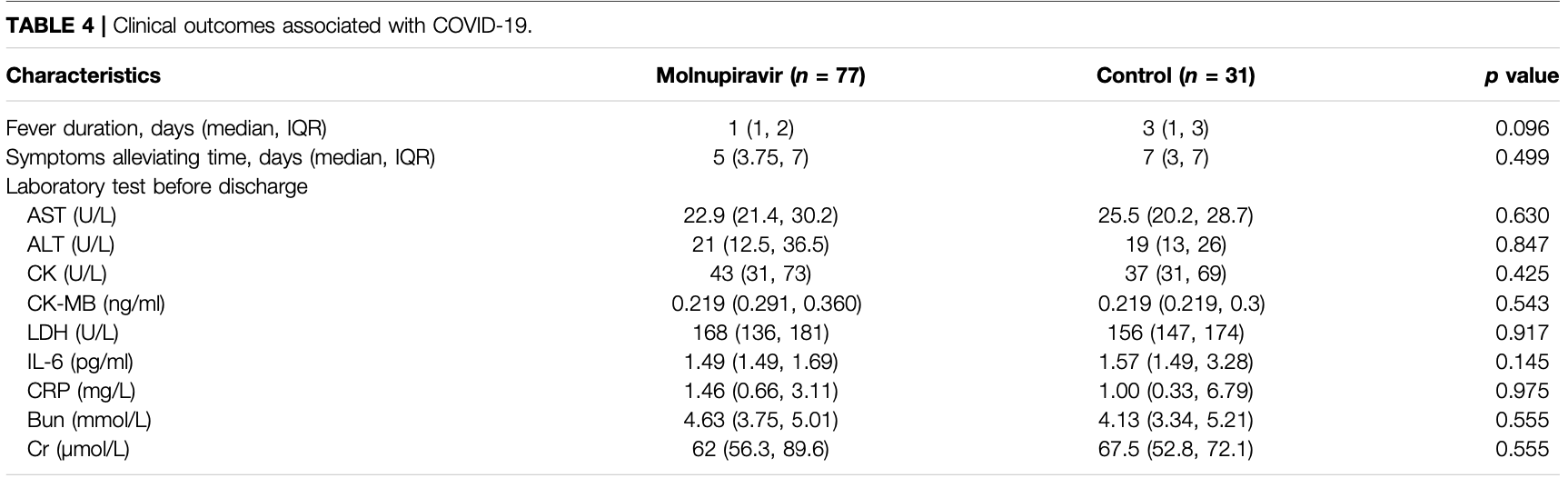
Antiviral Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir Against Omicron Variant Infection: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.939573, ChiCTR2200056817, Jun 2022
RCT 116 mild/moderate COVID-19 patients in China, showing improved viral clearance with treatment.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments25.
|
recovery time, 28.6% lower, relative time 0.71, p = 0.50, treatment 77, control 31.
|
|
time to viral-, 10.0% lower, relative time 0.90, p = 0.009, treatment 76, control 31.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 51.1% lower, RR 0.49, p = 0.02, treatment 18 of 76 (23.7%), control 15 of 31 (48.4%), NNT 4.0, day 10.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 36.7% lower, RR 0.63, p < 0.001, treatment 45 of 76 (59.2%), control 29 of 31 (93.5%), NNT 2.9, day 7.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 18.4% lower, RR 0.82, p = 0.009, treatment 62 of 76 (81.6%), control 31 of 31 (100.0%), NNT 5.4, day 5.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
23.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Zou et al., 15 Jun 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, China, peer-reviewed, 16 authors, study period 3 March, 2022 - 21 March, 2022, trial ChiCTR2200056817.
Contact: lis.lisong@gmail.com, luhongzhou@szsy.sustech.edu.cn, zhongwu@bmi.ac.cn, szsy_lyx@szsy.sustech.edu.cn.
Antiviral Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir Against Omicron Variant Infection: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.939573
Background: The rapid worldwide spread of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 has unleashed a new wave of COVID-19 outbreaks. The efficacy of molnupiravir, an approved drug, is still unknown in patients infected with the Omicron variant. Objective: Evaluated the antiviral efficacy and safety of molnupiravir in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, with symptom duration within 5 days. Methods: We conducted a randomized, controlled trial involving patients with mild or moderate COVID-19. Patients were randomized to orally receive molnupiravir (800 mg) plus basic treatment or only basic treatment for 5 days (BID). The antiviral efficacy of the drug was evaluated using reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. Results: Results showed that the time of viral RNA clearance (primary endpoint) was significantly decreased in the molnupiravir group (median, 9 days) compared to the control group (median, 10 days) (Log-Rank p = 0.0092). Of patients receiving molnupiravir, 18.42% achieved viral RNA clearance on day 5 of treatment, compared to the control group (0%) (p = 0.0092). On day 7, 40.79%, and 6.45% of patients in the molnupiravir and control groups, respectively, achieved viral RNA clearance (p = 0.0004). In addition, molnupiravir has a good safety profile, and no serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusion: Molnupiravir significantly accelerated the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron RNA clearance in patients with COVID-19.
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen (No. 2022-034-02) . The patients/ participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.939573/ full#supplementary-material Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Publisher's Note: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Arora, Zhang, Rocha, Sidarovich, Kempf et al., Comparable Neutralisation Evasion of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants BA.1, BA.2, and BA.3, Lancet. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(22)00224-9
Bernal, Gomes Da Silva, Musungaie, Kovalchuk, Gonzalez et al., Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Chen, Wang, Gilby, Wei, Omicron Variant (B.1.1.529): Infectivity, Vaccine Breakthrough, and Antibody Resistance, J. Chem. Inf. Model, doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.1c01451
Cheng, Ip, Chu, Tam, Chan et al., Rapid Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron Subvariant BA.2 in a Single-Source Community Outbreak, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac203
Fischer, Eron, Jr, Holman, Cohen et al., A Phase 2a Clinical Trial of Molnupiravir in Patients with COVID-19 Shows Accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA Clearance and Elimination of Infectious Virus, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430
He, Hong, Pan, Lu, Wei, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant: Characteristics and Prevention, MedComm, doi:10.1002/mco2.110
Merck, Merck and Ridgeback's Molnupiravir, an Oral COVID-19 Antiviral Medicine
Rosenke, Okumura, Lewis, Feldmann, Meade-White et al., Molnupiravir Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Variants Including Omicron in the Hamster Model, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.160108
Saxena, Kumar, Ansari, Paweska, Maurya et al., Characterization of the Novel SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant of Concern and its Global Perspective, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27524
Shuai, Chan, Hu, Chai, Yuen et al., Attenuated Replication and Pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04442-5
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Sakai-Tagawa, Fujisaki et al., Efficacy of Antibodies and Antiviral Drugs against Covid-19 Omicron Variant, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2119407
Uraki, Kiso, Iida, Imai, Takashita et al., Characterization and Antiviral Susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron/BA.2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04856-1
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.939573",
"ISSN": [
"1663-9812"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.939573",
"abstract": "<jats:p><jats:bold>Background:</jats:bold> The rapid worldwide spread of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 has unleashed a new wave of COVID-19 outbreaks. The efficacy of molnupiravir, an approved drug, is still unknown in patients infected with the Omicron variant.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Objective:</jats:bold> Evaluated the antiviral efficacy and safety of molnupiravir in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, with symptom duration within 5 days.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Methods:</jats:bold> We conducted a randomized, controlled trial involving patients with mild or moderate COVID-19. Patients were randomized to orally receive molnupiravir (800 mg) plus basic treatment or only basic treatment for 5 days (BID). The antiviral efficacy of the drug was evaluated using reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Results:</jats:bold> Results showed that the time of viral RNA clearance (primary endpoint) was significantly decreased in the molnupiravir group (median, 9 days) compared to the control group (median, 10 days) (Log-Rank <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.0092). Of patients receiving molnupiravir, 18.42% achieved viral RNA clearance on day 5 of treatment, compared to the control group (0%) (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.0092). On day 7, 40.79%, and 6.45% of patients in the molnupiravir and control groups, respectively, achieved viral RNA clearance (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.0004). In addition, molnupiravir has a good safety profile, and no serious adverse events were reported.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Conclusion:</jats:bold> Molnupiravir significantly accelerated the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron RNA clearance in patients with COVID-19.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Clinical Trial Registration:</jats:bold> [<jats:ext-link>chictr.org.cn</jats:ext-link>], identifier [ChiCTR2200056817].</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fphar.2022.939573"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zou",
"given": "Rongrong",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shu",
"given": "Dan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lan",
"given": "Jianfeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Guoyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Jinghan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Xiangyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Miaona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Chenhui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Jing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Huxiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Song",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Hongzhou",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhong",
"given": "Wu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Yingxia",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-15T08:09:33Z",
"timestamp": 1655280573000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-17T15:49:25Z",
"timestamp": 1655480965000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-27T02:50:02Z",
"timestamp": 1685155802792
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 14,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
15
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1655251200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.939573/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1473-3099(22)00224-9",
"article-title": "Comparable Neutralisation Evasion of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants BA.1, BA.2, and BA.3",
"author": "Arora",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Lancet. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.1c01451",
"article-title": "Omicron Variant (B.1.1.529): Infectivity, Vaccine Breakthrough, and Antibody Resistance",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "412",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Model",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac203",
"article-title": "Rapid Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron Subvariant BA.2 in a Single-Source Community Outbreak",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "ciac203",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430",
"article-title": "A Phase 2a Clinical Trial of Molnupiravir in Patients with COVID-19 Shows Accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA Clearance and Elimination of Infectious Virus",
"author": "Fischer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eabl7430",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "Food and Drug Administration",
"key": "B5",
"volume-title": "Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Authorizes Additional Oral Antiviral for Treatment of COVID-19 in Certain Adults",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mco2.110",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant: Characteristics and Prevention",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "838",
"journal-title": "MedComm",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "Merck",
"key": "B8",
"volume-title": "Merck and Ridgeback’s Molnupiravir, an Oral COVID-19 Antiviral Medicine, Receives First Authorization in the World",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.160108",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Variants Including Omicron in the Hamster Model",
"author": "Rosenke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e160108",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27524",
"article-title": "Characterization of the Novel SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant of Concern and its Global Perspective",
"author": "Saxena",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1738",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04442-5",
"article-title": "Attenuated Replication and Pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron",
"author": "Shuai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2119407",
"article-title": "Efficacy of Antibodies and Antiviral Drugs against Covid-19 Omicron Variant",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "995",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04856-1",
"article-title": "Characterization and Antiviral Susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron/BA.2",
"author": "Uraki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "B14",
"volume-title": "COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 14,
"references-count": 14,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.939573/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antiviral Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir Against Omicron Variant Infection: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "13"
}