Andrographolide suppresses SARS-CoV-2 infection by downregulating ACE2 expression: A mechanistic study
et al., Antiviral Therapy, doi:10.1177/13596535241259952, Jun 2024
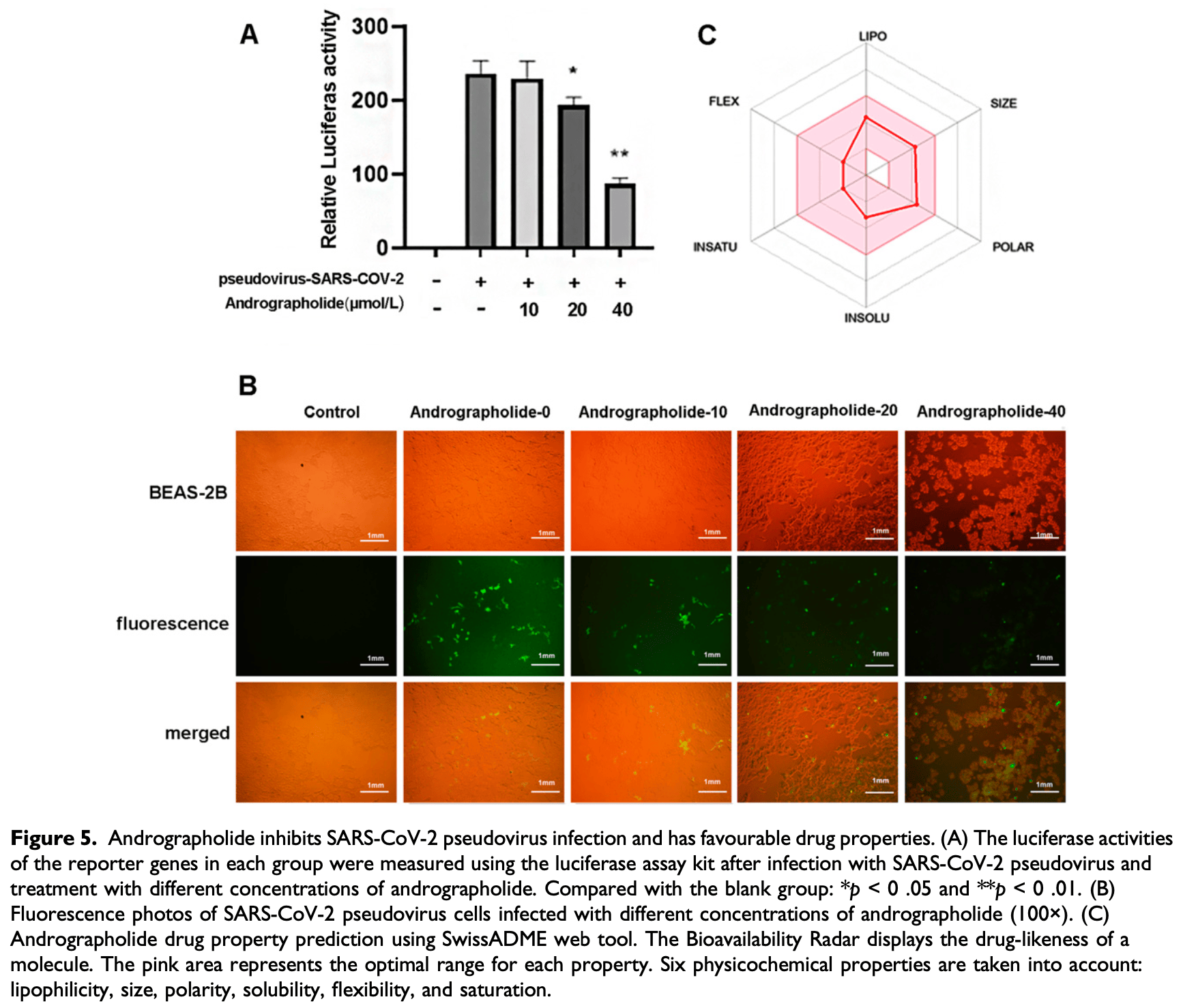
In vitro study showing that andrographolide downregulates ACE2 expression and inhibits SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus infection in a dose-dependent manner in human cells. Authors constructed a screening platform with a dual-luciferase reporter vector controlled by the ACE2 promoter. Out of 37 Chinese traditional medicinal herb compounds screened, andrographolide dose-dependently inhibited ACE2 transcription in HEK293T cells. RT-qPCR and Western blot confirmed andrographolide reduced ACE2 mRNA and protein expression in BEAS-2B bronchial epithelial cells. Pseudovirus assays demonstrated andrographolide inhibited SARS-CoV-2 infection in BEAS-2B cells.
25 preclinical studies support the efficacy of andrographolide for COVID-19:
In vitro studies demonstrate inhibition of the MproA,18 protein.
In vitro studies demonstrate efficacy in Calu-3B,18, A549C,14, and HUVECD,18 cells.
Animal studies demonstrate efficacy in Sprague Dawley miceE,18 and Golden Syrian hamstersF,14.
Andrographolide inhibits Mpro in a dose-dependent manner18, reduces ACE2 levels in the lung tissue of mice in combination with baicalein18, inhibits binding between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and ACE218, alleviates lung inflammation and cytokine storm in mice18, and improves survival and reduces lung inflammation via anti-inflammatory effects in Syrian hamsters14.
1.
Zhang et al., Effects and Mechanisms of Andrographolide for COVID-19: A Network Pharmacology-Based and Experimentally Validated Study, Natural Product Communications, doi:10.1177/1934578X241288428.
2.
Thomas et al., Cheminformatics approach to identify andrographolide derivatives as dual inhibitors of methyltransferases (nsp14 and nsp16) of SARS-CoV-2, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-58532-7.
3.
Arifin et al., Computational exploration of Andrographis paniculata herb compounds as potential antiviral agents targeting NSP3 (6W02) and NSP5 (7AR6) of SARS-COV-2, GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.30574/gscbps.2023.25.2.0292.
4.
Bhattarai et al., Investigating the binding affinity of andrographolide against human SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain through docking and molecular dynamics simulations, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, doi:10.1080/07391102.2023.2174596.
5.
Nguyen et al., The Potential of Ameliorating COVID-19 and Sequelae From Andrographis paniculata via Bioinformatics, Bioinformatics and Biology Insights, doi:10.1177/11779322221149622.
6.
Dassanayake et al., Molecular Docking and In-Silico Analysis of Natural Biomolecules against Dengue, Ebola, Zika, SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern and Monkeypox Virus, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms231911131.
7.
Ningrum et al., Potency Of Andrographolide, L-Mimosine And Asiaticoside Compound As Antiviral For Covid-19 Based On In Silico Method, Proceedings Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta Undergraduate Conference, doi:10.18196/umygrace.v2i2.418.
8.
Ravichandran et al., Identification of Potential Semisynthetic Andrographolide Derivatives to Combat COVID-19 by Targeting the SARS-COV-2 Spike Protein and Human ACE2 Receptor– An In-silico Approach, Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, doi:10.33263/BRIAC132.155.
9.
Saeheng et al., In Silico Prediction of Andrographolide Dosage Regimens for COVID-19 Treatment, The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, doi:10.1142/S0192415X22500732.
10.
Khanal et al., Combination of system biology to probe the anti-viral activity of andrographolide and its derivative against COVID-19, RSC Advances, doi:10.1039/D0RA10529E.
11.
Rehan et al., A Computational Approach Identified Andrographolide as a Potential Drug for Suppressing COVID-19-Induced Cytokine Storm, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.648250.
12.
Rajagopal et al., Activity of phytochemical constituents of Curcuma longa (turmeric) and Andrographis paniculata against coronavirus (COVID-19): an in silico approach, Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, doi:10.1186/s43094-020-00126-x.
13.
Dey et al., The role of andrographolide and its derivative in COVID-19 associated proteins and immune system, Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-35800/v1.
14.
Kongsomros et al., In vivo evaluation of Andrographis paniculata and Boesenbergia rotunda extract activity against SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant in Golden Syrian hamsters: Potential herbal alternative for COVID-19 treatment, Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.jtcme.2024.05.004.
15.
Chaopreecha et al., Andrographolide attenuates SARS-CoV-2 infection via an up-regulation of glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC), Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156279.
16.
Li et al., Andrographolide suppresses SARS-CoV-2 infection by downregulating ACE2 expression: A mechanistic study, Antiviral Therapy, doi:10.1177/13596535241259952.
17.
Low et al., The wide spectrum anti-inflammatory activity of andrographolide in comparison to NSAIDs: a promising therapeutic compound against the cytokine storm, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.02.21.581396.
18.
Wan et al., Synergistic inhibition effects of andrographolide and baicalin on coronavirus mechanisms by downregulation of ACE2 protein level, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-54722-5.
19.
Siridechakorn et al., Inhibitory efficiency of Andrographis paniculata extract on viral multiplication and nitric oxide production, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-46249-y.
a.
The main protease or Mpro, also known as 3CLpro or nsp5, is a cysteine protease that cleaves viral polyproteins into functional units needed for replication. Inhibiting Mpro disrupts the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle within the host cell, preventing the creation of new copies.
b.
Calu-3 is a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line with moderate ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. It provides a model of the human respiratory epithelium, but many not be ideal for modeling early stages of infection due to the moderate expression levels of ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
c.
A549 is a human lung carcinoma cell line with low ACE2 expression and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility. Viral entry/replication can be studied but the cells may not replicate all aspects of lung infection.
d.
HUVEC (Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells) are primary endothelial cells derived from the vein of the umbilical cord. They are used to study vascular biology, including inflammation, angiogenesis, and viral interactions with endothelial cells.
e.
An outbred multipurpose breed of albino mouse used extensively in medical research.
f.
A rodent model widely used in infectious disease research due to their susceptibility to viral infections and similar disease progression to humans.
Li et al., 14 Jun 2024, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: flong01@163.com, wentaoguo@126.com.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Andrographolide suppresses SARS-CoV-2 infection by downregulating ACE2 expression: A mechanistic study
Antiviral Therapy, doi:10.1177/13596535241259952
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is the receptor that enables SARS-CoV-2 to invade host cells. Previous studies have reported that reducing ACE2 expression may have an anti-SARS-CoV-2 effect. In this study, we constructed a pGL4.10-F2-ACE2 vector with double luciferase genes (firefly and Renilla luciferase) under the control of the ACE2 promoter and used it to screen compounds from Chinese traditional medicinal herbs (CTMHs) that can inhibit ACE2 transcription in human cells. We transfected HEK293T cells with pGL4.10-F2-ACE2 and treated them with CTMH compounds and then measured fluorescence to evaluate the indirect inhibition of ACE2 transcription. Out of 37 compounds tested, andrographolide demonstrated a dose-dependent inhibition of ACE2 transcription. We further confirmed by RT-qPCR and Western blot assays that andrographolide also reduced ACE2 expression in BEAS-2B cells in a dosedependent manner. Moreover, pseudovirus infection assays in BEAS-2B cells demonstrated that andrographolide can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in a dose-dependent manner. These results suggest that andrographolide has potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity and could be a candidate drug for COVID-19 prevention and treatment.
Author Contributions YG and HL participated in the experiments, collated data, visualized data, and performed statistical analysis. YR and LF reviewed the manuscript and provided funding. DL was responsible for research oversight. GZ and YL provided suggestions and ideas for manuscript writing. LF and WG contributed to research execution, management, and coordination. All authors contributed to the article and approved the final manuscript version.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This study received funding support from several sources, including the Guangdong Provincial Medical Science and Technology Research Fund Project (A2021440), the Guangdong Provincial Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Project (20211220), the Social Science Development Project of Dongguan City (20211800905542), the Guangdong Medical University Scientific Research Project (GDMUQ2021005), and the Discipline Construction Project of Guangdong Medical University (4SG21229GDGFY01).
ORCID iD Wentao Guo https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6194-5687
Supplemental Material Supplemental material for this article is available online.
References
An, Zhang, Duan, The direct evidence and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of COVID-19, Biomed Pharmacother
Brevini, Maes, Webb, FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2, Nature
Chen, Xue, Ye, Activity of andrographolide and its derivatives against influenza virus in Vivo and in Vitro, Biol Pharm Bull
Chuerduangphui, Nukpook, Pientong, Activity of 3,19-isopropylidinyl andrographolide against herpes simplex virus type 1 in an animal model, Antivir Chem Chemother
Daina, Michielin, Zoete, SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules, Sci Rep
Das, Das, Swain, Andrographolide induces anti-SARS-CoV-2 response through host-directed mechanism: an in silico study, Future Virol
Edwin, Vasantha-Srinivasan, Senthil-Nathan, Anti-dengue efficacy of bioactive andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata (Lamiales: Acanthaceae) against the primary dengue vector Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae), Acta Trop
Feng, Lu, Ma, A novel dual-luciferase assay for anti-HIV drug screening based on the CCR5/ CXCR4 promoters, J Virol Methods
Hao, Lv, Xu, Andrographolide: synthetic methods and biological activities, Mini Rev Med Chem
Hossain, Urbi, Karuniawati, Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Wall. ex Nees: An updated review of phytochemistry, antimicrobial pharmacology, and clinical safety and efficacy, Life
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat Rev Microbiol
Huang, Zhang, Zhang, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in the treatment of COVID-19 and other viral infections: efficacies and mechanisms, Pharmacol Ther
Ivanov, Goc, Ivanova, Inhibition of ACE2 expression by ascorbic acid alone and its combinations with other natural compounds, Infect Dis (Auckl)
Lee, Tseng, Young, Andrographolide exerts anti-hepatitis C virus activity by up-regulating haeme oxygenase-1 via the p38 MAPK/Nrf2 pathway in human hepatoma cells, Br J Pharmacol
Li, Grant, Richards, ACE2 as therapeutic agent, Clin Sci (Lond)
Malat, Ekalaksananan, Heawchaiyaphum, Andrographolide inhibits Epstein-Barr virus lytic reactivation in EBV-positive cancer cell lines through the modulation of epigenetic-related proteins, Molecules
Martellucci, Flacco, Cappadona, SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: an overview, Adv Biol Regul
Navya, Hosur, A computational study on hydroxychloroquine binding to target proteins related to SARS-COV-2 infection, Inform Med Unlocked
Nie, Li, Wu, Establishment and validation of a pseudovirus neutralization assay for SARS-CoV-2, Emerg Microbes Infect
Ou, Liu, Lei, Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV, Nat Commun
Patil, Jain, Andrographolide: a review of analytical methods, Journal of Chromatographic Science
Sarker, Panigrahi, Hardy, Glucocorticoids bind to SARS-CoV-2 S1 at multiple sites causing cooperative inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 S1 interaction with ACE2, Front Immunol
Seniya, Shrivastava, Singh, Analyzing the interaction of a herbal compound andrographolide from andrographis paniculata as a folklore against swine flu (H1N1), Asian Pac J Trop Dis
Shi, Huang, Chen, Andrographolide and its fluorescent derivative inhibit the main proteases of 2019-nCoV and SARS-CoV through covalent linkage, Biochem Biophys Res Commun
Wan, Li, Liao, Synergistic inhibition effects of andrographolide and baicalin on coronavirus mechanisms by downregulation of ACE2 protein level, Sci Rep
Wrapp, Wang, Corbett, Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation, Science
Wu, Dong, Chi, Traditional Chinese Medicine as a complementary therapy in combat with COVID-19-a review of evidence-based research and clinical practice, J Adv Nurs
Yang, Islam, Wang, Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of patients infected with 2019-new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): a review and perspective, Int J Biol Sci
Zalpoor, Bakhtiyari, Shapourian, Hesperetin as an anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent can inhibit COVID-19-associated cancer progression by suppressing intracellular signaling pathways, Inflammopharmacol
Zeng, Wei, Zhou, Andrographolide: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity and clinical trials and pharmaceutical researches, Phytother Res
Zhou, Yang, Wang, A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/13596535241259952",
"ISSN": [
"1359-6535",
"2040-2058"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/13596535241259952",
"abstract": "<jats:p> Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is the receptor that enables SARS-CoV-2 to invade host cells. Previous studies have reported that reducing ACE2 expression may have an anti-SARS-CoV-2 effect. In this study, we constructed a pGL4.10-F2-ACE2 vector with double luciferase genes (firefly and Renilla luciferase) under the control of the ACE2 promoter and used it to screen compounds from Chinese traditional medicinal herbs (CTMHs) that can inhibit ACE2 transcription in human cells. We transfected HEK293T cells with pGL4.10-F2-ACE2 and treated them with CTMH compounds and then measured fluorescence to evaluate the indirect inhibition of ACE2 transcription. Out of 37 compounds tested, andrographolide demonstrated a dose-dependent inhibition of ACE2 transcription. We further confirmed by RT-qPCR and Western blot assays that andrographolide also reduced ACE2 expression in BEAS-2B cells in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, pseudovirus infection assays in BEAS-2B cells demonstrated that andrographolide can inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in a dose-dependent manner. These results suggest that andrographolide has potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity and could be a candidate drug for COVID-19 prevention and treatment. </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/13596535241259952"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The First Dongguan Affiliated Hospital, Guangdong Medical University, Donguan, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pathogenic Organism Biology, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Qing",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The First Dongguan Affiliated Hospital, Guangdong Medical University, Donguan, China"
}
],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Hongmei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The First Dongguan Affiliated Hospital, Guangdong Medical University, Donguan, China"
}
],
"family": "Ruan",
"given": "Yongdui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathogenic Organism Biology, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Geng",
"given": "Yuxuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Basic Medicine, Guangdong Medical University, Donguan, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Zuguo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, DongGuan SongShan Lake Tung Wah Hospital, DongGuan, China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathogenic Organism Biology, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou, China"
}
],
"family": "Feng",
"given": "Long",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6194-5687",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The First Dongguan Affiliated Hospital, Guangdong Medical University, Donguan, China"
},
{
"name": "School of Basic Medicine, Guangdong Medical University, Donguan, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Wentao",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Antiviral Therapy",
"container-title-short": "Antiviral Therapy",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-14T10:18:38Z",
"timestamp": 1718360318000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-14T10:18:53Z",
"timestamp": 1718360333000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"A2021440"
],
"name": "Guangdong Provincial Medical Science and Technology Research Fund Project"
},
{
"award": [
"20211220"
],
"name": "Guangdong Provincial Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Project"
},
{
"award": [
"4SG21229GDGFY01"
],
"name": "Discipline Construction Project of Guangdong Medical University"
},
{
"award": [
"GDMUQ2021005"
],
"name": "Guangdong Medical University Scientific Research Project"
},
{
"award": [
"20211800905542"
],
"name": "Social Science Development Project of Dongguan City"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-15T00:29:02Z",
"timestamp": 1718411342720
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1717200000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/13596535241259952",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/13596535241259952",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/13596535241259952",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr1-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbior.2020.100736",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr2-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr3-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2507",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr4-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111267",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr5-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/life11040348",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.07.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2222-1808(14)60692-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.12440",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr9-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1248/bpb.32.1385",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr10-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27144666",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr11-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/20402066221089724",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr12-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2021-0171",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr13-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.08.086",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr14-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jviromet.2018.02.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr15-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-15562-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep42717",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr17-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20200570",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr18-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imu.2021.100714",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.906687",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr20-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05594-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr21-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.45538",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr22-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jan.14673",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr23-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107843",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr24-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1178633721994605",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr25-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-022-01054-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr26-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-024-54722-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr27-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7324",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr28-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/chromsci/bmaa091",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr29-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389557520666200429100326",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr30-13596535241259952"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1743767",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr31-13596535241259952"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/13596535241259952"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Andrographolide suppresses SARS-CoV-2 infection by downregulating ACE2 expression: A mechanistic study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy",
"volume": "29"
}