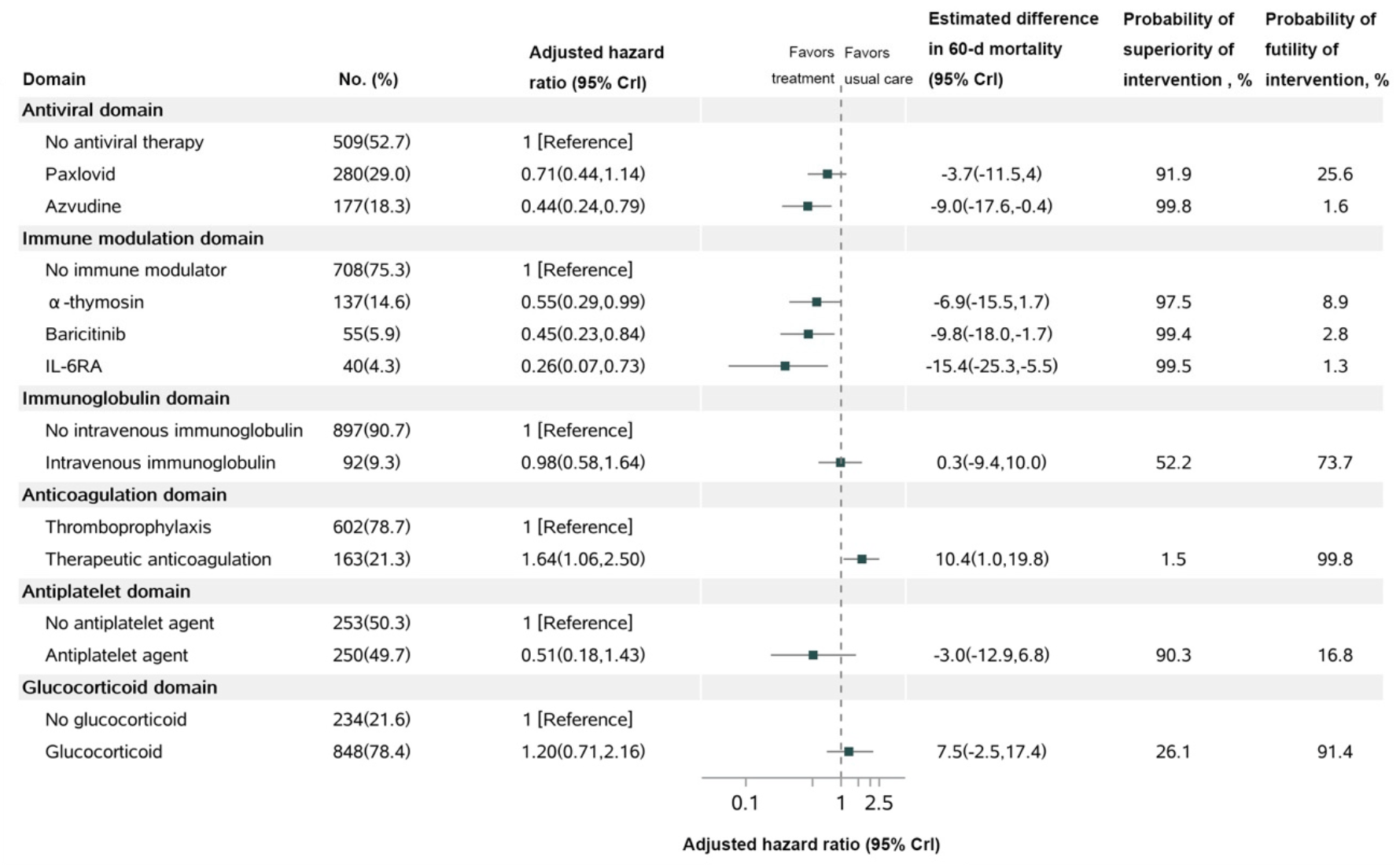
Composite Interventions on Outcomes of Severely and Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China
et al., Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11071859, Jul 2023
Retrospective 1,082 severely and critically ill COVID-19 patients in China showing lower 60 day mortality with azvudine. Mortality was also lower with paxlovid, but without statistical significance, and health related quality of life was significantly lower for paxlovid patients at 60 days.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
Study covers paxlovid and azvudine.
|
risk of death, 29.0% lower, HR 0.71, p = 0.16, treatment 280, control 509, adjusted per study, day 60.
|
|
relative HRQoL, 28.3% worse, RR 1.28, p < 0.001, treatment mean 0.46 (±0.42) n=237, control mean 0.59 (±0.41) n=456, day 60.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Shao et al., 23 Jul 2023, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 9 authors, study period 8 December, 2022 - 9 February, 2023.
Contact: huanggang@sumhs.edu.cn (corresponding author), shaojiasheng@jdhospital.com, rfan1@tulane.edu, cnguo22@m.fudan.edu.cn, huangxuyuan@jdhospital.com, guorunsheng@jdhospital.com, zhangfengdi@126.com, hujianrong@jdhospital.com, caoliou@jdhospital.com.
Composite Interventions on Outcomes of Severely and Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China
Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11071859
Background: The sixty-day effects of initial composite interventions for the treatment of severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 are not fully assessed. Methods: Using a Bayesian piecewise exponential model, we analyzed the 60-day mortality, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and disability in 1082 severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 between 8 December 2022 and 9 February 2023 in Shanghai, China. The final 60-day follow-up was completed on 10 April 2023. Results: Among 1082 patients (mean age, 78.0 years, 421 [38.9%] women), 139 patients (12.9%) died within 60 days. Azvudine had a 99.8% probability of improving 2-month survival (adjusted HR, 0.44 [95% credible interval, 0.24-0.79]), and Paxlovid had a 91.9% probability of improving 2-month survival (adjusted HR, 0.71 [95% credible interval, 0.44-1.14]) compared with the control. IL-6 receptor antagonist, baricitinib and a-thymosin each had a high probability of benefit (99.5%, 99.4%, and 97.5%, respectively) compared to their controls, while the probability of trail-defined statistical futility (HR > 0.83) was high for therapeutic anticoagulation (99.8%; HR, 1.64 [95% CrI, 1.06-2.50]) and glucocorticoid (91.4%; HR, 1.20 [95% CrI,). Paxlovid, Azvudine, and therapeutic anticoagulation showed a significant reduction in disability (p < 0.05) Conclusions: Among severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 who received 1 or more therapeutic interventions, treatment with Azvudine had a high probability of improved 60-day mortality compared with the control, indicating its potential in a resource-limited scenario. Treatment with an IL-6 receptor antagonist, baricitinib, and a-thymosin also had high probabilities of benefit in improving 2-month survival, among which a-thymosin could improve HRQoL. Treatment with Paxlovid, Azvudine, and therapeutic anticoagulation could significantly reduce disability at day 60.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Abdelhady, Abdelrazik, Abdi, Abdo, Abdulle et al., Effect of Convalescent Plasma on Organ Support-Free Days in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.18178
Bellet, Renga, Pariano, Stincardini, D'onofrio et al., COVID-19 and beyond: Reassessing the role of thymosin alpha1 in lung infections, Int. Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109949
Bolek, Samos, Jurica, Stanciakova, Pec et al., COVID-19 and the Response to Antiplatelet Therapy, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm12052038
Bradbury, Lawler, Stanworth, Mcverry, Mcquilten et al., Effect of Antiplatelet Therapy on Survival and Organ Support-Free Days in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.2910
Chinese Thoracic, Chinese Association Of Chest, Critical, Group, Expert consensus on treatment of severe COVID-19 caused by Omicron variants, Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi, doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20221230-00994
Cilloniz, Motos, Castaneda, Gabarrus, Barbe et al., Remdesivir and survival outcomes in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A multicentre observational cohort study, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2022.12.027
Dyer, COVID-19: China stops counting cases as models predict a million or more deaths, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.p2
Ely, Ramanan, Kartman, De Bono, Liao et al., Efficacy and safety of baricitinib plus standard of care for the treatment of critically ill hospitalised adults with COVID-19 on invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: An exploratory, randomised, placebo-controlled trial, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00006-6
Florescu, Stanciu, Zaharia, Kosa, Codreanu et al., Long-term (180-Day) Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 in the REMAP-CAP Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.23257
Goligher, Bradbury, Mcverry, Lawler, Berger et al., Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2103417
Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Huang, Li, Gu, Zhang, Ren et al., Health outcomes in people 2 years after surviving hospitalisation with COVID-19: A longitudinal cohort study, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00126-6
Huang, Yao, Gu, Wang, Ren et al., 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: A longitudinal cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01755-4
Ioannidis, Zonta, Levitt, Estimates of COVID-19 deaths in Mainland China after abandoning zero COVID policy, Eur. J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1111/eci.13956
Jimenez-Mora, Varela, Meneses-Echavez, Bidonde, Angarita-Fonseca et al., Patient-important outcomes reported in randomized controlled trials of pharmacologic treatments for COVID-19: A protocol of a META-epidemiological study, Syst. Rev, doi:10.1186/s13643-021-01838-8
Liu, Pan, Hu, Wu, Wang et al., Thymosin Alpha 1 Reduces the Mortality of Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 by Restoration of Lymphocytopenia and Reversion of Exhausted T Cells, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa630
Liu, Pan, Zhang, Li, Ma et al., Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: A multicenter randomized controlled study, Lancet Reg. Health West Pac, doi:10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694
Liu, Zhang, Lu, Li, Wu et al., Benefits of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin on mortality in patients with severe COVID-19: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1116738
Luo, Liu, Li, Guan, Jin et al., Estimating an EQ-5D-5L Value Set for China, Value Health, doi:10.1016/j.jval.2016.11.016
Martinez-Guerra, Gonzalez-Lara, Roman-Montes, Tamez-Torres, Dardon-Fierro et al., Outcomes of patients with severe and critical COVID-19 treated with dexamethasone: A prospective cohort study, Emerg. Microbes. Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2021.2011619
Salehi, Barkhori Mehni, Akbarian, Fattah Ghazi, Khajavi Rad et al., The outcome of using intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in critically ill COVID-19 patients': A retrospective, multi-centric cohort study, Eur. J. Med. Res, doi:10.1186/s40001-022-00637-8
Shao, Fan, Hu, Zhang, Lee et al., Clinical Progression and Outcome of Hospitalized Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant in Shanghai, China, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines10091409
Spaetgens, Nagy, Ten Cate, Antiplatelet Therapy in Patients With COVID-19-More Is Less?, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.23866
Wan, Wang, Mathur, Chan, Yan et al., Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase, J. Infect
Wang, Yu, Yu, Wang, Chen et al., Clinical features and outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the Omicron wave in Shanghai, China, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2022.08.001
Xu, Fan, Wang, Zou, Yu et al., Suppressed T cell-mediated immunity in patients with COVID-19: A clinical retrospective study in Wuhan, China, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.012
Ye, Wang, Mao, The pathogenesis and treatment of the 'Cytokine Storm' in COVID-19, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037
Yu, Chang, The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched, Innovation
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal. Transduct. Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms11071859",
"ISSN": [
"2076-2607"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071859",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: The sixty-day effects of initial composite interventions for the treatment of severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 are not fully assessed. Methods: Using a Bayesian piecewise exponential model, we analyzed the 60-day mortality, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and disability in 1082 severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 between 8 December 2022 and 9 February 2023 in Shanghai, China. The final 60-day follow-up was completed on 10 April 2023. Results: Among 1082 patients (mean age, 78.0 years, 421 [38.9%] women), 139 patients (12.9%) died within 60 days. Azvudine had a 99.8% probability of improving 2-month survival (adjusted HR, 0.44 [95% credible interval, 0.24–0.79]), and Paxlovid had a 91.9% probability of improving 2-month survival (adjusted HR, 0.71 [95% credible interval, 0.44–1.14]) compared with the control. IL-6 receptor antagonist, baricitinib and a-thymosin each had a high probability of benefit (99.5%, 99.4%, and 97.5%, respectively) compared to their controls, while the probability of trail-defined statistical futility (HR > 0.83) was high for therapeutic anticoagulation (99.8%; HR, 1.64 [95% CrI, 1.06–2.50]) and glucocorticoid (91.4%; HR, 1.20 [95% CrI, 0.71–2.16]). Paxlovid, Azvudine, and therapeutic anticoagulation showed a significant reduction in disability (p < 0.05) Conclusions: Among severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 who received 1 or more therapeutic interventions, treatment with Azvudine had a high probability of improved 60-day mortality compared with the control, indicating its potential in a resource-limited scenario. Treatment with an IL-6 receptor antagonist, baricitinib, and a-thymosin also had high probabilities of benefit in improving 2-month survival, among which a-thymosin could improve HRQoL. Treatment with Paxlovid, Azvudine, and therapeutic anticoagulation could significantly reduce disability at day 60.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"microorganisms11071859"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6345-5350",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Rheumatology, Jiading District Central Hospital Affiliated Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201899, China"
},
{
"name": "Tulane National Primate Research Center, Tulane University School of Medicine, 18703 Three Rivers Road, Covington, LA 70433, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Shao",
"given": "Jiasheng",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0814-0548",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tulane National Primate Research Center, Tulane University School of Medicine, 18703 Three Rivers Road, Covington, LA 70433, USA"
},
{
"name": "Genomics, Biotechnology Center, Center for Molecular and Cellular Bioengineering, Technische Universität, 01307 Dresden, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fan",
"given": "Rong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Shanghai Institute of Infectious Disease and Biosecurity, School of Public Health, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China"
}
],
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Chengnan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Urology, Renji Hospital, Shanghai JiaoTong University, Shanghai 200127, China"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Xuyuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of General Surgery, Jiading District Central Hospital Affiliated Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201899, China"
}
],
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Runsheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Fengdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory Medicine, Jiading District Central Hospital Affiliated Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201899, China"
}
],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Jianrong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Gang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology, Molecular Cell Lab for Kidney Disease, Shanghai Peritoneal Dialysis Research Center, Ren Ji Hospital, Uremia Diagnosis and Treatment Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200127, China"
}
],
"family": "Cao",
"given": "Liou",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Microorganisms",
"container-title-short": "Microorganisms",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-24T05:08:11Z",
"timestamp": 1690175291000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-24T06:24:59Z",
"timestamp": 1690179899000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82127807"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"18DZ2260400"
],
"name": "Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging"
},
{
"award": [
"20MC2020004"
],
"name": "Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences Clinical Research Centre for Metabolic Vascular Diseases Project"
},
{
"award": [
"JDKW-2021-0022"
],
"name": "Science and Technology Commission of Jiading District"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-15T12:02:09Z",
"timestamp": 1707998529374
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1690070400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/7/1859/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1859",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1111/eci.13956",
"article-title": "Estimates of COVID-19 deaths in Mainland China after abandoning zero COVID policy",
"author": "Ioannidis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13956",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.p2",
"article-title": "COVID-19: China stops counting cases as models predict a million or more deaths",
"author": "Dyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "380",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.08.001",
"article-title": "Clinical features and outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 during the Omicron wave in Shanghai, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e27",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.07.03.22277169",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "Shao, J., Fan, R., Hu, J., Zhang, T., Lee, C., Huang, X., Wang, F., Liang, H., Jin, Y., and Jiang, Y. (2022). Clinical Progression and Outcome of Hospitalized Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant in Shanghai, China. Vaccines, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01755-4",
"article-title": "1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: A longitudinal cohort study",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "747",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "398",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00126-6",
"article-title": "Health outcomes in people 2 years after surviving hospitalisation with COVID-19: A longitudinal cohort study",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "863",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037",
"article-title": "The pathogenesis and treatment of the ‘Cytokine Storm’ in COVID-19",
"author": "Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "607",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.12.027",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and survival outcomes in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A multicentre observational cohort study",
"author": "Cilloniz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "256",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.23257",
"article-title": "Long-term (180-Day) Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 in the REMAP-CAP Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Florescu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.18178",
"article-title": "Effect of Convalescent Plasma on Organ Support-Free Days in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Abdelhady",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1690",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2103417",
"article-title": "Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Goligher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "777",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.2910",
"article-title": "Effect of Antiplatelet Therapy on Survival and Organ Support-Free Days in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Bradbury",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1247",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.029",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir reduce mortality risk during post-acute COVID-19 phase",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "622",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (2023, July 18). Diagnosis and Treatment Plan for COVID-19 (Trial Version 10). in Chinese, Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/zhengcwj/202301/32de5b2ff9bf4eaa88e75bdf7223a65a.shtml."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00006-6",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of baricitinib plus standard of care for the treatment of critically ill hospitalised adults with COVID-19 on invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: An exploratory, randomised, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Ely",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Üstün, T.B., Kostanjesek, N., Chatterji, S., and Rehm, J. (2010). Measuring Health and Disability, Manual for WHO Disability Assessment Schedule, WHODAS 2.0, WHO."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jval.2016.11.016",
"article-title": "Estimating an EQ-5D-5L Value Set for China",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "662",
"journal-title": "Value Health",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2021.2011619",
"article-title": "Outcomes of patients with severe and critical COVID-19 treated with dexamethasone: A prospective cohort study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "50",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes. Infect.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13643-021-01838-8",
"article-title": "Patient-important outcomes reported in randomized controlled trials of pharmacologic treatments for COVID-19: A protocol of a META-epidemiological study",
"author": "Varela",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "289",
"journal-title": "Syst. Rev.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100694",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Paxlovid in severe adult patients with SARS-Cov-2 infection: A multicenter randomized controlled study",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100694",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg. Health West Pac.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "414",
"journal-title": "Signal. Transduct. Target Ther.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Expert consensus on treatment of severe COVID-19 caused by Omicron variants",
"first-page": "101",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.012",
"article-title": "Suppressed T cell-mediated immunity in patients with COVID-19: A clinical retrospective study in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e51",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa630",
"article-title": "Thymosin Alpha 1 Reduces the Mortality of Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 by Restoration of Lymphocytopenia and Reversion of Exhausted T Cells",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2150",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109949",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and beyond: Reassessing the role of thymosin alpha1 in lung infections",
"author": "Bellet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109949",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1116738",
"article-title": "Benefits of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin on mortality in patients with severe COVID-19: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1116738",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-022-00637-8",
"article-title": "The outcome of using intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in critically ill COVID-19 patients’: A retrospective, multi-centric cohort study",
"author": "Salehi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Med. Res.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.23866",
"article-title": "Antiplatelet Therapy in Patients With COVID-19-More Is Less?",
"author": "Spaetgens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm12052038",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_30",
"unstructured": "Bolek, T., Samos, M., Jurica, J., Stanciakova, L., Pec, M.J., Skornova, I., Galajda, P., Stasko, J., Mokan, M., and Kubisz, P. (2023). COVID-19 and the Response to Antiplatelet Therapy. J. Clin. Med., 12."
},
{
"article-title": "The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched",
"author": "Yu",
"first-page": "100321",
"journal-title": "Innovation",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/7/1859"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Composite Interventions on Outcomes of Severely and Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "11"
}