SARS-CoV-2 Remdesivir Exposure Leads to Different Evolutionary Pathways That Converge in Moderate Levels of Drug Resistance
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17081055, Jul 2025
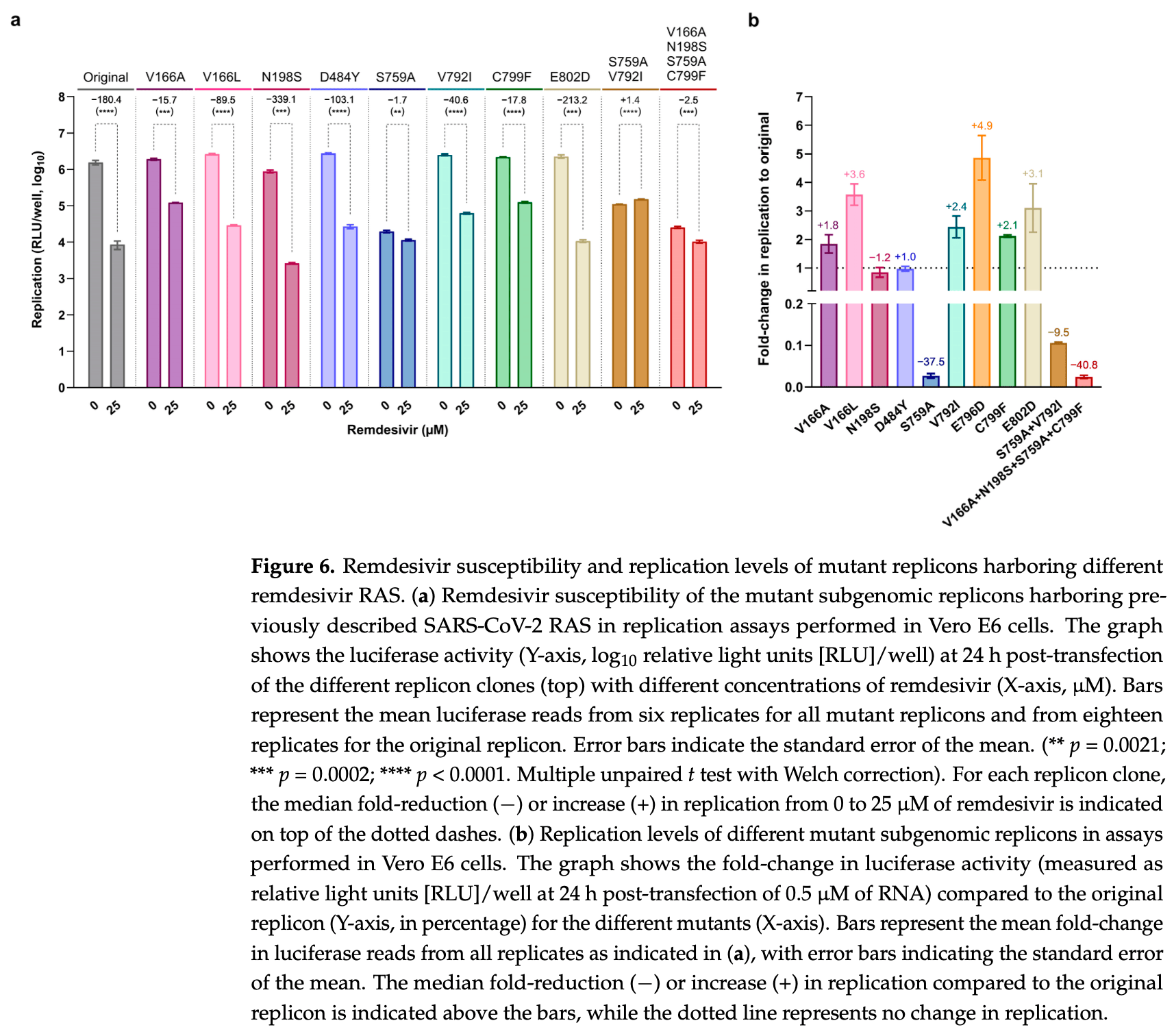
In vitro and hamster study showing that SARS-CoV-2 can develop resistance to remdesivir through multiple evolutionary pathways.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Fernandez-Antunez et al., 29 Jul 2025, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Contact: santseharayra@sund.ku.dk (corresponding author), carlota.fernandez.antunez@regionh.dk, line.ryberg@sund.ku.dk, kuan.wang@regionh.dk, pham@sund.ku.dk, lotte.scheibelein.mikkelsen@regionh.dk, ulrik@sund.ku.dk, kholmbeck@sund.ku.dk, jbukh@sund.ku.dk, katoh@sund.ku.dk, elvang@sund.ku.dk.
SARS-CoV-2 Remdesivir Exposure Leads to Different Evolutionary Pathways That Converge in Moderate Levels of Drug Resistance
Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17081055
Various SARS-CoV-2 remdesivir resistance-associated substitutions (RAS) have been reported, but a comprehensive comparison of their resistance levels is lacking. We identified novel RAS and performed head-to-head comparisons with known RAS in Vero E6 cells. A remdesivir escape polyclonal virus exhibited a 3.6-fold increase in remdesivir EC 50 and mutations throughout the genome, including substitutions in nsp12 (E796D) and nsp14 (A255S). However, in reverse-genetics infectious assays, viruses harboring both these substitutions exhibited only a slight decrease in remdesivir susceptibility (1.3-fold increase in EC 50 ). The nsp12-E796D substitution did not impair viral fitness (Vero E6 cells or Syrian hamsters) and was reported in a remdesivir-treated COVID-19 patient. In replication assays, a subgenomic replicon containing nsp12-E796D+nsp14-A255S led to a 16.1-fold increase in replication under remdesivir treatment. A comparison with known RAS showed that S759A, located in the active site of nsp12, conferred the highest remdesivir resistance (106.1fold increase in replication). Nsp12-RAS V166A/L, V792I, E796D or C799F, all adjacent to the active site, caused intermediate resistance (2.0-to 11.5-fold), whereas N198S, D484Y, or E802D, located farther from the active site, showed no resistance (≤2.0-fold). In conclusion, our classification system, correlating replication under remdesivir treatment with RAS location in nsp12, shows that most nsp12-RAS cause moderate resistance.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https: //www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v17081055/s1 , Supporting Methods; Figure S1 : Antiviral activity of remdesivir, GS-441524, obeldesivir, and molnupiravir; Figure S2 : Competitive fitness of original and RDV escape viruses; Figure S3 : Neutralizing curves of hamster plasma samples; Figure S4 : Principal component analysis of nsp12-motif D in a nsp7-nsp8-nsp12 molecular dynamics simulation; Table S1 : Genotypic characterization of remdesivir resistance selection experiment-derived viruses; Table S2 : Genotypic characterization of mutant viruses; Table S3 : Histopathological analysis of animal lungs.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
Bakan, Meireles, Bahar, Prody, Protein Dynamics Inferred from Theory and Experiments, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr168
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19-Final Report, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Binderup, Galli, Fossat, Fernandez-Antunez, Mikkelsen et al., Differential activity of nucleotide analogs against tick-borne encephalitis and yellow fever viruses in human cell lines, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2023.06.002
Checkmahomed, Carbonneau, Du Pont, Riola, Perry et al., In Vitro Selection of Remdesivir-Resistant SARS-CoV-2 Demonstrates High Barrier to Resistance, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/aac.00198-22
Cho, Saunders, Butler, Zhang, Xu et al., Synthesis and antiviral activity of a series of 1 ′ -substituted 4-aza-7,9-dideazaadenosine C-nucleosides, Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett, doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.02.105
Cihlar, Mackman, Journey of remdesivir from the inhibition of hepatitis C virus to the treatment of COVID-19, Antivir. Ther, doi:10.1177/13596535221082773
Collier, Monit, Gupta, The Impact of HIV-1 Drug Escape on the Global Treatment Landscape, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2019.06.010
Fahnøe, Pham, Fernandez-Antunez, Costa, Rivera-Rangel et al., Versatile SARS-CoV-2 Reverse-Genetics Systems for the Study of Antiviral Resistance and Replication, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14020172
Fernandez-Antunez, Wang, Fahnøe, Mikkelsen, Gottwein et al., Characterization of multi-DAA resistance using a novel hepatitis C virus genotype 3a infectious culture system, Hepatology, doi:10.1097/HEP.0000000000000353
Gallego, Sheldon, Moreno, Gregori, Quer et al., Barrier-Independent, Fitness-Associated Differences in Sofosbuvir Efficacy against Hepatitis C Virus, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.00581-16
Gammeltoft, Zhou, Duarte Hernandez, Galli, Offersgaard et al., Hepatitis C Virus Protease Inhibitors Show Differential Efficacy and Interactions with Remdesivir for Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.02680-20
Gammeltoft, Zhou, Ryberg, Pham, Binderup et al., Substitutions in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Selected by Protease Inhibitor Boceprevir Confer Resistance to Nirmatrelvir, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15091970
Gandhi, Klein, Robertson, Peña-Hernández, Lin et al., De novo emergence of a remdesivir resistance mutation during treatment of persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection in an immunocompromised patient: A case report, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29104-y
Gao, Yan, Huang, Liu, Zhao et al., Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb7498
Godwin, Polsonetti, Caron, Oppelt, Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19: A Narrative Review, Infect. Dis. Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-023-00900-3
Graepel, Lu, Case, Sexton, Smith et al., Proofreading-Deficient Coronaviruses Adapt for Increased Fitness over Long-Term Passage without Reversion of Exoribonuclease-Inactivating Mutations, mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.01503-17
Harvey, Carabelli, Jackson, Gupta, Thomson et al., SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0
Hedskog, Rodriguez, Roychoudhury, Huang, Jerome et al., Viral Resistance Analyses from the Remdesivir Phase 3 Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial-1 (ACTT-1), J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiad270
Hedskog, Spinner, Protzer, Hoffmann, Ko et al., No Remdesivir Resistance Observed in the Phase 3 Severe and Moderate COVID-19 SIMPLE Trials, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16040546
Heyer, Günther, Robitaille, Lütgehetmann, Addo et al., Remdesivir-induced emergence of SARS-CoV2 variants in patients with prolonged infection, Cell Rep. Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100735
Hirotsu, Kobayashi, Kakizaki, Saito, Tsutsui et al., Multidrug-resistant mutations to antiviral and antibody therapy in an immunocompromised patient infected with SARS-CoV-2, Med, doi:10.1016/j.medj.2023.08.001
Hogan, Duerr, Dimartino, Marier, Hochman et al., Remdesivir Resistance in Transplant Recipients with Persistent Coronavirus Disease, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac769
Humphrey, Dalke, Schulten, Vmd, Visual molecular dynamics, J. Mol. Graph, doi:10.1016/0263-7855(96)00018-5
Igari, Sakao, Ishige, Saito, Murata et al., Dynamic diversity of SARS-CoV-2 genetic mutations in a lung transplantation patient with persistent COVID-19, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-47941-x
Li, Cao, Li, Cong, Li et al., Remdesivir Metabolite GS-441524 Effectively Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Mouse Models, J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01929
Ling-Hu, Simons, Rios-Guzman, Carvalho, Agnes et al., The impact of remdesivir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in vivo, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.182376
Lo, Jordan, Arvey, Sudhamsu, Shrivastava-Ranjan et al., GS-5734 and its parent nucleoside analog inhibit Filo-, Pneumo-, and Paramyxoviruses, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/srep43395
Lo, Kariv, Hao, Gammeltoft, Bukh et al., Replication capacity and susceptibility of nirmatrelvir-resistant mutants to next-generation Mpro inhibitors in a SARS-CoV-2 replicon system, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.106022
Ma, Wu, Shaw, Gao, Wang et al., Structural basis and functional analysis of the SARS coronavirus nsp14-nsp10 complex, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci
Mackman, Hui, Perron, Murakami, Palmiotti et al., Prodrugs of a 1 ′ -CN-4-Aza-7,9-dideazaadenosine C-Nucleoside Leading to the Discovery of Remdesivir (GS-5734) as a Potent Inhibitor of Respiratory Syncytial Virus with Efficacy in the African Green Monkey Model of RSV, J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00071
Mackman, Kalla, Babusis, Pitts, Barrett et al., Discovery of GS-5245 (Obeldesivir), an Oral Prodrug of Nucleoside GS-441524 That Exhibits Antiviral Efficacy in SARS-CoV-2-Infected African Green Monkeys, J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00750
Malone, Perry, Olinares, Lee, Chen et al., Structural basis for substrate selection by the SARS-CoV-2 replicase, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05664-3
Martinot, Jary, Fafi-Kremer, Leducq, Delagreverie et al., Emerging RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Mutation in a Remdesivir-Treated B-cell Immunodeficient Patient with Protracted Coronavirus Disease, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1474
Mejer, Fahnøe, Galli, Ramirez, Weiland et al., Mutations Identified in the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Polymerase of Patients with Chronic HCV Treated with Ribavirin Cause Resistance and Affect Viral Replication Fidelity, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.01417-20
Nooruzzaman, Johnson, Rani, Finkelsztein, Caserta et al., Emergence of transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants with decreased sensitivity to antivirals in immunocompromised patients with persistent infections, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-51924-3
Offersgaard, Duarte Hernandez, Feng, Marichal-Gallardo, Holmbeck et al., An inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine induced cross-neutralizing persisting antibodies and protected against challenge in small animals, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.105949
Pawlotsky, Retreatment of Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients with Direct-Acting Antiviral Failures, Semin. Liver Dis, doi:10.1055/s-0039-1687823
Peng, Peng, Yuan, Wang, Zhao et al., Structural Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase Inhibition by Favipiravir, Innovation, doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100080
Pham, Underwood, Binderup, Fahnøe, Fernandez-Antunez et al., Neutralisation resistance of SARS-CoV-2 spike-variants is primarily mediated by synergistic receptor binding domain substitutions, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2024.2412643
Pruijssers, George, Schäfer, Leist, Gralinksi et al., Remdesivir Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in Human Lung Cells and Chimeric SARS-CoV Expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA Polymerase in Mice, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107940
Ramirez, Fernandez-Antunez, Galli, Underwood, Pham et al., Overcoming Culture Restriction for SARS-CoV-2 in Human Cells Facilitates the Screening of Compounds Inhibiting Viral Replication, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.00097-21
Reed, Muench, A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints, Am. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a118408
Rodriguez, Lee, Li, Martin, Han et al., SARS-CoV-2 resistance analyses from the Phase 3 PINETREE study of remdesivir treatment in nonhospitalized participants, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/aac.01238-24
Sama, Selisko, Falcou, Fattorini, Piorkowski et al., The effects of Remdesivir's functional groups on its antiviral potency and resistance against the SARS-CoV-2 polymerase, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.106034
Schreiber, Rodner, Oberberg, Anhlan, Bletz et al., The host-targeted antiviral drug Zapnometinib exhibits a high barrier to the development of SARS-CoV-2 resistance, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105840
Shannon, Canard, Kill or corrupt: Mechanisms of action and drug-resistance of nucleotide analogues against SARS-CoV-2, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105501
Shaw Research, Molecular Dynamics Simulations Related to SARS-CoV-2
Sheahan, Sims, Graham, Menachery, Gralinski et al., Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses, Sci. Transl. Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653
Smyk, Szydłowska, Szulc, Majewska, Evolution of Influenza Viruses-Drug Resistance, Treatment Options, and Prospects, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms232012244
Stevens, Pruijssers, Lee, Gordon, Tchesnokov et al., Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase confer resistance to remdesivir by distinct mechanisms, Sci. Transl. Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abo0718
Sun, Xie, Bu, Zhong, Zeng, Molecular characteristics, immune evasion, and impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01039-2
Szemiel, Merits, Orton, Maclean, Pinto et al., In vitro selection of Remdesivir resistance suggests evolutionary predictability of SARS-CoV-2, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009929
Tamura, Choudhary, Deo, Yousuf, Gomez et al., Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Resistance After Antiviral Treatment, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.35431
Tanimoto, Itoh, Okumura, Bucket brigade" using lysine residues in RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2, Biophys. J, doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2021.07.026
Tanino, Nishioka, Yamamoto, Watanabe, Daidoji et al., Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 with Dual-Drug Resistant Mutations During a Long-Term Infection in a Kidney Transplant Recipient, Infect. Drug Resist, doi:10.2147/IDR.S438915
Torii, Kim, Koseki, Suzuki, Iwanami et al., Increased flexibility of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-binding site causes resistance to remdesivir, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1011231
Truong, Ryutov, Pandey, Yee, Goldberg et al., Increased viral variants in children and young adults with impaired humoral immunity and persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection: A consecutive case series, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103355
Underwood, Sølund, Fernandez-Antunez, Villadsen, Winckelmann et al., Neutralisation titres against SARS-CoV-2 are sustained 6 months after onset of symptoms in individuals with mild COVID-19, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103519
Warren, Jordan, Lo, Ray, Mackman et al., Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature17180
Williamson, Feldmann, Schwarz, Meade-White, Porter et al., Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2423-5
Yang, Multani, Garrigues, Oh, Hemarajata et al., Transient SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Mutations after Remdesivir Treatment for Chronic COVID-19 in Two Transplant Recipients: Case Report and Intra-Host Viral Genomic Investigation, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11082096
Zhou, Gammeltoft, Ryberg, Pham, Tjørnelund et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Sci. Adv, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197
Zhou, Gilmore, Ramirez, Settels, Gammeltoft et al., In vitro efficacy of artemisinin-based treatments against SARS-CoV-2, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-93361-y
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v17081055",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4915"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v17081055",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Various SARS-CoV-2 remdesivir resistance-associated substitutions (RAS) have been reported, but a comprehensive comparison of their resistance levels is lacking. We identified novel RAS and performed head-to-head comparisons with known RAS in Vero E6 cells. A remdesivir escape polyclonal virus exhibited a 3.6-fold increase in remdesivir EC50 and mutations throughout the genome, including substitutions in nsp12 (E796D) and nsp14 (A255S). However, in reverse-genetics infectious assays, viruses harboring both these substitutions exhibited only a slight decrease in remdesivir susceptibility (1.3-fold increase in EC50). The nsp12-E796D substitution did not impair viral fitness (Vero E6 cells or Syrian hamsters) and was reported in a remdesivir-treated COVID-19 patient. In replication assays, a subgenomic replicon containing nsp12-E796D+nsp14-A255S led to a 16.1-fold increase in replication under remdesivir treatment. A comparison with known RAS showed that S759A, located in the active site of nsp12, conferred the highest remdesivir resistance (106.1-fold increase in replication). Nsp12-RAS V166A/L, V792I, E796D or C799F, all adjacent to the active site, caused intermediate resistance (2.0- to 11.5-fold), whereas N198S, D484Y, or E802D, located farther from the active site, showed no resistance (≤2.0-fold). In conclusion, our classification system, correlating replication under remdesivir treatment with RAS location in nsp12, shows that most nsp12-RAS cause moderate resistance.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"v17081055"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3505-4733",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Copenhagen Hepatitis C Program (CO-HEP), Department of Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen University Hospital, 2650 Hvidovre and Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fernandez-Antunez",
"given": "Carlota",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Copenhagen Hepatitis C Program (CO-HEP), Department of Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen University Hospital, 2650 Hvidovre and Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark"
}
],
"family": "Ryberg",
"given": "Line A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Copenhagen Hepatitis C Program (CO-HEP), Department of Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen University Hospital, 2650 Hvidovre and Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Kuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Copenhagen Hepatitis C Program (CO-HEP), Department of Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen University Hospital, 2650 Hvidovre and Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark"
}
],
"family": "Pham",
"given": "Long V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Copenhagen Hepatitis C Program (CO-HEP), Department of Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen University Hospital, 2650 Hvidovre and Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark"
}
],
"family": "Mikkelsen",
"given": "Lotte S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Copenhagen Hepatitis C Program (CO-HEP), Department of Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen University Hospital, 2650 Hvidovre and Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark"
}
],
"family": "Fahnøe",
"given": "Ulrik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 1870 Frederiksberg, Denmark"
}
],
"family": "Hartmann",
"given": "Katrine T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 1870 Frederiksberg, Denmark"
}
],
"family": "Jensen",
"given": "Henrik E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Copenhagen Hepatitis C Program (CO-HEP), Department of Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen University Hospital, 2650 Hvidovre and Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark"
}
],
"family": "Holmbeck",
"given": "Kenn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7815-4806",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Copenhagen Hepatitis C Program (CO-HEP), Department of Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen University Hospital, 2650 Hvidovre and Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bukh",
"given": "Jens",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3699-1814",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Copenhagen Hepatitis C Program (CO-HEP), Department of Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen University Hospital, 2650 Hvidovre and Department of Immunology and Microbiology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, 2200 Copenhagen, Denmark"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ramirez",
"given": "Santseharay",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viruses",
"container-title-short": "Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-29T08:00:41Z",
"timestamp": 1753776041000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-29T08:04:47Z",
"timestamp": 1753776287000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100013826",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100013826",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Candys Foundation"
},
{
"name": "Region H Foundation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100009708",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100009708",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Novo Nordisk Foundation"
},
{
"name": "Independent Research Fund Denmark"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001825",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100001825",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Danish Agency for Science and Higher Education"
},
{
"name": "Mauritzen La Fontaine Fonden"
},
{
"name": "Mauritzen La Fontaine Familiefond"
},
{
"name": "Sygeforsikring “danmark”"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-30T15:44:50Z",
"timestamp": 1753890290910,
"version": "3.41.2"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1753747200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/17/8/1055/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1055",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1177/13596535221082773",
"article-title": "Journey of remdesivir from the inhibition of hepatitis C virus to the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Cihlar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135965352210827",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Ther.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.02.105",
"article-title": "Synthesis and antiviral activity of a series of 1′-substituted 4-aza-7,9-dideazaadenosine C-nucleosides",
"author": "Cho",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2705",
"journal-title": "Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep43395",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_3",
"unstructured": "Lo, M.K., Jordan, R., Arvey, A., Sudhamsu, J., Shrivastava-Ranjan, P., Hotard, A.L., Flint, M., McMullan, L.K., Siegel, D., and Clarke, M.O. (2017). GS-5734 and its parent nucleoside analog inhibit Filo-, Pneumo-, and Paramyxoviruses. Sci. Rep., 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00071",
"article-title": "Prodrugs of a 1′-CN-4-Aza-7,9-dideazaadenosine C-Nucleoside Leading to the Discovery of Remdesivir (GS-5734) as a Potent Inhibitor of Respiratory Syncytial Virus with Efficacy in the African Green Monkey Model of RSV",
"author": "Mackman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5001",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature17180",
"article-title": "Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys",
"author": "Warren",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "381",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "531",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2023.06.002",
"article-title": "Differential activity of nucleotide analogs against tick-borne encephalitis and yellow fever viruses in human cell lines",
"author": "Binderup",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "179",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "585",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653",
"article-title": "Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses",
"author": "Sheahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eaal3653",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107940",
"article-title": "Remdesivir Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in Human Lung Cells and Chimeric SARS-CoV Expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA Polymerase in Mice",
"author": "Pruijssers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107940",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2423-5",
"article-title": "Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "585",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00097-21",
"article-title": "Overcoming Culture Restriction for SARS-CoV-2 in Human Cells Facilitates the Screening of Compounds Inhibiting Viral Replication",
"author": "Ramirez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0009721",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19—Final Report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium (2022). Remdesivir and three other drugs for hospitalised patients with COVID-19: Final results of the WHO Solidarity randomised trial and updated meta-analyses. Lancet, 399, 1941–1953."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-023-00900-3",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19: A Narrative Review",
"author": "Godwin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. Ther.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"key": "ref_14",
"unstructured": "EMA (European Medicines Agency) (2025, July 03). Authorised COVID-19 Treatments n.d. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/public-health-threats/coronavirus-disease-covid-19/covid-19-medicines."
},
{
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) (2025, July 03). Coronavirus (COVID-19)|Drugs. n.d, Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/emergency-preparedness-drugs/coronavirus-covid-19-drugs."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape",
"author": "Harvey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0039-1687823",
"article-title": "Retreatment of Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients with Direct-Acting Antiviral Failures",
"author": "Pawlotsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "354",
"journal-title": "Semin. Liver Dis.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2019.06.010",
"article-title": "The Impact of HIV-1 Drug Escape on the Global Treatment Landscape",
"author": "Collier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms232012244",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "Smyk, J.M., Szydłowska, N., Szulc, W., and Majewska, A. (2022). Evolution of Influenza Viruses—Drug Resistance, Treatment Options, and Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.add7197",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eadd7197",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiad270",
"article-title": "Viral Resistance Analyses from the Remdesivir Phase 3 Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial-1 (ACTT-1)",
"author": "Hedskog",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1263",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "228",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v16040546",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "Hedskog, C., Spinner, C.D., Protzer, U., Hoffmann, D., Ko, C., Gottlieb, R.L., Askar, M., Roestenberg, M., de Vries, J.J., and Carbo, E.C. (2024). No Remdesivir Resistance Observed in the Phase 3 Severe and Moderate COVID-19 SIMPLE Trials. Viruses, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.01238-24",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 resistance analyses from the Phase 3 PINETREE study of remdesivir treatment in nonhospitalized participants",
"author": "Rodriguez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01238-24",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms11082096",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Yang, S., Multani, A., Garrigues, J.M., Oh, M.S., Hemarajata, P., Burleson, T., Green, N.M., Oliai, C., Gaynor, P.T., and Beaird, O.E. (2023). Transient SARS-CoV-2 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Mutations after Remdesivir Treatment for Chronic COVID-19 in Two Transplant Recipients: Case Report and Intra-Host Viral Genomic Investigation. Microorganisms, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100735",
"article-title": "Remdesivir-induced emergence of SARS-CoV2 variants in patients with prolonged infection",
"author": "Heyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100735",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep. Med.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medj.2023.08.001",
"article-title": "Multidrug-resistant mutations to antiviral and antibody therapy in an immunocompromised patient infected with SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Hirotsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "813",
"journal-title": "Med",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1474",
"article-title": "Emerging RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Mutation in a Remdesivir-Treated B-cell Immunodeficient Patient with Protracted Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"author": "Martinot",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1762",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S438915",
"article-title": "Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 with Dual-Drug Resistant Mutations During a Long-Term Infection in a Kidney Transplant Recipient",
"author": "Tanino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "531",
"journal-title": "Infect. Drug Resist.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac769",
"article-title": "Remdesivir Resistance in Transplant Recipients with Persistent Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"author": "Hogan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "342",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-024-51924-3",
"article-title": "Emergence of transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants with decreased sensitivity to antivirals in immunocompromised patients with persistent infections",
"author": "Nooruzzaman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7999",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-024-47941-x",
"article-title": "Dynamic diversity of SARS-CoV-2 genetic mutations in a lung transplantation patient with persistent COVID-19",
"author": "Igari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3604",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-29104-y",
"article-title": "De novo emergence of a remdesivir resistance mutation during treatment of persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection in an immunocompromised patient: A case report",
"author": "Gandhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1547",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.35431",
"article-title": "Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Resistance After Antiviral Treatment",
"author": "Tamura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2435431",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.00198-22",
"article-title": "In Vitro Selection of Remdesivir-Resistant SARS-CoV-2 Demonstrates High Barrier to Resistance",
"author": "Checkmahomed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00198-22",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1011231",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "Torii, S., Kim, K.S., Koseki, J., Suzuki, R., Iwanami, S., Fujita, Y., Jeong, Y.D., Ito, J., Asakura, H., and Nagashima, M. (2023). Increased flexibility of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-binding site causes resistance to remdesivir. PLoS Pathog., 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abo0718",
"article-title": "Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase confer resistance to remdesivir by distinct mechanisms",
"author": "Stevens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabo0718",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009929",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_37",
"unstructured": "Szemiel, A.M., Merits, A., Orton, R.J., MacLean, O.A., Pinto, R.M., Wickenhagen, A., Lieber, G., Turnbull, M.L., Wang, S., and Furnon, W. (2021). In vitro selection of Remdesivir resistance suggests evolutionary predictability of SARS-CoV-2. PLoS Pathog., 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.106034",
"article-title": "The effects of Remdesivir’s functional groups on its antiviral potency and resistance against the SARS-CoV-2 polymerase",
"author": "Sama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106034",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "232",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105840",
"article-title": "The host-targeted antiviral drug Zapnometinib exhibits a high barrier to the development of SARS-CoV-2 resistance",
"author": "Schreiber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105840",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "225",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15091970",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Gammeltoft, K.A., Zhou, Y., Ryberg, L.A., Pham, L.V., Binderup, A., Hernandez, C.R.D., Offersgaard, A., Fahnøe, U., Peters, G.H., and Ramirez, S. (2023). Substitutions in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Selected by Protease Inhibitor Boceprevir Confer Resistance to Nirmatrelvir. Viruses, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-93361-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_41",
"unstructured": "Zhou, Y., Gilmore, K., Ramirez, S., Settels, E., Gammeltoft, K.A., Pham, L.V., Fahnøe, U., Feng, S., Offersgaard, A., and Trimpert, J. (2021). In vitro efficacy of artemisinin-based treatments against SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14020172",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Fahnøe, U., Pham, L.V., Fernandez-Antunez, C., Costa, R., Rivera-Rangel, L.R., Galli, A., Feng, S., Mikkelsen, L.S., Gottwein, J.M., and Scheel, T.K. (2022). Versatile SARS-CoV-2 Reverse-Genetics Systems for the Study of Antiviral Resistance and Replication. Viruses, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2024.2412643",
"article-title": "Neutralisation resistance of SARS-CoV-2 spike-variants is primarily mediated by synergistic receptor binding domain substitutions",
"author": "Pham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2412643",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a118408",
"article-title": "A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints",
"author": "Reed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "493",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Epidemiol.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "27",
"year": "1938"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02680-20",
"article-title": "Hepatitis C Virus Protease Inhibitors Show Differential Efficacy and Interactions with Remdesivir for Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 In Vitro",
"author": "Gammeltoft",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e02680-20",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2023.105949",
"article-title": "An inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine induced cross-neutralizing persisting antibodies and protected against challenge in small animals",
"author": "Offersgaard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105949",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103519",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Underwood, A.P., Sølund, C., Fernandez-Antunez, C., Villadsen, S.L., Winckelmann, A.A., Bollerup, S., Mikkelsen, L.S., Sørensen, A.-L., Feng, S., and Fahnøe, U. (2021). Neutralisation titres against SARS-CoV-2 are sustained 6 months after onset of symptoms in individuals with mild COVID-19. EBioMedicine, 71."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01417-20",
"article-title": "Mutations Identified in the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Polymerase of Patients with Chronic HCV Treated with Ribavirin Cause Resistance and Affect Viral Replication Fidelity",
"author": "Mejer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01417-20",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_49",
"unstructured": "(The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, 2021). The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.5.0."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05664-3",
"article-title": "Structural basis for substrate selection by the SARS-CoV-2 replicase",
"author": "Malone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "781",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "614",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb7498",
"article-title": "Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "779",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_52",
"unstructured": "D.E. Shaw Research (2021, January 22). Molecular Dynamics Simulations Related to SARS-CoV-2. D.E. Shaw Research Technical Data. Available online: https://www.deshawresearch.com/downloads/download_trajectory_sarscov2.cgi/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btr168",
"article-title": "ProDy: Protein Dynamics Inferred from Theory and Experiments",
"author": "Bakan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1575",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0263-7855(96)00018-5",
"article-title": "VMD: Visual molecular dynamics",
"author": "Humphrey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Graph.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "14",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01929",
"article-title": "Remdesivir Metabolite GS-441524 Effectively Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Mouse Models",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2785",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00750",
"article-title": "Discovery of GS-5245 (Obeldesivir), an Oral Prodrug of Nucleoside GS-441524 That Exhibits Antiviral Efficacy in SARS-CoV-2-Infected African Green Monkeys",
"author": "Mackman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11701",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Structural Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase Inhibition by Favipiravir",
"author": "Peng",
"first-page": "100080",
"journal-title": "Innovation",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpj.2021.07.026",
"article-title": "“Bucket brigade” using lysine residues in RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Tanimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3615",
"journal-title": "Biophys. J.",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103355",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_59",
"unstructured": "Truong, T.T., Ryutov, A., Pandey, U., Yee, R., Goldberg, L., Bhojwani, D., Aguayo-Hiraldo, P., Pinsky, B.A., Pekosz, A., and Shen, L. (2021). Increased viral variants in children and young adults with impaired humoral immunity and persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection: A consecutive case series. EBioMedicine, 67."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00581-16",
"article-title": "Barrier-Independent, Fitness-Associated Differences in Sofosbuvir Efficacy against Hepatitis C Virus",
"author": "Gallego",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3786",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/HEP.0000000000000353",
"article-title": "Characterization of multi-DAA resistance using a novel hepatitis C virus genotype 3a infectious culture system",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "621",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.01503-17",
"article-title": "Proofreading-Deficient Coronaviruses Adapt for Increased Fitness over Long-Term Passage without Reversion of Exoribonuclease-Inactivating Mutations",
"author": "Graepel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01503-17",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-01039-2",
"article-title": "Molecular characteristics, immune evasion, and impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "202",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.182376",
"article-title": "The impact of remdesivir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in vivo",
"author": "Simons",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e182376",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.106022",
"article-title": "Replication capacity and susceptibility of nirmatrelvir-resistant mutants to next-generation Mpro inhibitors in a SARS-CoV-2 replicon system",
"author": "Lo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106022",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "231",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105501",
"article-title": "Kill or corrupt: Mechanisms of action and drug-resistance of nucleotide analogues against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shannon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105501",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "210",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1508686112",
"article-title": "Structural basis and functional analysis of the SARS coronavirus nsp14–nsp10 complex",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9436",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 67,
"references-count": 67,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/17/8/1055"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 Remdesivir Exposure Leads to Different Evolutionary Pathways That Converge in Moderate Levels of Drug Resistance",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "17"
}