Remdesivir and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab698, Aug 2021
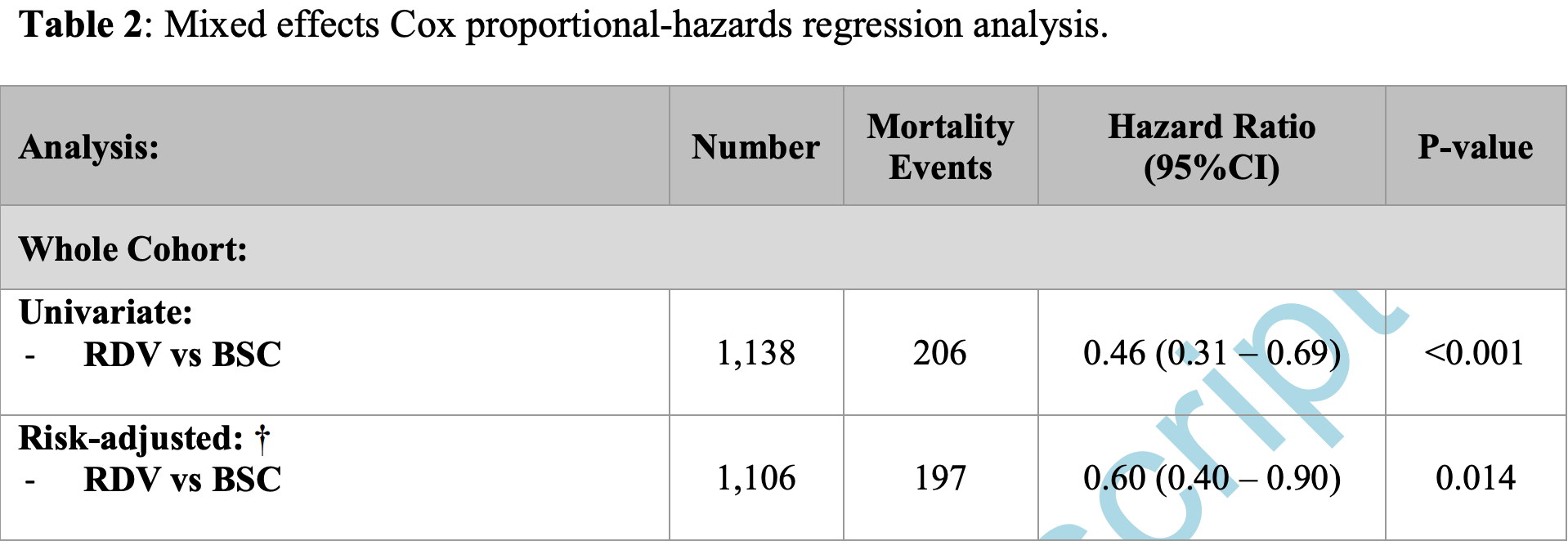
Retrospective 1,138 hospitalized patients in the USA, 286 treated with remdesivir, showing lower mortality with treatment. Age was not included in the adjustments (authors excluded variables that contributed to another score, in this case age is in Pneumonia Severity Index).
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments15.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
Results may differ in countries with improved SOC.
|
risk of death, 34.7% lower, HR 0.65, p = 0.01, treatment 33 of 286 (11.5%), control 173 of 852 (20.3%), NNT 11, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 44.0% lower, HR 0.56, p = 0.04, treatment 286, control 852, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards, day 30, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
13.
Mohammed et al., Bradycardia associated with remdesivir treatment in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: A propensity score-matched analysis, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000044501.
Diaz et al., 19 Aug 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 45 authors.
doi:10.1093/cid/ciab698/6352176
From an early retrospective cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients, remdesivir use is associated with lower mortality compared to best supportive care. The effect remains the same for the subgroup of patients requiring low flow oxygen at baseline, similar to the ACTT-1 results.
Disclaimer The manufacturer of RDV (Gilead Sciences, Inc.) and the sponsor of ACTT-1 (NIH NIAID) approved the reuse of data for this study, but was not involved in study design, data preparation, data analysis or manuscript preparation. A c c e p t e d M a n u s c r i p t
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 -Final Report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Cavalcanti, Zampieri, Rosa, Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2019014
Fine, Auble, Yealy, A prediction rule to identify low-risk patients with community-acquired pneumonia, N Engl J Med. Jan, doi:10.1056/NEJM199701233360402
Geleris, Sun, Platt, Observational Study of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2012410
Goldman, Lye, Hui, Remdesivir for 5 or 10 Days in Patients with Severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2015301
Gordon, Tchesnokov, Feng, Porter, Gotte, The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.AC120.013056
Grein, Ohmagari, Shin, Compassionate Use of Remdesivir for Patients with Severe Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2007016
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med. Mar, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001191
Horby, Mafham, Effect of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022926
Olender, Perez, Go, Remdesivir for Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Versus a Cohort Receiving Standard of Care, Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1041
Pan, Peto, Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for Covid-19 -Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2023184
Rosenberg, Dufort, Udo, Association of Treatment With Hydroxychloroquine or Azithromycin With In-Hospital Mortality in Patients With COVID-19 in New York State, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8630
Skipper, Pastick, Engen, Hydroxychloroquine in Nonhospitalized Adults With Early COVID-19 : A Randomized Trial, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M20-4207
Spinner, Gottlieb, Criner, Effect of Remdesivir vs Standard Care on Clinical Status at 11 Days in Patients With Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA. Sep, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.16349
Tang, Cao, Han, Hydroxychloroquine in patients with mainly mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019: open label, randomised controlled trial, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1849
Yao, Ye, Zhang, Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa237
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab698",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab698",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The impact of remdesivir (RDV) on mortality rates in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is controversial, and the mortality effect in subgroups of baseline disease severity has been incompletely explored. The purpose of this study was to assess the association of RDV with mortality rates in patients with COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this retrospective cohort study we compared persons receiving RDV with those receiving best supportive care (BSC). Patients hospitalized between 28 February and 28 May 2020 with laboratory-confirmed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection were included with the development of COVID-19 pneumonia on chest radiography and hypoxia requiring supplemental oxygen or oxygen saturation ≤94% with room air. The primary outcome was overall survival, assessed with time-dependent Cox proportional hazards regression and multivariable adjustment, including calendar time, baseline patient characteristics, corticosteroid use, and random effects for hospital.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A total of 1138 patients were enrolled, including 286 who received RDV and 852 treated with BSC, 400 of whom received hydroxychloroquine. Corticosteroids were used in 20.4% of the cohort (12.6% in RDV and 23% in BSC). Comparing persons receiving RDV with those receiving BSC, the hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) for death was 0.46 (.31–.69) in the univariate model (P &lt; .001) and 0.60 (.40–.90) in the risk-adjusted model (P = .01). In the subgroup of persons with baseline use of low-flow oxygen, the hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) for death in RDV compared with BSC was 0.63 (.39–1.00; P = .049).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Treatment with RDV was associated with lower mortality rates than BSC. These findings remain the same in the subgroup with baseline use of low-flow oxygen.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Providence Regional Medical Center Everett , Everett, Washington , USA"
},
{
"name": "Washington State University Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine, Internal Medicine Residency , Spokane, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Diaz",
"given": "George A",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Providence Oregon Region Shared Services , Portland, Oregon , USA"
}
],
"family": "Christensen",
"given": "Alyssa B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Providence St Vincent Medical Center , Portland, Oregon , USA"
}
],
"family": "Pusch",
"given": "Tobias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Washington State University Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine, Internal Medicine Residency , Spokane, Washington , USA"
},
{
"name": "Division of Medicine, Section of Internal Medicine, Providence Regional Medical Center Everett , Everett, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Goulet",
"given": "Delaney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Cardiovascular Analytics, Research and Data Science, Providence St Joseph Health , Portland, Oregon , USA"
}
],
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Shu-Ching",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Cardiovascular Analytics, Research and Data Science, Providence St Joseph Health , Portland, Oregon , USA"
}
],
"family": "Grunkemeier",
"given": "Gary L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Cardiovascular Analytics, Research and Data Science, Providence St Joseph Health , Portland, Oregon , USA"
}
],
"family": "McKelvey",
"given": "Paul A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Analytics, Providence St Joseph Health , Renton, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Robicsek",
"given": "Ari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Analytics, Providence St Joseph Health , Renton, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "French",
"given": "Tom",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Analytics, Providence St Joseph Health , Renton, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Parsons",
"given": "Guilford T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Analytics, Providence St Joseph Health , Renton, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Doherty",
"given": "Glenn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Analytics, Providence St Joseph Health , Renton, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Laurenson",
"given": "Charles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for Systems Biology , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Roper",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for Systems Biology , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hadlock",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Providence St Vincent Medical Center , Portland, Oregon , USA"
}
],
"family": "Cover",
"given": "Cameron J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Providence Oregon Region Shared Services , Portland, Oregon , USA"
}
],
"family": "Footer",
"given": "Brent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Hospital Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Hoag Memorial Hospital Presbyterian , Newport Beach, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Philip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Swedish Medical Center , Seattle, Washington , USA"
},
{
"name": "Swedish Center for Research and Innovation, Swedish Medical Center , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Micikas",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Providence St Vincent Medical Center , Portland, Oregon , USA"
}
],
"family": "Marfori",
"given": "Jennifer E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Washington State University Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine, Internal Medicine Residency , Spokane, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Cronenweth",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Washington State University Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine, Internal Medicine Residency , Spokane, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Mukkamala",
"given": "Yogavedya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Washington State University Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine, Internal Medicine Residency , Spokane, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Mackiewicz",
"given": "Jamie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Washington State University Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine, Internal Medicine Residency , Spokane, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Rai",
"given": "Ekra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Washington State University Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine, Internal Medicine Residency , Spokane, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Matson",
"given": "Martha Dickinson",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Swedish Center for Research and Innovation, Swedish Medical Center , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Davila",
"given": "Jodie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Swedish Center for Research and Innovation, Swedish Medical Center , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Rueda",
"given": "Justin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Swedish Center for Research and Innovation, Swedish Medical Center , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Tipton",
"given": "Reda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Swedish Center for Research and Innovation, Swedish Medical Center , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Algren",
"given": "Heather",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Spokane Teaching Health Clinic , Spokane, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "Brittney C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sound Critical Care, Sacred Heart Medical Center , Spokane, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Malkoski",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cardiology, Providence St. Vincent Medical Center , Portland, Oregon , USA"
}
],
"family": "Gluckman",
"given": "Tyler",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pacific University, School of Pharmacy , Hillsboro, Oregon , USA"
}
],
"family": "Tallman",
"given": "Gregory B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Providence Sacred Heart Medical Center , Spokane, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Arguinchona",
"given": "Henry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "John Wayne Cancer Institute and Cancer Clinic, Providence St Johns Health Center , Santa Monica, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hammond",
"given": "Terese C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Providence St. Peter’s Hospital , Olympia, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Standaert",
"given": "Steven",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Providence St Patrick Hospital , Missoula, Montana , USA"
}
],
"family": "Christensen",
"given": "Joshua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases, Kadlec Regional Medical Center , Richland, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Echaiz",
"given": "Jose F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Providence Regional Medical Center Everett , Everett, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Providence Regional Medical Center Everett , Everett, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "McClung",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Providence Regional Medical Center Everett , Everett, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Pacifico",
"given": "Albert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Hospital Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Hoag Memorial Hospital Presbyterian , Newport Beach, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Fee",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Hospital Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Hoag Memorial Hospital Presbyterian , Newport Beach, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sarafian",
"given": "Farjad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Swedish Medical Center , Seattle, Washington , USA"
},
{
"name": "Swedish Center for Research and Innovation, Swedish Medical Center , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Berrington",
"given": "William R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Swedish Medical Center , Seattle, Washington , USA"
},
{
"name": "Swedish Center for Research and Innovation, Swedish Medical Center , Seattle, Washington , USA"
},
{
"name": "Division of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, University of Washington , Seattle, Washington , USA"
}
],
"family": "Goldman",
"given": "Jason D",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-11T03:12:56Z",
"timestamp": 1628651576000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-31T22:54:43Z",
"timestamp": 1654037683000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-26T10:21:33Z",
"timestamp": 1711448493456
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 21,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
14
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
30
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 5,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1629331200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciab698/40830924/ciab698.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/74/10/1812/43893786/ciab698.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/74/10/1812/43893786/ciab698.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1812-1820",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
14
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.AC120.013056",
"article-title": "The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4773",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0001",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0002",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"article-title": "Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19—interim WHO Solidarity Trial results",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0003",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1041",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) versus a cohort receiving standard of care",
"author": "Olender",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0004",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2022926",
"article-title": "Effect of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2030",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0005",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2019014",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin in mild-to-moderate Covid-19",
"author": "Cavalcanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2041",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0006",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2012410",
"article-title": "Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "Geleris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2411",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0007",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8630",
"article-title": "Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York State",
"author": "Rosenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2493",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0008",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-4207",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine in nonhospitalized adults with early COVID-19: a randomized trial",
"author": "Skipper",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "623",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0009",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1849",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine in patients with mainly mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019: open label, randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1849",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0010",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001191",
"article-title": "First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States",
"author": "Holshue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "929",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0011",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015301",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid-19",
"author": "Goldman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1827",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0012",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.16349",
"article-title": "Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Spinner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1048",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0013",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007016",
"article-title": "Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19",
"author": "Grein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2327",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0014",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "US Food and Drug Administration.",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa237",
"article-title": "In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)",
"author": "Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "732",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0016",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM199701233360402",
"article-title": "A prediction rule to identify low-risk patients with community-acquired pneumonia",
"author": "Fine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "243",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0017",
"volume": "336",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization.",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0018"
},
{
"author": "R Core Team.",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19—preliminary report",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0020",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012",
"article-title": "COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal",
"author": "Siddiqi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "405",
"journal-title": "J Heart Lung Transplant",
"key": "2022053122502159300_CIT0021",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 21,
"references-count": 21,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/74/10/1812/6352176"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Remdesivir and Mortality in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "74"
}