Possible Impact of Vitamin D Status and Supplementation on SARS-CoV-2 Infection Risk and COVID-19 Symptoms in a Cohort of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15010169, Dec 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Prospective study of 106 IBD patients in Italy, showing lower risk of IgG positivity with vitamin D supplementation. Vitamin D levels below 30 ng/mL were associated with a higher probability of symptomatic cases.
This is the 108th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of IgG positive, 88.4% lower, OR 0.12, p = 0.002, treatment 43, control 63, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
De Nicolò et al., 29 Dec 2022, prospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period January 2021 - April 2021, dosage not specified.
Contact: amedeo.denicolo@unito.it (corresponding author).
Possible Impact of Vitamin D Status and Supplementation on SARS-CoV-2 Infection Risk and COVID-19 Symptoms in a Cohort of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15010169
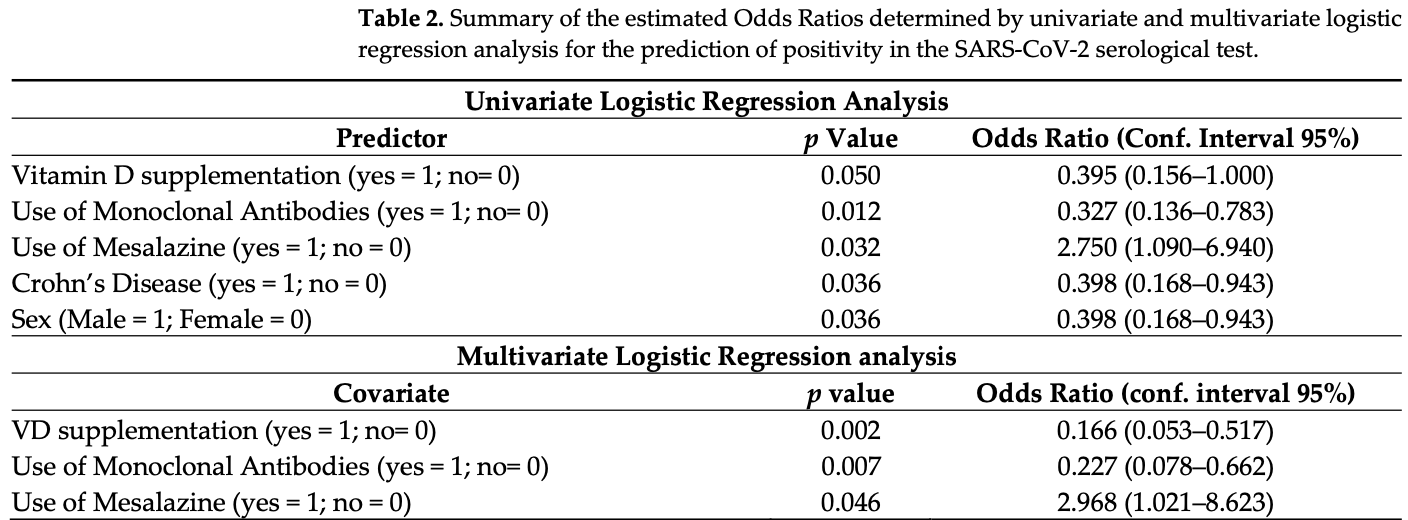
The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic represents a global health challenge, particularly considering concomitant diseases. Patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) can be considered a population at risk. On the other hand, the risk of developing IBD and COVID-19 have both been described as modulated by vitamin D (VD) levels. In this work, a cohort of 106 adult patients affected by IBD was prospectively enrolled, during the second wave of the pandemic in Italy. In these patients, VD plasma levels, demographic, and clinical characteristics were tested for a correlation/an association with the risk of infection with SARS-CoV-2 in the study period (antispike IgG positivity) and the severity of COVID-19 symptoms. By multivariate logistic regression analysis, VD supplementation (Odds Ratio; OR 0.116, p = 0.002), therapy with monoclonal antibodies (OR 0.227, p = 0.007), and the use of mesalazine (OR 2.968, p = 0.046) were found to be independent predictors of SARS-CoV-2 positivity. Moreover, hypertension was associated with severe disease (p = 0.019), while a VD level higher than 30 ng/mL (p = 0.031, OR 0.078) was associated with asymptomatic infection. No interplay between IBD activity and COVID-19 risk of infection or symptoms was observed. These results confirm the importance of VD levels in defining the risk of COVID-19 and give encouraging data about the safety of maintaining immunomodulatory treatments for IBD during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Anbarcioglu, Kirtiloglu, Ozturk, Kolbakir, Acikgoz et al., Vitamin D deficiency in patients with aggressive periodontitis, Oral Dis, doi:10.1111/odi.12968
Arboleda, Urcuqui-Inchima, Vitamin, Supplementation: A Potential Approach for Coronavirus/COVID-19 Therapeutics? Front, Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01523
Arora, Patel, Nicol, Field, Restori et al., Vitamin D and the Ability to Produce 1,25(OH)(2)D Are Critical for Protection from Viral Infection of the Lungs, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14153061
Azrielant, Shoenfeld, Vitamin D and the Immune System, Isr. Med. Assoc. J
Balestrieri, Ribolsi, Guarino, Emerenziani, Altomare et al., Nutritional Aspects in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12020372
Benskin, A Basic Review of the Preliminary Evidence That COVID-19 Risk and Severity Is Increased in Vitamin D Deficiency, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.00513
Bezzio, Armuzzi, Furfaro, Ardizzone, Milla et al., Therapies for inflammatory bowel disease do not pose additional risks for adverse outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection: An IG-IBD study, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.16663
Bezzio, Saibeni, Variola, Allocca, Massari et al., Outcomes of COVID-19 in 79 patients with IBD in Italy: An IG-IBD study, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321411
Boglione, Cusato, De Nicolo, Cariti, Di Perri et al., Role of CYP27B1+2838 promoter polymorphism in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B HBeAg negative with PEG-interferon, J. Viral Hepat, doi:10.1111/jvh.12288
Calcagno, Ghisetti, Emanuele, Trunfio, Faraoni et al., Risk for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Healthcare Workers, Emerg. Infect. Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2701.203027
Cascella, Rajnik, Aleem, Dulebohn, Di Napoli et al., Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19
Castillo, Entrenas Costa, Vaquero Barrios, Alcala Diaz, Lopez Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Chauss, Freiwald, Mcgregor, Yan, Wang et al., Autocrine vitamin D signaling switches off pro-inflammatory programs of TH1 cells, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-021-01080-3
Coperchini, Ricci, Croce, Denegri, Ruggiero et al., Modulation of ACE-2 mRNA by inflammatory cytokines in human thyroid cells: A pilot study, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-021-02807-w
Courbebaisse, Cavalier, Vitamin, in 2020: An Old Pro-Hormone with Potential Effects beyond Mineral Metabolism, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113378
Cusato, Allegra, Boglione, De Nicolo, Baietto et al., Vitamin D pathway gene variants and HCV-2/3 therapy outcomes, Antivir. Ther, doi:10.3851/IMP2853
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, De Nicolo et al., 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Are Lower in Patients with Positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051359
De Nicolò, Avataneo, Cusato, Palermiti, Mula et al., Analytical Validation and Clinical Application of Rapid Serological Tests for SARS-CoV-2 Suitable for Large-Scale Screening, Diagnostics, doi:10.3390/diagnostics11050869
Dickie, Church, Coulthard, Mathews, Emery et al., Vitamin D3 down-regulates intracellular Toll-like receptor 9 expression and Toll-like receptor 9-induced IL-6 production in human monocytes, Rheumatology, doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keq124
Dipasquale, Lo Presti, Milani, Corsello, Agostoni et al., Vitamin D in Prevention of Autoimmune Diseases, Front. Biosci. Landmark, doi:10.31083/j.fbl2710288
Dragasevic, Stankovic, Kotur, Milutinovic, Milovanovic et al., Genetic Aspects of Micronutrients Important for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Life, doi:10.3390/life12101623
Ecco, Update on COVID-19 and IBD
Gallelli, Mannino, Luciani, De Sire, Mancuso et al., Vitamin D Serum Levels in Subjects Tested for SARS-CoV-2: What Are the Differences among Acute, Healed, and Negative COVID-19 Patients? A Multicenter Real-Practice Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13113932
Gibbons, Norton, Mccullough, Meltzer, Lavigne et al., Association between vitamin D supplementation and COVID-19 infection and mortality, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-24053-4
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Gordon, Hanley et al., Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
Holick, The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: Approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention, Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-017-9424-1
Huang, Lian, Song, Ma, Lian et al., Clinical features of severe patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann. Transl. Med, doi:10.21037/atm-20-2124
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Singh, Mahor et al., Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z
Jin, Lian, Hu, Gao, Zheng et al., Epidemiological, clinical and virological characteristics of 74 cases of coronavirus-infected disease 2019 (COVID-19) with gastrointestinal symptoms, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320926
Katz, Yue, Xue, Increased risk for COVID-19 in patients with vitamin D deficiency, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111106
Kolls, Garry, Role of the T cell vitamin D receptor in severe COVID-19, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-021-01098-7
Lu, Clinical presentations of inflammatory bowel disease: East meets West, J. Chin. Med. Assoc, doi:10.1016/j.jcma.2016.09.005
Maaser, Sturm, Vavricka, Kucharzik, Fiorino et al., ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications, J. Crohns Colitis, doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy113
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Pazoki, Kafan et al., Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239799
Martineau, Cantorna, Vitamin D for COVID-19: Where are we now?, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-022-00765-6
Martineau, Vitamin D in the prevention or treatment of COVID-19, Proc. Nutr. Soc, doi:10.1017/S0029665122002798
Matheu, Back, Mondoc, Issazadeh-Navikas, Dual effects of vitamin D-induced alteration of TH1/TH2 cytokine expression: Enhancing IgE production and decreasing airway eosinophilia in murine allergic airway disease, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1016/s0091-6749
Mehta, Gracias, Croft, TNF activity and T cells, Cytokine, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2016.08.003
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics with COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Munshi, Hussein, Toraih, Elshazli, Jardak et al., Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26360
Murai, Fernandes, Antonangelo, Gualano, Pereira, Effect of a Single High-Dose Vitamin D3 on the Length of Hospital Stay of Severely 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-Deficient Patients with COVID-19, Clinics, doi:10.6061/clinics/2021/e3549
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a Single High Dose of Vitamin D3 on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Moderate to Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26848
Neurath, COVID-19 and immunomodulation in IBD, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321269
Sanson, De Nicolo, Zerbato, Segat, Koncan et al., A combined role for low vitamin D and low albumin circulating levels as strong predictors of worse outcome in COVID-19 patients, Ir. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1007/s11845-022-02952-9
Sekine, Perez-Potti, Rivera-Ballesteros, Stralin, Gorin et al., Robust T Cell Immunity in Convalescent Individuals with Asymptomatic or Mild COVID-19, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.017
Siew, Hilmi, Blake, Bhayat, Adsul et al., Low Frequency of Opportunistic Infections in Patients Receiving Vedolizumab in Clinical Trials and Post-Marketing Setting, Inflamm. Bowel Dis, doi:10.1093/ibd/izy153
Vatn, Sandvik, Inflammatory bowel disease, Scand. J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.3109/00365521.2015.1033000
Villasis-Keever, Lopez-Alarcon, Miranda-Novales, Zurita-Cruz, Barrada-Vazquez et al., Efficacy and Safety of Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 in Frontline Healthcare Workers. A Randomized Clinical Trial, Arch. Med. Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003
Wang, Wang, Li, Chen, Han et al., Human Cathelicidin Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Killing Two Birds with One Stone, ACS Infect. Dis, doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00096
Wong, Lui, Sung, Covid-19 and the digestive system, J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1111/jgh.15047
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk Factors Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern. Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
Wu, Liu, Deng, The Role of Vitamin D in Immune System and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, J. Inflamm. Res, doi:10.2147/JIR.S363840
Zhang, Leung, Richers, Liu, Remigio et al., Vitamin D inhibits monocyte/macrophage proinflammatory cytokine production by targeting MAPK phosphatase-1, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102412
Zhang, Wu, Role of vitamin D in immune responses and autoimmune diseases, with emphasis on its role in multiple sclerosis, Neurosci. Bull, doi:10.1007/s12264-010-0731-8
Zhao, Zhang, Wu, Li, Liu et al., Protective role of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 in the mucosal injury and epithelial barrier disruption in DSS-induced acute colitis in mice, BMC Gastroenterol, doi:10.1186/1471-230X-12-57
Zurita-Cruz, Fonseca-Tenorio, Villasis-Keever, Lopez-Alarcon, Parra-Ortega et al., Efficacy and safety of vitamin D supplementation in hospitalized COVID-19 pediatric patients: A randomized controlled trial, Front. Pediatr, doi:10.3389/fped.2022.943529
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15010169",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu15010169",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic represents a global health challenge, particularly considering concomitant diseases. Patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) can be considered a population at risk. On the other hand, the risk of developing IBD and COVID-19 have both been described as modulated by vitamin D (VD) levels. In this work, a cohort of 106 adult patients affected by IBD was prospectively enrolled, during the second wave of the pandemic in Italy. In these patients, VD plasma levels, demographic, and clinical characteristics were tested for a correlation/an association with the risk of infection with SARS-CoV-2 in the study period (anti-spike IgG positivity) and the severity of COVID-19 symptoms. By multivariate logistic regression analysis, VD supplementation (Odds Ratio; OR 0.116, p = 0.002), therapy with monoclonal antibodies (OR 0.227, p = 0.007), and the use of mesalazine (OR 2.968, p = 0.046) were found to be independent predictors of SARS-CoV-2 positivity. Moreover, hypertension was associated with severe disease (p = 0.019), while a VD level higher than 30 ng/mL (p = 0.031, OR 0.078) was associated with asymptomatic infection. No interplay between IBD activity and COVID-19 risk of infection or symptoms was observed. These results confirm the importance of VD levels in defining the risk of COVID-19 and give encouraging data about the safety of maintaining immunomodulatory treatments for IBD during the COVID-19 pandemic.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu15010169"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5973-9948",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "De Nicolò",
"given": "Amedeo De",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1977-9694",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cusato",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bezzio",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saibeni",
"given": "Simone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6904-7638",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vernero",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Disabato",
"given": "Michela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caviglia",
"given": "Gian Paolo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ianniello",
"given": "Alice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8540-6709",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Manca",
"given": "Alessandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1321-4126",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "D’Avolio",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9421-3087",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ribaldone",
"given": "Davide Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-30T08:18:18Z",
"timestamp": 1672388298000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-30T08:55:24Z",
"timestamp": 1672390524000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-31T06:10:30Z",
"timestamp": 1672467030516
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672272000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/1/169/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "169",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/1/169"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Possible Impact of Vitamin D Status and Supplementation on SARS-CoV-2 Infection Risk and COVID-19 Symptoms in a Cohort of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "15"
}
