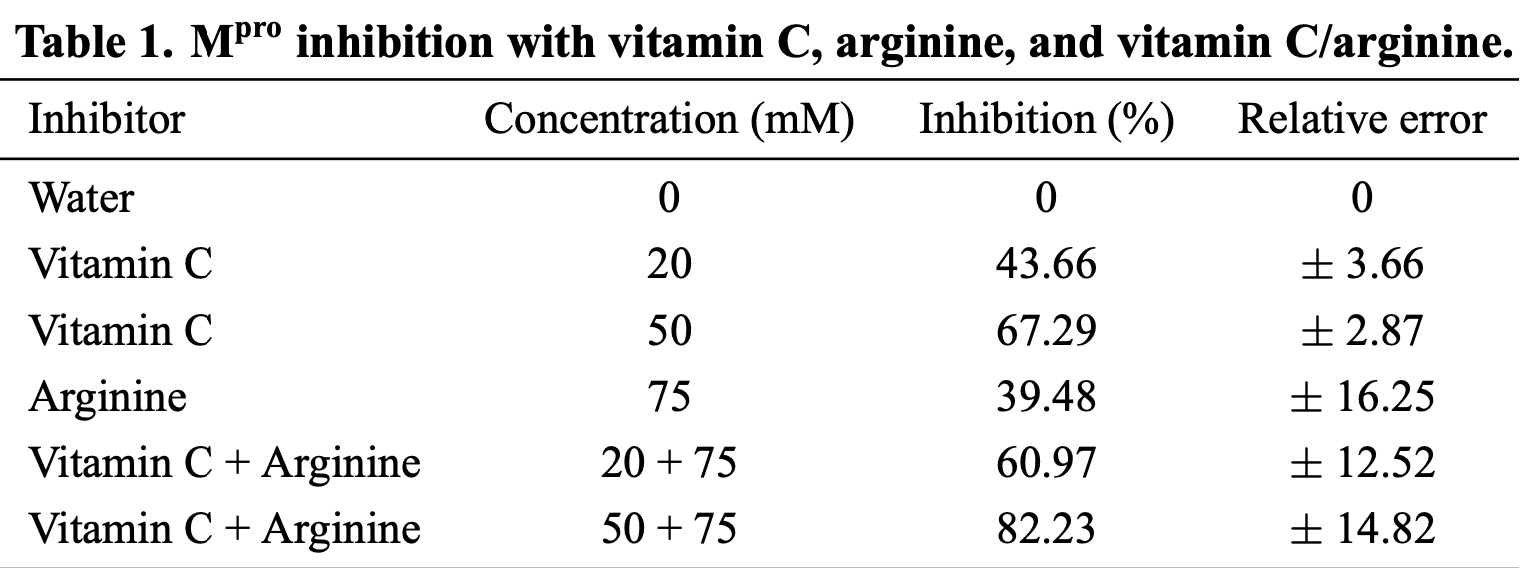
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro with Vitamin C, L-Arginine and a Vitamin C/L-Arginine Combination
et al., Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark, doi:10.31083/j.fbl2801008, Jan 2023
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro study showing inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro with vitamin C, L-arginine, and improved inhibition with the combination of both.
17 preclinical studies support the efficacy of vitamin C for COVID-19:
Vitamin C has been identified by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) as having sufficient evidence for a causal relationship between intake and optimal immune system function15-17.
Vitamin C plays a key role in the immune system, supporting the production and function of leukocytes, or white blood cells, which defend against infection and disease, including the production of lymphocytes, which make antibodies, and enhancing phagocytosis, the process by which immune system cells ingest and destroy viruses and infected cells.
Vitamin C is an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Vitamin C inhibits SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro7,11, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2 levels in a dose-dependent manner12, and may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by acting as an antioxidant and potentially reducing the reactive oxygen species (ROS) production induced by the spike protein that contributes to the activation of profibrotic pathways9.
Vitamin C reduces inflammation, oxidative stress, and NETosis, supporting immune function and vascular protection18.
Intracellular levels of vitamin C decline during COVID-19 hospitalization suggesting ongoing utilization and depletion of vitamin C19.
Threonic acid, a metabolite of vitamin C, is lower in mild and severe cases, consistent with increased need for and metabolization of vitamin C with moderate infection, but more limited ability to produce threonic acid in severe infection due to depletion or existing lower levels of vitamin C20.
Symptomatic COVID-19 is associated with a lower frequency of natural killer (NK) cells, and vitamin C has been shown to improve NK cell numbers and functioning21,22.
1.
Najimi et al., Phytochemical Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry: Targeting the ACE2‐RBD Interaction with l‐Tartaric Acid, l‐Ascorbic Acid, and Curcuma longa Extract, ChemistrySelect, doi:10.1002/slct.202406035.
2.
Rajamanickam et al., Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105.
3.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
4.
Morales-Bayuelo et al., New findings on ligand series used as SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibitors within the frameworks of molecular docking, molecular quantum similarity and chemical reactivity indices, F1000Research, doi:10.12688/f1000research.123550.3.
5.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
6.
Pandya et al., Unravelling Vitamin B12 as a potential inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2: A computational approach, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2022.100951.
7.
Malla et al., Vitamin C inhibits SARS coronavirus-2 main protease essential for viral replication, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.05.02.442358.
8.
Kumar et al., In silico virtual screening-based study of nutraceuticals predicts the therapeutic potentials of folic acid and its derivatives against COVID-19, VirusDisease, doi:10.1007/s13337-020-00643-6.
9.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
10.
Moatasim et al., Potent Antiviral Activity of Vitamin B12 against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, and Human Coronavirus 229E, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11112777.
11.
Đukić et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro with Vitamin C, L-Arginine and a Vitamin C/L-Arginine Combination, Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark, doi:10.31083/j.fbl2801008.
12.
Zuo et al., Vitamin C promotes ACE2 degradation and protects against SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, EMBO reports, doi:10.15252/embr.202256374.
13.
Hajdrik et al., In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694.
14.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
15.
Galmés et al., Suboptimal Consumption of Relevant Immune System Micronutrients Is Associated with a Worse Impact of COVID-19 in Spanish Populations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14112254.
16.
Galmés (B) et al., Current State of Evidence: Influence of Nutritional and Nutrigenetic Factors on Immunity in the COVID-19 Pandemic Framework, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092738.
17.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin C and protection of DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage (ID 129, 138, 143, 148), antioxidant function of lutein (ID 146), maintenance of vision (ID 141, 142), collagen formation (ID 130, 131, 136, 137, 149), function of the nervous system (ID 133), function of the immune system (ID 134), function of the immune system during and after extreme physical exercise (ID 144), non-haem iron absorption (ID 132, 147), energy-yielding metabolism (ID 135), and relief in case of irritation in the upper respiratory tract (ID 1714, 1715) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1226.
18.
Xie et al., The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6.
19.
Boerenkamp et al., Low Levels of Serum and Intracellular Vitamin C in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15163653.
20.
Albóniga et al., Differential abundance of lipids and metabolites related to SARS-CoV-2 infection and susceptibility, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-40999-5.
Đukić et al., 13 Jan 2023, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Contact: sanja@vinca.rs (corresponding author).
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro with Vitamin C, L-Arginine and a Vitamin C/L-Arginine Combination
Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark, doi:10.31083/j.fbl2801008
Background: Drug resistance is a critical problem in health care that affects therapy outcomes and requires new approaches to drug design. SARS-CoV-2 M pro mutations are of concern as they can potentially reduce therapeutic efficacy. Viral infections are amongst the many disorders for which nutraceuticals have been employed as an adjunct therapy. The aim of this study was to examine the potential in vitro activity of L-arginine and vitamin C against SARS-CoV-2 M pro . Methods: The M pro inhibition assay was developed by cloning, expression, purification, and characterization of M pro . Selected compounds were then screened for protease inhibition. Results: Larginine was found to be active against SARS-CoV-2 M pro , while a vitamin C/L-arginine combination had a synergistic antiviral action against M pro . These findings confirm the results of our previous in silico repurposing study that showed L-arginine and vitamin C were potential M pro inhibitors. Moreover, they suggest a possible molecular mechanism to explain the beneficial effect of arginine in COVID patients. Conclusions: The findings of the current study are important because they help to identify COVID-19 treatments that are efficient, inexpensive, and have a favorable safety profile. The results of this study also suggest a possible adjuvant nutritional strategy for COVID-19 that could be used in conjunction with pharmacological agents.
Author Contributions Conceptualization-RP, SP and SG; performed the experiments-RP, NK, and IĐ; validation-NK, and RP; analyzed the data-NK, IĐ, MS, and RP; investigation-NK, IĐ, and MS; resources-RP; writing, original draft preparation-RP, SG, MS, SBP, JM and JP; writing, review and editing-SG, SBP, MS, SP and RP; visualization-IĐ, NK, RP; supervision-RP; project administration-RP, SG, JM, and MS. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Abobaker, Alzwi, Alraied, Overview of the possible role of vitamin C in management of COVID-19, Pharmacological Reports
Alvares, Conte-Junior, Silva, Paschoalin, Acute L-Arginine supplementation does not increase nitric oxide production in healthy subjects, Nutrition & Metabolism
Bogdański, Suliburska, Szulińska, Sikora, Walkowiak et al., L-Arginine and vitamin C attenuate proatherogenic effects of high-fat diet on biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction in rats, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy
Chen, Liu, Gao, Sun, Chao et al., Inhalation of nitric oxide in the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome: a rescue trial in Beijing, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Defelice, The nutraceutical revolution: its impact on food industry R&D, Trends in Food Science & Technology
Doan, Lakhman, Boje, Blood-brain barrier transport studies of organic guanidino cations using an in situ brain perfusion technique, Brain Research
Drouin, Godin, Pagé, The genetics of vitamin C loss in vertebrates, Current Genomics
Erickson, Rhea, Knopp, Banks, Interactions of SARS-CoV-2 with the Blood-Brain Barrier, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Feyaerts, Luyten, Vitamin C as prophylaxis and adjunctive medical treatment for COVID-19?, Nutrition
Fiorentino, Coppola, Izzo, Annunziata, Bernardo et al., Effects of adding L-arginine orally to standard therapy in patients with COVID-19: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Results of the first interim analysis, EClinicalMedicine
Grzegorowska, Lorkowski, Possible Correlations between Atherosclerosis, Acute Coronary Syndromes and COVID-19, Journal of Clinical Medicine
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, The New England Journal of Medicine
Guarner, Three Emerging Coronaviruses in Two Decades: The Story of SARS, MERS, and Now COVID-19, American Journal of Clinical Pathology
Hazan, Stollman, Bozkurt, Papoutsis, Daniels, Lost microbes of COVID-19: Bifidobacterium, Faecalibacterium depletion and decreased microbiome diversity associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection severity, BMJ Open Gastroenterology
Hill, Cowen, Using combination therapy to thwart drug resistance, Future Microbiology
Hoang, Shaw, Fang, Han, Possible application of high-dose vitamin C in the prevention and therapy of coronavirus infection, Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance
Holford, Carr, Jovic, Ali, Whitaker et al., Vitamin C-An Adjunctive Therapy for Respiratory Infection, Sepsis and COVID-19, Nutrients
Holford, Carr, Zawari, Vizcaychipi, Vitamin C Intervention for Critical COVID-19: A Pragmatic Review of the Current Level of Evidence, Life
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Ivarsson, Addgene plasmid #
Izzo, Trimarco, Mone, Aloè, Marzani, Combining L-Arginine with vitamin C improves long-COVID symptoms: The LINCOLN Survey, Pharmacological Research
Jezovnik, Poredos, Oxidative stress and atherosclerosis, European Society of Cardiology
Kneller, Phillips, Neill, Jedrzejczak, Stols et al., Structural plasticity of SARS-CoV-2 3CL M pro active site cavity revealed by room temperature X-ray crystallography, Nature Communications
Kontermann, Dual targeting strategies with bispecific antibodies, Taylor & Francis
Krishnamoorthy, Fakhro, Identification of mutation resistance coldspots for targeting the SARS-CoV2 main protease, IUBMB Life
Li, Wu, Important roles of amino acids in immune responses, The British Journal of Nutrition
Malla, Pandey, Aldama, Feliz, Noda et al., Vitamin C Binds to SARS Coronavirus-2 Main Protease Essential for Viral Replication
Najjar, Najjar, Chong, Pramanik, Kirsch et al., Central nervous system complications associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: integrative concepts of pathophysiology and case reports, Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2020;
Sencanski, Perovic, Pajovic, Adzic, Paessler et al., Drug Repurposing for Candidate SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors by a Novel In Silico Method, Molecules
Shu, Yang, He, Effect of ascorbic acid and cysteine hydrochloride on growth of Bifidobacterium bifidum, Advance Journal of Food Science and Technology
Singh, Kumar, Pal, Kumari, Bahadur, L-amino-acids as immunity booster against COVID-19: DFT, molecular docking and MD simulations, Journal of Molecular Structure
Skwarecki, Nowak, Milewska, Amino Acid and Peptide-Based Antiviral Agents, ChemMedChem
Subedi, Tchen, Gaire, Hu, Hu, Adjunctive Nutraceutical Therapies for COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Veljkovic, Glisic, Perovic, Veljkovic, The role of longrange intermolecular interactions in discovery of new drugs, Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.31083/j.fbl2801008",
"ISSN": [
"2768-6701"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.31083/j.fbl2801008",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Đukić",
"given": "Ivana",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaličanin",
"given": "Nevena",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sencanski",
"given": "Milan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pajovic",
"given": "Snezana B.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milicevic",
"given": "Jelena",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prljic",
"given": "Jelena",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paessler",
"given": "Slobodan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prodanović",
"given": "Radivoje",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Glisic",
"given": "Sanja",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark",
"container-title-short": "Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed)",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-13T09:20:10Z",
"timestamp": 1673601610000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-13T09:20:17Z",
"timestamp": 1673601617000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-14T06:15:06Z",
"timestamp": 1673676906896
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
13
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.imrpress.com/journal/FBL/28/1/10.31083/j.fbl2801008",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "16242",
"original-title": [],
"page": "8",
"prefix": "10.31083",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
13
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "IMR Press",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.imrpress.com/journal/FBL/28/1/10.31083/j.fbl2801008"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Immunology and Microbiology",
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro with Vitamin C, L-Arginine and a Vitamin C/L-Arginine Combination",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "28"
}
