Molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus usual care in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial
et al., The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3, RECOVERY, NCT04381936, May 2024 (preprint)
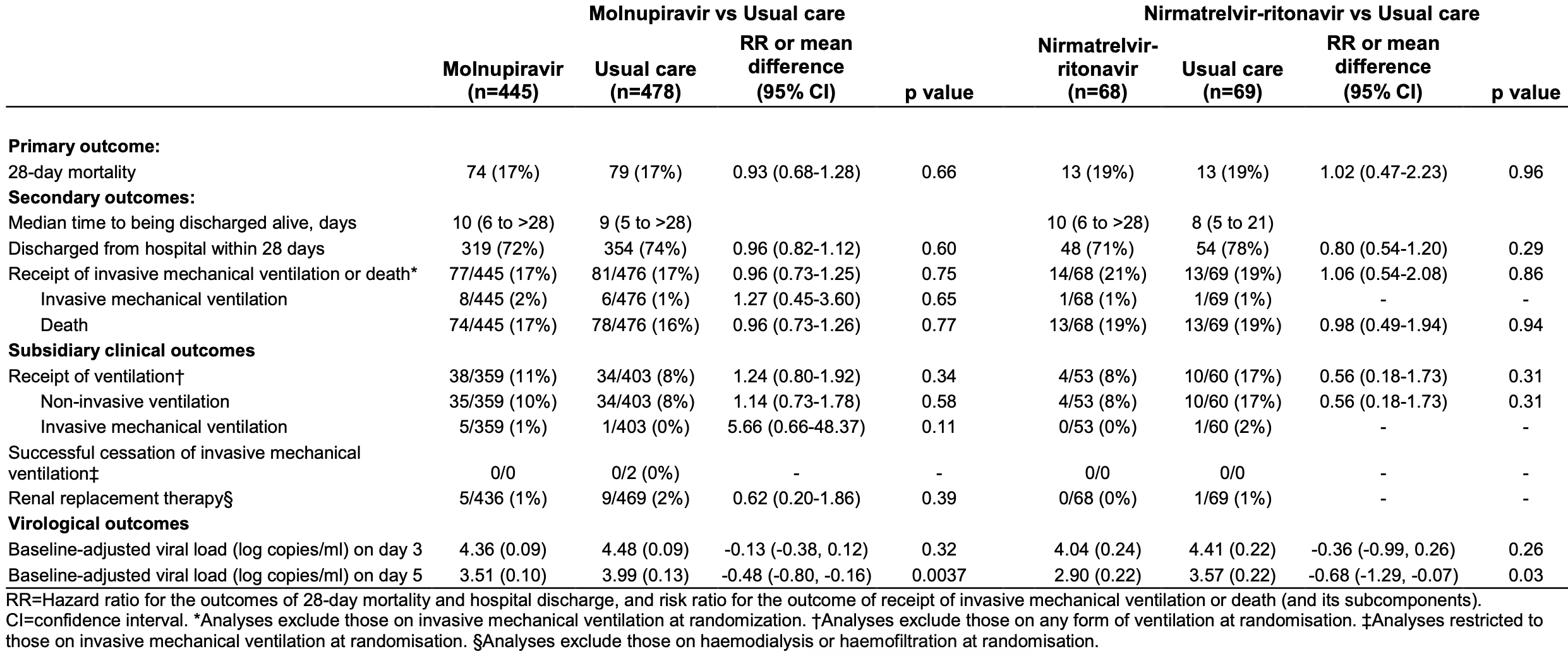
RECOVERY RCT showing no significant differences in mortality, ventilation, or discharge with either molnupiravir (923 patients) or paxlovid (137 patients). Viral load was improved with treatment but did not translate into clinical benefit, which may in part be due to side effects of treatment.
The treatment delay was notably shorter compared to other treatments in this trial - 4 and 5 days from onset for paxlovid and molnupiravir.
There was an exactly one year delay in publication after completion of recruitment. No press release or results are shown on the trial web site. In contrast, a press release was issued for the HCQ arm on the same day that recruitment ended. The one year delay may be a maximum delay due to EU Clinical Trials registration and associated regulatory requirements for the release of results.
There was an additional almost one year delay for the journal publication.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
Study covers molnupiravir and paxlovid.
|
risk of death, 11.3% higher, RR 1.11, p = 0.55, treatment 57 of 445 (12.8%), control 55 of 478 (11.5%), COVID-19, day 28, Supp. Table 4.
|
|
risk of death, 7.0% lower, HR 0.93, p = 0.66, treatment 74 of 445 (16.6%), control 79 of 478 (16.5%), adjusted per study, all cause, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, day 28.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 42.6% higher, RR 1.43, p = 0.59, treatment 8 of 445 (1.8%), control 6 of 476 (1.3%).
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 9.1% higher, RR 1.09, p = 0.46, treatment 126 of 445 (28.3%), control 124 of 478 (25.9%).
|
|
time to discharge, 11.1% higher, relative time 1.11, treatment 445, control 478.
|
|
viral load, 12.0% lower, relative load 0.88, p < 0.001, treatment mean 3.51 (±0.1) n=445, control mean 3.99 (±0.13) n=478.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
Horby et al., 24 May 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 39 authors, study period 24 January, 2022 - 24 May, 2023, average treatment delay 5.0 days, trial NCT04381936 (history) (RECOVERY).
Contact: recoverytrial@ndph.ox.ac.uk.
open-label, platform trial
doi:10.1101/2024.05.23.24307731
a randomised, controlled,
Declaration of interests The authors have no conflict of interest or financial relationships relevant to the submitted work to disclose. No form of payment was given to anyone to produce the manuscript. All authors have completed and submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. The Nuffield Department of Population Health at the University of Oxford has a staff policy of not accepting honoraria or consultancy fees directly or indirectly from industry (see https://www.ndph.ox.ac.uk/files/about/ndph-independenceof-research-policy-jun-20.pdf).
Conflicts of interest No form of payment was given to anyone to produce the manuscript. The Nuffield Department of Population Health at the University of Oxford has a staff policy of not accepting honoraria or consultancy fees directly or indirectly from industry (see -0.68 (-1.29, -0.07) 0.03 RR=Hazard ratio for the outcomes of 28-day mortality and hospital discharge, and risk ratio for the outcome of receipt of invasive mechanical ventilation or death (and its subcomponents). CI=confidence interval. *Analyses exclude those on invasive mechanical ventilation at randomization. †Analyses exclude those on any form of ventilation at randomisation. ‡Analyses restricted to those on invasive mechanical ventilation at randomisation. §Analyses exclude those on haemodialysis or haemofiltration at randomisation.
References
Amstutz, Speich, Mentré, Effects of remdesivir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a systematic review and individual patient data metaanalysis of randomised controlled trials, Lancet Respir Med
Arribas, Bhagani, Lobo, Randomized Trial of Molnupiravir or Placebo in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19, NEJM Evid
Bergeri, Whelan, Ware, Global SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence from January 2020 to April 2022: A systematic review and meta-analysis of standardized population-based studies, PLoS Med
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients, N Engl J Med
Butler, Hobbs, Gbinigie, Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial, Lancet Lond Engl
Constantinides, Webster, Gentry, Rapid turnaround multiplex sequencing of SARS-CoV-2: comparing tiling amplicon protocol performance, medRxiv
Fischer, Eron, Holman, an Oral Antiviral Treatment for COVID-19
Gottlieb, Vaca, Paredes, Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe Covid-19 in Outpatients, N Engl J Med
Group, Horby, Mafham, Effect of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Group, Horby, Peto, Dimethyl fumarate in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Nat Commun
Hammond, Fountaine, Yunis, Nirmatrelvir for Vaccinated or Unvaccinated Adult Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Khoo, Fitzgerald, Saunders, Molnupiravir versus placebo in unvaccinated and vaccinated patients with early SARS-CoV-2 infection in the UK (AGILE CST-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2 trial, Lancet Infect Dis
Liu, Pan, Zhang, Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study, Lancet Reg Health West Pac
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science
Recovery Collaborative, Aspirin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet Lond Engl
Recovery Collaborative, Azithromycin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet Lond Engl
Recovery Collaborative, Colchicine in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet Respir Med
Recovery Collaborative, Higher dose corticosteroids in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 who are hypoxic but not requiring ventilatory support (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet Lond Engl
Sheahan, Sims, Zhou, An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice, Sci Transl Med
Strizki, Gaspar, Howe, Molnupiravir maintains antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants and exhibits a high barrier to the development of resistance, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGN-COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody Cocktail, in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Who Solidarity, Consortium, Remdesivir and three other drugs for hospitalised patients with COVID-19: final results of the WHO Solidarity randomised trial and updated meta-analyses, Lancet Lond Engl
Yoon, Toots, Lee, Orally Efficacious Broad-Spectrum Ribonucleoside Analog Inhibitor of Influenza and Respiratory Syncytial Viruses, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1473-3099(25)00093-3",
"ISSN": [
"1473-3099"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3",
"alternative-id": [
"S1473309925000933"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir plus usual care versus usual care alone in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00169-0"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abani",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbas",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbas",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbas",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbas",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbas",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbasi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbass",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbott",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdallah",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdelaziz",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdelfattah",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdelqader",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdul",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdul",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdul",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdul Rasheed",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdulakeem",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdul-Kadir",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdullah",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdulmumeen",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdul-Raheem",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdulshukkoor",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdusamad",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abed El Khaleq",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abedalla",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abeer Ul Amna",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abel",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abernethy",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abeywickrema",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abhinaya",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abidin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aboaba",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aboagye-Odei",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aboah",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aboelela",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abo-Leyah",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abouelela",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abou-Haggar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abouibrahim",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abousamra",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abouzaid",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abraham",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abraham",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abraheem",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abrams",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abrams",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abu",
"given": "HJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abu-Arafeh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abubacker",
"given": "SM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abung",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abusamra",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aceampong",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Achara",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Acharya",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Acheampong",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Acheampong",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Acheampong",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Acheson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Achieng",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Acosta",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Acquah",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Acton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adabie-Ankrah",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adair",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adam",
"given": "AS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adam",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adam",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adamali",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adamczyk",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adamu-Ikeme",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adatia",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adcock",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Addai-Boampong",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Addo",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adeagbo",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adebiyi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adedeji",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adegeye",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adegoke",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adell",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adenwalla",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adeoye",
"given": "FW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adesemoye",
"given": "OA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adewunmi",
"given": "EO",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adeyanju",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adeyemi",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adeyemo",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adhikari",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adhikari",
"given": "SA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adhikary",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aditya",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adjepong",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adkins",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adnan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adriaanse",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aeron-Thomas",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Affleck",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Afnan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Afridi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Afrim",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Afriyie",
"given": "FA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aftab",
"given": "ZA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Afum-Adjei Awuah",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Agarwal",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Agasiya",
"given": "PN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Agbeko",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Agbo",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aggarwal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aghababaie",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aguilar Jimenez",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Agyekum",
"given": "JA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Agyen",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahadome",
"given": "EK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahamed Sadiq",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahammed Nazeer",
"given": "MH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmad",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmad",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "BAR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "MC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "RA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "SG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "SH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed Ali",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed Mohamud",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmer",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahonia",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aidoo",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aiken",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ail",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ainsworth",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aissa",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aitken",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ajay",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ajibode",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ajmi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akhtar",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akili",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akinbiyi",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akindolie",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akinfenwa",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akinkugbe",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akinpelu",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akram",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aktinade",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akudi",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al Aaraj",
"given": "ASAR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al Balushi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al Dakhola",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al Swaifi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Abadi",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alabi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aladangady",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alafifi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alam",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alam",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Asadi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alatzoglou",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Albert",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Albertus",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Albon",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alcala",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alcorn",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alcorn",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldana",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alderdice",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldesouki",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldouri",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldridge",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aldridge",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ale",
"given": "RM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alegria",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alexander",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alexander",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alexander",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alexander",
"given": "PDG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-fori",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alghazawi",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alhabsha",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Hakim",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alhameed",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Hayali",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Hity",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "FR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aliberti",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alina",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alipustain",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alisjahbana",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aliyuda",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alizadeh",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Jibury",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Juboori",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Khalil",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alkhudhayri",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alkhusheh",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allan",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allan",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allanson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allcock",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alli",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allison",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allman",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allsop",
"given": "HK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allsop",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allsup",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Almahroos",
"given": "AFT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Moasseb",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Obaidi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alomari",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Rabahi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Ramadhani",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Saadi",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Sammarraie",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alshaer",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Shahi Salman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Shamkhani",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alsheikh",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Sheklly",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Altaf",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alty",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alvarez",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alvarez Corral",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alveyn",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alzetani",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amamou",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amar",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ambalavanan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ambrogetti",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ambrose",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ameen",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amelia Ganefianty",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ames",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amezaga",
"given": "MR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amin",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amin",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amin",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amit",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amjad",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amjad",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amoah-Dankwa",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amoako-Adusei",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amosun",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amsal",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amsha",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amuasi",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amutio Martin",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amy",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anada",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anand",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anandappa",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anantapatnaikuni",
"given": "SD",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andari",
"given": "NKN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andreou",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andrews",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andrews",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aneke",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ang",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ang",
"given": "WW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Angel",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Angela",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Angelini",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anguvaa",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anichtchik",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anim-Somuah",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aniruddhan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Annett",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anning",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ansah",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anstey",
"given": "PJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anstey",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anthony",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anthony-Pillai",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Antill",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Antonina",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anu",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anwar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Anwar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Apetri",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Apostolopoulos",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Appleby",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Appleyard",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aquino",
"given": "MF",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Araba",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aransiola",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Araujo",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Archer",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Archer",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Archer",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arcoria",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ardley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arhin-Sam",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arias",
"given": "A-M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aribike",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arimoto",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arisanti",
"given": "NLPE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arkley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Armah",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Armata",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Armistead",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Armitage",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Armstrong",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Armstrong",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Armstrong",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Armstrong",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Armtrong",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arndt",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arnison-Newgass",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arnold",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arnold",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arnott",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arora",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arora",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arora",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arora",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arter",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arthur",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Artini",
"given": "NM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arumaithurai",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arya",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arya",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aryal",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asandei",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asare",
"given": "GA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asghar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asghar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashab",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashbrook-Raby",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashby",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashcroft",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashcroft",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asher",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashfak",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashfaq",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asiamah",
"given": "HA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashish",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashley",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashman-Flavell",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashok",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashour",
"given": "A-E-A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashraf",
"given": "MZ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashraf",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashraq",
"given": "MB",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashton",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashworth",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashworth",
"given": "FJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashworth",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aslam",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aslam",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aslam",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aslett",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asogan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asrar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Assaf",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Astin-Chamberlain",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Atabudzi",
"given": "YE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Athavale",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Athorne",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Atkins",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Atkins",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Atkins",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Atkinson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Atkinson",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Atomode",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Atraskiewicz",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Attia",
"given": "AA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Attubato",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Attwood",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aubrey",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Auer",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aujayeb",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aung",
"given": "AT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aung",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aung",
"given": "HWW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aung",
"given": "KK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aung",
"given": "KT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aung",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aung",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aung",
"given": "ZM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Austin",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Austin",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Auwal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Avari",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Avery",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aveyard",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Avis",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aviss",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Avram",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Avram",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Awadelkareem",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Awadzi",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Awaly",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Awan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Awisi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aya",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ayaz",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ayerh",
"given": "JM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ayers",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azam",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azeem",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azharuddin",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aziz",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aziz",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aziz",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aziz",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azkoul",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azman Shah",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azzopardi",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azzoug",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Babatunde",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Babi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Babiker",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Babington",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Babirecki",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Babores",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Babs-Osibodu",
"given": "AO",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bac",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bacciarelli",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bachar",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bachour",
"given": "M-E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bachti",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bacon",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bacon",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Badal",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Badat",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bader",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Badhan",
"given": "GR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Badhrinarayanan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bae",
"given": "JP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baggaley",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baggott",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bagley",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bagmane",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bagshaw",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bahadori",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bahurupi",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bailey",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bailey",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bailey",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bailey",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bailey",
"given": "MA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bailey",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bailey",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bailey",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baillie",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baillie",
"given": "JK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bain",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bains",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baird",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baird",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baird",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baird",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baird",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baird",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bajandouh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bajracharya",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "DC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "T-A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bakere",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bakerly",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baker-Moffatt",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bakhai",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bakhtiar",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bakoulas",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bakthavatsalam",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balachandran",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balasingam",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balaskas",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balasubramaniam",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balatoni",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balcombe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baldwin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baldwin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baldwin",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baldwin",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baldwin",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baldwin-Jones",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bale",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balfour",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ball",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ball",
"given": "Ro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ballard",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balluz",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balmforth",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balogh",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baltmr",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baluwala",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bambridge",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bamford",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bamford",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bamgboye",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bancroft",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bancroft",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Banda",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bandaru",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bandi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bandla",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bandyopadhyam",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Banerjee",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Banerjee",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bang",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baniya",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bani-Saad",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Banks",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Banks",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Banks",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bann",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bannister",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bannister",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Banton",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bao",
"given": "DG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bao",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baptist",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baqai",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baral",
"given": "AM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baral",
"given": "SC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baramova",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barber",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barbon",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barbosa",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barbour",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barclay",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barclay",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bardsley",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bareford",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bari",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barimbing",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barker",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barker",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barker",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barker",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barker",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barker",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barker",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barker-Williams",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barkha",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barla",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barlow",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barlow",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barlow",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnacle",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnard",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnes",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnes",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnes",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnes",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnetson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnett",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnett-Vanes",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barning",
"given": "PG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barnsley",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barr",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barr",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barr",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barr",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barratt",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barratt",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrera",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrett",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrett",
"given": "Fi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrett",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrett",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barrow",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bartholomew",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barthwal",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bartlett",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bartlett",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bartlett",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bartlett",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bartley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bartolmeu-Pires",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barton",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barton",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barton",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barton",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baruah",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baryschpolec",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bashir",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bashyal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Basker",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Basnet",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Basnyat",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Basoglu",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Basran",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bassett",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bassett",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bassford",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bassoy",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bastion",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bastola",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Basumatary",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Basvi",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Batac",
"given": "JA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bataduwaarachchi",
"given": "VR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bate",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bateman",
"given": "HJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bateman",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bateman",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bates",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bates",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bates",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bates",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Batham",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Batista",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Batla",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Batra",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Batty",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Batty",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Batty",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baum",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baumber",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bautista",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bawa",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bawa",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bawani",
"given": "FS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bax",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baxter",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baxter",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baxter",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bayes",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bayo",
"given": "L-A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bazari",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bazaz",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bazli",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beacham",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beadles",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beadon",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beak",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beale",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beard",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bearpark",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beasley",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beattie",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beaumont",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beaumont-Jewell",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beaver",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beavis",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beazley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beck",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beckett",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beckitt",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beckley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beddall",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beddows",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beeby",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beeby",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beech",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beecroft",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beer",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beer",
"given": "Sa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beety",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bega",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Begg",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Begg",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beghini",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Begum",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Begum",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Begum",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Behan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Behrouzi",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beishon",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beith",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Belcher",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Belfield",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Belfield",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Belgaumkar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bellamu",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bellamy",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bellamy",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bellini",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bellis",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bellis",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bendall",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benesh",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benetti",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bengu",
"given": "SA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benham",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benison-Horner",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benkenstein",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benn",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bennett",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bennett",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bennett",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bennett",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bennett",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bennett",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bennett",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bennett",
"given": "MR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bennett",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bennion",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benoy",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benson",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bentley",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bentley",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benton",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beranova",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beresford",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bergin",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bergstrom",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bernatoniene",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Berriman",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Berry",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Best",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Best",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bester",
"given": "A-M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beuvink",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bevan",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bevins",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bewick",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bexley",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beyatli",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beynon",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhadi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhagani",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhakta",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhalla",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhandal",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhandal",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhandari",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhandari",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhandari",
"given": "LN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhandari",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhanich Supapol",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhanot",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhanot",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhasin",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhat",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhat",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhatnagar",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhatt",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhayani",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhojwani",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhuie",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhuiyan",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhuiyan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bibby",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bibi",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bibi",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bibi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bicanic",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bidgood",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bigg",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Biggs",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Biju",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bikov",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Billingham",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Billings",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Binh",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Binns",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "BinRofaie",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bintcliffe",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Birch",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Birch",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Birchall",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bird",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Birt",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bishop",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bishop",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bishop",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bisnauthsing",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Biswas",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bittaye",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Biuk",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blachford",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Black",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Black",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Black",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Black",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Black",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Black",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blackgrove",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blackledge",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blackler",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blackley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blackman",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blackstock",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blair",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blakemore",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blamey",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bland",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blane",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blankley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blaxill",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blaylock",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blazeby",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blencowe",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bloom",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bloomfield",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bloss",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blowers",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blows",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bloxham",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blrd",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blundell",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blunsum",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blunt",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blunt",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blyth",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blyth",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blythe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Blythe",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boahen",
"given": "KA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boampoaa",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Board",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boatemah",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bobie",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bobruk",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bodalia",
"given": "PN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bodasing",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boden",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bodenham",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boehmer",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boffito",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bohanan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bohmova",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bohnacker",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bokhandi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bokhar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bokhari",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bokhari",
"given": "SO",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bokobza",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boles",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bolger",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bonaconsa",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bond",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bond",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bond",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bond",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bone",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boniface",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bonney",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bonney",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Booker",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boot",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boothroyd",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Borbone",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Borman",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bosence",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bostock",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Botting",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bottrill",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bouattia",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bough",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boughton",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boult",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boumrah",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bourke",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bourke",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bourne",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bousfield",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boustred",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bowes",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bowker",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bowker",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bowler",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bowman",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bowman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bowmer",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bowring",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bowyer",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boyd",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boyd",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boyd",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boyer",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boyle",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boyle",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boyle",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boyles",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brace",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bracken",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bradder",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bradley",
"given": "CJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bradley",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bradley-Potts",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bradshaw",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bradshaw",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brady",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brady",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brady",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Braga Sardo",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Braganza",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Braithwaite",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brammer",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Branch",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brankin-Frisby",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brannigan",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brattan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bray",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bray",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brazil",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brear",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brear",
"given": "Tr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brearey",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bremner",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brend",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bresges",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bressington",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bretland",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brewer",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bridgett",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bridgwood",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brigham",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bright",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brightling",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brigstock",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brimfield",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brinksman",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brinkworth",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brittain-Long",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Britten",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Britton",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Broad",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Broadhead",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Broadhurst",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Broadley",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Broadway",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brockelsby",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brocken",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brockley",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brodsky",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brogan",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brohan",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brokke",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brolly",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bromley",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooke-Ball",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooker",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brookes",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooking",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooks",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooks",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooks",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooks",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooks",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooks",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooks",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brooks",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Broom",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Broomhead",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Broughton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Broughton",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brouns",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Browne",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Browne",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Browne",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Browne",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brownlee",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brraka",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bruce",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bruce",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brudlo",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brunchi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brunskill",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brunton",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brunton",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bryant",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bryden",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brzezicki",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buazon",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buch",
"given": "MH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buchan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buchanan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buche",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buck",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buck",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buckland",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buckley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buckley",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buckley",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buckley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buckman",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Budds",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bugg",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bujazia",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bukhari",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bukhari",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bulbulia",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bull",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bull",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bull",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bull",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bull",
"given": "Th",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bullock",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bullock",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bulteel",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bumunarachchi",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bungue-Tuble",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burbidge",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burchett",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burda",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burden",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burden",
"given": "TG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burgess",
"given": "Mi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burgess",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burgess",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burhan",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burhan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burke",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burke",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burnard",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burnett",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burnett",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burns",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burns",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burns",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burns",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burrage",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burrows",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burston",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burton",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burton",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burton",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burton",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burton",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butar butar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butcher",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butt",
"given": "A-T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butt",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butt",
"given": "MM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butterworth",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Butterworth-Cowin",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buttery",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buttle",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Button",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buttress",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bye",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Byrne",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Byrne",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Byrne-Watts",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "C",
"given": "NK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cabandugama",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cabrero",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caddy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cade",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cadwgan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cahilog",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cahyareny",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cairney",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Calderwood",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caldow",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cale",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Calisti",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Callaghan",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Callaghan",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Callens",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Callum",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Calver",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cambell-Kelly",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Camburn",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cameron",
"given": "DR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cameron",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cameron",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cameron",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Camm",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cammack",
"given": "FD",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campbell Hewson",
"given": "Q",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Camsooksai",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Canclini",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Candido",
"given": "SM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Candlish",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caneja",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cann",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cann",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cannan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cannon",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cannon",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cannon",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cannon",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cannons",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Canonizado",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cantliff",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cap",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cap",
"given": "NT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caplin",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Capocci",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caponi",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Capp",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Capstick",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Capstick",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caraenache",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Card",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cardwell",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carey",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carey",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carlin",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carlin",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carmichael",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carmody",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carnahan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caroline",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carpenter",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carr",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carrasco",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carrington",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carroll",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carroll",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cart",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cartwright",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cartwright",
"given": "J-A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carty",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carty",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carungcong",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carver",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carver",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carver",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Casey",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cassells",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Castiello",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Castle",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Castles",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caswell",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Catana",
"given": "AM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cate",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Catelan Zborowski",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cathcart",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cathie",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Catibog",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Catley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Catlow",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caudwell",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cavazza",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cave",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cave",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cavinato",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cawa",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cawley",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caws",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cawthorne",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cendl",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Century",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cernova",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cesay",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cetti",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chabane",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chablani",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chabo",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chacko",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chadwick",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chadwick",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chadwick",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chakkarapani",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chakraborty",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chakraborty",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chakravorty",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chalakova",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chalise",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chalise",
"given": "BS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chalmers",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chalmers",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chamberlain",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chamberlain",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chambers",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chambers",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chambers",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chambers",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "R (P-C)",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "XHS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chandler",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chandler",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chandler",
"given": "KJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chandler",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chandler",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chandra",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chandran",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chandrasekaran",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chanh",
"given": "HQ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaplin",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaplin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chappell",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Charalambou",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Charles",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Charlton",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Charlton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chatar",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chatha",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chatterton",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chau",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaube",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhary",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhary",
"given": "MYN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhary",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhry",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhry",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhuri",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhuri",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaudhury",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chauhan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chauhan",
"given": "RS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chaulagain",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chavasse",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chavasse",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chawla",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheater",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheaveau",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheeld",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheeseman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "HM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "LY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chenoweth",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheong",
"given": "CH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cherian",
"given": "JJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cherian",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cherrie",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheshire",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheung",
"given": "CK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheung",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheung",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheung",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheyne",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chhabra",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chia",
"given": "WL",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chiang",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chiapparino",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chicano",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chikara",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chikungwa",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chikwanha",
"given": "ZA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chilcott",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chilcott",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chilvers",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chimbo",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chin",
"given": "KW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chin",
"given": "WJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chineka",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chingale",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chinonso",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chin-Saad",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chirgwin",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chisem",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chisenga",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chisholm",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chisnall",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chiswick",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chita",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chitalia",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chiu",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chiverton",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chivima",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chmiel",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Choi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Choon Kon Yune",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chopra",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Choudhary",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Choudhury",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Choudhury",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chow",
"given": "B-L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chowdhury",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chowdhury",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chrisopoulou",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christenssen",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christian",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christides",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christie",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christmas",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christoforou",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christopherson",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christou",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Christy",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chrysostomou",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chua",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chudgar",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chudleigh",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chukkambotla",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chukwu",
"given": "ME",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chukwulobelu",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chung",
"given": "CY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Church",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Church",
"given": "SR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Churchill",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cianci",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cicconi",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cinardo",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cipinova",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cipriano",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clamp",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clancy",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clapham",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clare",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clare",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clarke",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clarke",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clarke",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clarke",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clarke",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Claxton",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Claxton",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clay",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clayton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clayton",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clayton",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clayton-Smith",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clearyb",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cleaver",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cleeton",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clement",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clemente de la Torre",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clements",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clements",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clenton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cliff",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clifford",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clifford",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clive",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clouston",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clubb",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clueit",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clutterbuck",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Clyne",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coakley",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coakley",
"given": "PGL",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cobain",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cochrane",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cochrane",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cockayne",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cockerell",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cockerill",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cocks",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Codling",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coetzee",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coey",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cohn",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coke",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coker",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colbeck",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colbert",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cole",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cole",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coleman",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coleman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coleman",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coles",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colin",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colino-Acevedo",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colley",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collie",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collier",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collier",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collier",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collingwood",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collini",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collinson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collinson",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collinson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Collis",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colmar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colton",
"given": "HE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colville",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Colvin",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Combes",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Comer",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Comerford",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Concannon",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Condliffe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Condliffe",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Connell",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Connell",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Connell",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Connelly",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Connolly",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Connor",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conroy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conroy",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conteh",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Convery",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conway",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conway",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conway",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conyngham",
"given": "J-A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooke",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooke",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooke",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooke",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooke",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooke",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooke",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cooray",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cope",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corbet",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corbett",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corbishley",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corcoran",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cordell",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cordle",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corfield",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corless",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corlett",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cornwell",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cornwell",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corogeanu",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corr",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corredera",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corrigan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corry",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Corser",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cort",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cosgrove",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cosier",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Costa",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Costa",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coston",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cotgrove",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coton",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cottam",
"given": "L-J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cotter",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cotterill",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cotton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Couch",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coulding",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coull",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Counsell",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Counter",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coupland",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Courtney",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Courtney",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cousins",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coutts",
"given": "AJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cowan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cowan",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cowan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cowell",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cowen",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cowman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cowton",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cox",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cox",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cox",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cox",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cox",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Coy",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cradduck-Bamford",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Craig",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Craig",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Craig",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Craighead",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cramp",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cranston",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crasta",
"given": "SS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crause",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crawford",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crawford",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crawford",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crawshaw",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Creagh-Brown",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Creamer",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Creaser-Myers",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cremona",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cremona",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crepet",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cresswell",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cribb",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crichton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crilly",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crisp",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crisp",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crocombe",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Croft",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crooks",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crosby",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cross",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cross",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crothers",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crotty",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crouch",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crow",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crowder",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crowley",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crowley",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Croysdill",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cruickshank",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cruickshank",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cruise",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cruz",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cruz Cervera",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cryans",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cui",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cui",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cullen",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cummings-Fosong",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cunliffe",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cunningham",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cupitt",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Curgenven",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Curnow",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Curran",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Curran",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Currie",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Currie",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Currie",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Curtis",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Curtis",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Curtis",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Curtis",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Curtis",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cuthbertson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cuthill",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cutler",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cutts",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Czekaj",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Czylok",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D'Souza",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "da Rocha",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dadzie",
"given": "GS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dafalla",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dagens",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daggett",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daglish",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dahiya",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dale",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dale",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dale",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dale",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dales",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D'Alessandro",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dalgleish",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dallow",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D'aloia",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dalton",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dalton",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daly",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Damani",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Damm",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dan",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Danga",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dangerfield",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daniel",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daniel",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daniels",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dann",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Danso",
"given": "KG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Danso-Bamfo",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dao",
"given": "QT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Darby",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Darbyshire",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Darbyshire",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dargan",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dark",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Darlington",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Darnell",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Darton",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Darylile",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Das",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Das",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Das",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daschel",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dasgin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Datta",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daunt",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dave",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davenport",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davey",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "David",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davidson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davidson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davidson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davidson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davis",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davis",
"given": "J-A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davis",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davis",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davis-Cook",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davison",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawe",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawe",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawkins",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawson",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawson",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dawson",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daxter",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Day",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Day",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D'Costa",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Fonseka",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Freitas",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Los Santos Dominguez",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Pretto",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Santana Miranda",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Sausmarez",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Silva",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Silva",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Sousa",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Sousa",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Souza",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Souza",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Soyza",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Vere",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Vos",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deacon",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dealing",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dean",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dean",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dean",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dean",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dean",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deane",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dear",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dearden",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deas",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Debbie",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Debreceni",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deelchand",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deeley",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deery",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Defever",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Del Forno",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dela Rosa",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De-La-Cedra",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dell",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Demetriou",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "DeMets",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Democratis",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Denham",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Denis",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Denley",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Denmade",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dent",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dent",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dent",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Denton",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Denwood",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deole",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Depala",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Depante",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dermody",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Desai",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Desai",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deshpande",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deshpande",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Devkota",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Devkota",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Devonport",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Devonport",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dey",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dey",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Deylami",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhaliwal",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhangar",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhani",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhanoa",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhariwal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dharmasena",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhasmana",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhillon",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhillon",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhillon",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhimal",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhiru",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dhorajiwala",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dias",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diaz",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diaz-Pratt",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dibas",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dickerson",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dicks",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dickson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dickson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Digby",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Digpal",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dillane",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diment",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dimitri",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dimitriadis",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Din",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dinh",
"given": "TH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dinh",
"given": "TTT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dipheko",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dipper",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dipro",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dirmantaite",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dismore",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ditchfield",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diver",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diwakar",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diwan",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dixon",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dixon",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dixon",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Djeugam",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dlamini",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dlouhy",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D'Mello",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dmitri",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Do",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dobbie",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dobranszky Oroian",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dobson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dobson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Docherty",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dockrell",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dodd",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dodds",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dodds",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dodds",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dogra",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doherty",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doherty",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doherty",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doi",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doig",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doke",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dolan",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dolman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dolman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donald",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donald",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donaldson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donaldson",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donaldson",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donaldson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dong",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donkor",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donlon",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donnachie",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donnelly",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donnelly",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donnison",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donohoe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donohoe",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Donohue",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dooks",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doonan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doorn",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doran",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dore",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dorey",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dorgan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dos Santos",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dosani",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dosanjh",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dospinescu",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doss",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doudouliaki",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dougherty",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doughty",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Douglas",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Douse",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dow",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dowden",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dower",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dowling",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Downer",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Downes",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Downes",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Downes",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Downey",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Downey",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Downing",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Downs",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dowson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dragan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dragos",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drain",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drake",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drew",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drewett",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drexel",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Driscoll",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drogan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drosos",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drummond",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drury",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Druryk",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Druyeh",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dryburgh-Jones",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Drysdale",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dsouza",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Du Thinh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duah",
"given": "IK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dube",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dube",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duberley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duckenfield",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duckles-Leech",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duff",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duffield",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duffy",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duffy",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dufour",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duggan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dugh",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duhoky",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duignan",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dulay",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dummer",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duncan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duncan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duncan",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duncan",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duncan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duncan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dundas",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dung",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dung",
"given": "NTP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunleavy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunleavy",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunn",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunn",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunn",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunn",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunn",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunne",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunne",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunning",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunphy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duong",
"given": "TTH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duraiswamy",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duran",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "DuRand",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durdle",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duric",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durie",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durie",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durogbola",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durojaiye",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durrans",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durrant",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durrington",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duru",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duvnjak",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dwarakanath",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dwarakanath",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dwomoh Nkrumah",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dwyer",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dyar",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dyball",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dyer",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dymond",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dymond",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dzidzomu",
"given": "ED",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eades",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eadie",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eadie",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eagles",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eapen",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Earl",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Early",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Earwaker",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easom",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "East",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easthope",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easton",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easton",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eatough",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ebigbola",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ebon",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eccles",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eccles",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eddings",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eddleston",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edgar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edgerley",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edmond",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edmondson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edmunds",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eades",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eadie",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eadie",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eagles",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eapen",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Earl",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Early",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Earwaker",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easom",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "East",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easthope",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easton",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easton",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eatough",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ebigbola",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ebon",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eccles",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eccles",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eddings",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eddleston",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edgar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edgerley",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edmond",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edmondson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edmunds",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eades",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eadie",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eadie",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eagles",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eapen",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Earl",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Early",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Earwaker",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easom",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "East",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easthope",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easton",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Easton",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eatough",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ebigbola",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ebon",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eccles",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eccles",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eddings",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eddleston",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edgar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edgerley",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edmond",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edmondson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edmunds",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elliot",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elliott",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elliott",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elliott",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elliott",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ellwood",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elmahdi",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elmahi",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elmasry",
"given": "H-M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "El-Naggar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elndari",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elneima",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elokl",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elradi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elsaadany",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elsayed",
"given": "MASA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "El-Sayeh",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "El-Sbahi",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elsebaei",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elsefi",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "El-Shakankery",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elsheikh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "El-Taweel",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elyoussfi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emberey",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emberson",
"given": "JR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emberton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emery",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emmanuel",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emmerson",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emms",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emond",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emonts",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Enachi",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Enenche",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Engden",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "English",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Enimpah",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Entwistle",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Enyi",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Erotocritou",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eskander",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Esmail",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Essa",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Everden",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Everden",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Every",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evison",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evison",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ezenduka",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faccenda",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fahel",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fahmay",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fairbairn",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fairbairn",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fairbairn",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fairclough",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fairlie",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fairweather",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fajardo",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Falcone",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Falconer",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fallon",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fallow",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faluyi",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fancois",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farah",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farah",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farah",
"given": "Q",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fard",
"given": "NZ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fares",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farg",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farmer",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farmer",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farmery",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farnworth",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farook",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farooq",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farooq",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farquhar",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farr",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farrell",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farrell",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farrukh",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farthing",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farzana",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fasina",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fatemi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fatemi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fathima",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fatimah",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faulkner",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faust",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Favager",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fawad",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fawke",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fawohunre",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fazal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fazleen",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fearby",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fearnley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Feben",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fedel",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fedorova",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fegan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Felongo",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Felton",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Felton",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fenlon",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fenn",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fennelly",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fenner",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fenton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fenton",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferenando",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferguson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferguson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferguson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferguson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferguson",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernandes",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernandez",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernandez",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernandez",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernandez Lopez",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernandez Roman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernando",
"given": "CJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fernando",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Feroz",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferranti",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferrari",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferrelly",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferrera",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferriman",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferron",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fethers",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Field",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Field",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Field",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fielder",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fieldhouse",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fielding",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fielding",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fielding",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fikree",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Filipa",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Filson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finbow",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finch",
"given": "DJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finch",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finch",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finch",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fineman",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finlayson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finlayson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finn",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finn",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finnerty",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finney",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finucane",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fiouni",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fiquet",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Firi",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fisher",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fisher",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fishman",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fishwick",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fitton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fitzgerald",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fitzjohn",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flaherty",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flanagan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flanders",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flaris",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fleming",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fleming",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fleming",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fleming",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flesher",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fletcher",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fletcher",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fletcher",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fletcher",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flett",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flewitt",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flockhart",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flood",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Floodgate",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flor",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Florence",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flowerdew",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Floyd",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flynn",
"given": "MJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Flynn",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foden",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fofana",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fogarty",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foley",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Folkes",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fong",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Font",
"given": "DM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foo",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foo",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foot",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foot",
"given": "HR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foot",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forbes",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ford",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ford",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fordham",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foreman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forester",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forkan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fornolles",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forrest",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forsey",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forsey",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forshall",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forster",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forsyth",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foster",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foster",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foster",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foster",
"given": "RA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foster",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foulds",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foulds",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fowe",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fowkes",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fowler",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fowler",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fowler",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foxton",
"given": "S-J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fraile",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frake",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Francioni",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Francis",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Francis",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Francis",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Francis-Bacon",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frankland",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Franklin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Franklin",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fraser",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fratila",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frayling",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fredlund",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Freeman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Freeman",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Freeman",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Freeman",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Freeman",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Freer",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "French",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "French",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Freshwater",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frise",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fromson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frosh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frost",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frost",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Froud",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frowd",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fryatt",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Frygier",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fuller",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fuller",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fuller",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fullerton",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fung",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fung",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Funnell",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Furness",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fyfe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "G",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gabbitas",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gabriel",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gabriel",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gachi",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gaffarena",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gage",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gahir",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gajebasia",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gajewska-Knapik",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gajmer",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galani",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gale",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gale",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gale",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gale",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gali",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gallagher",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gallagher",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gallagher",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gallagher",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gallam",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galliford",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galloway",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galloway",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galloway",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galvin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galvis",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gamble",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gamble",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gammon",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gan",
"given": "CN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ganaie",
"given": "MB",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ganapathi",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ganapathy",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gandhi",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gandhi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ganesh",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ganeshanathan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ganguly",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gani",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ganley",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garcia",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garden",
"given": "E-J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gardener",
"given": "AD",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gardiner",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gardiner",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gardiner",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gardiner",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gardiner-Hill",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gardner",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gardner",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garfield",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garg",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garg",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garlick",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garner",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garner",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garner",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garner",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garr",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garrero",
"given": "KA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gartaula",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garty",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gascoyne",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gashau",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gatenby",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gaughan",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gaurav",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gavrila",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gaylard",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gayle",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Geddie",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gedge",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gee",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Geele",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Geerthan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gellamucho",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gelly",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gelmon",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gelves-Zapata",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Genato",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gent",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gent",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Geoghegan",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "George",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "George",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "George",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "George",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "George",
"given": "VP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Georges",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Georgiou",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gerard",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gerdes",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Germain",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gerrish",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Getachew",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gethin",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gettings",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghanayem",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghavami Kia",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghazal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gherman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghosh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghosh",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghosh",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghosh",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giang",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giang",
"given": "TV",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giannopoulou",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibani",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibb",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibbison",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibbons",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibson",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gigi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilbert",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilbert",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilbert",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giles",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilham",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gill",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gill",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gillen",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gillesen",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gillespie",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gillham",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gillian",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilliland",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gillott",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilmour",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilmour",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gilmour",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ginn",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ginting",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giokanini-Royal",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gipson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giri",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Girling",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gisby",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gkioni",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gkoritsa",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gkrania-Klotsas",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gladwell",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glanville",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glasgow",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glasgow",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glass",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glass",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glaysher",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gledhill",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glenday",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glennon",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glossop",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glover",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glover",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glover",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glover Bengtsson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glowski",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glynn",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gnanalingam",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goddard",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goddard",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Godden",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Godden",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Godlee",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Godson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Godwin",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gogoi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gohel",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goiriz",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gokaraju",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goldacre",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goldsmith",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goldsmith",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gomersall",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gomez",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gomez-Marcos",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gondal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gonzalez",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodall",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodall",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodenough",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodfellow",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodfellow",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodlife",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodwin",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodwin",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodwin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goodyear",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gooentilleke",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goonasekara",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gooseman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gopal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gordon",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gordon",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gore",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gorick",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gorman",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gormely",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gorniok",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gorog",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gorst",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gorsuch",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gosai",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gosling",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gosling",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gosney",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goss",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gotham",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gott",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goudie",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gould",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gould",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goumalatsou",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gourbault",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Govind",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Govindan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gowans",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gowda",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gowda",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gower",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goyal",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goyal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Graham",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Graham",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Graham",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Graham",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Graham",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Graham-Brown",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grahamslaw",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grana",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grandison",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grandjean",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grant",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grant",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grant",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grant",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grant",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gravell",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Graves",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gray",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gray",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gray",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gray",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gray",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gray",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gray",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gray",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grayson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Greaves",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Greaves",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "AS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "CA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Greene",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Greenfield",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Greenhalgh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Greenwood",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Greer",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gregory",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gregory",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gregory",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Greig",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grenfell",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grenier",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grenville",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gresty",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grevatt",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grey",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gribben",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gribbin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gribble",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grieg",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grieve",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffin",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffin",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffin",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffith",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffiths",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffiths",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffiths",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffiths",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffiths",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffiths",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffiths",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Griffiths",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grigoriadou",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grigsby",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grist",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grobovaite",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grogono",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grondin",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Groome",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grose",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grosu",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grounds",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grout",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grover",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Groves",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grubb",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grundy",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guarino",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gudur",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guerin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guettari",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gulati",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gulia",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gunasekara",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gunasekera",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gunawardena",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gunganah",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gunn",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gunter",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "AK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta-Wright",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guratsky",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gureviciute",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gurram",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gurung",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gurung",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gurung",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gurung",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gurung Rai",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guth",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guthrine",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gyambrah",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gyanwali",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gyawali",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ha",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ha",
"given": "NT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ha",
"given": "NX",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Habibi",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hack",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hackett",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hackney",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hacon",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haddad",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hadfield",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hadfield",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hadfield",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hadjiandreou",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hadjisavvas",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haestier",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hafiz",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hafiz-Ur-Rehman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hafsa",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hagan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hague",
"given": "JW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hague",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haider",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haigh",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haile",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hailstone",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haines",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hainey",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hair",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hairsine",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hajnik",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hake",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hakeem",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haldeos",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Halder",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hale",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hale",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Halevy",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Halford",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Halford",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Halim",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hallas",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hallas",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hallett",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Halliday",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hallman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Halls",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamdollah-Zadeh",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamed-Adekale",
"given": "IA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hameed",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hameed",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamers",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamid",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamie",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamill",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamilton",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamilton",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamilton",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamilton",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamilton",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamilton",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamilton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamlin",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamlyn",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hammans",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hammersley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hammerton",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hammond",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hammond",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hammond",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hammond",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hammonds",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamoodi",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hampshire",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hampson",
"given": "JA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hampson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hampson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamzah",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Han",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanci",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hand",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Handayani",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Handford",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Handrean",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Handzewniak",
"given": "NK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haney",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hang",
"given": "DTT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hang",
"given": "VTK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanh",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanif",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanison",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hannah",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hannington",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hannun",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanrath",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanratty",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hansen",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanson",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hao",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haqiqi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haque",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harcourt",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harden",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harding",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hardman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hardwick",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hardy",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hardy",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hardy",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haresh",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harford",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hargadon",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hargraves",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hargreaves",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haris",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harlock",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harman",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harman",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harmer",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haroon",
"given": "MA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harper",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harper",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harper",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harper",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harper",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrhy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrington",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrington",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrington-Davies",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "M-C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "OA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harrod",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hart",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hart",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hartley",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hartley",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hartley",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hartley",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hartrey",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hartridge",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hartshorn",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harvey",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harvey",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harwood",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harwood",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harzeli",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haselden",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hasford",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hashem",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hashimm",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hashimoto",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hashmi",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haslam",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haslam",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hasnip",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hassan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hassan",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hassasing",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hassell",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hassell",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hastings",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hastings",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hastings",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hathaway-Lees",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hatton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hau",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Havinden-Williams",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Havlik",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawcutt",
"given": "DB",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawes",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawes",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawes",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawker",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawkins",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawkins",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawkins",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawkins",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawley",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hawley-Jones",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haworth",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hay",
"given": "AW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hay",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayat",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayat",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayathu",
"given": "M-R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayes",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayes",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayes",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayes",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayes",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayle",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haylett",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haynes",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haynes",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayre",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hays",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haysom",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayward",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haywood",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haywood Hasford",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hazelton",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hazenberg",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "He",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Headon",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heal",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Healy",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Healy",
"given": "JL",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hearn",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heasman",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heath",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heath",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heath",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heaton",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heavens",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hebbron",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heckman",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hector",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heddon",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hedges",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hedges",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heeley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heeney",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heinink",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heire",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Helgesen",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hemingway",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hemmila",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hemmings",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hemphill",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hemsley",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henderson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henderson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henderson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henderson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henry",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henry",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henry",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henry",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henry",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Henshall",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Herdman",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Herdman-Grant",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Herkes",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hermans",
"given": "LE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hernandez",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heron",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heron",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Herrington",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heselden",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heslop",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heslop",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hester",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hetherington",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hetherington",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hettiarachchi",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hettiarachchi",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hewer",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hewertson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hewetson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hewins",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hewitson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hewitt",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hewitt",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hewitt",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hey",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heyderman",
"given": "RS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heydtmann",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heys",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heywood",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hibbert",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hickey",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hickey",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hickey",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hickman",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hicks",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hicks",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hicks",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hien",
"given": "PTT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hien",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hien",
"given": "TT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Higbee",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Higgins",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Higham",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Highcock",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Highgate",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hikmat",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hilldrith",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hillman-Cooper",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hilton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hilton",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hinch",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hindle",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hindley",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hindmarsh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hine",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hinshaw",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hird",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hirst",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hirst",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hives",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hlaing",
"given": "HM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ho",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ho",
"given": "DKK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ho",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hoa",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hoa",
"given": "LNM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hoare",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hobden",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hobden",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hobrok",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hobson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodge",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodge",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodgen",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodgetts",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodgkins",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodgkinson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodgson",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodgson",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodgson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodgson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodkinson",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hodson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hogan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hogben",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hogg",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hoggett",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holborow",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holbrook",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holbrook",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holden",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holden",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holden",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holden",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holder",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holdhof",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holdsworth",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holland",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holland",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holland",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holland",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holland",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hollands",
"given": "ML",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holliday",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holliday",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holliday",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holling",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hollos",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hollos",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holloway",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holloway",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hollowday",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hollyer",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holmes",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holmes",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holmes",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holroyd",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holroyd-Hind",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holt",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holt",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holyome",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Home",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Homewood",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hong",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hoole",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hooper",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hope",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hopkins",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horby",
"given": "PW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horler",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hormis",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hornan",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hornby",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horne",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horne",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horner",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horrobin",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horsford",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horsford",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horsham",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horsley",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horsley",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hosea",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hoskins",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hossain",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hossain",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hough",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hough",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Houghton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Houghton",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Houlihan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Housely",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Houston",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hovvels",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "How",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howaniec",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howard",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howard",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howard",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howard",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howard",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howard-Griffin",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howard-Sandy",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howe",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howell",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howells",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howie",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howlett",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howlett",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Howman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hrycaiczuk",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Htet",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Htoon",
"given": "NZ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Htwe",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huah",
"given": "COH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hubbard",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huckle",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huda",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hudak",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hudig",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hudson",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hudson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hudson",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hufton",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huggins",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huhn",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hui",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hulbert",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hull",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hull",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hull",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hulme",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hulme",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hulse",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hulston",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hum",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hume",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Humphrey",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Humphries",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Humphries",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hung",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunt",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunt",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunt",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunt",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunt",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunt",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunt",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunter",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunter",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunter",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunter",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunter",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunter",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hunter",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huntington",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huq",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hurditch",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hurdman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hurley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hurley",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Husain",
"given": "MA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Husaini",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussam El-Din",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussein",
"given": "SFEM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussein",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussey",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussien",
"given": "AH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hutchinson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hutchinson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hutchinson",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hutchinson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hutchinson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hutsby",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hutton",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huy",
"given": "NQ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huyen",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huyen",
"given": "NTT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huyen",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huyen",
"given": "TB",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huyen Thuong",
"given": "NT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huynh",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hydes",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hyde-Wyatt",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hynes",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hyslop",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iakovou",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibison",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibraheim",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Icke",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Idowu",
"given": "AI",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Idrees",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Idrees",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iftikhar",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iftikhar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Igwe",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Igwe",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ijaz",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ikomi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iles",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iliodromiti",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ilsley",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ilves",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ilyas",
"given": "FM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imam-Gutierrez",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imray",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imtiaz",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingham",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingham",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingle",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inglis",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inglis-Hawkes",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingram",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingram",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingram",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Innes",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inns",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inpadhas",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inweregbu",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ionescu",
"given": "AA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ionita",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iordanov",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ipe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal Sait",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irabor",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irisari",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irons",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irshad",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irshad",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irvine",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irvine",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irving",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ishak",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Isherwood",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Isitt",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Islam",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Islam",
"given": "MDT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Islam",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ison",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Israa",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Isralls",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Istiqomah",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ivan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ivenso",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ivin",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ivy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iwanikiw",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ixer",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iyer",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iakovou",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibison",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibraheim",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibrahim",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Icke",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Idowu",
"given": "AI",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Idrees",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Idrees",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iftikhar",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iftikhar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Igwe",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Igwe",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ijaz",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ikomi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iles",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iliodromiti",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ilsley",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ilves",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ilyas",
"given": "FM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imam-Gutierrez",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imray",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imtiaz",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingham",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingham",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingle",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inglis",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inglis-Hawkes",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingram",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingram",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ingram",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Innes",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inns",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inpadhas",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inweregbu",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ionescu",
"given": "AA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ionita",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iordanov",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ipe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iqbal Sait",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irabor",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irisari",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irons",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irshad",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irshad",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irvine",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irvine",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Irving",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ishak",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Isherwood",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Isitt",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Islam",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Islam",
"given": "MDT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Islam",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ismail",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ison",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Israa",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Isralls",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Istiqomah",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ivan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ivenso",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ivin",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ivy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iwanikiw",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ixer",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iyer",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jabbar",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jack",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jacob",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jacob",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jacob",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jacques",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jadhav",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jafar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jafferji",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaffery",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jagadish",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jagannathan",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jagne",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jagpal",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jain",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jain",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaiswal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jajbhay",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaki",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jali",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jallow",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaly",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jama",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamal",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jameel",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jameson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamieson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamison",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jane",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Janes",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Janmohamed",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Japp",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaques",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jardim",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jardine",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jarman",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jarnell",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jarvie",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jarvis",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jarvis",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jastrzebska",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Javed",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Javier",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jawad",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jawaheer",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayachandran",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayachandran",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayadev",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayakumar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayaram",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayaram",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayasekera",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayatilleke",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayebalan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeater",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeddi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeebun",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeelani",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffery",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffrey",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffrey",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffreys",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffs",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffs",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeganathan Ponraj",
"given": "JP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jegede",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jemima",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkin",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jennings",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jennings",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jennings",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jennings",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jerome",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jerry",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jervis",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jessup-Dunton",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jesus Silva",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jetha",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jethwa",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jha",
"given": "RK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jhanji",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jian",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiao",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jimenez",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jimenez Gil",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jith",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joefield",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johal",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johannessen",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johari",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "John",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "John",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "John",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johns",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johns",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnstone",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnstone",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnstone",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joishy",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "CE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "KE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "LM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "PH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "RE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jonnalagadda",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jordache",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jordan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jordan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jose",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jose",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jose",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "PA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Josiah",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joy",
"given": "DK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joy",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joyce",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ju",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ju Wen Kwek",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Judd",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jude",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Judge",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juhl",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jujjavarapu",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juniper",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juszczak",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jyothish",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jabbar",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jack",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jacob",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jacob",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jacob",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jacques",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jafar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jafferji",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaffery",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jagadish",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jagannathan",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jagne",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jagpal",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jain",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jain",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaiswal",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaiswal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jajbhay",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaki",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jallow",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaly",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jama",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamal",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jameel",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "James",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jameson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamieson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamison",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jane",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Janes",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Janmohamed",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Japp",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaques",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jardim",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jardine",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jarman",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jarnell",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jarvie",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jarvis",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jarvis",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jastrzebska",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Javed",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Javier",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jawad",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jawaheer",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayachandran",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayachandran",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayadev",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayakumar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayaram",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayaram",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayasekera",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayatilleke",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayebalan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeater",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeddi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeebun",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeelani",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffery",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffrey",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffrey",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffreys",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffs",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeffs",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeganathan Ponraj",
"given": "JP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jegede",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jemima",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkin",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jennings",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jennings",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jennings",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jennings",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jerome",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jerry",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jervis",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jessup-Dunton",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jesus Silva",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jetha",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jethwa",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jha",
"given": "RK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jhanji",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jian",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiao",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jimenez",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jimenez Gil",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jith",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joefield",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johal",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johannessen",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johari",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "John",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "John",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "John",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johns",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johns",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnstone",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnstone",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Johnstone",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joishy",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "CE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "KE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "LM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "PH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "RE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jonnalagadda",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jordache",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jordan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jordan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jose",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jose",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jose",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "PA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Josiah",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joy",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joyce",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ju",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ju Wen Kwek",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Judd",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jude",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Judge",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juhl",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jujjavarapu",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juniper",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juszczak",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jyothish",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kabiru Dawa",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kacar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kadad",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kadam",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kader",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kailey",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kain",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kakoullis",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kakrani",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kala Bhushan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalayi",
"given": "RJK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaliannan Periyasami",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalita",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalla",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kallistrou",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalmus Eliasz",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalsoom",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kam",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamara",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamath",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamath",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamath",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamerkar",
"given": "SA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kametas",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamfose",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamundi",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kanabar",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kane",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kanitkar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kankam",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kannan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kant",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kapil",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kapoor",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kapoor",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaprapina",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kara",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karbasi",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karelia",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kark",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karkey",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karki",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karki",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karmali",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karunanithi",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karunaratne",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kasianczuk",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kasiappan Balasubramanian",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kasipandian",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kassam",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kathirgamachelvam",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kati",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Katsande",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaul",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaur",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaur",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaur",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaur",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kausar",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kavanagh",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kavanagh",
"given": "s",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kawser",
"given": "MAA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kay",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kay",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kay",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kay",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kayappurathu",
"given": "JN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kayastha",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaye",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kazeem",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "KC",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ke",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keady",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kearns",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kearsley",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keating",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keating",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keddie-Gray",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keegan",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keen",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keenan",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kefas",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kegg",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keith",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keke",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kellett",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelliher",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelly-Baxter",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kelsall",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keltos",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kemp",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kendall",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kendall-Smith",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kennard",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kennedy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kennedy",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kennedy",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kennedy-Hay",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kenny",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kent",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keogan",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keough",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kernaghan",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kerr",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kerrison",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kerry",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kerslake",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kerslake",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kerss",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keshet-Price",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kestelyn",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Keyte",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khadar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khadka",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khai",
"given": "NV",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khairunnisa",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalid",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalid",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalid",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalid",
"given": "MU",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalid",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalifa",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalil",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalil",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "MA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan Tharin",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khanh",
"given": "NH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khatana",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khatri",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khatun",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khatun",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kheia",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khera",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khiem",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khiem",
"given": "DP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khin",
"given": "HHE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khoa",
"given": "TD",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khoja",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khokhar",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khong",
"given": "MQ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khoo",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khuong",
"given": "VT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khurana",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kibaru",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kibutu",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kidd",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kidd",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kidney",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kidney",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kieffer",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kien",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kien",
"given": "TV",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kilbane",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kilby",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Killen",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kilner",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kilroy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "JW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kimber",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kimber",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King-Oakley",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kingsmore",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kinnear",
"given": "DJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kinney",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kiran",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kirby",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kirk",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kirk",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kirkby",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kirkham",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kirkman",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kirkpatrick",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kirwan",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kitching",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kitto",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kittridge",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kjoa",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Klaczek",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kleemann",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kmachia",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "KN",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knapp",
"given": "CP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knibbs",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knight",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knight",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knight",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knight",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knight",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knights",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knights",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knolle",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knopp",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knowles",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knowles",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knowles",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knox",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Knox",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koch",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kocsor",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kodituwakku",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koduri",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koe",
"given": "YJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koirala",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koirata",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kolakaluri",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kolodziej",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kolokouri",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kon",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Konar",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kononen",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Konstantinidis",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kontogonis",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koo",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koopmans",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kopyj",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Korcierz",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Korolewicz",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koshy",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kosmidis",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kosztolanyi",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kotecha",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kothandaraman",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kothavale",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koukou",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kountourgioti",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kouranloo",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kousar",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kousteni",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koutalopoula",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kovac",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kozak Eskenazia",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krasauskas",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krishnamurthy",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krishnamurthy",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krishnan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krishnan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krishnapalli",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krizak",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krueper",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krupej",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krzowski",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kubaisi",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kubheka",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kubisz-Pudelko",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kuckreja",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kudsk-Iversen",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kudzinskas",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kukadiya",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kulkarni",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumala Dewi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kuma-Mintah",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar Panda",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kundu",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kunst",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kunwar",
"given": "SS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kupiec",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kurani",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kurdy",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kuriakose",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kurian",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kurmars",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kuronen-Stewart",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kusangaya",
"given": "RS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kushakovsky",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kutera",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kuverji",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kyei-Mensah",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kyepa",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kyere-Diabour",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kyi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kyi",
"given": "NM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kyle",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kyriaki",
"given": "K-T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Labao",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Labuschagne",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lacey",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lack",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lacson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ladan",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ladlow",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lafferty",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lagnado",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laha",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lahane",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lai",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lai",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laidler",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laing",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laing-Faiers",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laity",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lake",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lakeman",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lalloo",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lalloo",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lam",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lam",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lamb",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lamb",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lamb",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lambert",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lambert",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lameirinhas",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lami",
"given": "MKG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lamont",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lamparski",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lamrani",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lanaghan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lancona-Malcolm",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Landers",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Landray",
"given": "MJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lane",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lane",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lang",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lang",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Langer",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Langley",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Langoya",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Langridge",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Langthorne",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Langton",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lara",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Large",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lartey",
"given": "LN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lassa",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Last",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Latham",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Latham",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Latheef",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Latif",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Latt",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laura",
"given": "GG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laurenson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lavington",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Law",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Law",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Law",
"given": "KY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Law",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Law",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawless",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawrence",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawrence",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawrence",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawrence",
"given": "HM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawrence",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawrie",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lawson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lay",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laybourne",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Laycock",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Layug",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lazo",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Le",
"given": "DH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Le",
"given": "TT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Le",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lea",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lea",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leach",
"given": "LE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leadbitter",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leahy",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lean",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leandro",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leaning",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leary",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leason",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ledingham",
"given": "MA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "SH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "X",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lees",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lees",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Legge",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leggett",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leigh-Ellis",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leitch",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leitch",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lekoudis",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lemessy",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lemoine",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lenagh",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leng",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lennon",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lennon",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leonard",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leonard",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leong",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leopold",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lepiarczyk",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leslie",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lestari",
"given": "EN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lester",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Levell",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Levett",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Levynska",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis-Clarke",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewszuk",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewthwaite",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liao",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Licence",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lieberman",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liebeschuetz",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Light",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lightfoot",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lillie",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lillis",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "ET",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "WS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Limb",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Limbu",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Limbu",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Linares",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Linden",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lindergard",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lindley",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lindsay",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lindsay",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lindsay",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lindsay- Clarke",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ling",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lingam",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Linh",
"given": "NVH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Linh",
"given": "VD",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Linkson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Linn",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Linney",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lippold",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lipscomb",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lipscomb",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lipskis",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lisboa",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lister",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Little",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Little",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Littlejohn",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "X",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Llanera",
"given": "DK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Llewellyn",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Llewelyn",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lloyd",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lloyd",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lloyd",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lo",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loader",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lobosco",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lock",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lock",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Locke",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Locke",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Locke",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lockett",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lodge",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lodhia",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lofthouse",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loftus",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Logan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Logue",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loh",
"given": "SY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lokanathan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lomme",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "London",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Long",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Long",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Longbottom",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Longhurst",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Longshaw",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Longstaffe",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lonnen",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lonsdale",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Looby",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loosley",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lopes",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lopez",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lopez",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lord",
"given": "RW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lord",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lorimer",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loro",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lorusso",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loughlin",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lovegrove",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loveless",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lovell",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loverdou",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Low",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Low",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Low",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lowe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lowe",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lowe",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lowe",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lowe",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lowe",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lowsby",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lowthorpe",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lubimbi",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lubina Solomon",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lucas",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lucas",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lucey",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lucey",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luck",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lui",
"given": "LH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luintel",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luke",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luke",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lungu",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lunia",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lunn",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luscombe",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luveta",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luximon",
"given": "CN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lwin",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lwin",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lye",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lyell",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lyka",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lynas",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lynch",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lynch",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lynch",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maamari",
"given": "R-G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mabb",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mabelin",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mabeza",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macaro",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macconaill",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macdonald",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macduff",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macfadyen",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macfarlane",
"given": "JG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macfarlane",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macfarlane",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macharia",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MacInnes",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MacIntyre",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MacIntyre",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mack",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackay",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackay",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackay",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackenzie",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackenzie",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MacKenzie Ross",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackey",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackie",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackie",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackie",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackinlay",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackintosh",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mackintosh",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MacLeod",
"given": "MJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macleod",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macmahon",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MacNair",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macphee",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macpherson",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Macrae",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MacRaild",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madani",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madden",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madden",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madden-McKee",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maddison",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madeja",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madhivathanan",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madhusudhana",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madu",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madziva",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mafham",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Magar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Magee",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Magezi",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maghsoodi",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Magier",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Magnaye",
"given": "LM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Magriplis",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Magtalas",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Magula",
"given": "NP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahabir",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahadevan-Bava",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahajan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maharajh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maharjan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maharjan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahaveer",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahay",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahay",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahdi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahdi",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahdi",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahendiran",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahendran",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maher",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maheswaran",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maheswaran",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maheswaran",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahjoob-Afag",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahmood",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahmood",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahmood",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahmood",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahmood",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahmoud",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahmud",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahony",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahungu",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maiga",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mair",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Majekdunmi",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Majid",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Major",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Major",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Majumdar",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Majumder",
"given": "MKH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mak",
"given": "TLA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Makan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Makanju",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Makin",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Makinde",
"given": "W-O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Makkeyah",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Makoetlane",
"given": "ON",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Malanca",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Malcolm",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Malein",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Malhan",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Malicka",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Malik",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Malik",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maljk",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mallett",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mallinder",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mallison",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mallon",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Malone",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maloney",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mamman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Man",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Man",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mancinelli",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mancuso-Marcello",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mandal",
"given": "SK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mandal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Manders",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Manderson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mandeville",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mane",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Manhas",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maniero",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Manikonda",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Manjra",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mankiewitz",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mann",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Manning",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Manning",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mannion",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mansi",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Manso",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mansour",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mansour",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mansour",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mapfunde",
"given": "IT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mappa",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maqsood",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maraj",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marchand",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marcus",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marcyniuk",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marecka",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maren",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Margabanthu",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Margalef",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Margarit",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Margaritopoulos",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Margarson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maria del Rocio",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maria Pfyl",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mariano",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maric",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Markham",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marks",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marks",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marks",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marler",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marouzet",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marriott",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marriott",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marriott",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marsden",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marsden",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marsden",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marsden",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marsden",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marsh",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marsh",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marsh",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martindale",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martineau",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martinez",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martinez Garrido",
"given": "JC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martin-Lazaro",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maruthamuthu",
"given": "VK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marwan",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maryan",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mary-Genetu",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maryosh",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Masani",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mascagni",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maseda",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maseko",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mashate",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mashhoudi",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mashta",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Masih",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Masih",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maskell",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maskell",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maskey",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Masoli",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mason",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mason",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mason",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Masood",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Masood",
"given": "MT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Masood",
"given": "SSME",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Massa",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Massey",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Masters",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Masud",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matapure",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matei",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matewe",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matey",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matharu",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathen",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mather",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mather",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathers",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matheson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathew",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathew",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathew",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathew",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathews",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathias",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mathioudakis",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matibela",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matila",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matimba-Mupaya",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matin",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matisa",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matkins",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matonhodze",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matovu",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mattappillil",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matthews",
"given": "AJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matthews",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matthews",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mattocks",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maughan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maulidya",
"given": "TT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mawson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maxton",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maxwell",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maxwell",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "May",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "May",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "May",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayanagao",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maycock",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayer",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayers",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maynard",
"given": "VA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayne",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayo",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayola",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayor",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mazen",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mazhani",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mazzella",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mburu",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mbuyisha",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mc Cague",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McAleese",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McAlinden",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McAllister",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McAlpine",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McAlpine",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McAndrew",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McAuley",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McAuliffe",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McBrearty",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McBride",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McBuigan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McBurney",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCabe",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCafferty",
"given": "GL",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCafferty",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCairn",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCammon",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCammon",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCann",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCann",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCarrick",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCarron",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCarthy",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCarthy",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCarthy",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCaughey",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McClay",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McClelland",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McClintock",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCloskey",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCollum",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCorkindale",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCormack",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCormick",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCormick",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCourt",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCrae",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCready",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCreath",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCreedy",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCue",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCullagh",
"given": "IJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCullagh",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCullagh",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCullough",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCullough",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCullough",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCullough",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCurrach",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDermott",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDermott",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDermott",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDevitt",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDill",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDonald",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDonald",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDonald",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDonald",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDonald",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDonald",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDonnell",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDougall",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDougall",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McDougall",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McEleavy",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McElwaine",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McEntee",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McEvoy",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McEwan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McEwen",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McFadden",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McFarland",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McFarland",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McFarland",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McFlynn",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGarry",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGarvey",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGeachan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGee",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGenily",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGettigan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGettrick",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGhee",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGill",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGinnity",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGlinchey",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGlone",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGlynn",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGoldrick",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGough",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGovern",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGovern",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGowan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGown",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGrath",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGregor",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGuigan",
"given": "MP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGuinness",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McGuire",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McHugh",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McInnes",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McInnes",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McIntosh",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McIntyre",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McIntyre",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKay",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKeag",
"given": "CP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKeane",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKee",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKeever",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKenna",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKenna",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKenzie",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKeogh",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKerr",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKie",
"given": "AM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mckie",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mckie",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McKnight",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McLachlan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McLaren",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McLaren",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McLarty",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mclaughlan",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McLaughlin",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McLay",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McLeish",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McLennan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McLure",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMahon",
"given": "AM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMahon",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMahon",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMahon",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McManus",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMaster",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMaster",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMaster",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mcmeeken",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMeekin",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMillan",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMillen",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMinn",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMorrow",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMullen",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McMurran",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McNally",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McNeela",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McNeil",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McNeill",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McNeill",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McNeill",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McNelis",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McNulty",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McNulty",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McParland",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McPhail",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McQueen",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McSkeane",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McSorland",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McSorley",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McTaggart",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McTaggart",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mead",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mead",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meadows",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meakin",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mearns",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mearns",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mears",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mears",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meda",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mediana",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Medine",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Medveczky",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meehan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meeks",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Megan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meghani",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meghjee",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Megson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mehar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mehmood",
"given": "MN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mehra",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meintjes",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meirill",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meiring",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mejri",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mekonnen",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melander",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melinte",
"given": "A-S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mellersh",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melling",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mellish",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mellor",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mellor",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mellor",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mellor",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mellows",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melnic",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melville",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melville",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melville",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Membrey",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mencias",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mendelski",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mendelson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mendonca",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meney",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Menezes",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mensah",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mensshan",
"given": "JE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mentzer",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Menzies",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Menzies",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mepham",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mercer",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mercer",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Merchant",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Merchant",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mercioniu",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meredith",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Merida Morillas",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Merrick",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Merritt",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Merritt",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Merron",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Merwaha",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Message",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Messenger",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Metcalf-Cuenca",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Metcalfe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Metcalfe",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Metcalfe",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Metherell",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Metryka",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mew",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meyrick",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mguni",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mhlongo",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miah",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miah",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miah",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mian",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mic",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Micah-Amuah",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Micallef",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Michael",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Michael",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Michalak",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Michalca-Mason",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Michalec",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Middle",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Middleton",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Middleton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Middleton",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Middleton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mieres",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mihalca-Mason",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mikolasch",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milgate",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Millar",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Millar",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Millard",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miller-Biot",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miller-Fik",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Millett",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milligan",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milligan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milligan",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milliken",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Millington",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Millington",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Millington",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mills",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mills",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mills",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Millward",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miln",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milne",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milne",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milne",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milner",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milner",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Min",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mindel",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Minh",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Minkah",
"given": "PA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Minnis",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Minnis",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Minou",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Minskip",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Minton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miranda",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mirela",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mirza",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Misbahuddin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mishra",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mishra",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mishra",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mishra",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Misra",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mistry",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mistry",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mital",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitchard",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitchell",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitchell",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitchell",
"given": "LJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitchell",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitchelmore",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitra",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitra",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitra",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mlambo",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moakes",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moar",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moatt",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mock Font",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Modgil",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohamed",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohamed",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohamed",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohammad",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohammad",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohammed",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohammed",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohammed",
"given": "YNS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohamud",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moharram",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mok",
"given": "H-P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mok",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mokogwu",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Molina",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moller-Christensen",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mollet",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Molloholli",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Molloy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Molloy",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Molyneux",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Molyneux",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Momoniat",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Monaghan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Monaghan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mongolu",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Monika",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Monsell",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Montasser",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Montgomery",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Montgomery",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moodley",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moody",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moody",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moon",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moon",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moon",
"given": "J-H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moon",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moonan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moondi",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moorby",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moorcroft",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "DAJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moores",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morab",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morales",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moramorell",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moran",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moray",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moreno-Cuesta",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgan-Jones",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgan-Smith",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morilla",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morley",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morley",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morley",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "M-A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morrison",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morrison",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morrison",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morrissey",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morrow",
"given": "AC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morrow",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morselli",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mortem",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mortland",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morton",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morzaria",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mosby",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moseley",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moshal",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moshy",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moss",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moss",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moss",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moss",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mostafa",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moth",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Motherwell",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mottershaw",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moudgil",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mouland",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moulds",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moulton",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mounce",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mousley",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mowatt",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moxham",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moya",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moyo",
"given": "Q",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mshengu",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mtuwa",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muazzam",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muazzam",
"given": "IA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muchenje",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mudawi",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muddegowda",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mufti",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mugal",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mughal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muglu",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muhammad",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muhammad",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muir",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mukherjee",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mukherjee",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mukhtar",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mukhtar",
"given": "SAA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mukimbiri",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mulcahy",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mulcahy",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mulgrew",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mulhearn",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mulla",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mullan",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mullasseril Kutten",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mullen",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mullett",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mulligan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mulligan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mumelj",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mumford",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Munavvar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Munby",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Munday",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Munro",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Munt",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mupudzi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murad",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muraina",
"given": "OH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muralidhara",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murdoch",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murira",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murray",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murray",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murray",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murray",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murray",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murray",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murtagh",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murthy",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murton",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muru",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Musanhu",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mushabe",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mushtaq",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Musini",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mustafa",
"given": "AMM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mustafa",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mustafa",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mustapha",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mustfa",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mustufvi",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mutch",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mutch",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mutema",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muthukrishnan",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mutton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muzengi",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mwadeyi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mwale",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mwaura",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Myagerimath",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Myers",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Myers",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Myerson",
"given": "JS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Myint",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Myint",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mynott",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Myslivecek",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nabayego",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nadar",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nadeem",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nadheem",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nadjm",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naeem",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naeem",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naeem",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nafees",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nafei",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naftalia",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nagarajan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naglik",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nagra",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nagra",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naguib",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naguleswaran",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nagumantry",
"given": "KS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naicker",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naidoo",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naidoo",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naik",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naik",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naik",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nair",
"given": "DS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nair",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nair",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naisbitt",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naismith",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nakiboneka-Ssenabulya",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nallapareddy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nallapeta",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nallasivan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nam",
"given": "HX",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nanda",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nandani",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nandwani",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naqvi",
"given": "AR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naqvi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naqvi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nasa",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nash",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nasheed",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nasimudeen",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nasir",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nasronudin",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nasser",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Natarajan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Natarajan",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Natarajan",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Natarajan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nath",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nathaniel",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nathvani",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nathwani",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nava",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Navaneetham",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Navaratnam",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Navarra",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naveed",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Navin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nawaz",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nawaz",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nayar",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naylor",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nayyar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naz",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naz",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nazari",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nazir",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nazir",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ncomanzi",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ndefo",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ndoumbe",
"given": "NB",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neary",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Negmeldin",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neil",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neill",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neils",
"given": "HE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nejad",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nel",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nel",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nelson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nelson",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nelson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nelson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nelson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nelson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nelwan",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nelwan",
"given": "EJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nemane",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nepal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nethercott",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Netherton",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nettleton",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neupane",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neupane",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newby",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newby",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newcombe",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newell",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newman",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newman",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newman",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newman",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newman",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newport",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Newton",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "AYKC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "HEJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "KW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "WJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "YWM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ngan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ngo",
"given": "TH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ngui",
"given": "GCE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ngumo",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "HK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "MT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "NT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "NTT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "Q",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "TH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "THT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "TT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "TTN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "TT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "TTP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ngwenya",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nhi",
"given": "NY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nic Fhogartaigh",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicholas",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicholas",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicholas",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicholls",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicholls",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicholls",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicholson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nickson",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicol",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicol",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicola",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicoll",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nightingale",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nikita",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nikolaos",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nikonovich",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nilsson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nimako",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nimako",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nimmo",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ninan",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ninh",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nirmalan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Niroula",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nisar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nisar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nisar",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nisbett",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nisha James",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nishat",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nishiyama",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nix",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nixon",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nixon",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nizam Ud Din",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nizami",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nizamis",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Njafuh",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noakes",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noba",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noble",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noble",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noe",
"given": "HM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nolan",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nolasco",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noor",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noori",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Norcliffe",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Norman",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Norman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Norris",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Norris",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Norris",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nortcliffe",
"given": "SA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "North",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "North",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "North",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Northfield",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Northover",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nortje",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Norton",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Norton",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Notman",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nourein",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Novak",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Novas Duarte",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Novis",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nowak",
"given": "JA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nu",
"given": "KP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nugdallah",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nugent",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nugent",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nugroho",
"given": "CW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Numbere",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nundlall",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nune",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nunn",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nunn",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nunnick",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nupa",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nur",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nurgat",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nurpeni",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nuttall",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nwafor",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nwajiugo",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nyamugunduru",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nyanor",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nyirenda",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nyland",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rinn",
"given": "DO",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shea",
"given": "DO",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Toole",
"given": "MO",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Hara",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Hara",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Keefe",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Reilly",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Rourke",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oakley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oakley",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oakley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oanh",
"given": "HTK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Obale",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oboh",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Brien",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Brien",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Brien",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Brien",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Brien",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Brien",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Brien",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Bryan",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Obukofe",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Callaghan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Connell",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "OConnor",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Connor",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Connor",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Odam",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oddie",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oddy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Odedina",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Odedra",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Odelberg",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Odell",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oderinde",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Odone",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Donohoe",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Donovan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Odysseos-Beaumont",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Farrell",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Offord",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Flaherty",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ofori",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ogbara",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ogilvie",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Gorman",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ogunjembola",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ogunkeye",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ohia",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ojha",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ojha",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ojo",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'kane",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Kane",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okeke",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "OKell",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okines",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okpala",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okpo",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okpoko",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okubanjo",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oladipo",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olaivar",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olaiya",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olatujoye",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Old",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oleszkiewicz",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliver",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliver",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliver",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliver",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliver",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliver",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliver-Commey",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olokoto",
"given": "NO",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olonipile",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olufuwa",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Olukoya",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oluwole-Ojo",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Malley",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Omale",
"given": "IV",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Omane-Donkor",
"given": "PK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Omar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Omar",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Omer",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Omoregie",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Neill",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Neill",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ong",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Onuoha",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Onyeagor",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oo",
"given": "CN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oo",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ooi",
"given": "HC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ooi",
"given": "SH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oomatia",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Opata",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Opena",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oram",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ord",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ord",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oreilly",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orekoya",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Riordan",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Riordan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orlikowska",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orme",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orme",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Rourke",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orr",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orr",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osadcow",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osagie",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osanlou",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osborne",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osborne",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osborne",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osborne",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osborne",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osbourne",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osei-Bobie",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osman",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osman",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Osoata",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ostermann",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Sullivan",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Sullivan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oteng",
"given": "MA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Otey",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Otite",
"given": "OK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Toole",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ouyang",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Owen",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Owen",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Owens",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Owoo",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Owoseni",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Owston",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oxlade",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ozdes",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pack",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Packham",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Packham",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paczko",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Padden",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Padmakumar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Page",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Page",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Page",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Page",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Page",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paget",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pagett",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pai",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paisley",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pajak",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pakou",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pakozdi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palacios",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palagiri Sai",
"given": "VB",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palaniappan",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palanivelu",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palfreeman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palfrey",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palissery",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palit",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pallipparambil Antony",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palmer",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palmer",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palmer",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palmer",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palmer",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pambouka",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pamphlett",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pandey",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pandian",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pandya",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pandya",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paneru",
"given": "HR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Panes",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pang",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pang",
"given": "YW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pangeni",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pannell",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pannu",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pant",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Panthakalam",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pantin",
"given": "CT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pao",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Papaconstantinou",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Papavarnavas",
"given": "NS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Papineni",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paques",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paracha",
"given": "AW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paradowski",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parambil",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paranamana",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parashar",
"given": "SR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parberry",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parekh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parekh",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parfitt",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parfrey",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parikh",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parish",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Park",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parkash",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parkin",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parkinson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parkinson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parkinson",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parmar",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parmar",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parris",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parrish",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parry",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parry",
"given": "HC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parslow-Williams",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parsonage",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parsons",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parsons",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parsons",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Partridge",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parvez",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parvin",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Passby",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Passey",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Passmore",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pastrana",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patachako",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patal",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patch",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paterson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pathak",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pathan",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patience",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patience",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patil",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patmore",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patole",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paton",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patrick",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patrick",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patrick",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patten",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pattenden",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patterson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patterson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patterson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patterson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patterson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pattrick",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paudel",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paudel",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paudel",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paudel",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paul",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paul",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pauls",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paulus",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pavely",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pavitt",
"given": "MJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pavord",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Payne",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Payne",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Payne",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Payne",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peacock",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peacock",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peake",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pearce",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pearse",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pearson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pearson",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pearson",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pearson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pearson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pearson",
"given": "SA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peasley",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peddie",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peebles",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peek",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peer",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peerbhoy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pegg",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peggie",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peggie",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peglar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peirce",
"given": "BH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peirse",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pelham",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pemberton",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Penacerrada",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pender",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pendlebury",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pendlebury",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Penfold",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Penman",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Penman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Penman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Penner",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Penney",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pennington",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Penny",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pepperell",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Percival",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pereira",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pereira",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pereira Dias Alves",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perera",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perera",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perez",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perez",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perinpanathan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Periyasamy",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perkins",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pernicova",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perritt",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perry",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perry",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perry",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perumpral",
"given": "TM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pessoa-Amorim",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petch",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peter",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peters",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peters",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peters",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peters",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peters",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peterson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petersen",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peto",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petras",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petrova",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petrova",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petrovics",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pettigrew",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pezard-Snell",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pfeffer",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phalod",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pham",
"given": "NT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pham",
"given": "VP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phan",
"given": "TTH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phanish",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phelan",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Philbey",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Philbin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phillips",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phillips",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phillips",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phillips",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phillips",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phillips",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phillips",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phipps",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phipps",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phong",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phong",
"given": "NT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phongsathorn",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phuc",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phuc",
"given": "PV",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phull",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phung",
"given": "HTK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phuong",
"given": "HM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phuong",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phuyal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phyo",
"given": "AK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "PI",
"given": "MTT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pick",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pickard",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pickering",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pickering",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pickering",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pickett",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pickles",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pickstock",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pickwell-Smith",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pieniazek",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Piercy",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pieris",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pilgrim",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pillai",
"given": "PA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pillay",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pilling",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pilsworth",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pinches",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pinches",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pine",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pinjala",
"given": "MT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pintus",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Piper",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pirani",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pitchford",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pittman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pitts",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Plaatjies",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Platt",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pleass",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Plowright",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Plummer",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Plumptre",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pobjoy",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pogreban",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poku",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poku",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Polgarova",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pollard",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pollock",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poluyi",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Polwarth",
"given": "GJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pomery",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ponce",
"given": "IMF",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ponnusamy",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ponnusamy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ponnuswamy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ponte Bettencourt dos Reis",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pooboni",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poole",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poole",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poole",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poon",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poonian",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Porteous",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Porteous",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Porter",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Porter",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Porter",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Porter",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Posada",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Postlethwaite",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potdar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pothecary",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pothina",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potla",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potoczna",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pott",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potter",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potter",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potter",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potter",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potton",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potts",
"given": "JB",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potts",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potts",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poudel",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poudyal",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poultney",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poulton",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poustie",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Powell",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Powell",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Powell",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Power",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Power",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Power",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poxon",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poyner",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poyner",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prabhu",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prabowo",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pradhan",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pradip",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prady",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prananingtias",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prasad",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prasad",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prasad",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prasanth Raj",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prasath",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pratiwi",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pratley",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pratt",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prayuda",
"given": "CB",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Preiss",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prendergast",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prentice",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prentice",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prescott",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Presland",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prest",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Preston",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pretorius",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prevatt",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prew",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Price",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Price",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Price",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Price",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Price",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Price",
"given": "LJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Price",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Price",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Price-Eland",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Priest",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prieto",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Primrose",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prince",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prince",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prince",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pringle",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prior-Ong",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pristopan",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pritchard",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pritchard",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pritchard",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Priyash",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Procter",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Proctor",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Protopapas",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Proudfoot",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prudon",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pryor",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pudi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puffett",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pugh",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pugh",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pugh",
"given": "MT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pugh",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pugh",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puisa",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puji Lestari",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puliyakkadi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pullen",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Punia",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Punnilath Abdulsamad",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purandare",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purchase",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purdue",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purdy",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purewal",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purnell",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pursell",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purssord",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purves",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purvis",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puspatriani",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Putensen",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Putu",
"given": "SI",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puvaneswaran",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puxty",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puxty",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Puyrigaud",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pyart",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pye",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pynn",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qadeer",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qayum",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quah",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quaid",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quail",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quamina",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quang",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quang",
"given": "NN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quarm",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quartermaine",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quartey",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quasim",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quaye",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quayle",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quek",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quenby",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qui",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qui",
"given": "X",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quick",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quigley",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quijano-Campos",
"given": "J-C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quindoyos",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quinn",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quinn",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quinn",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quist",
"given": "LJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quratulain",
"given": "Q",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qureshi",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qureshi",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qureshi",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qureshi",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qureshi",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qureshi",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qurratulain",
"given": "Q",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qutab",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quyen",
"given": "DTH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quyen",
"given": "NTH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rabbani",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rabinowicz",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raceala",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rachid",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rachman",
"given": "BE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rachman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rad",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Radford",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Radford",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Radhakrishnan",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rafferty",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rafiq",
"given": "MY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rafiq",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rafique",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rafique",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rafique",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ragatha",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raghunathan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raguro",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raha",
"given": "SD",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahama",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahardjani",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahilly",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahim",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahimi",
"given": "AH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahimi",
"given": "HR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahman",
"given": "SU",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahmany",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rai",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rai",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raisova",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raithatha",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raj",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajagopal",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajagopalan",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajaiah",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajalingam",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajasekaran",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajasri",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajbhandari",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajbhandari",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajeswaran",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajeswary",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajkanna",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajkumar",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajmohan",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rallan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ralston",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ralston",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ram",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramabhadran",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramali",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramali",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramanan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramanna",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramasamy",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rambe",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramchandani",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramdin",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramirez",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramirez",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramnarain",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramnarine",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramos",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rampling",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramraj",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramsay",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramshaw",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rana",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rana",
"given": "GF",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rana",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rana",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rand",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rand",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Randheva",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ranga",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rangar",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rangarajan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ranjan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rank",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ranka",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rankhelawon",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rankin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rao",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rao",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rao",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rasheed",
"given": "AA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rashid",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rason",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raspa",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rastogi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rasul",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ratcliff",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ratcliffe",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rath",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rath",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rather",
"given": "MI",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rathod",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rathore",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ratnakumar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ratoff",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rattehalli",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ravaccia",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raval",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ravencroft",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raw",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raw",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rawal",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rawashdeh",
"given": "SA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rawlins",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ray",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raymond-White",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raynard",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rayner",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rayner",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raynsford",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Razvi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Razvi",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Read",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Read",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reay",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reddington",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reddy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reddy",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Redfearn",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Redfern-Walsh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Redknap",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Redman",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Redome",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Redome",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reed",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reed",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rees",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rees",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rees",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rees",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rees",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rees",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rees",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rees-Jones",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Regan",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Regan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Regan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Regan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rege",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Regmi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rehan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rehman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rehman",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rehman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rehman",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reid",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reid",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reid",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reilly",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reilly",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reith",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reka",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Remegoso",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rengan",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Renouf",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Renshaw",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Renu Vattekkat",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reschreiter",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Revels",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Revill",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rewitzky",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rey",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reynard",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reynish",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reynolds",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reynolds",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rhodes",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riaz",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ribeiro",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rice",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rice",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rice",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rich",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richards",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richards",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richards",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richardson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richardson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richardson",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richardson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richardson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richardson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riches",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riches",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richmond",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Richmond",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ricketts",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rickman",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riddell",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ridgway",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ridha",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ridley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ridley",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rieck",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rigby",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rigby",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rigler",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rijal",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rika",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riley",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riley",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riley",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rimainar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rimba",
"given": "ZVP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rimmer",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rina",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rintoul",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riordan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ripley",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rippon",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rishton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riste",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ritchie",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ritchie",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ritchings",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rivera Ortega",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rivers",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rizvi",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rizvi",
"given": "SAS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rizvi",
"given": "SHM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robb",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robbins",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robertson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robertson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robertson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robertson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robertson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robertson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robertson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robin",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rocca",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roche",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roche",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodden",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roddick",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roddy",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roddy",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roderick",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodger",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodger",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodger",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodger",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodgers",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodgers",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodgers",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodgers",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodriguez-Belmonte",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roe",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roehr",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rojkova",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roka",
"given": "KK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rokadiya",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rollins",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rollo",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rolls",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rond-Alliston",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rook",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rooney",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rooney",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosaroso",
"given": "LP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosby",
"given": "EJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rose",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rose",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rose",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosier",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roskilly",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ross",
"given": "GA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ross",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ross",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rossdale",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ross-Parker",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rostron",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosyid",
"given": "AN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rothman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rothwell",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roughley",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rourke",
"given": "CA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowan",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowe",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowe-Leete",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowlands",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowlands",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowley",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roycroft",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roynon-Reed",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Royson",
"given": "AR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rozewicz",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rudenko",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rudrakumar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rudran",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ruff",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rughani",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rule",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rundell",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rushforth",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rushmer",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rusk",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Russell",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Russell",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Russo",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rutgers",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rutkowski",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryan",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryan",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryan",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryan-Wakeling",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rybka",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryder",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ryder",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saad",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saalmink",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sabale",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sabaretnam",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sadiq",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sadler",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saffy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sage",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sagoo",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sagrir",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saha",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saha",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sahdev",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sahedra",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sahota",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Said",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saini",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saini",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saint",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sairam",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sajid",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sakthi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sakuri",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saladi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salam",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salberg",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salciute",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saleeb",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saleh",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salih",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salih",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salim",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salisbury",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saliu",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salmon",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salmon",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salutous",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sam",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sam",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samakomva",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saminathan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samlal",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sammons",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sammut",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sammut",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sammut",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sammut",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sampath",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sampson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sampson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samuel",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samuel",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samuel",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samuel",
"given": "TDL",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samuel",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samuels",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samuels",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samways",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samyraju",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sana",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanchez",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanchez Gonzalez",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanda-Gomez",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sandercock",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanders",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanderson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanderson",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sandhu",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sandhu",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sandow",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sandrey",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sands",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanga",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sangha",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanghera",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sangombe",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanju",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sankaran",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santos",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santos Ferreira De Almeida",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santosh",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanyal",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanz-Cepero",
"given": "AF",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sapkota",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saragih",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saralaya",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saraswati",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saraswatula",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saravanamuthu",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarawade",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarella",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarfatti",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sargent",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sari",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sari",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarkar",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarkar",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarkar",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarkar",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarma",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarmiento",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarwar",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sass",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Satchithananthasivam",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sathe",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sathianandan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sathyanarayanan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sathyanarayanan",
"given": "SJP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sathyapalan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Satodia",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saulite",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saunders",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saunders",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saunders",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saunderson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Savill",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Savlani",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saxena",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saxton",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sayan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sayers",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scaletta",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scanlon",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scanlon",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scarratt",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scattergood",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schadenberg",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schafers",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schneblen",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schofield",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schofield",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schofield",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scholes",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scholes",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schoolmeesters",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schumacher",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schunke",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schuster Bruce",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schwarz",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scobie",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scoones",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scorrer",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scourfield",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scrase",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scriven",
"given": "NA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scullion",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scullion",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seager",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seagrave",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seaman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sear",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seaton",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seatter",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seckington",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sedano",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seddon",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sedgwick",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "See",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seelarbokus",
"given": "MA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sefton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Segovia",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seidu",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sekadde",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Selby",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Selby",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sellar",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sellars",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sellers",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Selley",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sellick",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Selvadurai",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Selvarajah",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Selvaskandan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Selvendran",
"given": "SS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Selwyn",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Semmens",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Semple",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sen",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sen",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sen",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sengupta",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sengupta",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Senra",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Senya",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Serafimova",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sernicola",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sethi",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sethi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Setty",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seward",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sewdin",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sewell",
"given": "T-A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seymour",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seymour",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shabbir",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shackley",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shafi",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shafique",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "H-A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Q",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "SH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahad",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahnazari",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahzad",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahzeb",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaibu",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaida",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaikh",
"given": "AY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaikh",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shail",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaji",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shakeel",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shakya",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shalan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shameem",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shamim",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shamji",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shams",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shams",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shamsah",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shanahan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharaf",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharif",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "SD",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharp",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharp",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharp",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharp",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharp",
"given": "LM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharratt",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharrocks",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shashaa",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "TG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shawcross",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shawcross",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shawe",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shayler",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shedwell",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheffield",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shehata",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheik",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheikh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheikh",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shelley",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shelton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shenoy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shenton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shephardson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shepherd",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shepherd",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shepherd",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shepherd",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheppard",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheppeard",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheridan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheridan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sherridan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sherris",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sherwin",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shibly",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shiham",
"given": "FF",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shilladay",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shillitoe",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shingadia",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shioi",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shirgaonkar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shirley",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shirt",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shonubi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shoote",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shorrocks",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shortman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shotton",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shotton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shovelton",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shpuza",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shrestha",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shrestha",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shrestha",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shrestha",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shrestha",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shuker",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shurlock",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shurmer",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shuvo",
"given": "ER",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siabi",
"given": "SK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siame",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siamia",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siaw-Frimpong",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siddavaram",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siddique",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siddique",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siddique",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siddle",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sidebotham",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sidebottom",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sievers",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siggens",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sikondari",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Silanas",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Silva",
"given": "SV",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Silva Moniz",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sim",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simangan",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simbi",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sime",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simmons",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simmons",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simms",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simon",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simon",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simon",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpkins",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sinclair",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sing",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singhal",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singizi",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singler",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sinha",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sinha",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sinha",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sinha",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sisson",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sithiravel",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sivakumar",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sivakumar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sivakumran",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sivanadarajah",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sivasothy",
"given": "P-R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skaria",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skehan",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skelly",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skelton",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skene",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skinner",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skinner",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skinner",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skorko",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skorupinska",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skorupinska",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Slack",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Slack",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Slade",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Slade",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Slater",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Slawson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Slingsby",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sloan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sloan",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sloan",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sloane",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Slowinska",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Small",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Small",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Small",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smallridge",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smalls",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smallshaw",
"given": "KD",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smallwood",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smart",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smart",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smeaton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smit",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "MA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smolen",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smuts",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smyth",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Snell",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Snell",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Snell",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "So",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "So",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sobama",
"given": "RF",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sobande",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sobowiec Kouman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sobrino Diaz",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sohail",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sohal",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soiza",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Solademi",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soleimani",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Solesbury",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soliman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Solis",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Solly",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Solomon",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Somalanka",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Somashekar",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sommerfield",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soni",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sonia",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sonoiki",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soo",
"given": "S-C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soor",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soothill",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soren",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sothinathan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sothirajah",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sousa",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soussi",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Southam",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Southern",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Southern",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Southern",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Southin",
"given": "SM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Southwell",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Southworth",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sowden",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sowter",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spalding",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spata",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Speare",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spears",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spears",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Speirs",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Speirs",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spence",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spence",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spencer",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spencer",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spencer",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spencer",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spencer",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spickett",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spillane",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spiller",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spinks",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spinks",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spittle",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spray",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spriggs",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Spring",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Squires",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Squires",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Squires",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sreenivasan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sreenivasan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sri",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sri Paranthamen",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Srikantaiah",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Srinivasan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Srinivasan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Srirajamadhuveeti",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Srirathan",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ssiabi",
"given": "SK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stacey",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stacpoole",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stadon",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stagg",
"given": "WJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Staines",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Staines",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stammers",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stanciu",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stanczuk",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Standley",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Staniforth",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stanton",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stanton",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Staples",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stapley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Staplin",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stark",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Starkey",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Starnes",
"given": "DS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Starr",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stead",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stebbing",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Steele",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Steer",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Steer",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stefania",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stefanowska",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Steffensen",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stemp",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stenson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stephens",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stephensen",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stephenson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sterrenburg",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stevens",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stevens",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stevens",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stevenson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stevenson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stevenson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Steward",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stewart",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stewart",
"given": "DA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stewart",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stewart",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stewart",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stickley",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stiller",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stirrup",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stock",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stockdale",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stocker",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stockham",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stockton",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stoddard",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stoffberg",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stokes",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stone",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stone",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stone",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stoner",
"given": "E-J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Storey",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Storton",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stourton",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Strachan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Strait",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stratton",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stratton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Straw",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Streit",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stride",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stringer",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Strong-Sheldrake",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Struik",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stuart",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stubbs",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stubbs",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sturdy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sturney",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stuttard",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suarez",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Subba",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Subbe",
"given": "CP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Subramaniam",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Subramanian",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Subramanian",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Subudhi",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suckling",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sudershan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sugden",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suherman",
"given": "PA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sukla",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sukumaran",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suleiman",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suliman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suliman",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sultan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sumardi",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sundar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sundaram",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sundhar",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sung",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sunni",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suntharalingam",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sur",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suresh",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suresh",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suresh",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Surtees",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Susan",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suter",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suthar",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sutherland",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sutherland",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sutherland",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sutinyte",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sutton",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sutton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sutu",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Svensson",
"given": "M-L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Svirpliene",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swain",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swain",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swaine",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swales",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swanson-Low",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swart",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sweetman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swift",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swift",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swift",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swingler",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swinhoe",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swist-Szulik",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swithenbank",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Syed",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sykes",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sykes",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sykes",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sylvester",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Symington",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Symon",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Syndercombe",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Syrimi",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Syson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szabo",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szabó",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szakmany",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szarazova",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szekely",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szekeres",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szeto",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Szymiczek",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tabish",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tadros",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tageldin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tague",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tahir",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tahir",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tai",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tait",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Takyi",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Talbot",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Talbot -Smith",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Talbot-Ponsonby",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tallent",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tallon",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Talukdar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "BT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "JS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "WT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tana",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanner",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanney",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanqueray",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanton",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tantri",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tanzil-Al-Imran",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tarft",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taribagil",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tarin",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tariq",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tarpey",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tarr",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tarrant",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tasiou",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tate",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tate",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tate",
"given": "ML",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tate",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tatham",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tavares",
"given": "SS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tavoukjian",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tay",
"given": "SAI",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "CA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor-Siddons",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taynton",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Te",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teasdale",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teasdale",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teasdale",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tebbutt",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tee",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teeluck",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tejero Moya",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tejwani",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Telfer",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teli",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tempany",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Temple",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Temple",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tench",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teoh",
"given": "YH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tereszkowski-Kaminski",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Terrett",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Terry",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tesha",
"given": "TIM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tetla",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tewari",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tewkesbury",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Texeira",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tey",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thach",
"given": "PN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thake",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thakker",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thakker",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thakrar",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thakuri",
"given": "BJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thamu",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thao",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thao",
"given": "HP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thao",
"given": "NN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thao",
"given": "NT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thapa",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thatcher",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thayanandan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thazhatheyil",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thein",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Theocharidou",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thet",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thevarajah",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thevendra",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thi",
"given": "VTK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thien",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thiri Phoo",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thirlwall",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thirumaran",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "JL",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomasson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas-Turner",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomson",
"given": "BG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thorburn",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thorn",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thorne",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thorne",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thornton",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thornton",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thornton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thornton",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thornton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thornton",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thorpe",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thorpe",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thorpe",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thozthumparambil",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thrasyvoulou",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thraves",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thu",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thu",
"given": "NM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thueux",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thuong",
"given": "NTH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thu-Ta",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thuy",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thuy",
"given": "DTT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thwaiotes",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thwaites",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thwaites",
"given": "CL",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thwaites",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tiberi",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tieger",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tierney",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tighe",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tilbey",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Till",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tiller",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tiller",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Timerick",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Timlick",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Timmins",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Timmis",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Timms",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Timoroksa",
"given": "A-M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tinashe",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tingley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tinker",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tinkler",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tinkler",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tipper",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tirumalai Adisesh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tivenan",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tluchowska",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "T-Michael",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Todd",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Todd",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Todd",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Toffoletti",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tohfa",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tohill",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tolson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tomas",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tomasova",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tomlin",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tomlins",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tomlinson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tomlinson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tonkin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tonna",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Toohey",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Topham",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Topping",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torokwa",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torrance",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Touma",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tous Sampol",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tousis",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tout",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tovey",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Towersey",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Townley",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tozer",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tran",
"given": "DK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tran",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tran",
"given": "HB",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tran",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tran",
"given": "NB",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tran",
"given": "VG",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tran",
"given": "VK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trang",
"given": "NTH",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tranter",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Travers",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Travill",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Traynor",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trethowan",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Treus Gude",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trevelyan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trewick",
"given": "NA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tridente",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trieu",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Triggs",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trim",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trimmings",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trinick",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tripathy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trivedi",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Troedson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tropman",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trotter",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trous",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trower",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trowsdale Stannard",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trudgill",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Truell",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Truman",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Truslove",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trussell",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trussell",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsakiridou",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsang",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsang",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsawayo",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsilimpari",
"given": "KK",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsinaslanidis",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsitsi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tso",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tu",
"given": "HTC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tucker",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tucker",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tucker",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tudor",
"given": "DE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tufail",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tuff",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tuffney",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tully",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tulus Satriasih",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tunesi",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tung",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tung",
"given": "DQ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turbitt",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turel",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turgut",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turley",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turnbull",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "LC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner-bone",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turney",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turvey",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tuyen",
"given": "NTM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tweed",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tweed",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Twemlow",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Twohey",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tyagi",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tyagi",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tyer",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tyler",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tyler",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tyzack",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tzavaras",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tzinieris",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uddin",
"given": "AW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uddin",
"given": "MS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uddin",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ugoji",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ukaegbu",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ul Haq",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ul Hassan",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ul-Haq",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ullah",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Um",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Umaipalan",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Umate",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Umeadi",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Umeh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Umeojiako",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ummat",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Underhill",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Underwood",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Underwood",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Unsworth",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uppal",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uppal",
"given": "VS",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Upson",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ur Rasool",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uriel",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Urruela",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uru",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Usher",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Usher",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Usher",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Usher-Rea",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ustianowski",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Usuf",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Utomo",
"given": "FN",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uzu",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vaccari",
"given": "LC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vaghela",
"given": "U",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vaidya",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vail",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valecka",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valentine",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valeria",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vallabhaneni",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valleri",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vallotton",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vamplew",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vamvakiti",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vamvakopoulos",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Van",
"given": "CTC",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Van Blydenstein",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "van Bruggen",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "van de Venne",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "van der Meer",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "van der Stelt",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Van Doorn",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "van Koutrik",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Van Loggerenberg",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vance-Daniel",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vancheeswaran",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vandeyoon",
"given": "SI",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vankayalapati",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vanmali",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vansomeren",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Van't Hoff",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vara",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vardy",
"given": "SJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varghese",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varghese",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varney",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varnier",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varouxaki",
"given": "A-N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Varquez",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vasadi",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vass",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vassell",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vasu",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vasudevan",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vatish",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vaughan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vayalaman",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vayapooree",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vaz",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Veale",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Veerasamy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Velankar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Velauthar",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Veli",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vella",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Velugupati",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Velusamy",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Venables",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Venditti",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Venkataramakrishnan",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Venn",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Venter",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ventilacion",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vere",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Veres",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vergnano",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Verling",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Verma",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vernall",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vernon",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vertue",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Verueco",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Verula",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Veterini",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vethanayagam",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vettikumaran",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Veys",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vickers",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Victor",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Victoria",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vidaillac",
"given": "CP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vidler",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vijayakumar",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vijayaraghavan Nalini",
"given": "VW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vilcinskaite",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vileito",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vilimiene",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vinall",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vinay",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vinayakarao",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vincent",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vincent",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vinh",
"given": "NQ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Virdee",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Virgilio",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Virk",
"given": "AM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Visentin",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vitaglione",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vithian",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vittoria",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vivekananthan",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vlad",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vlies",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "von Oven",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vooght",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vu Thai",
"given": "KT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vutipongsatorn",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vuylsteke",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vyras",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wach",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wadams",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wadd",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waddington",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wade",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wadsley",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wadsworth",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wafa",
"given": "SEI",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wagstaff",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wagstaff",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wahab",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wahbi",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waheed Adigun",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waidyanatha",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waite",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wake",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wakefield",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wakeford",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wakinshaw",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waldeck",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walden",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walding",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waldron",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waldron",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wales",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wali",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wallace",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wallbutton",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wallen",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wallendszus",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waller",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waller",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wallis",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wallis",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wallis",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walmsley",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walsh",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walsh",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walsh",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walstow",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walter",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walters",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walters",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walters",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walton",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walton",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walton",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walton",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wanda",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wands",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wane",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warbrick",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warburton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warden",
"given": "SA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wardere",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wardle",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wardy",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waring",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waring",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warmington",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warner",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warner",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warnock",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warran",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warren",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warren",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warren",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warren",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warrender",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warren-Miell",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warris",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Warwick",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wassall",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wasserman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wasson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watchorn",
"given": "HJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waterfall",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waters",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waters",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waterstone",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watkin",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watkins",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watkins",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watkins",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watkins",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "AJR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "JGR",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watters",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watterson",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wattimena",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watts",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watts",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watts",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waugh",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wayman",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wayman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wazir",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weatherhead",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weatherly",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Webb",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Webb",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Webb",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Webb",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Websdale",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Webster",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Webster",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Webster",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Webster",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wedlin",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wee",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weerakoon",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weerasinghe",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weeratunga",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weetman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weichert",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Welch",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Welch",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Welch",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Welch",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Welch",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Welham",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weller",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wellings",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wells",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wellstead",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Welsh",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Welsh",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Welters",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Welton",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wenn",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wentworth",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wesonga",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wesseldine",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "West",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "West",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "West",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "West",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Western",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Westhead",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weston",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Westwood",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Westwood",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Westwood",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wetherill",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wheaver",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wheeler",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whelan",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whelband",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whileman",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whitcher",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whitehead",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whitehorn",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whitehouse",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whitehouse",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whitehouse",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whiteley",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whiteley",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whiteley",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whitham",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whitlingum",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whitmore",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whittaker",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whittam",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whittington",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whittle",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Whittle",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiafe",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiblin",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wickens",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Widdrington",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wieboldt",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wieringa",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiesender",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiffen",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wight",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wignall",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wignall",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilce",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilcock",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilcock",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilcox",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wild",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wild",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wild",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilde",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilding",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilding",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wildsmith",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wileman",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiles",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiles",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilhelmsen",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiliams",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilkie",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilkin",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilkins",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilkins",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilkins",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilkinson",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilkinson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilkinson",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilkinson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilkinson",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Willetts",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "CV",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "JD",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Willis",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Willis",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Willis",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wills",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Willsher",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Willshire",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Willson",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Willson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "K-A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Win",
"given": "KLY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Win",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Win",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Win",
"given": "TT",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Win",
"given": "WYW",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winckworth",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winder",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winder",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winearl",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winmill",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winn",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winpenny",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winslow",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winter",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winter",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winter-Goodwin",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winterton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winwood",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wischhusen",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wisdom",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wise",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiselka",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiseman",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiseman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wishart",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "WIshlade",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Witele",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Withers",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wittes",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wixted",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wodehouse",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wolf",
"given": "W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wolff",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wolffsohn",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wolf-Roberts",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wolodimeroff",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wolstencroft",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "C-H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "C-M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "JSY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "KY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "MY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wongkyezeng",
"given": "AA",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodall",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodfield",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodford",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodford",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodford",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodhead",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodhead",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodland",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodmansey",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woods",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woods",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woods",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woods",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woodward",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woolcock",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wooldridge",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woolf",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woollard",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woollen",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woolley",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woolley",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Woosey",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wootton",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wootton",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Worley",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Worton",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wraight",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wray",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wren",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wren",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wrey Brown",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wroe",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wroe",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wubetu",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wulandari",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wulandari",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wurie",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wyatt",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wyn-Griffiths",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wynter",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xavier",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xhikola",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xia",
"given": "BE",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xia",
"given": "Z",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yacoba",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yadav",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yakubi",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yanagisawa",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Y",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yanney",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yap",
"given": "WL",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yaqoob",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yasmin",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yates",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yates",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yates",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yates",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yates",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yates",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ye",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yearwood Martin",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yein",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yelnoorkar",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yen",
"given": "LM",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yeoh",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yeung",
"given": "CY",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yew",
"given": "P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yewatkar",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ylquimiche Melly",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ynter",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yong",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yorke",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Youens",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Younes Ibrahim",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Young",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Young",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Young",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yousafzar",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Youssouf",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yousuf",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yovita",
"given": "H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "JSJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yufaniaputri",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yung",
"given": "B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yusef",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yusef",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yusuf",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zafar",
"given": "A-S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zagalo",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zaher",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zahoor",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zainab",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zak",
"given": "T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zaki",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zakir",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zalewska",
"given": "K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zamalloa",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zaman",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zaman",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zamikula",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zammit",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zammit-Mangion",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zawadzka",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zayed",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zebracki",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zehnder",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeidan",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeinali",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "X",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zia",
"given": "M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zibdeh",
"given": "O",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zill-E-Huma",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zin",
"given": "ET",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zincone",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zindoga",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zinkin",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zinyemba",
"given": "V",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zipitis",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zitter",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zmierczak",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zubikarai",
"given": "G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zubir",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zuhra",
"given": "N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zulaikha",
"given": "R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zulfikar",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zullo",
"given": "C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zuriaga-Alvaro",
"given": "A",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"em-consulte.com",
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-15T22:34:30Z",
"timestamp": 1747348470000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-15T22:34:34Z",
"timestamp": 1747348474000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100014013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100014013",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "UK Research and Innovation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100010269",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100010269",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Wellcome Trust"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-15T23:10:09Z",
"timestamp": 1747350609381,
"version": "3.40.5"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1746057600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1746057600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1740528000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1473309925000933?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1473309925000933?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with COVID-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib1",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"article-title": "Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 in outpatients",
"author": "Gottlieb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "305",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib2",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib3",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00163-5",
"article-title": "Casirivimab and imdevimab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "665",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib4",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1004107",
"article-title": "Global SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence from January 2020 to April 2022: a systematic review and meta-analysis of standardized population-based studies",
"author": "Bergeri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib5",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00519-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and three other drugs for hospitalised patients with COVID-19: final results of the WHO Solidarity randomised trial and updated meta-analyses",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1941",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib7",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00528-8",
"article-title": "Effects of remdesivir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Amstutz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "453",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib8",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00766-18",
"article-title": "Orally efficacious broad-spectrum ribonucleoside analog inhibitor of influenza and respiratory syncytial viruses",
"author": "Yoon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00766",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib9",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abb5883",
"article-title": "An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice",
"author": "Sheahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib10",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.00953-23",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir maintains antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants and exhibits a high barrier to the development of resistance",
"author": "Strizki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib11",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6",
"article-title": "A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes",
"author": "Sanderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "594",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib12",
"volume": "623",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib13",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Butler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib14",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/EVIDoa2100044",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of molnupiravir or placebo in patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "Arribas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "NEJM Evid",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib15",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"article-title": "An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1586",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib16",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2309003",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with COVID-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1186",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib17",
"volume": "390",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter randomized controlled study",
"author": "Liu",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health West Pac",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib18",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib19",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2022926",
"article-title": "Effect of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2030",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib20",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4",
"article-title": "Lopinavir–ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1345",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib21",
"volume": "396",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00149-5",
"article-title": "Azithromycin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "605",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib22",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1637",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib23",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2049",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib24",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Aspirin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib25",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01109-6",
"article-title": "Baricitinib in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial and updated meta-analysis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib26",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00510-X",
"article-title": "Higher dose corticosteroids in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 who are hypoxic but not requiring ventilatory support (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1499",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib27",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Rapid turnaround multiplex sequencing of SARS-CoV-2: comparing tiling amplicon protocol performance",
"author": "Constantinides",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00644-2",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir versus placebo in unvaccinated and vaccinated patients with early SARS-CoV-2 infection in the UK (AGILE CST-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2 trial",
"author": "Khoo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "183",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib29",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus",
"author": "Fischer",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00093-3_bib30",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1473309925000933"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir plus usual care versus usual care alone in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}