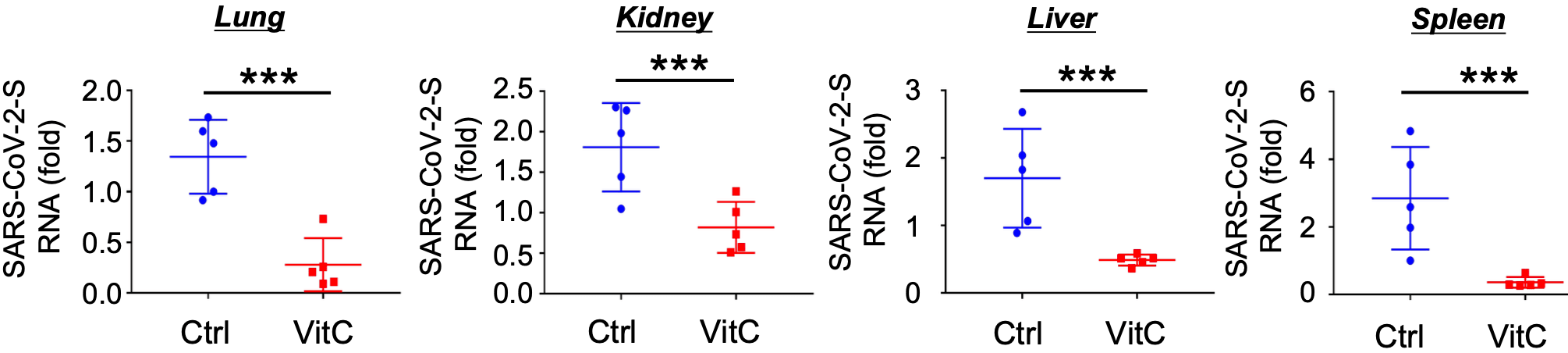
Vitamin C promotes ACE2 degradation and protects against SARS‐CoV‐2 infection
et al., EMBO reports, doi:10.15252/embr.202256374, Jul 2022 (preprint)
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro and mouse study showing that vitamin C inhibits SARS-CoV-2. Vitamin C lowered ACE2 protein levels in a dose-dependent manner at a concentration of 1-10mM in both cell and humanized ACE2 mouse models.
17 preclinical studies support the efficacy of vitamin C for COVID-19:
Vitamin C has been identified by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) as having sufficient evidence for a causal relationship between intake and optimal immune system function15-17.
Vitamin C plays a key role in the immune system, supporting the production and function of leukocytes, or white blood cells, which defend against infection and disease, including the production of lymphocytes, which make antibodies, and enhancing phagocytosis, the process by which immune system cells ingest and destroy viruses and infected cells.
Vitamin C is an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Vitamin C inhibits SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro7,11, inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2 levels in a dose-dependent manner12, and may limit COVID-19 induced cardiac damage by acting as an antioxidant and potentially reducing the reactive oxygen species (ROS) production induced by the spike protein that contributes to the activation of profibrotic pathways9.
Vitamin C reduces inflammation, oxidative stress, and NETosis, supporting immune function and vascular protection18.
Intracellular levels of vitamin C decline during COVID-19 hospitalization suggesting ongoing utilization and depletion of vitamin C19.
Threonic acid, a metabolite of vitamin C, is lower in mild and severe cases, consistent with increased need for and metabolization of vitamin C with moderate infection, but more limited ability to produce threonic acid in severe infection due to depletion or existing lower levels of vitamin C20.
Symptomatic COVID-19 is associated with a lower frequency of natural killer (NK) cells, and vitamin C has been shown to improve NK cell numbers and functioning21,22.
1.
Najimi et al., Phytochemical Inhibitors of SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry: Targeting the ACE2‐RBD Interaction with l‐Tartaric Acid, l‐Ascorbic Acid, and Curcuma longa Extract, ChemistrySelect, doi:10.1002/slct.202406035.
2.
Rajamanickam et al., Exploring the Potential of Siddha Formulation MilagaiKudineer-Derived Phytotherapeutics Against SARS-CoV-2: An In-Silico Investigation for Antiviral Intervention, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, doi:10.26502/fjppr.0105.
3.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
4.
Morales-Bayuelo et al., New findings on ligand series used as SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibitors within the frameworks of molecular docking, molecular quantum similarity and chemical reactivity indices, F1000Research, doi:10.12688/f1000research.123550.3.
5.
Alkafaas et al., A study on the effect of natural products against the transmission of B.1.1.529 Omicron, Virology Journal, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-02160-6.
6.
Pandya et al., Unravelling Vitamin B12 as a potential inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2: A computational approach, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2022.100951.
7.
Malla et al., Vitamin C inhibits SARS coronavirus-2 main protease essential for viral replication, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.05.02.442358.
8.
Kumar et al., In silico virtual screening-based study of nutraceuticals predicts the therapeutic potentials of folic acid and its derivatives against COVID-19, VirusDisease, doi:10.1007/s13337-020-00643-6.
9.
Van Tin et al., Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Activates Cardiac Fibrogenesis through NLRP3 Inflammasomes and NF-κB Signaling, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161331.
10.
Moatasim et al., Potent Antiviral Activity of Vitamin B12 against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, and Human Coronavirus 229E, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11112777.
11.
Đukić et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro with Vitamin C, L-Arginine and a Vitamin C/L-Arginine Combination, Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark, doi:10.31083/j.fbl2801008.
12.
Zuo et al., Vitamin C promotes ACE2 degradation and protects against SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, EMBO reports, doi:10.15252/embr.202256374.
13.
Hajdrik et al., In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694.
14.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
15.
Galmés et al., Suboptimal Consumption of Relevant Immune System Micronutrients Is Associated with a Worse Impact of COVID-19 in Spanish Populations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14112254.
16.
Galmés (B) et al., Current State of Evidence: Influence of Nutritional and Nutrigenetic Factors on Immunity in the COVID-19 Pandemic Framework, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092738.
17.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin C and protection of DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage (ID 129, 138, 143, 148), antioxidant function of lutein (ID 146), maintenance of vision (ID 141, 142), collagen formation (ID 130, 131, 136, 137, 149), function of the nervous system (ID 133), function of the immune system (ID 134), function of the immune system during and after extreme physical exercise (ID 144), non-haem iron absorption (ID 132, 147), energy-yielding metabolism (ID 135), and relief in case of irritation in the upper respiratory tract (ID 1714, 1715) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1226.
18.
Xie et al., The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death, Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6.
19.
Boerenkamp et al., Low Levels of Serum and Intracellular Vitamin C in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15163653.
20.
Albóniga et al., Differential abundance of lipids and metabolites related to SARS-CoV-2 infection and susceptibility, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-40999-5.
Zuo et al., 15 Jul 2022, China, peer-reviewed, 15 authors.
Contact: huizheng@suda.edu.cn (corresponding author).
Abstract: bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.14.499651; this version posted July 15, 2022. The copyright holder for this preprint (which
was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. It is made
available under aCC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license.
1
Vitamin C is an efficient natural product for prevention of
2
SARS-CoV-2 infection by targeting ACE2 in both cell and in
3
vivo mouse models
4
5
Yibo Zuo,1,2 Zhijin Zheng,1,2 Yingkang Huang,5 Jiuyi He,1,2 Lichao Zang,4
6
Tengfei Ren,1,2 Xinhua Cao,1,2 Ying Miao,1,2 Yukang Yuan,1,2 Yanli Liu,3 Feng
7
Ma,5 Sheng Tian,3 Jianfeng Dai,1,2 Qiang Ding,6 Hui Zheng1,2,7,*
8
9
1
International Institute of Infection and Immunity, Institutes of Biology and Medical
10
Sciences, Suzhou
11
2
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Suzhou
12
3
College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Suzhou
13
4
The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Changzhou
14
Soochow University, Jiangsu 215123, China
15
5
16
of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 10005; Suzhou
17
Institute of Systems Medicine, Jiangsu 215123, China
18
6
19
Innovation Center for Structural Biology, Tsinghua University, Beijing 10084, China
20
7
21
*Correspondence: huizheng@suda.edu.cn
CAMS Key Laboratory of Synthetic Biology Regulatory Elements, Chinese Academy
Center for Infectious Disease Research, School of Medicine, Beijing Advanced
Lead contact
22
23
24
1
bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.14.499651; this version posted July 15, 2022. The copyright holder for this preprint (which
was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. It is made
available under aCC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license.
25
SUMMARY
26
ACE2 is a major receptor for cell entry of SARS-CoV-2. Despite advances in
27
targeting ACE2 to inhibit SARS-CoV-2's binding, how to efficiently and flexibly
28
control ACE2 levels for prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection has not been
29
explored. Here, we revealed Vitamin C (VitC) administration as an effective
30
strategy to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection. VitC reduced ACE2 protein levels in
31
a dose-dependent manner, while partial reduction of ACE2 can greatly restrict
32
SARS-CoV-2 infection. Further studies uncovered that USP50 is a crucial
33
regulator of ACE2 protein levels, and VitC blocks the USP50-ACE2 interaction,
34
thus promoting K48-linked polyubiquitination at Lys788 and degradation of
35
ACE2, without disrupting ACE2 transcriptional expression. Importantly, VitC
36
administration reduced host ACE2 and largely blocked SARS-CoV-2 infection
37
in mice. This study identified an in vivo ACE2 balance controlled by both
38
USP50 and an essential nutrient VitC, and revealed a critical role and
39
application of VitC in daily protection from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
40
41
Highlights
42
VitC reduces ACE2 protein levels in a dose-dependent manner
43
VitC and USP50 regulate K48-linked ubiquitination at Lys788 of ACE2
44
VitC blocks the interaction between USP50 and ACE2
45
VitC administration lowers host ACE2 and prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection
46
in vivo
47
48
2
bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.14.499651; this version posted July 15, 2022. The copyright holder for this preprint (which
was not certified by..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embr.202256374",
"ISSN": [
"1469-221X",
"1469-3178"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.15252/embr.202256374",
"alternative-id": [
"10.15252/embr.202256374"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1908-6054",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Institute of Infection and Immunity Institutes of Biology and Medical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
},
{
"name": "Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zuo",
"given": "Yibo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Institute of Infection and Immunity Institutes of Biology and Medical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
},
{
"name": "Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "Zhijin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CAMS Key Laboratory of Synthetic Biology Regulatory Elements Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College Beijing China"
},
{
"name": "Suzhou Institute of Systems Medicine Suzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Yingkang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Institute of Infection and Immunity Institutes of Biology and Medical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
},
{
"name": "Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"family": "He",
"given": "Jiuyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Changzhou Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Zang",
"given": "Lichao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Institute of Infection and Immunity Institutes of Biology and Medical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
},
{
"name": "Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Ren",
"given": "Tengfei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Institute of Infection and Immunity Institutes of Biology and Medical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
},
{
"name": "Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Cao",
"given": "Xinhua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Institute of Infection and Immunity Institutes of Biology and Medical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
},
{
"name": "Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Miao",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3153-2408",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Institute of Infection and Immunity Institutes of Biology and Medical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
},
{
"name": "Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Yukang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Yanli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2975-0118",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CAMS Key Laboratory of Synthetic Biology Regulatory Elements Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College Beijing China"
},
{
"name": "Suzhou Institute of Systems Medicine Suzhou China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Feng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1871-8390",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Institute of Infection and Immunity Institutes of Biology and Medical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
},
{
"name": "Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dai",
"given": "Jianfeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Tian",
"given": "Sheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Infectious Disease Research, School of Medicine, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology Tsinghua University Beijing China"
}
],
"family": "Ding",
"given": "Qiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4325-4946",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International Institute of Infection and Immunity Institutes of Biology and Medical Sciences, Soochow University Suzhou China"
},
{
"name": "Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, Soochow University Suzhou China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "EMBO reports",
"container-title-short": "EMBO Reports",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-06T10:49:56Z",
"timestamp": 1678099796000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-06T10:50:18Z",
"timestamp": 1678099818000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"31970846",
"32100568"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012246",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-07T05:37:31Z",
"timestamp": 1678167451182
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1678060800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1678060800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.15252/embr.202256374",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.15252/embr.202256374",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.15252/embr.202256374",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "79",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.15252",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "EMBO",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jim-2017-000622",
"article-title": "Induction of deubiquitinating enzyme USP50 during erythropoiesis and its potential role in the regulation of Ku70 stability",
"author": "Cai J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Investig Med",
"key": "e_1_2_9_2_1",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14712598.2022.2078160",
"article-title": "Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies for COVID‐19 management: an update",
"author": "Chavda VP",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "763",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Biol Ther",
"key": "e_1_2_9_3_1",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0506390102",
"article-title": "Pharmacologic ascorbic acid concentrations selectively kill cancer cells: action as a pro‐drug to deliver hydrogen peroxide to tissues",
"author": "Chen Q",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13604",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "e_1_2_9_4_1",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature00786",
"article-title": "Angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function",
"author": "Crackower MA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "822",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "e_1_2_9_5_1",
"volume": "417",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.RES.87.5.e1",
"article-title": "A novel angiotensin‐converting enzyme‐related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1‐9",
"author": "Donoghue M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E1‐9",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "e_1_2_9_6_1",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41585-021-00542-5",
"article-title": "Implications of testicular ACE2 and the renin‐angiotensin system for SARS‐CoV‐2 on testis function",
"author": "Edenfield RC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Urol",
"key": "e_1_2_9_7_1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.510461",
"article-title": "Effect of angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiac angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2",
"author": "Ferrario CM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2605",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "e_1_2_9_8_1",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.202557",
"article-title": "The efficiency and safety of high‐dose vitamin C in patients with COVID‐19: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Gao D",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7020",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "e_1_2_9_9_1",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.59177",
"article-title": "A mechanistic model and therapeutic interventions for COVID‐19 involving a RAS‐mediated bradykinin storm",
"author": "Garvin MR",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e59177",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "e_1_2_9_10_1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan WJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "e_1_2_9_11_1",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3",
"article-title": "Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID‐19",
"author": "Gupta A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1017",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "e_1_2_9_12_1",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS‐CoV‐2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "e_1_2_9_13_1",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gku1267",
"article-title": "PhosphoSitePlus, 2014: mutations, PTMs and recalibrations",
"author": "Hornbeck PV",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "D512",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "e_1_2_9_14_1",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_9_15_1",
"unstructured": "HornbeckPV ZhangB MurrayB KornhauserJM LathamV SkrzypekE(2015b)PhosphoSitePlus ACE2 human(https://www.phosphosite.org/proteinAction.action?id=14935&showAllSites=true). [DATASET]"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009439",
"article-title": "A novel cell culture system modeling the SARS‐CoV‐2 life cycle",
"author": "Ju X",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1009439",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "e_1_2_9_16_1",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/375146a0",
"article-title": "Male‐female differences in fertility and blood pressure in ACE‐deficient mice",
"author": "Krege JH",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "e_1_2_9_17_1",
"volume": "375",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2006.03.001",
"article-title": "Angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2 in lung diseases",
"author": "Kuba K",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Pharmacol",
"key": "e_1_2_9_18_1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijo.2015.2840",
"article-title": "SIAH1‐induced p34SEI‐1 polyubiquitination/degradation mediates p53 preferential vitamin C cytotoxicity",
"author": "Lee S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1377",
"journal-title": "Int J Oncol",
"key": "e_1_2_9_19_1",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.93.8.3704",
"article-title": "Vitamin C pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers: evidence for a recommended dietary allowance",
"author": "Levine M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3704",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "e_1_2_9_20_1",
"volume": "93",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1830715",
"article-title": "Establishment of replication‐competent vesicular stomatitis virus‐based recombinant viruses suitable for SARS‐CoV‐2 entry and neutralization assays",
"author": "Li H",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2269",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "e_1_2_9_21_1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x",
"article-title": "Expression of the SARS‐CoV‐2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues",
"author": "Li MY",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Poverty",
"key": "e_1_2_9_22_1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/thno.63751",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial STAT3 exacerbates LPS‐induced sepsis by driving CPT1a‐mediated fatty acid oxidation",
"author": "Li R",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "976",
"journal-title": "Theranostics",
"key": "e_1_2_9_23_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5082860",
"article-title": "Regulation of vitamin C homeostasis during deficiency",
"author": "Lindblad M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2860",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "e_1_2_9_24_1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11102412",
"article-title": "The pharmacokinetics of vitamin C",
"author": "Lykkesfeldt J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2412",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "e_1_2_9_25_1",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacc.2018.01.058",
"article-title": "Angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors in hypertension: to use or not to use?",
"author": "Messerli FH",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1474",
"journal-title": "J Am Coll Cardiol",
"key": "e_1_2_9_26_1",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15406/jlprr.2021.08.00250",
"article-title": "Regulation of ACE‐2 enzyme by hyperoxia in lung epithelial cells by post‐translational modification",
"author": "Mohamed T",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "47",
"journal-title": "J Lung Pulm Respir Res",
"key": "e_1_2_9_27_1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcpt.12323",
"article-title": "Elimination of ascorbic acid after high‐dose infusion in prostate cancer patients: a pharmacokinetic evaluation",
"author": "Nielsen TK",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol",
"key": "e_1_2_9_28_1",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-140-7-200404060-00010",
"article-title": "Vitamin C pharmacokinetics: implications for oral and intravenous use",
"author": "Padayatty SJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "533",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "e_1_2_9_29_1",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102324",
"article-title": "Vitamin C and COVID‐19 treatment: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Rawat D",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102324",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "e_1_2_9_30_1",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms5763",
"article-title": "Screening of DUB activity and specificity by MALDI‐TOF mass spectrometry",
"author": "Ritorto MS",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4763",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "e_1_2_9_31_1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389450117666160727142401",
"article-title": "The anti‐inflammatory potential of ACE2/Angiotensin‐(1‐7)/Mas receptor axis: evidence from basic and clinical research",
"author": "Rodrigues Prestes TR",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1301",
"journal-title": "Curr Drug Targets",
"key": "e_1_2_9_32_1",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ddr.21679",
"article-title": "Telmisartan as tentative angiotensin receptor blocker therapeutic for COVID‐19",
"author": "Rothlin RP",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "768",
"journal-title": "Drug Dev Res",
"key": "e_1_2_9_33_1",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.048191",
"article-title": "MDM2‐mediated ubiquitination of angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2 contributes to the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension",
"author": "Shen H",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1190",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "e_1_2_9_34_1",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00280-013-2179-9",
"article-title": "Phase I clinical trial to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of high‐dose intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with advanced cancer",
"author": "Stephenson CM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Cancer Chemother Pharmacol",
"key": "e_1_2_9_35_1",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-020-0242-z",
"article-title": "Mechano‐genomic regulation of coronaviruses and its interplay with ageing",
"author": "Uhler C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "247",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol",
"key": "e_1_2_9_36_1",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/157016110793563924",
"article-title": "Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers in the treatment of hypertension: should they be used together?",
"author": "Verdecchia P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "742",
"journal-title": "Curr Vasc Pharmacol",
"key": "e_1_2_9_37_1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02165-17",
"article-title": "Vitamin C potentiates the killing of mycobacterium tuberculosis by the first‐line tuberculosis drugs isoniazid and rifampin in mice",
"author": "Vilcheze C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e02165‐17",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "e_1_2_9_38_1",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11684-021-0837-6",
"article-title": "Degradation of SARS‐CoV‐2 receptor ACE2 by the E3 ubiquitin ligase Skp2 in lung epithelial cells",
"author": "Wang G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "e_1_2_9_39_1",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41401-021-00735-z",
"article-title": "Discovery of potential small molecular SARS‐CoV‐2 entry blockers targeting the spike protein",
"author": "Wang L",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "788",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmacol Sin",
"key": "e_1_2_9_40_1",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.ajkd.2005.08.018",
"article-title": "Underuse of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers in elderly patients with diabetes",
"author": "Winkelmayer WC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1080",
"journal-title": "Am J Kidney Dis",
"key": "e_1_2_9_41_1",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2507",
"article-title": "Cryo‐EM structure of the 2019‐nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation",
"author": "Wrapp D",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1260",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "e_1_2_9_42_1",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00672-4",
"article-title": "Structural and biochemical mechanism for increased infectivity and immune evasion of omicron BA.2 variant compared to BA.1 and their possible mouse origins",
"author": "Xu Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "609",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "e_1_2_9_43_1",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00845",
"article-title": "Vitamin C inhibits ubiquitination of glutamate transporter 1 (GLT‐1) in astrocytes by downregulating HECTD1",
"author": "Zeng X",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "676",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem Nerosci",
"key": "e_1_2_9_44_1",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.035",
"article-title": "SARS‐CoV‐2 receptor ACE2 is an interferon‐stimulated Gene in human airway epithelial cells and is detected in specific cell subsets across tissues",
"author": "Ziegler CGK",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1016",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "e_1_2_9_45_1",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-14948-z",
"article-title": "Regulation of the linear ubiquitination of STAT1 controls antiviral interferon signaling",
"author": "Zuo Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1146",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "e_1_2_9_46_1",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abj3887",
"article-title": "LATS1 is a central signal transmitter for achieving full type‐I interferon activity",
"author": "Zuo Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabj3887",
"journal-title": "Sci Adv",
"key": "e_1_2_9_47_1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 46,
"references-count": 46,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.15252/embr.202256374"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Genetics",
"Molecular Biology",
"Biochemistry"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin C promotes ACE2 degradation and protects against SARS‐CoV‐2 infection",
"type": "journal-article"
}
