nedjat, Rafiei, Hosseinzadeh-Attar, Effect of single-dose injection of vitamin D on immune cytokines in ulcerative colitis patients: a randomized placebocontrolled trial, APMIS, doi:10.1111/apm.12982
Tabrizi, Moosazadeh, Akbari, Dabbaghmanesh, Mohamadkhani et al., High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among Iranian population: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Iran J Med Sci
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?, Clin Med (Lond), doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301
Yin, Wunderink, MERS, SARS and other coronaviruses as causes of pneumonia, Respirology, doi:10.1111/resp.13196
Yu, Ke, Luo, Guo, Wu, Effect of Pandemic-Related Confinement on Vitamin D Status Among Children Aged 0-6 Years in Guangzhou, China: A Cross-Sectional Study, Risk Manag Healthc Policy, doi:10.2147/RMHP.S282495
Yılmaz, Şen, Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for COVID-19 in children?, Pediatr Pulmonol, doi:10.1002/ppul.25106
Zumla, Hui, Perlman, Middle East respiratory syndrome, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60454-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4081/ejtm.2022.10453",
"ISSN": [
"2037-7460",
"2037-7452"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10453",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Vitamin has a major role in the functions of the immune system, and the efficacy of this vitamin in reducing inflammation has been identified. Considering the effects of vitamin D, this study research was performed for investigating the relationship between vitamin D and the severity of COVID-19 in children. This cross-sectional study was performed on 101 children infected with the new coronavirus from September 2020 to October 2021. Information on vitamin D levels, demographic factors, and clinical and laboratory findings were documented in information forms and prepared for statistical analyses. The average of children was 2.85 ± 0.85 years. Low oxygen saturation was observed in 35.3% of infected children. The level of involvement was higher in subjects with vitamin D levels higher than 30 and less than 10 ng/ml (p = 0.04). Clinical signs in cases with deficient and sufficient vitamin D levels were more severe in terms of tachypnea and tachycardia (p = 0.01). Children with vitamin D lower than 10 ng/ml showed more frequency (p = 0.02). Cases with moderate vitamin D had fewer gastrointestinal complications (p = 0.03). Also, oxygen levels were lower in children who had low levels of vitamin D (p = 0.02). Vitamin D levels were associated with levels of involvement, tachycardia, tachypnea, clinical signs, gastrointestinal problems, and O2 levels. Moderate vitamin D levels in children are a critical issue that should be considered.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karimian",
"given": "Pegah",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tahami",
"given": "Motahareh Sadat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sayyahfar",
"given": "Shirin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aghajani Delavar",
"given": "Motahare",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "European Journal of Translational Myology",
"container-title-short": "Eur J Transl Myol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-20T08:40:47Z",
"timestamp": 1650444047000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-08T11:56:43Z",
"timestamp": 1657281403000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-23T05:49:45Z",
"timestamp": 1713851385792
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 6,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
8
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1650412800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.pagepressjournals.org/index.php/bam/article/download/10453/10049",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.pagepressjournals.org/index.php/bam/article/download/10453/10049",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2549",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.4081",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "PAGEPress Publications",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60454-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50495"
},
{
"key": "50496",
"unstructured": "Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC, Napoli RD. Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19) [Updated 2020 Mar 20]. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Petersburg, FL, USA, 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2003.08.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50497"
},
{
"key": "50498",
"unstructured": "Imperial College London. Report 2: estimating the potential total number of novel coronavirus cases in Wuhan City, China. Jan 2020. https://www .imperial.ac.uk/mrc-globalinfectiousdisease-analysis/news--wuhan-coronavirus."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/resp.13196",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50499"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2020-0834",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50500"
},
{
"key": "50501",
"unstructured": "Tabrizi R, Moosazadeh M, Akbari , Dabbaghmanesh MH, Mohamadkhani M, Asemi Z, et al. High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among Iranian population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Iran J Med Sci 2018; 43(2): 125-139 (Persian)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.ccm.0000726440.30551.47",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50502"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mnfr.201000174",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50503"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/5813095",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50504"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra070553",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50505"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.24699",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50506"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apm.12982",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50507"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50508"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12010236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50509"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50510"
},
{
"key": "50511",
"unstructured": "Azadeh H, Hedayatizadeh-Omran A, Saeedi M, Vahedi-Larijani L, Mehravaran H, Heydari K. Serum Vitamin D Concentrations in CoVID19 Patients. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci. 2021; 31 (195) :30-36. URL: http://jmums.mazums.ac.ir /article-1-16104-en.html"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50512"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.25106",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50513"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2011-3029",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50514"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.648546",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50515"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26360",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50516"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50517"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50518"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-021-00984-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50519"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-020-02372-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50520"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665111003351",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50521"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50522"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101789",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50523"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01327-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50524"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12935-021-02129-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50525"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/RMHP.S282495",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "50526"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.pagepressjournals.org/index.php/bam/article/view/10453"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Association of vitamin D and severity of COVID-19 in children",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "32"
}
