Recombinant interleukin-2 stimulates lymphocyte recovery in patients with severe COVID-19
et al., Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, doi:10.3892/etm.2021.9658, Jan 2021
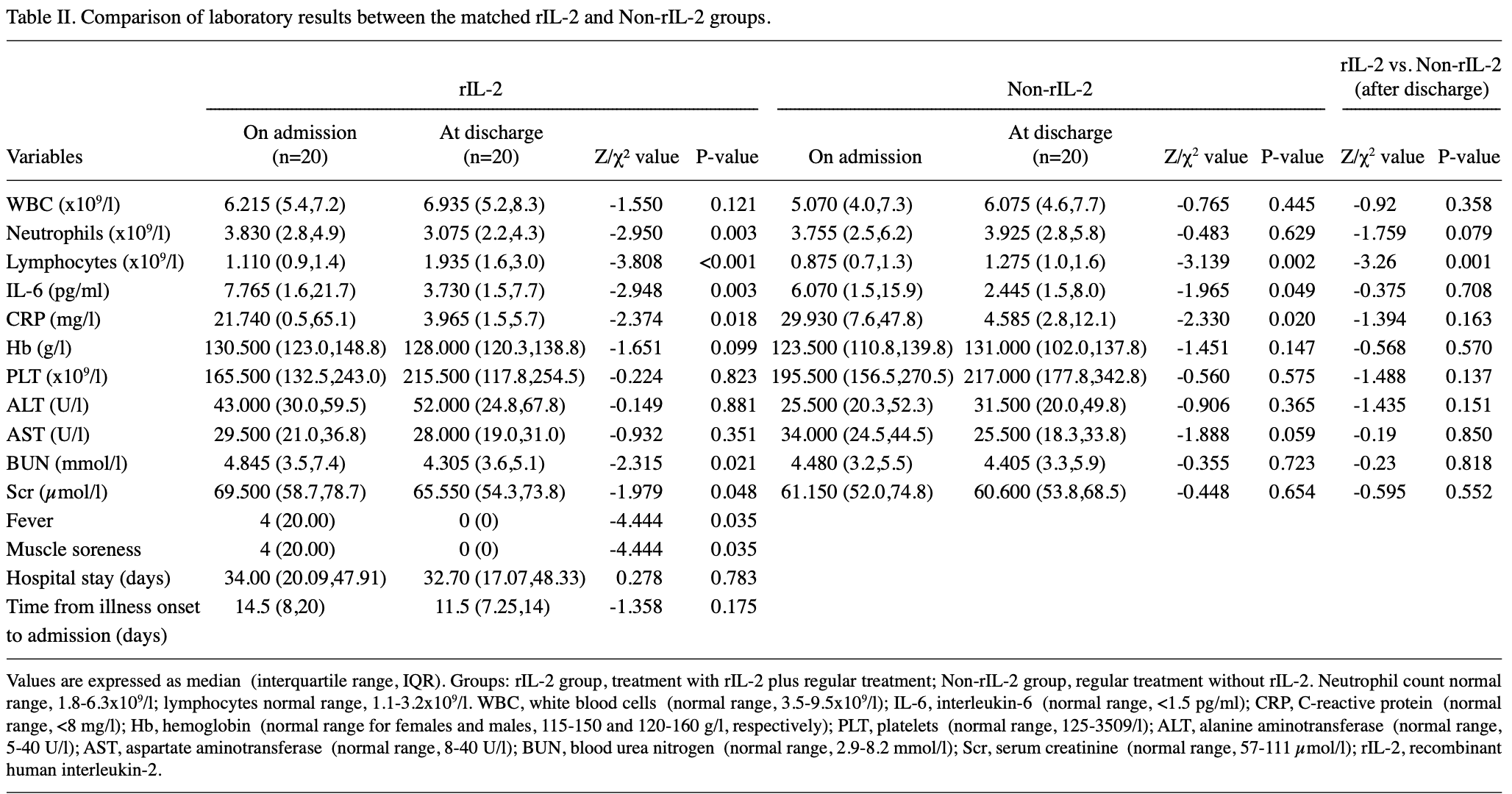
PSM retrospective 59 hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 showing that recombinant human interleukin-2 (rIL-2) treatment significantly increased lymphocyte counts. There were no significant differences in C-reactive protein or IL-6 levels between groups, or in hospital length of stay.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
hospitalization time, 4.0% higher, relative time 1.04, p = 0.78, treatment 21, control 43, propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zhu et al., 18 Jan 2021, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 29 January, 2020 - 29 February, 2020.
Contact: pinghe@hust.edu.cn.
Recombinant interleukin-2 stimulates lymphocyte recovery in patients with severe COVID-19
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, doi:10.3892/etm.2021.9658
A recently identified type of pneumonia, referred to as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2, has rapidly spread worldwide. Lymphopenia and a proinflammatory cytokine storm frequently occur in patients with severe COVID-19. However, to the best of our knowledge, no specific immunomodulatory therapy for COVID-19 has been reported to date. In the present retrospective case-control study, the potential therapeutic effect of recombinant human interleukin-2 (rIL-2) in patients with severe COVID-19 was demonstrated. A total of 59 patients with severe COVID-19 were admitted to the Union Hospital of Tongji Medical College (Wuhan, China) between 29th January 2020 and 29th February 2020 and were included in the present study. In total, 20 patients received subcutaneous injection of rIL-2 (1 million IU per day) for 7-10 days in addition to regular treatment and were classified as the rIL-2 group. Furthermore, 20 of the 39 patients receiving regular treatment, without the intervention of rIL-2, were matched as the control group. Patients in these two groups were subjected to propensity score matching in terms of clinical characteristics such as age, sex, symptoms, signs, laboratory data and comorbidities. Changes in the lymphocyte count, as well as IL-6 and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, were analyzed at the time of admission and discharge and any differences between the rIL-2 and non-rIL-2 groups were determined. The results demonstrated an increase in the lymphocyte count and a decrease in CRP levels in the rIL-2 group compared with that in the non-rIL-2 group. The difference in the change of the lymphocyte count between the rIL-2 group and non-rIL-2 group was statistically significant (P<0.01). Although CRP levels were decreased to a greater extent in the rIL-2 group, the difference between the two groups was not statistically significant (P>0.05). Collectively, the present results suggested that administration of rIL-2 may be a prospective adjuvant therapy for patients with severe COVID-19 and its effects may be mediated by increasing lymphocyte numbers.
Authors' contributions PH and MEZ designed study, performed statistical analysis and wrote the manuscript. MEZ, QW, BW, SZ and LK collected data, analyzed data and interpreted references for the paper. MEZ and QW checked and confirmed the authenticity of the raw data. Moreover, all authors participated in the reviewing and revision of this paper critically. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate The study protocols were approved and informed consent from the patients was waived by the ethics committee of Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Wuhan, China).
Patient consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
Chen, Wu, Guo, Cao, Huang et al., Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Clin Invest
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study, Lancet
Crespo, Caragol, Falcó, Ribera, Pahissa, Efficacy of recombinant interleukin-2 (rIL-2) in patients with advanced HIV-1 infection and blunted immune response to HAART, Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin
Dimitriou, Matter, Mangana, Urosevic-Maiwald, Micaletto et al., Cytokine release syndrome during sequential treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors and kinase inhibitors for metastatic melanoma, J Immunother
He, Zhang, Wei, Sun, Chen et al., Low-dose interleukin-2 treatment selectively modulates CD4(+) T cell subsets in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, Nat Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Liu, Li, Liu, Liang, Wang et al., Longitudinal characteristics of lymphocyte responses and cytokine profiles in the peripheral blood of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients, EBioMedicine
Mahmoudpour, Jankowski, Valerio, Becker, Espinola-Klein et al., Safety of low-dose subcutaneous recombinant interleukin-2: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Sci Rep
Nagayama, Takahashi, Takahashi, Ogami, Ikebuchi et al., IL-2LAK therapy for refractory acute monoblastic leukemia relapsing after unrelated allogeneic bone marrow transplantation, Bone Marrow Transplant
Ni, Chen, Huang, Han, Xu et al., Combating COVID-19 with integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine in China, Acta Pharm Sin B
Nunnari, Sanfilippo, Castrogiovanni, Imbesi, Volti et al., Network perturbation analysis in human bronchial epithelial cells following SARS-CoV2 infection, Exp Cell Res
Overwijk, Tagliaferri, Zalevsky, Engineering IL-2 to give new life to T cell immunotherapy, Annu Rev Med, doi:10.1146/annurev-med-073118-011031
Pett, Kelleher, Emery, Role of interleukin-2 in patients with HIV infection, Drugs
Ravalli, Musumeci, Coronavirus Outbreak in Italy: Physiological benefits of home-based exercise during pandemic, J Funct Morphol Kinesiol
Reddehase, Mutter, Koszinowski, In vivo application of recombinant interleukin 2 in the immunotherapy of established cytomegalovirus infection, J Exp Med
Sato, Keino, Nakayama, Kano, Okada, Effect of in vivo expansion of regulatory T cells with IL-2/anti-IL-2 antibody complex plus rapamycin on experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis, Ocul Immunol Inflamm, doi:10.1080/09273948.2020.1757119
Schub, Klemis, Schneitler, Mihm, Lepper et al., High levels of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells with restricted functionality in severe courses of COVID-19, JCI Insight
Shi, Wang, Yin, Ouyang, Pang et al., The inhibition of IL-2/IL-2R gives rise to CD8 + T cell and lymphocyte decrease through JAK1-STAT5 in critical patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, Cell Death Dis
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, JAMA
Wen, Su, Tang, Le, Zhang et al., Immune cell profiling of COVID-19 patients in the recovery stage by single-cell sequencing, Cell Discov
Zhou, Opalinska, Sohal, Yu, Mo et al., Aberrant epigenetic and genetic marks are seen in myelodysplastic leukocytes and reveal Dock4 as a candidate pathogenic gene on chromosome 7q, J Biol Chem
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3892/etm.2021.9658",
"ISSN": [
"1792-0981",
"1792-1015"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.9658",
"article-number": "227",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430022, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Meng-En",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430022, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Qian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430022, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Shaoqiong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430022, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Bin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430022, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "Ke",
"given": "Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Geriatrics, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430022, P.R. China"
}
],
"family": "He",
"given": "Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Exp Ther Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-18T09:58:45Z",
"timestamp": 1610963925000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-02T11:42:43Z",
"timestamp": 1646221363000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-09T19:29:53Z",
"timestamp": 1744226993089
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 11,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
18
]
]
}
},
"member": "2249",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3892",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "Spandidos Publications",
"reference": [
{
"key": "key20220302133927_b1-etm-0-0-09658"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jfmk5020031",
"article-title": "Coronavirus Outbreak in Italy: Physiological benefits of home-based exercise during pandemic",
"author": "Ravalli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "31",
"journal-title": "J Funct Morphol Kinesiol",
"key": "key20220302133927_b2-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CJI.0000000000000236",
"article-title": "Cytokine release syndrome during sequential treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors and kinase inhibitors for metastatic melanoma",
"author": "Dimitriou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "J Immunother",
"key": "key20220302133927_b3-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "key20220302133927_b4-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112204",
"article-title": "Network perturbation analysis in human bronchial epithelial cells following SARS-CoV2 infection",
"author": "Nunnari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "112204",
"journal-title": "Exp Cell Res",
"key": "key20220302133927_b5-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102763",
"article-title": "Longitudinal characteristics of lymphocyte responses and cytokine profiles in the peripheral blood of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "102763",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "key20220302133927_b6-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-020-0168-9",
"article-title": "Immune cell profiling of COVID-19 patients in the recovery stage by single-cell sequencing",
"author": "Wen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "31",
"journal-title": "Cell Discov",
"key": "key20220302133927_b7-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "key20220302133927_b8-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2020.06.009",
"article-title": "Combating COVID-19 with integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine in China",
"author": "Ni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1149",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharm Sin B",
"key": "key20220302133927_b9-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bmt.1701550",
"article-title": "IL-2LAK therapy for refractory acute monoblastic leukemia relapsing after unrelated allogeneic bone marrow transplantation",
"author": "Nagayama",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "183",
"journal-title": "Bone Marrow Transplant",
"key": "key20220302133927_b10-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "23",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "key20220302133927_b11-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"article-title": "Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2620",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "key20220302133927_b12-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/10898620-000000000-00000",
"article-title": "Role of interleukin-2 in patients with HIV infection",
"author": "Pett",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1115",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "key20220302133927_b13-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-020-2636-4",
"article-title": "The inhibition of IL-2/IL-2R gives rise to CD8+ T cell and lymphocyte decrease through JAK1-STAT5 in critical patients with COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "429",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis",
"key": "key20220302133927_b14-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-43530-x",
"article-title": "Safety of low-dose subcutaneous recombinant interleukin-2: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Mahmoudpour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "7145",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "key20220302133927_b15-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.165.3.650",
"article-title": "In vivo application of recombinant interleukin 2 in the immunotherapy of established cytomegalovirus infection",
"author": "Reddehase",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "650",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "key20220302133927_b16-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "165",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1157/13114392",
"article-title": "Efficacy of recombinant interleukin-2 (rIL-2) in patients with advanced HIV-1 infection and blunted immune response to HAART",
"author": "Crespo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin",
"key": "key20220302133927_b17-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.4148",
"article-title": "Low-dose interleukin-2 treatment selectively modulates CD4(+) T cell subsets in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "991",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "key20220302133927_b18-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M111.235028",
"article-title": "Aberrant epigenetic and genetic marks are seen in myelodysplastic leukocytes and reveal Dock4 as a candidate pathogenic gene on chromosome 7q",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "25211",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "key20220302133927_b19-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "286",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.142167",
"article-title": "High levels of SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells with restricted functionality in severe courses of COVID-19",
"author": "Schub",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "key20220302133927_b20-etm-0-0-09658",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Sato",
"key": "key20220302133927_b21-etm-0-0-09658"
},
{
"author": "Overwijk",
"key": "key20220302133927_b22-etm-0-0-09658"
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-40006/v1",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/etm.2021.9658"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Recombinant interleukin-2 stimulates lymphocyte recovery in patients with severe COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "21"
}