Efficacy of COVID-19 Oral antivirals in hospitalised oldest-old with high morbidity burden: a target trial emulation study
et al., Age and Ageing, doi:10.1093/ageing/afae180, Aug 2024
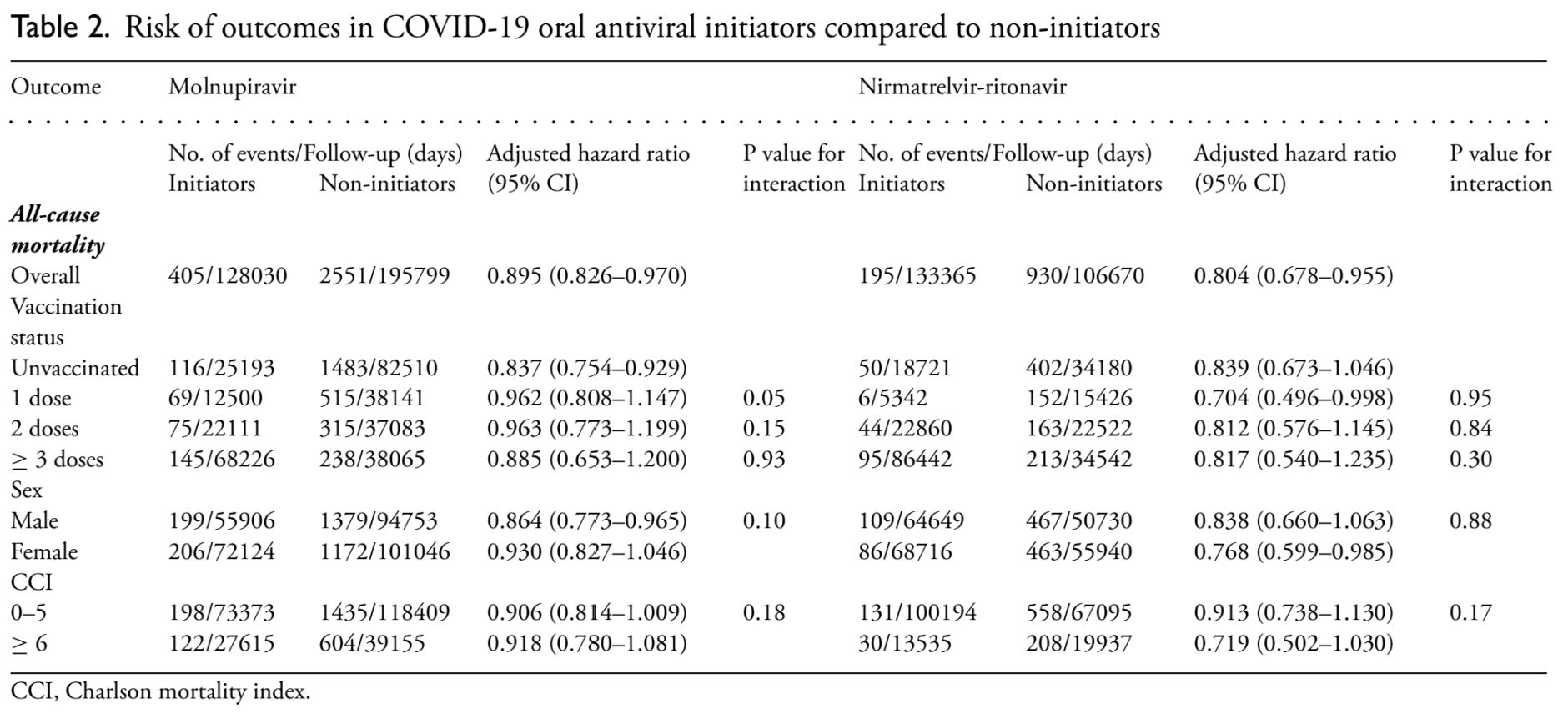
Target trial emulation study of 13,642 (molnupiravir) and 9,553 (paxlovid) elderly hospitalized patients in Hong Kong showing lower mortality with treatment.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments25.
Study covers molnupiravir and paxlovid.
|
risk of death, 10.5% lower, HR 0.90, p = 0.007, treatment 4,975, control 8,667, day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
23.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Lai et al., 14 Aug 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ageing/afae180",
"ISSN": [
"0002-0729",
"1468-2834"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afae180",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir are orally administered pharmacotherapies for mild to moderate COVID-19. However, the effectiveness of these drugs among very old (≥80 years), hospitalised patients remains unclear, limiting the risk–benefit assessment of these antivirals in this specific group. This study investigates the effectiveness of these antivirals in reducing mortality among this group of hospitalised patients with COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Using a territory-wide public healthcare database in Hong Kong, a target trial emulation study was conducted with data from 13 642 eligible participants for the molnupiravir trial and 9553 for the nirmatrelvir-ritonavir trial. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality. Immortal time and confounding bias was minimised using cloning-censoring-weighting approach. Mortality odds ratios were estimated by pooled logistic regression after adjusting confounding biases by stabilised inverse probability weights.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Both molnupiravir (HR: 0.895, 95% CI: 0.826–0.970) and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (HR: 0.804, 95% CI: 0.678–0.955) demonstrated moderate mortality risk reduction among oldest-old hospitalised patients. No significant interaction was observed between oral antiviral treatment and vaccination status. The 28-day risk of mortality was lower in initiators than non-initiators for both molnupiravir (risk difference: −1.09%, 95% CI: −2.29, 0.11) and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (risk difference: −1.71%, 95% CI: −3.30, −0.16) trials. The effectiveness of these medications was observed regardless of the patients’ prior vaccination status.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir are moderately effective in reducing mortality risk among hospitalised oldest-old patients with COVID-19, regardless of their vaccination status.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9121-1959",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Safe Medication Practice and Research , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine and Primary Care , School of Clinical Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , School of Clinical Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Laboratory of Data Discovery for Health (D24H) , 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science Park, Tai Po District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lai",
"given": "Francisco Tsz Tsun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine and Primary Care , School of Clinical Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , School of Clinical Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Boyuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Safe Medication Practice and Research , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
}
],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Cuiling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1513-8726",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Data Discovery for Health (D24H) , 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science Park, Tai Po District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "School of Nursing , Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "School of Public Health , Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Advanced Data Analytics for Medical Science (ADAMS) Limited , 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science Park, Tai Po District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chui",
"given": "Celine Sze Ling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Safe Medication Practice and Research , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Laboratory of Data Discovery for Health (D24H) , 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science Park, Tai Po District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine , School of Clinical Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 102 Pok Fu Lam Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , School of Clinical Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 102 Pok Fu Lam Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Xue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Safe Medication Practice and Research , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Laboratory of Data Discovery for Health (D24H) , 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science Park, Tai Po District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
}
],
"family": "Cheung",
"given": "Ching Lung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8242-0014",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Safe Medication Practice and Research , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Laboratory of Data Discovery for Health (D24H) , 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science Park, Tai Po District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Aston Pharmacy School, Aston University , Birmingham, B4 7ET , United Kingdom"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, The University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen Hospital , 1 Haiyuan First Road, Futian District, Shenzhen , China"
},
{
"name": "School of Pharmacy, Macau University of Science and Technology , Avenida Wai Long, Taipa, Macau , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Ian Chi Kei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Safe Medication Practice and Research , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Laboratory of Data Discovery for Health (D24H) , 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science Park, Tai Po District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Esther Wai Yin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6275-1147",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Safe Medication Practice and Research , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine and Primary Care , School of Clinical Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "The University of Hong Kong , School of Clinical Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, , 21 Sassoon Road, Southern District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Laboratory of Data Discovery for Health (D24H) , 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science Park, Tai Po District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
},
{
"name": "Advanced Data Analytics for Medical Science (ADAMS) Limited , 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science Park, Tai Po District, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wan",
"given": "Eric Yuk Fai",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Age and Ageing",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-14T15:26:27Z",
"timestamp": 1723649187000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-14T15:26:50Z",
"timestamp": 1723649210000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Health and Medical Research Fund Research on COVID-19"
},
{
"name": "Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region"
},
{
"name": "Research Grants Council"
},
{
"name": "Collaborative Research Fund"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100022720",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Health Bureau"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-15T00:19:03Z",
"timestamp": 1723681143148
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/pages/standard-publication-reuse-rights",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1722470400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ageing/article-pdf/53/8/afae180/58817538/afae180.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ageing/article-pdf/53/8/afae180/58817538/afae180.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
14
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref1",
"year": "5, 2023"
},
{
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref2",
"year": "1, 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac180",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: Oral coronavirus disease 2019 antiviral drugs",
"author": "Saravolatz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "165",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref3",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2022.05.024",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of molnupiravir for COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Fatima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "118",
"journal-title": "Eur J Intern Med",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref4",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir–ritonavir for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cheema",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref5",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref6",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/EVIDoa2100043",
"article-title": "Phase 2/3 trial of molnupiravir for treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized adults",
"author": "Caraco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "NEJM Evid",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref7",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/EVIDoa2100044",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of molnupiravir or placebo in patients hospitalized with Covid-19",
"author": "Arribas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "NEJM Evid",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref8",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med.",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref9",
"volume": "176"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.221608",
"article-title": "Population-based evaluation of the effectiveness of nirmatrelvir–ritonavir for reducing hospital admissions and mortality from COVID-19",
"author": "Schwartz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E220",
"journal-title": "Cmaj",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref10",
"volume": "195",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-3057",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref11",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ageing/afaa093",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in older people: a rapid clinical review",
"author": "Lithander",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "501",
"journal-title": "Age Ageing",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref12",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.02007.x",
"article-title": "Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: basic principles and practical applications",
"author": "Mangoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref13",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacc.2022.08.800",
"article-title": "Cardiovascular drug interactions with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in patients with COVID-19: JACC review topic of the week",
"author": "Abraham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1912",
"journal-title": "J Am Coll Cardiol",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref14",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00451-5",
"article-title": "Bell's palsy following vaccination with mRNA (BNT162b2) and inactivated (CoronaVac) SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: a case series and nested case-control study",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "64",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref15",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab989",
"article-title": "Epidemiology of acute myocarditis/pericarditis in Hong Kong adolescents following Comirnaty vaccination",
"author": "Chua",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "673",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref16",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221571",
"article-title": "Two-dose COVID-19 vaccination and possible arthritis flare among patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Hong Kong",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "564",
"journal-title": "Ann Rheum Dis",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref17",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-28068-3",
"article-title": "Multimorbidity and adverse events of special interest associated with Covid-19 vaccines in Hong Kong",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "411",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref18",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M21-3700",
"article-title": "Carditis after COVID-19 vaccination with a messenger RNA vaccine and an inactivated virus vaccine: a case–control study",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "362",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref19",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13453",
"article-title": "Post-Covid-19-vaccination adverse events and healthcare utilization among individuals with or without previous SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "864",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref20",
"volume": "291",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2021-326860",
"article-title": "Lack of inflammatory bowel disease flare-up following two-dose BNT162b2 vaccine: a population-based cohort study",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2608",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref21",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Herpes zoster related hospitalization after inactivated (CoronaVac) and mRNA (BNT162b2) SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: a self-controlled case series and nested case-control study",
"author": "Wan",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health West Pac",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref22",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/thy.2021.0684",
"article-title": "Safety of inactivated and mRNA COVID-19 vaccination among patients treated for hypothyroidism: a population-based cohort study",
"author": "Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Thyroid",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref23",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"journal-title": "Adv Clin Exp Med",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref24",
"volume": "32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref25",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-022-02715-4",
"article-title": "Individual and neighborhood risk factors of hospital admission and death during the COVID-19 pandemic: a population-based cohort study",
"author": "Bell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref26",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Association of Molnupiravir and Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir with preventable mortality, hospital admissions and related avoidable healthcare system cost among high-risk patients with mild to moderate COVID-19",
"author": "Wai",
"journal-title": "Lancet Reg Health West Pac",
"key": "2024081414092700600_ref27",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 27,
"references-count": 27,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ageing/article/doi/10.1093/ageing/afae180/7733454"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of COVID-19 Oral antivirals in hospitalised oldest-old with high morbidity burden: a target trial emulation study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "53"
}