Boosting Immunity: Synergistic Antiviral Effects of Luteolin, Vitamin C, Magnesium, and Zinc Against SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro
et al., Bioscience Reports, doi:10.1042/BSR20240617, Jul 2024
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
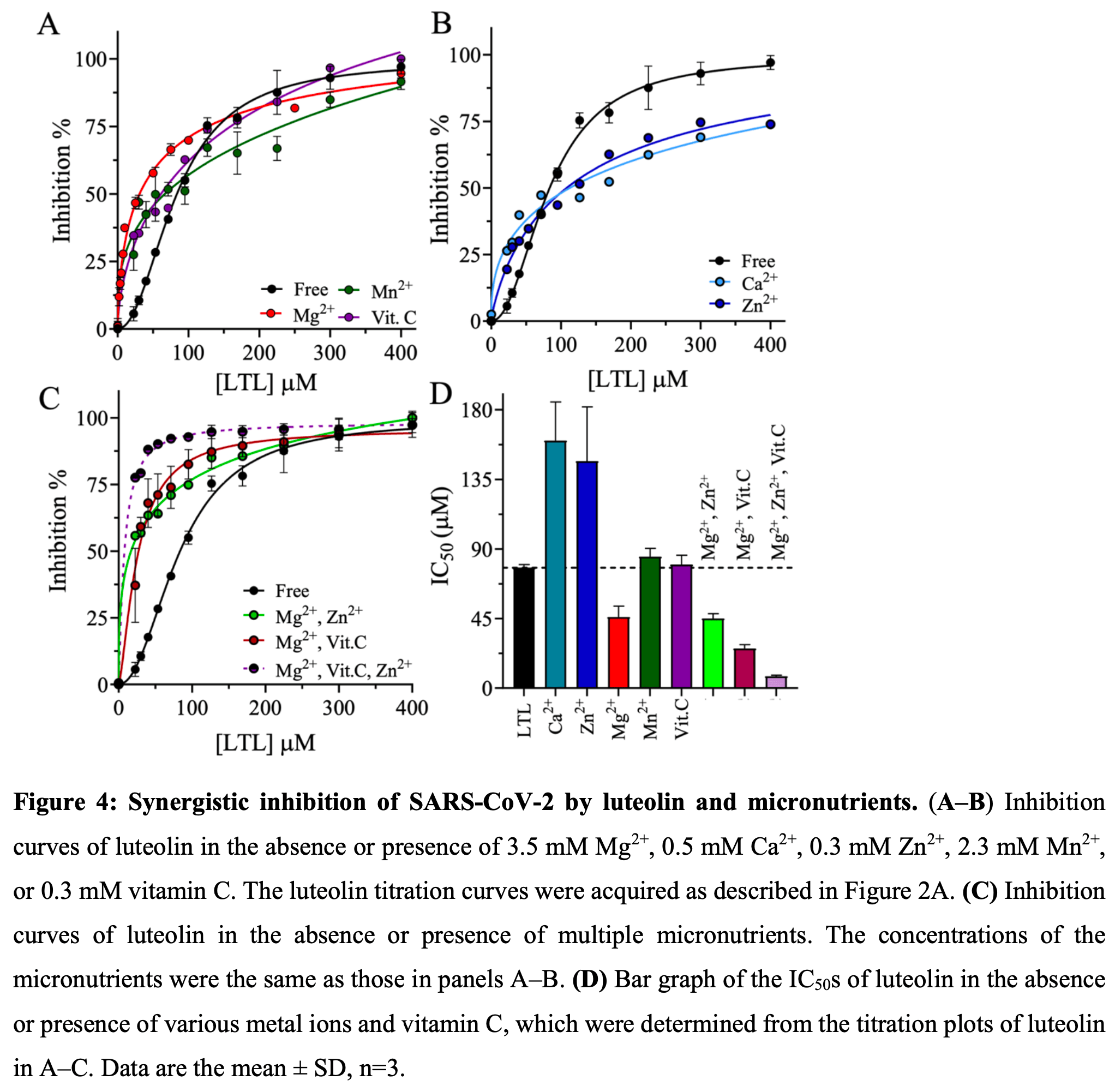
In vitro and in silico study showing synergistic antiviral effects of luteolin, vitamin C, magnesium, and zinc against SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro. Authors found that luteolin inhibited SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro with an IC50 of 78 μM, which decreased 10-fold to 7.6 μM in the presence of zinc, magnesium, and vitamin C.
17 preclinical studies support the efficacy of vitamin C for COVID-19:
Vitamin C has been identified by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) as having sufficient evidence for a causal relationship between intake and optimal immune system function15-17.
Vitamin C plays a key role in the immune system, supporting the production and function of leukocytes, or white blood cells, which defend against infection and disease, including the production of lymphocytes, which make antibodies, and enhancing phagocytosis, the process by which immune system cells ingest and destroy viruses and infected cells.
Vitamin C is an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Vitamin C inhibits SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro7,11, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2 levels in a dose-dependent manner12, and may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by acting as an antioxidant and potentially reducing the reactive oxygen species (ROS) production induced by the spike protein that contributes to the activation of profibrotic pathways9.
Vitamin C reduces inflammation, oxidative stress, and NETosis, supporting immune function and vascular protection18.
Intracellular levels of vitamin C decline during COVID-19 hospitalization suggesting ongoing utilization and depletion of vitamin C19.
Threonic acid, a metabolite of vitamin C, is lower in mild and severe cases, consistent with increased need for and metabolization of vitamin C with moderate infection, but more limited ability to produce threonic acid in severe infection due to depletion or existing lower levels of vitamin C20.
Symptomatic COVID-19 is associated with a lower frequency of natural killer (NK) cells, and vitamin C has been shown to improve NK cell numbers and functioning21,22.
Study covers vitamin C and zinc.
1.
Najimi et al., Phytochemical Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry: Targeting the ACE2‐RBD Interaction with l‐Tartaric Acid, l‐Ascorbic Acid, and Curcuma longa Extract, ChemistrySelect, doi:10.1002/slct.202406035.
2.
Rajamanickam et al., Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105.
3.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
4.
Morales-Bayuelo et al., New findings on ligand series used as SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibitors within the frameworks of molecular docking, molecular quantum similarity and chemical reactivity indices, F1000Research, doi:10.12688/f1000research.123550.3.
5.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
6.
Pandya et al., Unravelling Vitamin B12 as a potential inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2: A computational approach, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2022.100951.
7.
Malla et al., Vitamin C inhibits SARS coronavirus-2 main protease essential for viral replication, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.05.02.442358.
8.
Kumar et al., In silico virtual screening-based study of nutraceuticals predicts the therapeutic potentials of folic acid and its derivatives against COVID-19, VirusDisease, doi:10.1007/s13337-020-00643-6.
9.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
10.
Moatasim et al., Potent Antiviral Activity of Vitamin B12 against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, and Human Coronavirus 229E, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11112777.
11.
Đukić et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro with Vitamin C, L-Arginine and a Vitamin C/L-Arginine Combination, Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark, doi:10.31083/j.fbl2801008.
12.
Zuo et al., Vitamin C promotes ACE2 degradation and protects against SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, EMBO reports, doi:10.15252/embr.202256374.
13.
Hajdrik et al., In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694.
14.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
15.
Galmés et al., Suboptimal Consumption of Relevant Immune System Micronutrients Is Associated with a Worse Impact of COVID-19 in Spanish Populations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14112254.
16.
Galmés (B) et al., Current State of Evidence: Influence of Nutritional and Nutrigenetic Factors on Immunity in the COVID-19 Pandemic Framework, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092738.
17.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin C and protection of DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage (ID 129, 138, 143, 148), antioxidant function of lutein (ID 146), maintenance of vision (ID 141, 142), collagen formation (ID 130, 131, 136, 137, 149), function of the nervous system (ID 133), function of the immune system (ID 134), function of the immune system during and after extreme physical exercise (ID 144), non-haem iron absorption (ID 132, 147), energy-yielding metabolism (ID 135), and relief in case of irritation in the upper respiratory tract (ID 1714, 1715) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1226.
18.
Xie et al., The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6.
19.
Boerenkamp et al., Low Levels of Serum and Intracellular Vitamin C in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15163653.
20.
Albóniga et al., Differential abundance of lipids and metabolites related to SARS-CoV-2 infection and susceptibility, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-40999-5.
Ferreira et al., 24 Jul 2024, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Boosting Immunity: Synergistic Antiviral Effects of Luteolin, Vitamin C, Magnesium, and Zinc Against SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro
doi:10.1042/BSR20240617/959341/bsr-2024
SARS-CoV-2 was first discovered in 2019 and has disseminated throughout the globe to pandemic levels, imposing significant health and economic burdens. Although vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 have been developed, their long-term efficacy and specificity have not been determined, and antiviral drugs remain necessary. Flavonoids, which are commonly found in plants, fruits, and vegetables and are part of the human diet, have attracted considerable attention as potential therapeutic agents due to their antiviral and antimicrobial activities and effects on other biological activities, such as inflammation. This study uses a combination of biochemical, cellular, molecular dynamics, and molecular docking experiments to provide compelling evidence that the flavonoid luteolin (2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4H-chromen-4one) has antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro) that is synergistically enhanced by magnesium, zinc, and vitamin C. The IC 50 of luteolin against 2 µM 3CLpro is 78 µM and decreases 10-fold to 7.6 µM in the presence of zinc, magnesium, and vitamin C. Thermodynamic stability analyses revealed that luteolin has minimal effects on the structure of 3CLpro, whereas metal ions and vitamin C significantly alter the thermodynamic stability of the protease. Interactome analysis uncovered potential host-virus interactions and functional clusters associated with luteolin activity, supporting the relevance of this flavone for combating SARS-CoV-2 infection. This comprehensive investigation sheds light on luteolin's therapeutic potential and provides insights into its mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2. The novel formulation of luteolin, magnesium, zinc, and vitamin C may be an effective avenue for treating COVID-19 patients.
This research was partially carried out using the Core Technology Platforms resources at New York University Abu Dhabi.
Conflict of Interest JF, TC, NS, and WR are part of a US provisional patent application filed by New York University Abu Dhabi and ProPhase Labs.
References
Abraham, Murtola, Schulz, Páll, Smith et al., GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers, SoftwareX, doi:10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001
Adhikari, Amin, Jha, Dissecting the Drug Development Strategies Against SARS-CoV-2 Through Diverse Computational Modeling Techniques, doi:10.1007/7653_2020_46
Ahmad, Batool, Ul Ain, Kim, Choi, Exploring the Binding Mechanism of PF-07321332 SARS-CoV-2 Protease Inhibitor through Molecular Dynamics and Binding Free Energy Simulations, Int J Mol Sci, doi:912410.3390/ijms22179124
Ahmadian, Bahramsoltani, Kaempferol: an encouraging flavonoid for COVID-19, Bol. Latinoam. Caribe Plantas Med. Aromat, doi:10.37360/blacpma.20.19.5.33
Al Adem, Ferreira, Fadl, Mustafa, Rabeh, Key Allosteric and Active Site Residues of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Promising Drug Targets, Biochem J
Al Adem, Ferreira, Fadl, Rabeh, pH profiles of 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro) from SARS-CoV-2 elucidate its catalytic mechanism and a histidine residue critical for activity, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102790
Alexander, Tinkov, Strand, Alehagen, Skalny et al., Early Nutritional Interventions with Zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D for Raising Anti-Viral Resistance Against Progressive COVID-19, Nutrients
Amporndanai, Meng, Shang, Jin, Rogers et al., Inhibition mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by ebselen and its derivatives, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23313-7
Andreini, Arnesano, Rosato, The zinc proteome of SARS-CoV-2, Metallomics
Arentz, Hunter, Yang, Goldenberg, Beardsley et al., Zinc for the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 and other acute viral respiratory infections: a rapid review, Adv Integr Med, doi:10.1016/j.aimed.2020.07.009
Artese, Svicher, Costa, Salpini, Di Maio et al., Current status of antivirals and druggable targets of SARS CoV-2 and other human pathogenic coronaviruses, Drug Resist. Updat, doi:10.1016/j.drup.2020.100721
Baez-Santos, St John, Mesecar, The SARS-coronavirus papain-like protease: Structure, function and inhibition by designed antiviral compounds, Antivir Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.12.015
Baier, Nazaruk, Galicka, Szyszka, Inhibitory influence of natural flavonoids on human protein kinase CK2 isoforms: effect of the regulatory subunit, Mol Cell Biochem, doi:10.1007/s11010-017-3228-1
Barnes, Role of HDAC2 in the pathophysiology of COPD, Annu Rev Physiol, doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163257
Barocas, So-Armah, Cheng, Lioznov, Baum et al., Zinc deficiency and advanced liver fibrosis among HIV and hepatitis C co-infected anti-retroviral naïve persons with alcohol use in Russia, PloS one, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0218852
Bhardwaj, Liu, Leibowitz, Kao, The coronavirus endoribonuclease Nsp15 interacts with retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.07012-11
Borbone, Piccialli, Roviello, Oliviero, Nucleoside Analogs and Nucleoside Precursors as Drugs in the Fight against SARS-CoV-2 and Other Coronaviruses, Molecules
Bouhaddou, Memon, Meyer, White, Rezelj et al., The Global Phosphorylation Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.034
Cai, Yu, Wang, Liang, Richard, Arginine methylation of SARS-Cov-2 nucleocapsid protein regulates RNA binding, its ability to suppress stress granule formation, and viral replication, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100821
Chambial, Dwivedi, Shukla, John, Sharma, Vitamin C in disease prevention and cure: an overview, Indian J Clin Biochem, doi:10.1007/s12291-013-0375-3
Chatr-Aryamontri, Oughtred, Boucher, Rust, Chang et al., The BioGRID interaction database: 2017 update, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkw1102101
Chen, Li, Luo, Liu, Xu et al., Binding interaction of quercetin-3-betagalactoside and its synthetic derivatives with SARS-CoV 3CL(pro): structure-activity relationship studies reveal salient pharmacophore features, Bioorg Med Chem
Clauset, Newman, Moore, Finding community structure in very large networks, Phys Rev E, doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.70.066111108
Couto, Campos, Vasconcelos, Michelon-Barbosa, Corsi, MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels in plasma are altered and associated with mortality in COVID-19 patients, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112067
Csárdi, Nepusz, The igraph software package for complex network research, Int J complex syst
Du, Cooper, Chen, Lee, Rong et al., Discovery of chebulagic acid and punicalagin as novel allosteric inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 3CL(pro), Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105075
Du, Zheng, Disoma, Li, Chen et al., Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, an active ingredient of Traditional Chinese Medicines, inhibits the 3CLpro activity of SARS-CoV-2, Int J Bio Macromo, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.012
Fan, Qian, Qian, Li, Antiviral activity of luteolin against Japanese encephalitis virus, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2016.04.021
Ferreira, Fadl, Ilter, Pekel, Rezgui et al., Dimethyl sulfoxide reduces the stability but enhances catalytic activity of the main SARS-CoV-2 protease 3CLpro, Faseb J, doi:10.1096/fj.202100994
Ferreira, Fadl, Villanueva, Rabeh, Catalytic Dyad Residues His41 and Cys145 Impact the Catalytic Activity and Overall Conformational Fold of the Main SARS-CoV-2 Protease 3-Chymotrypsin-Like Protease, Front. Chem, doi:.910.3389/fchem.2021.692168
Ferreira, Rabeh, Biochemical and biophysical characterization of the main protease, 3-chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro) from the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV 2, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-79357-0
Gao, Qin, Chen, Zhu, Hou et al., Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease, Acta Pharm Sin B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2020.08.014
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Hamada, Vitamins, omega-3, magnesium, manganese, and thyme can boost our immunity and protect against COVID-19, Eur. J. Biol. Res, doi:10.5281/zenodo.3990659
Hanwell, Curtis, Lonie, Vandermeersch, Zurek et al., Avogadro: an advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform, Journal of Cheminformatics
He, Garmire, Prediction of repurposed drugs for treating lung injury in COVID-19, F1000Res, doi:10.12688/f1000research.23996.2
Hermjakob, Montecchi-Palazzi, Bader, Wojcik, Salwinski et al., The HUPO PSI's molecular interaction format--a community standard for the representation of protein interaction data, Nat Biotechnol, doi:10.1038/nbt926102
Jiang, Yao, Zhao, Wu, Huang et al., Comparative review of respiratory diseases caused by coronaviruses and influenza A viruses during epidemic season, Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.005
Jin, Zhao, Sun, Zhang, Wang et al., Structural basis for the inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by antineoplastic drug carmofur, Nat Struct Mol Biol, doi:10.1038/s41594-020-0440-6
Jo, Kim, Iyer, Im, CHARMM-GUI: a web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM, J Comput Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.20945
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Justin, From Proteins to Perturbed Hamiltonians: A Suite of Tutorials for the GROMACS-2018 Molecular Simulation Package, Living Journal of Computational Molecular Science, doi:110.33011/livecoms.1.1.5068
Kang, Choi, Lee, Kwon, Luteolin isolated from the flowers of Lonicera japonica suppresses inflammatory mediator release by blocking NF-kappaB and MAPKs activation pathways in HMC-1 cells, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules15010385
Kao, To, Ng, Tsui, Lee et al., Characterization of SARS-CoV main protease and identification of biologically active small molecule inhibitors using a continuous fluorescence-based assay, FEBS Lett, doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.09.026
Karplus, Diederichs, Linking crystallographic model and data quality, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1218231
Kim, Ronai, PRMT5 function and targeting in cancer, Cell Stress, doi:10.15698/cst2020.08.228
Kim, Son, Chang, Kang, Anti-inflammatory plant flavonoids and cellular action mechanisms, J Pharmacol Sci, doi:10.1254/jphs.crj04003x
Kleywegt, Brunger, Checking your imagination: applications of the free R value, Structure, doi:10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00097-4
Knipping, Garssen, Van't Land, An evaluation of the inhibitory effects against rotavirus infection of edible plant extracts, Virol J
Konno, Kobayashi, Senda, Funai, Seki et al., 3CL Protease Inhibitors with an Electrophilic Arylketone Moiety as Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents, J Med Chem
Kumar, Chandel, Raj, Rathi, In silico identification of potent FDA approved drugs against Coronavirus COVID-19 main protease: A drug repurposing approach
Kumar, Kubota, Chernov, Kasuya, Potential role of zinc supplementation in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19, MedHypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109848
Laskowski, Swindells, LigPlot+: Multiple Ligand-Protein Interaction Diagrams for Drug Discovery, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, doi:10.1021/ci200227
Liang, Characterization and inhibition of SARS-coronavirus main protease, Curr Top Med Chem, doi:10.2174/156802606776287090
Ma, Hu, Townsend, Lagarias, Marty et al., Ebselen, Disulfiram, Carmofur, PX-12, Tideglusib, and Shikonin Are Nonspecific Promiscuous SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors, ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci, doi:10.1021/acsptsci.0c00130
Ma, Sacco, Hurst, Townsend, Hu et al., Boceprevir, GC-376, and calpain inhibitors II, XII inhibit SARS-CoV-2 viral replication by targeting the viral main protease, Cell Research, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0356-z
Maere, Heymans, Kuiper, BiNGO: a Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of Gene Ontology categories in Biological Networks, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/
Maffucci, Contini, In Silico Drug Repurposing for SARS-CoV-2 Main Proteinase and Spike Proteins, Journal of Proteome Research, doi:10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00383
Malone, Urakova, Snijder, Campbell, Structures and functions of coronavirus replication-transcription complexes and their relevance for SARS-CoV-2 drug design, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00432-z
Maurya, Kumar, Bhatt, Saxena, Therapeutic Development and Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease, doi:10.1007/978-981-15-4814-7_10
Mehla, Bivalkar-Mehla, Chauhan, A flavonoid, luteolin, cripples HIV-1 by abrogation of tat function, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027915
Molavi, Razi, Mirmotalebisohi, Adibi, Sameni et al., Identification of FDA approved drugs against SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and 3chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro), drug repurposing approach, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111544
Morris, Huey, Lindstrom, Sanner, Belew et al., AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility, Journal of computational chemistry, doi:10.1002/jcc.21256
Mucsi, Gyulai, Beladi, Combined effects of flavonoids and acyclovir against herpesviruses in cell cultures, Acta Microbiol Hung
Murali, Sivasubramanian, Vincent, Murugan, Giridaran et al., Anti-chikungunya activity of luteolin and apigenin rich fraction from Cynodon dactylon, Asian Pac J Trop Med, doi:10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60343-6
Nabi-Afjadi, Karami, Goudarzi, Alipourfard, Bahreini, The effect of vitamin D, magnesium and zinc supplements on interferon signaling pathways and their relationship to control SARS-CoV-2 infection, Clin Mol Allergy, doi:10.1186/s12948-021-00161-w
Nagesh, Husain, Influenza A Virus Dysregulates Host Histone Deacetylase 1 That Inhibits Viral Infection in Lung Epithelial Cells, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00126-16
Name, Souza, Vasconcelos, Prado, Pereira, Zinc, Vitamin D and Vitamin C: Perspectives for COVID-19 With a Focus on Physical Tissue Barrier Integrity, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2020.606398
Nunes, Costa, Santos, Fonseca, Ferreira et al., Successful application of virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulations against antimalarial molecular targets, Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, doi:10.1590/0074-02760160207
Pal, Squitti, Picozza, Pawar, Rongioletti et al., Zinc and COVID-19: Basis of Current Clinical Trials, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-020-02437-9
Pavlova, Lynch, Daidone, Zanetti-Polzi, Smith et al., Inhibitor binding influences the protonation states of histidines in SARS-CoV-2 main protease, Chem Sci, doi:10.1039/D0SC04942E
Pettersen, Goddard, Huang, Couch, Greenblatt et al., UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis, J Comput Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.20084
Pillaiyar, Manickam, Namasivayam, Hayashi, Jung, An Overview of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 3CL Protease Inhibitors: Peptidomimetics and Small Molecule Chemotherapy, J Med Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01461
Rani, Goyal, Bhatnagar, Manhas, Goel et al., Potential molecular mechanisms of zinc-and copper-mediated antiviral activity on COVID-19, Nutr Res, doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2021.05.008
Read, Obeid, Ahlenstiel, Ahlenstiel, The Role of Zinc in Antiviral Immunity, Adv Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmz013
Rondanelli, Miccono, Lamburghini, Avanzato, Riva et al., Self-Care for Common Colds: The Pivotal Role of Vitamin D, Vitamin C, Zinc, and Echinacea in Three Main Immune Interactive Clusters (Physical Barriers, Innate and Adaptive Immunity) Involved during an Episode of Common Colds-Practical Advice on Dosages and on the Time to Take These Nutrients/Botanicals in order to Prevent or Treat Common Colds, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, doi:10.1155/2018/5813095
Rut, Lv, Zmudzinski, Patchett, Nayak et al., Activity profiling and crystal structures of inhibitor-bound SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease: A framework for anti-COVID-19 drug design, Sci Adv
Ryu, Jeong, Kim, Kim, Park et al., Biflavonoids from Torreya nucifera displaying SARS-CoV 3CLpro inhibition, Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2010.09.035
Sadati, Gheibi, Ranjbar, Hashemzadeh, Docking study of flavonoid derivatives as potent inhibitors of influenza H1N1 virus neuraminidase, Biomed Rep, doi:10.3892/br.2018.1173
Saksena, Bonam, Miranda-Saksena, Epigenetic Lens to Visualize the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection in COVID-19 Pandemic, Front Genet, doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.581726
Saksena, Current and Future Challenges In Drug Therapeutics for Sars-Cov-2 Infection in Covid-19 Pandemic, Am. J. Biomed. Res, doi:10.34297/AJBSR.2020.09.001374
Schoeman, Fielding, Coronavirus envelope protein: current knowledge, Virol J
Seelinger, Merfort, Schempp, Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic activities of luteolin, Planta Med, doi:10.1055/s-0028-1088314
Shannon, Markiel, Ozier, Baliga, Wang et al., Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks, Genome Res, doi:10.1101/gr.1239303106
Shawan, Halder, Hasan, Luteolin and abyssinone II as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2: an in silico molecular modeling approach in battling the COVID-19 outbreak, Bull Natl Res Cent
Shetler, Ferreira, Cardoso, Silva, Saksena et al., Therapeutic potential of metal ions for COVID-19: insights from the papain-like protease of SARS-CoV-2, Biochem J, doi:10.1042/bcj20220380
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Aschner, Gritsenko et al., Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for COVID-19 (Review), Int J Mol Med, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4575
Skrajnowska, Bobrowska-Korczak, Role of Zinc in Immune System and Anti-Cancer Defense Mechanisms, Nutrients
Su, Yao, Zhao, Li, Liu et al., Discovery of baicalin and baicalein as novel, natural product inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease in vitro, doi:10.1101/2020.04.13.038687
Szklarczyk, Gable, Lyon, Junge, Wyder et al., STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genomewide experimental datasets, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gky1131103
Szklarczyk, Gable, Nastou, Lyon, Kirsch et al., The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa1074104
Szklarczyk, Santos, Von Mering, Jensen, Bork et al., STITCH 5: augmenting protein-chemical interaction networks with tissue and affinity data, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1277105
Tea, Ospina Stella, Aggarwal, Ross Darley, Pilli et al., SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies: Longevity, breadth, and evasion by emerging viral variants, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003656
Trott, Olson, AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading, Journal of computational chemistry, doi:10.1002/jcc.21334
Vanommeslaeghe, Hatcher, Acharya, Kundu, Zhong et al., CHARMM general force field: A force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the CHARMM all-atom additive biological force fields, J Comput Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.21367100
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Weglarz-Tomczak, Tomczak, Talma, Burda-Grabowska, Giurg et al., Identification of ebselen and its analogues as potent covalent inhibitors of papain-like protease from SARS-CoV-2, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-83229-6
Westermaier, Barril, Scapozza, Virtual screening: an in silico tool for interlacing the chemical universe with the proteome, Methods, doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.08.001
Williamson, Clifford, Colonic metabolites of berry polyphenols: the missing link to biological activity?, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114510003946
Wintergerst, Maggini, Hornig, Immune-enhancing role of vitamin C and zinc and effect on clinical conditions, Ann Nutr Metab, doi:10.1159/000090495
Xu, Su, Jin, Chen, Li et al., Identification of Luteolin as Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus A16 Inhibitors through Reporter Viruses and Cell Viability-Based Screening, Viruses-Basel, doi:10.3390/v6072778
Xu, Ye, Li, Huang, Wang et al., NOS1 inhibits the interferon response of cancer cells by S-nitrosylation of HDAC2, J Exp Clin Cancer Res, doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1448-9
Xue, Yang, Shen, Zhao, Li et al., Production of authentic SARS-CoV M(pro) with enhanced activity: application as a novel tag-cleavage endopeptidase for protein overproduction, J Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.073
Yao, Jiang, Yu, Yan, Luteolin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro by suppressing MMP-2 and MMP-9 through the PI3K/AKT pathway, Food Funct, doi:10.1039/c8fo02013b
Yilmaz, Swanstrom, Schiffer, Improving Viral Protease Inhibitors to Counter Drug Resistance, Trends Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2016.03.010
Yu, Chen, Lan, Shen, Li, Computational screening of antagonists against the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) coronavirus by molecular docking, Int J Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106012
Zhou, Jin, Li, Huang, HPEPDOCK: a web server for blind peptide-protein docking based on a hierarchical algorithm, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gky357
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
