Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir in Mild COVID-19 Patients in India
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.31508, CTRI/2021/05/033739, Nov 2022
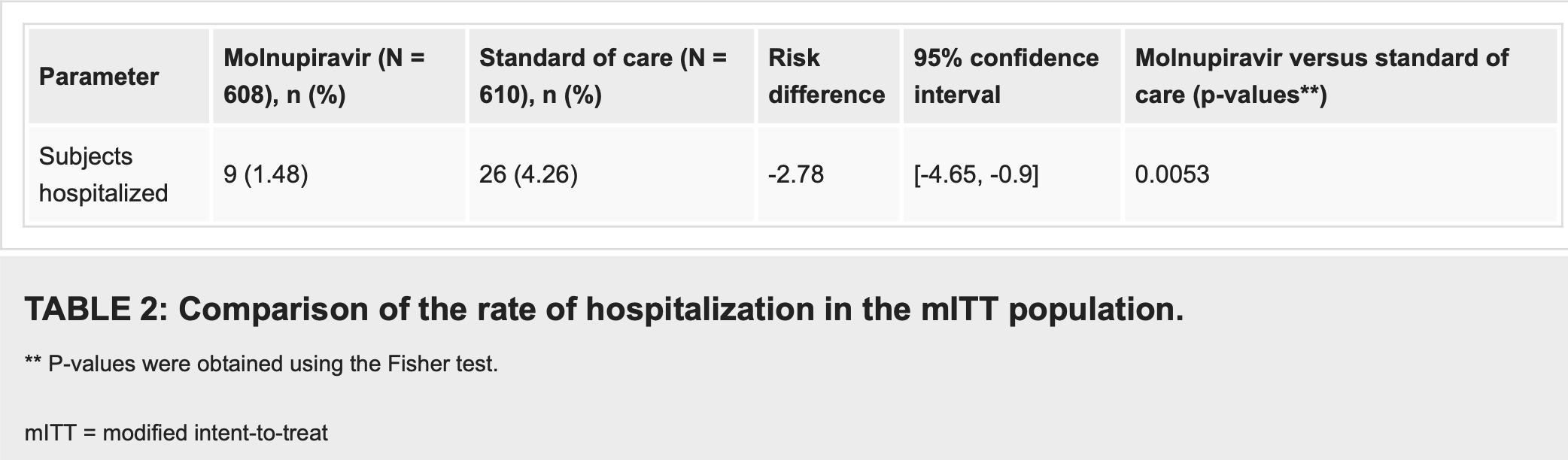
RCT 1,218 outpatients in India, showing lower hospitalization, better clinical improvement, and improved viral clearance with molnupiravir.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
|
risk of hospitalization, 65.3% lower, RR 0.35, p = 0.005, treatment 9 of 608 (1.5%), control 26 of 610 (4.3%), NNT 36.
|
|
risk of no clinical improvement, 52.8% lower, RR 0.47, p = 0.01, treatment 16 of 608 (2.6%), control 34 of 610 (5.6%), NNT 34, day 14.
|
|
relative improvement in Ct value, 48.4% better, RR 0.52, p < 0.001, treatment mean 9.5 (±7.0) n=608, control mean 4.9 (±10.6) n=610, day 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
Sinha et al., 14 Nov 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, India, peer-reviewed, 17 authors, study period May 2021 - August 2021, average treatment delay 2.0 days, licensee, trial CTRI/2021/05/033739.
Contact: leela.t@hetero.com.
Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir in Mild COVID-19 Patients in India
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.31508
Background At the peak of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the need for an orally administered agent to prevent the progression of acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection became increasingly evident, which was the impetus behind our investigations with molnupiravir. Molnupiravir has been shown to be effective in preventing hospitalizations and/or clinical complications in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. In this study, we evaluate the efficacy and safety of molnupiravir in Indian patients with mild SARS-CoV-2 infection and at least one risk factor for disease progression (CTRI/2021/05/033739).
Methodology This was a phase III, multicenter, randomized, open-label, controlled study conducted in Indian adults aged 18-60 years with mild SARS-CoV-2, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)-positive within 48 hours of enrollment in the study, and within five days of first symptom onset. Enrolled patients were randomized to treatment arms in a 1:1 ratio to receive molnupiravir or placebo in addition to the standard of care (SoC) for SARS-CoV-2 infection. The SoC was in compliance with Government of India guidelines that were in force at the time. The primary endpoint was the rate of hospitalization up to day 14. Safety endpoints included incidence of adverse events (AEs).
Results Eligible patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive molnupiravir in addition to SoC treatment (n = 608) or SoC alone (n = 610). In the molnupiravir group, nine (1.48%) patients required hospitalization versus 26 (4.26%) patients in the control group (risk difference = -2.78%; 95% CI = -4.65, -0.90; p = 0.0053). Overall, 45 (3.70%) patients reported 47 AEs during the study, most of which were mild and resolved completely. The molnupiravir group reported 30 AEs compared to 17 AEs in the control group. Headache and nausea were the two most commonly reported AEs.
Conclusions The molnupiravir arm showed a lower rate of hospitalization and a shorter time for the improvement of clinical symptoms coupled with early RT-PCR negativity. Molnupiravir was well tolerated, and AEs were mild and rare. The addition of molnupiravir to standard therapy has the potential to prevent the progression of mild COVID-19 disease to the severe form.
Additional Information
References
Cox, Wolf, Plemper, Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets, Nat Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-020-00835-2
Fischer Wa 2nd, Eron, Jr, Holman, A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430
Fischer, Eron, Holman, Molnupiravir, an oral antiviral treatment for COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.06.17.21258639
Iec Maharaja, Hospital, Ethics committee; Virinchi Hospitals Institutional Ethics Committee; Institutional Ethics Committee GGMC issued
Painter, Holman, Bush, Human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of molnupiravir, a novel broad-spectrum oral antiviral agent with activity against SARS-CoV-2, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.02428-20
Singh, Singh, Singh, Misra, An updated practical guideline on use of molnupiravir and comparison with agents having emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102396
Vasudevan, Ahlqvist, Mcgeough, A concise route to MK-4482 (EIDD-2801) from cytidine, Chem Commun (Camb), doi:10.1039/d0cc05944g
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.31508",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.31508",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sinha",
"given": "Shubhadeep",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "N",
"given": "Kumarasamy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suram",
"given": "Vasanth Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chary",
"given": "Sreenivasa S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naik",
"given": "Sunil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Veer Bahadur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jain",
"given": "Manish K",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suthar",
"given": "Chandra P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Borthakur",
"given": "Swapnav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sawardekar",
"given": "Vinayak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sk",
"given": "Noushadali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reddy",
"given": "Naveen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Talluri",
"given": "Leela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thakur",
"given": "Pankaj",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reddy",
"given": "Mohan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Panapakam",
"given": "Muralidhar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vattipalli",
"given": "Ramya",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cureus",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-15T04:33:55Z",
"timestamp": 1668486835000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-15T04:34:01Z",
"timestamp": 1668486841000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-16T05:42:36Z",
"timestamp": 1668577356316
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
14
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/118243-efficacy-and-safety-of-molnupiravir-in-mild-covid-19-patients-in-india",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4492",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cureus, Inc.",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpu.30542",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "FDA approves first treatment for COVID-19. (2020). Accessed. September 22, 2022: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-treatment-covid-19."
},
{
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 treatment. investigational drugs and other therapies. (2022). Accessed: September 22, 2022: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2500116-overview."
},
{
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "FDA halts use of COVID drugs ineffective against omicron. (2022). Accessed. September 22, 2022: https://www.webmd.com/lung/news/20220125/fda_halts_covid_drugs."
},
{
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Coronavirus (COVID-19) update. FDA authorizes new monoclonal antibody for treatment of COVID-19 that retains activity against omicron variant. (2022). Accessed: September 22, 2022: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-new-monoclonal-antibod...."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/d0cc05944g",
"article-title": "A concise route to MK-4482 (EIDD-2801) from cytidine",
"author": "Vasudevan N",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Chem Commun (Camb)",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Vasudevan N, Ahlqvist GP, McGeough CP, et al.. A concise route to MK-4482 (EIDD-2801) from cytidine. Chem Commun (Camb). 2020, 56:13363-4. 10.1039/d0cc05944g",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02428-20",
"article-title": "Human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of molnupiravir, a novel broad-spectrum oral antiviral agent with activity against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Painter WP",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Painter WP, Holman W, Bush JA, et al.. Human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of molnupiravir, a novel broad-spectrum oral antiviral agent with activity against SARS-CoV-2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021, 65:e02428-20. 10.1128/AAC.02428-20",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.06.17.21258639",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir, an oral antiviral treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "Fischer W",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Fischer W, Eron JJ, Holman W, et al.. Molnupiravir, an oral antiviral treatment for COVID-19. medRxiv. 2021, 10.1101/2021.06.17.21258639",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Merck and Ridgeback’s molnupiravir, an investigational oral antiviral COVID-19 treatment, receives special approval for emergency in Japan. (2021). Accessed. September 22, 2022: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20211224005081/en/."
},
{
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Emergency use authorization (EUA) for the emergency use of molnupiravir for the treatment of mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). (2022). Accessed. September 22, 2022: https://www.fda.gov/media/155053/download."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102396",
"article-title": "An updated practical guideline on use of molnupiravir and comparison with agents having emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Singh AK",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Singh AK, Singh A, Singh R, Misra A. An updated practical guideline on use of molnupiravir and comparison with agents having emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022, 16:102396. 10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102396",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Clinical guidance for management of adult COVID-19 patients, dated 22 Apr 2021. AIIMS/ICMR-COVID-19 National Task Force/Joint Monitoring Group (Dte. GHS). Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. (2021). Accessed. September 22, 2022: https://dghs.gov.in/WriteReadData/Orders/202104231216553337715COVIDManagementAlgorithm_22Apr21.pdf."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"article-title": "A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020, 20.e192-7. 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization - Uppsala Monitoring Centre System for standardised case causality assessment. (2018). Accessed. November 04, 2022: https://who-umc.org/media/164200/who-umc-causality-assessment_new-logo.pdf."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-00835-2",
"article-title": "Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets",
"author": "Cox RM",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Cox RM, Wolf JD, Plemper RK. Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets. Nat Microbiol. 2021, 6:11-8. 10.1038/s41564-020-00835-2",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430",
"article-title": "A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus",
"author": "Fischer WA 2nd",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Fischer WA 2nd, Eron JJ Jr, Holman W, et al.. A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus. Sci Transl Med. 2022, 14:eabl7430. 10.1126/scitranslmed.abl7430",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Merck and Ridgeback Biotherapeutics provide update on results from MOVe-OUT study of molnupiravir, an investigational oral antiviral medicine, in at risk adults with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. (2021). Accessed. September 22, 2022: https://www.merck.com/news/merck-and-ridgeback-biotherapeutics-provide-update-on-results-from-move-out-study-of-molnu...."
}
],
"reference-count": 16,
"references-count": 16,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/118243-efficacy-and-safety-of-molnupiravir-in-mild-covid-19-patients-in-india"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Aerospace Engineering"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir in Mild COVID-19 Patients in India",
"type": "journal-article"
}