SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein 1 Causes Aggregation of α-Synuclein via Microglia-Induced Inflammation and Production of Mitochondrial ROS: Potential Therapeutic Applications of Metformin
et al., Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines12061223, May 2024
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
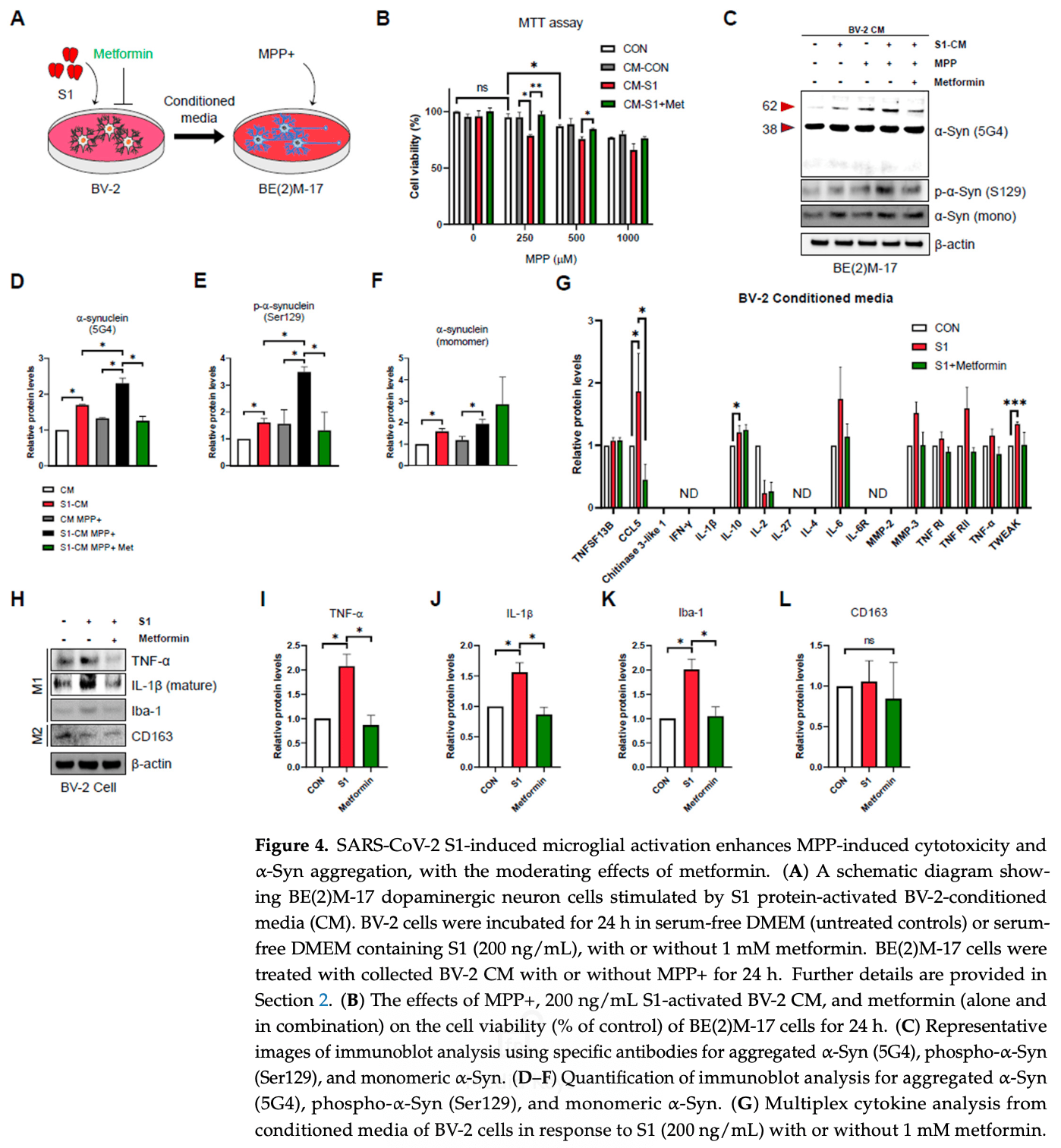
In vitro and rat study showing that the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 subunit causes aggregation of α-synuclein and microglial activation, which may contribute to the neurological symptoms seen in long COVID. In rats, intranasal administration of S1 increased α-synuclein aggregation and microglial activation in the brain 6 weeks later. In dopaminergic neurons, S1 increased α-synuclein aggregation via both microglial inflammatory responses and direct induction of mitochondrial damage. Metformin attenuated the S1-induced inflammatory response and α-synuclein aggregation.
18 preclinical studies support the efficacy of metformin for COVID-19:
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 non-COVID-19 preclinical studies showed that metformin inhibits pulmonary inflammation and oxidative stress, minimizes lung injury, and improves survival in animal models of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or acute lung injury (ALI)15.
Metformin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in vitro11,12, minimizes LPS-induced cytokine storm in a mouse model14, minimizes lung damage and fibrosis in a mouse model of LPS-induced ARDS10, may protect against SARS-CoV-2-induced neurological disorders9, may be beneficial via inhibitory effects on ORF3a-mediated inflammasome activation16, reduces UUO and FAN-induced kidney fibrosis10, increases mitochondrial function and decreases TGF-β-induced fibrosis, apoptosis, and inflammation markers in lung epithelial cells10, may reduce inflammation, oxidative stress, and thrombosis via regulating glucose metabolism2, attenuates spike protein S1-induced inflammatory response and α-synuclein aggregation8, may protect against COVID-19 cognitive impairment by suppressing HIF-1α stabilization and reducing neurodegenerative protein aggregation13, may reduce COVID-19 severity and long COVID by inhibiting NETosis via suppression of protein kinase C activation17, enhances interferon responses and reduces SARS-CoV-2 infection and inflammation in diabetic models by suppressing HIF-1α signaling7, may improve COVID-19 outcomes by preventing VDAC1 mistargeting to the plasma membrane, reducing ATP loss, and preserving immune cell function during cytokine storm18, reduces hyperglycemia-induced hepatic ACE2/TMPRSS2 up-regulation and SARS-CoV-2 entry6, may reduce COVID-19 severity by suppressing monocyte inflammatory responses and glycolytic activation via AMPK pathway modulation5, and may improve outcomes via modulation of immune responses with increased anti-inflammatory T lymphocyte gene expression and via enhanced gut microbiota diversity19.
1.
Tavares et al., Investigation of Interactions Between the Protein MPro and the Vanadium Complex VO(metf)2∙H2O: A Computational Approach for COVID-19 Treatment, Biophysica, doi:10.3390/biophysica5010004.
2.
Hou et al., Metformin is a potential therapeutic for COVID-19/LUAD by regulating glucose metabolism, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-63081-0.
3.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
4.
Lockwood, T., Coordination chemistry suggests that independently observed benefits of metformin and Zn2+ against COVID-19 are not independent, BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-024-00590-5.
5.
Maurmann et al., Immunoregulatory effect of metformin in monocytes exposed to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit 1, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.09.12.675877.
6.
Rao et al., Pathological Glucose Levels Enhance Entry Factor Expression and Hepatic SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection, Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, doi:10.1111/jcmm.70581.
7.
Joshi et al., Severe SARS‐CoV‐2 infection in diabetes was rescued in mice supplemented with metformin and/or αKG, and patients taking metformin, via HIF1α‐IFN axis, Clinical and Translational Medicine, doi:10.1002/ctm2.70275.
8.
Chang et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein 1 Causes Aggregation of α-Synuclein via Microglia-Induced Inflammation and Production of Mitochondrial ROS: Potential Therapeutic Applications of Metformin, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines12061223.
9.
Yang et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection causes dopaminergic neuron senescence, Cell Stem Cell, doi:10.1016/j.stem.2023.12.012.
10.
Miguel et al., Enhanced fatty acid oxidation through metformin and baicalin as therapy for COVID-19 and associated inflammatory states in lung and kidney, Redox Biology, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2023.102957.
11.
Ventura-López et al., Treatment with metformin glycinate reduces SARS-CoV-2 viral load: An in vitro model and randomized, double-blind, Phase IIb clinical trial, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113223.
12.
Parthasarathy et al., Metformin Suppresses SARS-CoV-2 in Cell Culture, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.11.18.469078.
13.
Lee et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein causes synaptic dysfunction and p-tau and α-synuclein aggregation leading cognitive impairment: The protective role of metformin, PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0336015.
14.
Taher et al., Anti‑inflammatory effect of metformin against an experimental model of LPS‑induced cytokine storm, Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, doi:10.3892/etm.2023.12114.
15.
Wang et al., Effects of metformin on acute respiratory distress syndrome in preclinical studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1215307.
16.
Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a Protein as a Therapeutic Target against COVID-19 and Long-Term Post-Infection Effects, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens13010075.
17.
Monsalve et al., NETosis: A key player in autoimmunity, COVID-19, and long COVID, Journal of Translational Autoimmunity, doi:10.1016/j.jtauto.2025.100280.
Chang et al., 31 May 2024, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: kohyoungho122@gmail.com (corresponding author), def9207@gmail.com, ntpeace@korea.kr, lhk215@korea.kr, jiyoung0220@gmail.com.
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein 1 Causes Aggregation of α-Synuclein via Microglia-Induced Inflammation and Production of Mitochondrial ROS: Potential Therapeutic Applications of Metformin
Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines12061223
Abnormal aggregation of α-synuclein is the hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases, classified as α-synucleinopathies, primarily occurring sporadically. Their onset is associated with an interaction between genetic susceptibility and environmental factors such as neurotoxins, oxidative stress, inflammation, and viral infections. Recently, evidence has suggested an association between neurological complications in long COVID (sometimes referred to as 'post-acute sequelae of COVID-19') and α-synucleinopathies, but its underlying mechanisms are not completely understood. In this study, we first showed that SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein 1 (S1) induces α-synuclein aggregation associated with activation of microglial cells in the rodent model. In vitro, we demonstrated that S1 increases aggregation of α-synuclein in BE(2)M-17 dopaminergic neurons via BV-2 microglia-mediated inflammatory responses. We also identified that S1 directly affects aggregation of α-synuclein in dopaminergic neurons through increasing mitochondrial ROS, though only under conditions of sufficient α-Syn accumulation. In addition, we observed a synergistic effect between S1 and the neurotoxin MPP+ S1 treatment. Combined with a low dose of MPP+, it boosted α-synuclein aggregation and mitochondrial ROS production compared to S1 or the MPP+ treatment group. Furthermore, we evaluated the therapeutic effects of metformin. The treatment of metformin suppressed the S1-induced inflammatory response and α-synucleinopathy. Our findings demonstrate that S1 promotes α-synucleinopathy via both microglia-mediated inflammation and mitochondrial ROS, and they provide pathological insights, as well as a foundation for the clinical management of α-synucleinopathies and the onset of neurological symptoms after the COVID-19 outbreak.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1. Supplementary Figure S1 . (A) Immunoblot analysis using his-tag specific antibody to identify that S1 enter to striatum of rat brain after intranasal administration. (B) Representative images of immunoblot analysis using specific antibody for aggregated α-Syn (5G4), phospho-α-Syn (Ser129), and monomeric α-Syn in 500 ng/mL S1-treated normal BE(2)M-17. (C-E) Quantification of immunoblot analysis for aggregated α-Syn (5G4), phospho-α-Syn (Ser129), and monomeric α-Syn. (F) Representative images of TH staining in the rat substantia nigra and (G) quantification of data. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3-5 per group, * p < 0.05). Supplementary Table S1 . Lists of antibodies. Author Contributions: M.H.C.: conceptualization, writing-original draft, methodology, data curation, investigation. J.H.P.: conceptualization, writing-review and editing, methodology, data curation, investigation. H.K.L.: writing-review and editing, methodology, investigation. J.Y.C.: conceptualization, writing-review and editing. Y.H.K.: conceptualization, funding acquisition, review and supervision, writing-review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The animal protocol used was reviewed and approved by the KCDC-Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (KCDC-IACUC; Approval..
References
Alafuzoff, Hartikainen, Chapter 24-Alpha-synucleinopathies
Almutairi, Sivandzade, Albekairi, Alqahtani, Cucullo, Neuroinflammation and Its Impact on the Pathogenesis of COVID-19, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.745789
Andrzejewski, Gravel, Pollak, St-Pierre, Metformin directly acts on mitochondria to alter cellular bioenergetics, Cancer Metab, doi:10.1186/2049-3002-2-12
Bae, Choi, Kim, Kim, Jung et al., TNF-α promotes α-synuclein propagation through stimulation of senescence-associated lysosomal exocytosis, Exp. Mol. Med, doi:10.1038/s12276-022-00789-x
Bourget, Adams, Morshead, Reduced microglia activation following metformin administration or microglia ablation is sufficient to prevent functional deficits in a mouse model of neonatal stroke, J. Neuroinflamm, doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02487-x
Bramante, Buse, Liebovitz, Nicklas, Puskarich et al., Outpatient treatment of COVID-19 and incidence of post-COVID-19 condition over 10 months (COVID-OUT): A multicentre, randomised, quadruple-blind, parallel-group, phase 3 trial, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00299-2
Cao, Nguyen, Tsai, Gao, Tian et al., The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces long-term transcriptional perturbations of mitochondrial metabolic genes, causes cardiac fibrosis, and reduces myocardial contractile in obese mice, Mol. Metab, doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101756
Choi, Chappard, Singh, Maclachlan, Rodrigues et al., Pathological structural conversion of α-synuclein at the mitochondria induces neuronal toxicity, Nat. Neurosci, doi:10.1038/s41593-022-01140-3
Clough, Inigo, Chandra, Chaves, Reynolds et al., Mitochondrial Dynamics in SARS-CoV2 Spike Protein Treated Human Microglia: Implications for Neuro-COVID, J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s11481-021-10015-6
Craddock, Mahajan, Krishnamachary, Spikes, Chalise et al., Persistent Presence of Spike protein and Viral RNA in the Circulation of Individuals with Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.08.07.22278520
Davis, Mccorkell, Vogel, Topol, Long, Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00846-2
Deleidi, Gasser, The role of inflammation in sporadic and familial Parkinson's disease, Cell. Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-013-1352-y
Dibona, Shah, Krause, Zhu, Voglewede et al., Metformin reduces neuroinflammation and improves cognitive functions after traumatic brain injury, Neurosci. Res, doi:10.1016/j.neures.2021.05.007
Faustini, Bono, Valerio, Pizzi, Spano et al., Mitochondria and α-Synuclein: Friends or Foes in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease?, Genes, doi:10.3390/genes8120377
Fearon, Fasano, Parkinson's Disease and the COVID-19 Pandemic, J. Park. Dis, doi:10.3233/JPD-202320
Ferreira, Moreira, De Araújo, Imamura, Damiano et al., Clinical, sociodemographic and environmental factors impact post-COVID-19 syndrome, J. Glob. Health, doi:10.7189/jogh.12.05029
Festa, Siddiqi, Jimenez-Sanchez, Won, Rob et al., Microglial-toneuronal CCR5 signaling regulates autophagy in neurodegeneration, Neuron, doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2023.04.006
Fontes-Dantas, Fernandes, Gutman, De Lima, Antonio et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein induces TLR4-mediated long-term cognitive dysfunction recapitulating post-COVID-19 syndrome in mice, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112189
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Harris, Tsui, Marion, Shen, Teschke, Association of Parkinson's disease with infections and occupational exposure to possible vectors, Mov. Disord, doi:10.1002/mds.25077
Huynh, Rethi, Lee, Higa, Kao et al., Spike Protein Impairs Mitochondrial Function in Human Cardiomyocytes: Mechanisms Underlying Cardiac Injury in COVID-19, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells12060877
Jang, Boltz, Sturm-Ramirez, Shepherd, Jiao et al., Highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus can enter the central nervous system and induce neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.0900096106
Jiang, Yu, Zhu, Wang, Tan et al., Acute metformin preconditioning confers neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischaemia by pre-activation of AMPK-dependent autophagy, Br. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bph.12655
Katila, Bhurtel, Shadfar, Srivastav, Neupane et al., Metformin lowers α-synuclein phosphorylation and upregulates neurotrophic factor in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease, Neuropharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.015
Kim, Bae, Jung, Choi, Shin et al., Inflammation promotes synucleinopathy propagation, Exp. Mol. Med, doi:10.1038/s12276-022-00895-w
Klein, Soung, Sissoko, Nordvig, Canoll et al., COVID-19 induces neuroinflammation and loss of hippocampal neurogenesis, Res. Sq, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1031824/v1
Kowall, Hantraye, Brouillet, Beal, Mckee et al., MPTP induces alpha-synuclein aggregation in the substantia nigra of baboons, NeuroReport, doi:10.1097/00001756-200001170-00041
Kwon, Koh, Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes, Transl. Neurodegener, doi:10.1186/s40035-020-00221-2
Lai, Shih, Ko, Tang, Hsueh, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105924
Langston, The MPTP Story, J. Park. Dis, doi:10.3233/JPD-179006
Lenz, Nelson, Microglia and Beyond: Innate Immune Cells As Regulators of Brain Development and Behavioral Function, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.00698
Lim, Chun, Lee, Lee, Neuroinflammation in Synucleinopathies, Brain Pathol, doi:10.1111/bpa.12371
Limphaibool, Iwanowski, Holstad, Kobylarek, Kozubski, Infectious Etiologies of Parkinsonism: Pathomechanisms and Clinical Implications, Front. Neurol, doi:10.3389/fneur.2019.00652
Lu, Su, Qiao, Bian, Ding et al., Metformin Prevents Dopaminergic Neuron Death in MPTP/P-Induced Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease via Autophagy and Mitochondrial ROS Clearance, Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol, doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyw047
Marreiros, Müller-Schiffmann, Trossbach, Prikulis, Hänsch et al., Disruption of cellular proteostasis by H1N1 influenza A virus causes α-synuclein aggregation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1906466117
Mccall, Henry, Reid, Taubenberger, Influenza RNA not Detected in Archival Brain Tissues from Acute Encephalitis Lethargica Cases or in Postencephalitic Parkinson Cases, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol, doi:10.1093/jnen/60.7.696
Mccann, Stevens, Cartwright, Halliday, α-Synucleinopathy phenotypes, Park. Relat. Disord, doi:10.1016/S1353-8020(13)70017-8
Menza, Defronzo Dobkin, Marin, Mark, Gara et al., The Role of Inflammatory Cytokines in Cognition and Other Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease, Psychosomatics
Ng, Feng, Yap, Lee, Tan et al., Long-Term Metformin Usage and Cognitive Function among Older Adults with Diabetes, J. Alzheimer's Dis, doi:10.3233/JAD-131901
Oh, Cho, Barcelon, Kim, Hong et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces cognitive deficit and anxiety-like behavior in mouse via non-cell autonomous hippocampal neuronal death, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-09410-7
Orihuela, Mcpherson, Harry, Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states, Br. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bph.13139
Parthasarathy, Tandel, Siddiqui, Harshan, Metformin suppresses SARS-CoV-2 in cell culture, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2022.199010
Patil, Jain, Ghumatkar, Tambe, Sathaye, Neuroprotective effect of metformin in MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease in mice, Neuroscience, doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.046
Patterson, Francisco, Yogendra, Long, Pise et al., Persistence of SARS CoV-2 S1 Protein in CD16+ Monocytes in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) up to 15 Months Post-Infection, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.746021
Patterson, Guevara-Coto, Yogendra, Francisco, Long et al., Immune-Based Prediction of COVID-19 Severity and Chronicity Decoded Using Machine Learning, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.700782
Pernicova, Korbonits Metformin-mode of action and clinical implications for diabetes and cancer, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/nrendo.2013.256
Prusiner, Neurodegenerative Diseases and Prions, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJM200105173442006
Rao, Hidayathullah, Hegde, Adhikari, Parkinsonism: An emerging post COVID sequelae, IDCases, doi:10.1016/j.idcr.2022.e01388
Reish, Standaert, Role of α-synuclein in inducing innate and adaptive immunity in Parkinson disease, J. Park. Dis, doi:10.3233/JPD-140491
Rong, Mai, Kapoor, Puelles, Czogalla et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Accumulation in the Skull-Meninges-Brain Axis: Potential Implications for Long-Term Neurological Complications in post-COVID-19, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.04.04.535604
Sadasivan, Sharp, Schultz-Cherry, Smeyne, Synergistic effects of influenza and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) can be eliminated by the use of influenza therapeutics: Experimental evidence for the multi-hit hypothesis, Npj Park. Dis, doi:10.1038/s41531-017-0019-z
Sato, Kato, Arawaka, The role of Ser129 phosphorylation of α-synuclein in neurodegeneration of Parkinson's disease: A review of in vivo models, Rev. Neurosci, doi:10.1515/revneuro-2012-0071
Schaller, Sharma, Dupee, Nguyen, Urueña et al., Ex vivo SARS-CoV-2 infection of human lung reveals heterogeneous host defense and therapeutic responses, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.148003
Schultheiß, Willscher, Paschold, Gottschick, Klee et al., From online data collection to identification of disease mechanisms: The IL-1ß, IL-6 and TNF-α cytokine triad is associated with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 in a digital research cohort, medRxiv
Shalash, Helmy, Salama, Gaber, El-Belkimy et al., A 6-month longitudinal study on worsening of Parkinson's disease during the COVID-19 pandemic, Npj Park. Dis, doi:10.1038/s41531-022-00376-x
Sheng, Chertow, Ambroggio, Mccall, Przygodzki et al., Autopsy series of 68 cases dying before and during the 1918 influenza pandemic peak, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1111179108
Stefanis, α-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease, Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med, doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a009399
Tang, Chong, Li, Liu, Liu et al., Correlation between Serum RANTES Levels and the Severity of Parkinson's Disease, Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev, doi:10.1155/2014/208408
Theoharides, Could SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Be Responsible for Long-COVID Syndrome?, Mol. Neurobiol, doi:10.1007/s12035-021-02696-0
Vanelzakker, Bues, Brusaferri, Kim, Saadi et al., Neuroinflammation in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) as assessed by [ C]PBR28 PET correlates with vascular disease measures, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.10.19.563117
Ventura-López, Cervantes-Luevano, Aguirre-Sánchez, Flores-Caballero, Alvarez-Delgado et al., Treatment with metformin glycinate reduces SARS-CoV-2 viral load: An in vitro model and randomized, double-blind, Phase IIb clinical trial, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113223
Vlajinac, Dzoljic, Maksimovic, Marinkovic, Sipetic et al., Infections as a risk factor for Parkinson's disease: A case-control study, Int. J. Neurosci, doi:10.3109/00207454.2012.760560
Wahlqvist, Lee, Hsu, Chuang, Lee et al., Metformin-inclusive sulfonylurea therapy reduces the risk of Parkinson's disease occurring with Type 2 diabetes in a Taiwanese population cohort, Park. Relat. Disord, doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.03.010
Wang, Dai, Deng, Xiao, Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Domain Accelerates α-Synuclein Phosphorylation and Aggregation in Cellular Models of Synucleinopathy, Mol. Neurobiol, doi:10.1007/s12035-023-03726-9
Wu, Shen, Jiang, Shen, Wang et al., Clinical characteristics and outcome of COVID-19 patients with Parkinson's disease: A hospital-based case-control study in Shanghai, China, Front. Aging Neurosci, doi:10.3389/fnagi.2023.1138418
Wu, Zhang, Huang, Ma, SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Interact with Alpha Synuclein and Induce Lewy Body-like Pathology In Vitro, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23063394
Xenos, Mecocci, Boccardi, A blast from the past: To tame time with metformin, Mech. Ageing Dev, doi:10.1016/j.mad.2022.111743
Xu, Xie, Al-Aly, Long-term neurologic outcomes of COVID-19, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-022-02001-z
Zekri-Nechar, Zamorano-León, Reche, Giner, López-De-Andrés et al., Spike Protein Subunits of SARS-CoV-2 Alter Mitochondrial Metabolism in Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells: Involvement of Factor Xa, Dis. Markers, doi:10.1155/2022/1118195
Zhao, An, Mao, Qu, Wang et al., CCL5 promotes LFA-1 expression in Th17 cells and induces LCK and ZAP70 activation in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, Front. Aging Neurosci, doi:10.3389/fnagi.2023.1250685
Łabuzek, Suchy, Gabryel, Bielecka, Liber et al., Quantification of metformin by the HPLC method in brain regions, cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of rats treated with lipopolysaccharide, Pharmacol. Rep, doi:10.1016/S1734-1140(10)70357-1
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines12061223",
"ISSN": [
"2227-9059"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061223",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Abnormal aggregation of α-synuclein is the hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases, classified as α-synucleinopathies, primarily occurring sporadically. Their onset is associated with an interaction between genetic susceptibility and environmental factors such as neurotoxins, oxidative stress, inflammation, and viral infections. Recently, evidence has suggested an association between neurological complications in long COVID (sometimes referred to as ‘post-acute sequelae of COVID-19’) and α-synucleinopathies, but its underlying mechanisms are not completely understood. In this study, we first showed that SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein 1 (S1) induces α-synuclein aggregation associated with activation of microglial cells in the rodent model. In vitro, we demonstrated that S1 increases aggregation of α-synuclein in BE(2)M-17 dopaminergic neurons via BV-2 microglia-mediated inflammatory responses. We also identified that S1 directly affects aggregation of α-synuclein in dopaminergic neurons through increasing mitochondrial ROS, though only under conditions of sufficient α-Syn accumulation. In addition, we observed a synergistic effect between S1 and the neurotoxin MPP+ S1 treatment. Combined with a low dose of MPP+, it boosted α-synuclein aggregation and mitochondrial ROS production compared to S1 or the MPP+ treatment group. Furthermore, we evaluated the therapeutic effects of metformin. The treatment of metformin suppressed the S1-induced inflammatory response and α-synucleinopathy. Our findings demonstrate that S1 promotes α-synucleinopathy via both microglia-mediated inflammation and mitochondrial ROS, and they provide pathological insights, as well as a foundation for the clinical management of α-synucleinopathies and the onset of neurological symptoms after the COVID-19 outbreak.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"biomedicines12061223"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Brain Diseases Research, Department of Chronic Disease Convergence Research, Korea National Institute of Health, 187 Osongsaengmyeong2(i)-ro, Osong-eup, Heungdeok-gu, Cheongju-si 28159, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Moon Han",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Brain Diseases Research, Department of Chronic Disease Convergence Research, Korea National Institute of Health, 187 Osongsaengmyeong2(i)-ro, Osong-eup, Heungdeok-gu, Cheongju-si 28159, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Park",
"given": "Jung Hyun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Brain Diseases Research, Department of Chronic Disease Convergence Research, Korea National Institute of Health, 187 Osongsaengmyeong2(i)-ro, Osong-eup, Heungdeok-gu, Cheongju-si 28159, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Hye Kyung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Brain Diseases Research, Department of Chronic Disease Convergence Research, Korea National Institute of Health, 187 Osongsaengmyeong2(i)-ro, Osong-eup, Heungdeok-gu, Cheongju-si 28159, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Ji Young",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9934-5321",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Brain Diseases Research, Department of Chronic Disease Convergence Research, Korea National Institute of Health, 187 Osongsaengmyeong2(i)-ro, Osong-eup, Heungdeok-gu, Cheongju-si 28159, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Koh",
"given": "Young Ho",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biomedicines",
"container-title-short": "Biomedicines",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-31T10:35:32Z",
"timestamp": 1717151732000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-31T12:48:14Z",
"timestamp": 1717159694000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"2021-NI-020-02"
],
"name": "Research of Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention"
},
{
"award": [
"2020-NI-024-02"
],
"name": "Research of Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-01T00:26:25Z",
"timestamp": 1717201585581
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1717113600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/12/6/1223/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1223",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "Kovacs, G.G., and Alafuzoff, I. (2018). Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Elsevier. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128023952000249."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1353-8020(13)70017-8",
"article-title": "α-Synucleinopathy phenotypes",
"author": "McCann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S62",
"journal-title": "Park. Relat. Disord.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/cshperspect.a009399",
"article-title": "α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease",
"author": "Stefanis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "a009399",
"journal-title": "Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM200105173442006",
"article-title": "Neurodegenerative Diseases and Prions",
"author": "Prusiner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1516",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "344",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-013-1352-y",
"article-title": "The role of inflammation in sporadic and familial Parkinson’s disease",
"author": "Deleidi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4259",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/00207454.2012.760560",
"article-title": "Infections as a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease: A case–control study",
"author": "Vlajinac",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "329",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mds.25077",
"article-title": "Association of Parkinson’s disease with infections and occupational exposure to possible vectors",
"author": "Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1111",
"journal-title": "Mov. Disord.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jnen/60.7.696",
"article-title": "Influenza RNA not Detected in Archival Brain Tissues from Acute Encephalitis Lethargica Cases or in Postencephalitic Parkinson Cases",
"author": "Mccall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "696",
"journal-title": "J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1111179108",
"article-title": "Autopsy series of 68 cases dying before and during the 1918 influenza pandemic peak",
"author": "Sheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16416",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1906466117",
"article-title": "Disruption of cellular proteostasis by H1N1 influenza A virus causes α-synuclein aggregation",
"author": "Marreiros",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6741",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0900096106",
"article-title": "Highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus can enter the central nervous system and induce neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration",
"author": "Jang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14063",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105924",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105924",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00846-2",
"article-title": "Long COVID: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations",
"author": "Davis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12035-021-02696-0",
"article-title": "Could SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Be Responsible for Long-COVID Syndrome?",
"author": "Theoharides",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1850",
"journal-title": "Mol. Neurobiol.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41531-022-00376-x",
"article-title": "A 6-month longitudinal study on worsening of Parkinson’s disease during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Shalash",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "Npj Park. Dis.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-02001-z",
"article-title": "Long-term neurologic outcomes of COVID-19",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2406",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Parkinson’s Disease and the COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "Fearon",
"first-page": "431",
"journal-title": "J. Park. Dis.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.idcr.2022.e01388",
"article-title": "Parkinsonism: An emerging post COVID sequelae",
"author": "Rao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01388",
"journal-title": "IDCases",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnagi.2023.1138418",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcome of COVID-19 patients with Parkinson’s disease: A hospital-based case–control study in Shanghai, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1138418",
"journal-title": "Front. Aging Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.10.19.563117",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_20",
"unstructured": "VanElzakker, M.B., Bues, H.F., Brusaferri, L., Kim, M., Saadi, D., Ratai, E.-M., Dougherty, D.D., and Loggia, M.L. (2023). Neuroinflammation in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) as assessed by [11C]PBR28 PET correlates with vascular disease measures. bioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.746021",
"article-title": "Persistence of SARS CoV-2 S1 Protein in CD16+ Monocytes in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) up to 15 Months Post-Infection",
"author": "Patterson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "746021",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.08.07.22278520",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "Craddock, V., Mahajan, A., Krishnamachary, B., Spikes, L., Chalise, P., and Dhillon, N.K. (2022). Persistent Presence of Spike protein and Viral RNA in the Circulation of Individuals with Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19. medRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.04.04.535604",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_23",
"unstructured": "Rong, Z., Mai, H., Kapoor, S., Puelles, V.G., Czogalla, J., Schädler, J., Vering, J., Delbridge, C., Steinke, H., and Frenzel, H. (2023). SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Accumulation in the Skull-Meninges-Brain Axis: Potential Implications for Long-Term Neurological Complications in post-COVID-19. bioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112189",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein induces TLR4-mediated long-term cognitive dysfunction recapitulating post-COVID-19 syndrome in mice",
"author": "Fernandes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112189",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-09410-7",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces cognitive deficit and anxiety-like behavior in mouse via non-cell autonomous hippocampal neuronal death",
"author": "Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5496",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40035-020-00221-2",
"article-title": "Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes",
"author": "Kwon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42",
"journal-title": "Transl. Neurodegener.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of α-synuclein in inducing innate and adaptive immunity in Parkinson disease",
"author": "Standaert",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Park. Dis.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/genes8120377",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_28",
"unstructured": "Faustini, G., Bono, F., Valerio, A., Pizzi, M., Spano, P., and Bellucci, A. (2017). Mitochondria and α-Synuclein: Friends or Foes in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease?. Genes, 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells12060877",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_29",
"unstructured": "Huynh, T.V., Rethi, L., Lee, T.-W., Higa, S., Kao, Y.-H., and Chen, Y.-J. (2023). Spike Protein Impairs Mitochondrial Function in Human Cardiomyocytes: Mechanisms Underlying Cardiac Injury in COVID-19. Cells, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101756",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces long-term transcriptional perturbations of mitochondrial metabolic genes, causes cardiac fibrosis, and reduces myocardial contractile in obese mice",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101756",
"journal-title": "Mol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11481-021-10015-6",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial Dynamics in SARS-CoV2 Spike Protein Treated Human Microglia: Implications for Neuro-COVID",
"author": "Clough",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "770",
"journal-title": "J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12035-023-03726-9",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Domain Accelerates α-Synuclein Phosphorylation and Aggregation in Cellular Models of Synucleinopathy",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2446",
"journal-title": "Mol. Neurobiol.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23063394",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Wu, Z., Zhang, X., Huang, Z., and Ma, K. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Interact with Alpha Synuclein and Induce Lewy Body-like Pathology In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrendo.2013.256",
"article-title": "Korbonits Metformin-mode of action and clinical implications for diabetes and cancer",
"author": "Pernicova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111743",
"article-title": "A blast from the past: To tame time with metformin",
"author": "Xenos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111743",
"journal-title": "Mech. Ageing Dev.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "208",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.015",
"article-title": "Metformin lowers α-synuclein phosphorylation and upregulates neurotrophic factor in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease",
"author": "Katila",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "396",
"journal-title": "Neuropharmacology",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1734-1140(10)70357-1",
"article-title": "Quantification of metformin by the HPLC method in brain regions, cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of rats treated with lipopolysaccharide",
"author": "Suchy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "956",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Rep.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.12655",
"article-title": "Acute metformin preconditioning confers neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischaemia by pre-activation of AMPK-dependent autophagy",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3146",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "171",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/JAD-131901",
"article-title": "Long-Term Metformin Usage and Cognitive Function among Older Adults with Diabetes",
"author": "Ng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "61",
"journal-title": "J. Alzheimer’s Dis.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.046",
"article-title": "Neuroprotective effect of metformin in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease in mice",
"author": "Patil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "747",
"journal-title": "Neuroscience",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "277",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.03.010",
"article-title": "Metformin-inclusive sulfonylurea therapy reduces the risk of Parkinson’s disease occurring with Type 2 diabetes in a Taiwanese population cohort",
"author": "Wahlqvist",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "753",
"journal-title": "Park. Relat. Disord.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ijnp/pyw047",
"article-title": "Metformin Prevents Dopaminergic Neuron Death in MPTP/P-Induced Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease via Autophagy and Mitochondrial ROS Clearance",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "pyw047",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.13139",
"article-title": "Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states",
"author": "Orihuela",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "649",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s12276-022-00895-w",
"article-title": "Inflammation promotes synucleinopathy propagation",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2148",
"journal-title": "Exp. Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bpa.12371",
"article-title": "Neuroinflammation in Synucleinopathies",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "404",
"journal-title": "Brain Pathol.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/revneuro-2012-0071",
"article-title": "The role of Ser129 phosphorylation of α-synuclein in neurodegeneration of Parkinson’s disease: A review of in vivo models",
"author": "Sato",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "115",
"journal-title": "Rev. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Spike Protein Subunits of SARS-CoV-2 Alter Mitochondrial Metabolism in Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells: Involvement of Factor Xa",
"author": "Reche",
"first-page": "1118195",
"journal-title": "Dis. Markers",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41593-022-01140-3",
"article-title": "Pathological structural conversion of α-synuclein at the mitochondria induces neuronal toxicity",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1134",
"journal-title": "Nat. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00001756-200001170-00041",
"article-title": "MPTP induces alpha-synuclein aggregation in the substantia nigra of baboons",
"author": "Kowall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"journal-title": "NeuroReport",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00299-2",
"article-title": "Outpatient treatment of COVID-19 and incidence of post-COVID-19 condition over 10 months (COVID-OUT): A multicentre, randomised, quadruple-blind, parallel-group, phase 3 trial",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1119",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12974-022-02487-x",
"article-title": "Reduced microglia activation following metformin administration or microglia ablation is sufficient to prevent functional deficits in a mouse model of neonatal stroke",
"author": "Bourget",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "J. Neuroinflamm.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.neures.2021.05.007",
"article-title": "Metformin reduces neuroinflammation and improves cognitive functions after traumatic brain injury",
"author": "DiBona",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "Neurosci. Res.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fneur.2019.00652",
"article-title": "Infectious Etiologies of Parkinsonism: Pathomechanisms and Clinical Implications",
"author": "Limphaibool",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "652",
"journal-title": "Front. Neurol.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.745789",
"article-title": "Neuroinflammation and Its Impact on the Pathogenesis of COVID-19",
"author": "Almutairi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "745789",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-1031824/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_55",
"unstructured": "Klein, R., Soung, A., Sissoko, C., Nordvig, A., Canoll, P., Mariani, M., Jiang, X., Bricker, T., Goldman, J., and Rosoklija, G. (2021). COVID-19 induces neuroinflammation and loss of hippocampal neurogenesis. Res. Sq."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.00698",
"article-title": "Microglia and Beyond: Innate Immune Cells As Regulators of Brain Development and Behavioral Function",
"author": "Lenz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "698",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.11.16.21266391",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_57",
"unstructured": "Schultheiß, C., Willscher, E., Paschold, L., Gottschick, C., Klee, B., Henkes, S.-S., Bosurgi, L., Dutzmann, J., Sedding, D., and Frese, T. (2021). From online data collection to identification of disease mechanisms: The IL-1ß, IL-6 and TNF-α cytokine triad is associated with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 in a digital research cohort. medRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.700782",
"article-title": "Immune-Based Prediction of COVID-19 Severity and Chronicity Decoded Using Machine Learning",
"author": "Patterson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "700782",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The Role of Inflammatory Cytokines in Cognition and Other Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease",
"author": "Menza",
"first-page": "474",
"journal-title": "Psychosomatics",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/208408",
"article-title": "Correlation between Serum RANTES Levels and the Severity of Parkinson’s Disease",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "208408",
"journal-title": "Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.neuron.2023.04.006",
"article-title": "Microglial-to-neuronal CCR5 signaling regulates autophagy in neurodegeneration",
"author": "Festa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2021",
"journal-title": "Neuron",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnagi.2023.1250685",
"article-title": "CCL5 promotes LFA-1 expression in Th17 cells and induces LCK and ZAP70 activation in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1250685",
"journal-title": "Front. Aging Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s12276-022-00789-x",
"article-title": "TNF-α promotes α-synuclein propagation through stimulation of senescence-associated lysosomal exocytosis",
"author": "Bae",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "788",
"journal-title": "Exp. Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7189/jogh.12.05029",
"article-title": "Clinical, sociodemographic and environmental factors impact post-COVID-19 syndrome",
"author": "Ferreira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "05029",
"journal-title": "J. Glob. Health",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "The MPTP Story",
"author": "Langston",
"first-page": "S11",
"journal-title": "J. Park. Dis.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41531-017-0019-z",
"article-title": "Synergistic effects of influenza and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) can be eliminated by the use of influenza therapeutics: Experimental evidence for the multi-hit hypothesis",
"author": "Sadasivan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "Npj Park. Dis.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2022.199010",
"article-title": "Metformin suppresses SARS-CoV-2 in cell culture",
"author": "Parthasarathy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "199010",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113223",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_68",
"unstructured": "Ventura-López, C., Cervantes-Luevano, K., Aguirre-Sánchez, J.S., Flores-Caballero, J.C., Alvarez-Delgado, C., Bernaldez-Sarabia, J., Sánchez-Campos, N., Lugo-Sánchez, L.A., Rodríguez-Vázquez, I.C., and Sander-Padilla, J.G. (2022). Treatment with metformin glycinate reduces SARS-CoV-2 viral load: An in vitro model and randomized, double-blind, Phase IIb clinical trial. Biomed. Pharmacother., 152."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.148003",
"article-title": "Ex vivo SARS-CoV-2 infection of human lung reveals heterogeneous host defense and therapeutic responses",
"author": "Schaller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e148003",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/2049-3002-2-12",
"article-title": "Metformin directly acts on mitochondria to alter cellular bioenergetics",
"author": "Andrzejewski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Cancer Metab.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 71,
"references-count": 71,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/12/6/1223"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein 1 Causes Aggregation of α-Synuclein via Microglia-Induced Inflammation and Production of Mitochondrial ROS: Potential Therapeutic Applications of Metformin",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}
