Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Resistance After Antiviral Treatment
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.35431, Sep 2024
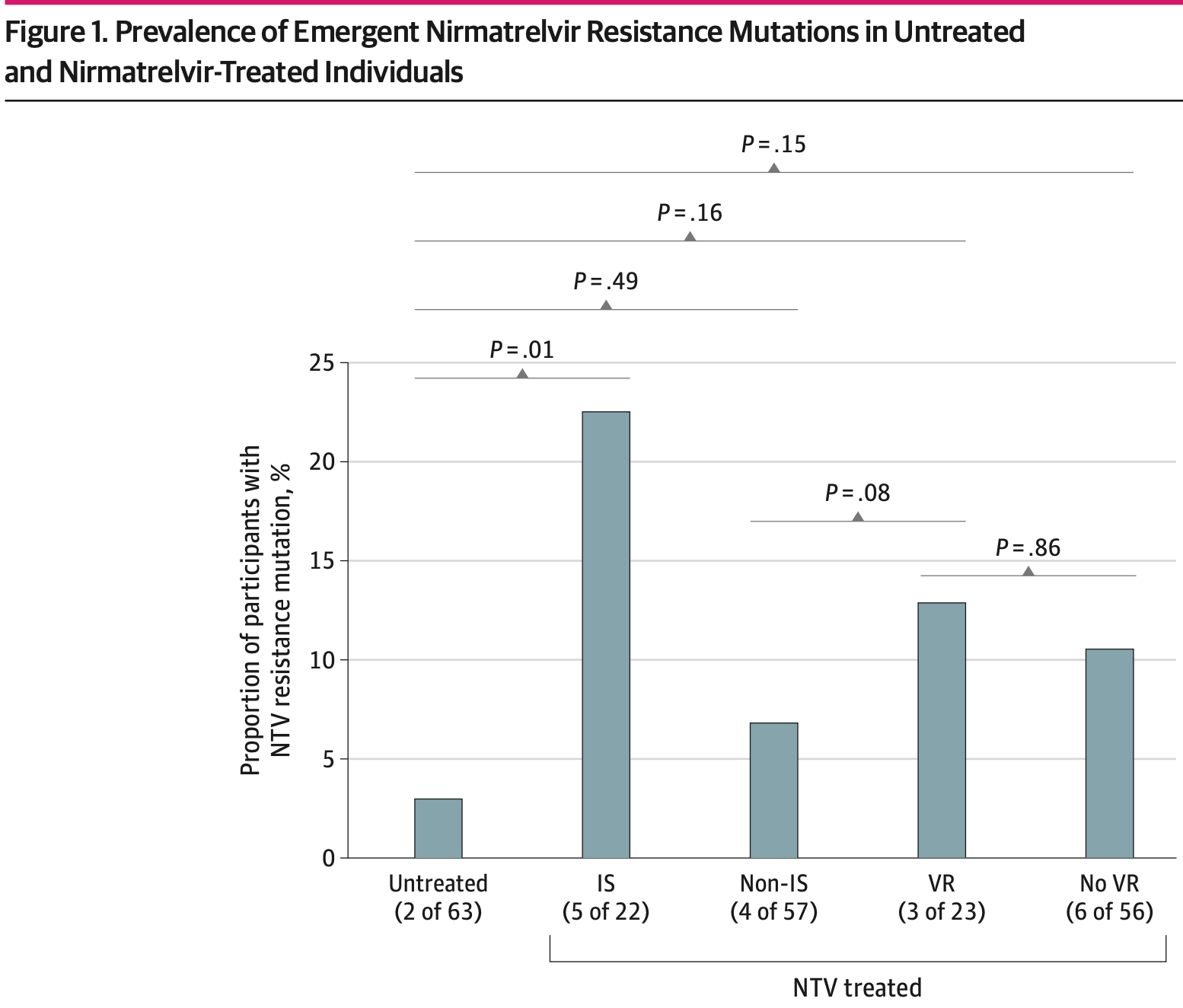
Prospective study of 156 outpatients showing emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations with nirmatrelvir treatment, especially in immunosuppressed individuals. Results support the use of combination antiviral therapy and host-directed treatments which may be key strategies in reducing the risk of resistance, especially in high-risk or immunosuppressed patients.
Tamura et al., 25 Sep 2024, prospective, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 56.0, 28 authors, study period May 2021 - October 2023.
Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Resistance After Antiviral Treatment
JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.35431
IMPORTANCE Previous studies have identified mutations in SARS-CoV-2 strains that confer resistance to nirmatrelvir, yet how often this resistance arises and its association with posttreatment virologic rebound is not well understood. OBJECTIVE To examine the prevalence of emergent antiviral resistance after nirmatrelvir treatment and its association with virologic rebound.
DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS This cohort study enrolled outpatient adults with acute COVID-19 infection from May 2021 to October 2023. Participants were divided into those who received antiviral therapy and those who did not. The study was conducted at a multicenter health care system in Boston, Massachusetts. EXPOSURE Treatment regimen, including none, nirmatrelvir, and remdesivir. MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary outcome was emergent SARS-CoV-2 antiviral resistance, defined as the detection of antiviral resistance mutations, which were not present at baseline, were previously associated with decreased antiviral efficacy, and emerged during or after completion of a participant's treatment. Next-generation sequencing was used to detect low frequency mutations down to 1% of the total viral population. RESULTS Overall, 156 participants (114 female [73.1%]; median [IQR] age, 56 [38-69] years) were included. Compared with 63 untreated individuals, the 79 who received nirmatrelvir were older and more commonly immunosuppressed. After sequencing viral RNA from participants' anterior nasal swabs, nirmatrelvir resistance mutations were detected in 9 individuals who received nirmatrelvir (11.4%) compared with 2 of those who did not (3.2%) (P = .09). Among the individuals treated with nirmatrelvir, those who were immunosuppressed had the highest frequency of resistance emergence (5 of 22 [22.7%]), significantly greater than untreated individuals (2 of 63 [3.1%]) (P = .01). Similar rates of nirmatrelvir resistance were found in those who had virologic rebound (3 of 23 [13.0%]) vs those who did not (6 of 56 [10.7%]) (P = .86). Most of these mutations (10 of 11 [90.9%]) were detected at low frequencies (<20% of viral population) and reverted to the wild type at subsequent time points. Emerging remdesivir resistance mutations were only detected in immunosuppressed individuals (2 of 14 [14.3%]) but were similarly low frequency and transient. Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data analysis showed no evidence of increased nirmatrelvir resistance in the United States after the authorization of nirmatrelvir.
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE In this cohort study of 156 participants, treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations were commonly detected, especially in individuals who were immunosuppressed. However, these mutations were generally present at low frequencies and were (continued) Key Points Question Is there an increased frequency of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral resistance in individuals receiving antiviral therapy? Findings In this cohort study with 156 participants,..
References
Boucau, Uddin, Marino, Characterization of virologic rebound following nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac512
Charness, Gupta, Stack, Rebound of SARS-CoV-2 infection after nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2206449
Choudhary, Chew, Deo, ACTIV-2/A5401 Study Team. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations during Bamlanivimab therapy in a phase II randomized clinical trial, Nat Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-022-01254-1
Costacurta, A comprehensive study of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M(pro)) inhibitor-resistant mutants selected in a VSV-based system. bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.09.22.558628
Edelstein, Boucau, Uddin, SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy: an observational study, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M23-1756
Fajnzylber, Regan, Coxen, Massachusetts Consortium for Pathogen Readiness. SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19057-5
Github, FASTQ-to-CodFreq pipeline for HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2
Greasley, Noell, Plotnikova, Structural basis for the in vitro efficacy of nirmatrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 variants, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101972
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Hirotsu, Kobayashi, Kakizaki, Multidrug-resistant mutations to antiviral and antibody therapy in an immunocompromised patient infected with SARS-CoV-2, Med, doi:10.1016/j.medj.2023.08.001
Huot, Planchais, Rosenbaum, SARS-CoV-2 viral persistence in lung alveolar macrophages is controlled by IFN-γ and NK cells, Nat Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-023-01661-4
Iketani, Mohri, Culbertson, Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05514-2
Jiang, Zhou, Zou, Evaluation of the inhibition potency of nirmatrelvir against main protease mutants of SARS-CoV-2 variants, Biochemistry, doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00075
Khare, Gurre, Freitas, GISAID's role in pandemic response, China CDC Wkly, doi:10.46234/ccdcw2021.255
Li, Choudhary, Regan, SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance and evolution varies by type and severity of immunodeficiency, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.adk1599
Li, Stella, Choudhary, Impact of pre-existing drug resistance on risk of virological failure in South Africa, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkab062
Noske, De Souza Silva, De Godoy, Mo, Structural basis of nirmatrelvir and ensitrelvir activity against naturally occurring polymorphisms of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2023.103004
Proal, Vanelzakker, Aleman, SARS-CoV-2 reservoir in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), Nat Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-023-01601-2
Rosenke, Lewis, Feldmann, Combined molnupiravir-nirmatrelvir treatment improves the inhibitory effect on SARS-CoV-2 in macaques, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.166485
Se, Symptoms, viral loads, and rebound among COVID-19 outpatients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir compared to propensity score-matched untreated individuals, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad696
Stevens, Pruijssers, Lee, Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase confer resistance to remdesivir by distinct mechanisms, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abo0718
Torii, Kim, Koseki, Genotype to Phenotype Japan (G2P-Japan) Consortium. Increased flexibility of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-binding site causes resistance to remdesivir, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1011231
Tzou, Tao, Pond, Shafer, Coronavirus Resistance Database (CoV-RDB): SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies, convalescent plasma, and plasma from vaccinated persons, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0261045
Ullrich, Ekanayake, Otting, Nitsche, Main protease mutants of SARS-CoV-2 variants remain susceptible to nirmatrelvir, Bioorg Med Chem Lett, doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128629
Zhou, Gammeltoft, Ryberg, Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Sci Adv, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197
Zuckerman, Bucris, Keidar-Friedman, Amsalem, Brosh-Nissimov, Nirmatrelvir resistance-de novo E166V/L50V mutations in an immunocompromised patient treated with prolonged nirmatrelvir/ritonavir monotherapy leading to clinical and virological treatment failure-a case report, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad494
Zuo, He, Liang, The persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in tissues and its association with long COVID symptoms: a cross-sectional cohort study in China, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00171-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.35431",
"ISSN": [
"2574-3805"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.35431",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi241054-4\"><jats:title>Importance</jats:title><jats:p>Previous studies have identified mutations in SARS-CoV-2 strains that confer resistance to nirmatrelvir, yet how often this resistance arises and its association with posttreatment virologic rebound is not well understood.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi241054-5\"><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To examine the prevalence of emergent antiviral resistance after nirmatrelvir treatment and its association with virologic rebound.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi241054-6\"><jats:title>Design, Setting, and Participants</jats:title><jats:p>This cohort study enrolled outpatient adults with acute COVID-19 infection from May 2021 to October 2023. Participants were divided into those who received antiviral therapy and those who did not. The study was conducted at a multicenter health care system in Boston, Massachusetts.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi241054-7\"><jats:title>Exposure</jats:title><jats:p>Treatment regimen, including none, nirmatrelvir, and remdesivir.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi241054-8\"><jats:title>Main Outcomes and Measures</jats:title><jats:p>The primary outcome was emergent SARS-CoV-2 antiviral resistance, defined as the detection of antiviral resistance mutations, which were not present at baseline, were previously associated with decreased antiviral efficacy, and emerged during or after completion of a participant’s treatment. Next-generation sequencing was used to detect low frequency mutations down to 1% of the total viral population.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi241054-9\"><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Overall, 156 participants (114 female [73.1%]; median [IQR] age, 56 [38-69] years) were included. Compared with 63 untreated individuals, the 79 who received nirmatrelvir were older and more commonly immunosuppressed. After sequencing viral RNA from participants’ anterior nasal swabs, nirmatrelvir resistance mutations were detected in 9 individuals who received nirmatrelvir (11.4%) compared with 2 of those who did not (3.2%) (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .09). Among the individuals treated with nirmatrelvir, those who were immunosuppressed had the highest frequency of resistance emergence (5 of 22 [22.7%]), significantly greater than untreated individuals (2 of 63 [3.1%]) (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .01). Similar rates of nirmatrelvir resistance were found in those who had virologic rebound (3 of 23 [13.0%]) vs those who did not (6 of 56 [10.7%]) (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .86). Most of these mutations (10 of 11 [90.9%]) were detected at low frequencies (&amp;lt;20% of viral population) and reverted to the wild type at subsequent time points. Emerging remdesivir resistance mutations were only detected in immunosuppressed individuals (2 of 14 [14.3%]) but were similarly low frequency and transient. Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data analysis showed no evidence of increased nirmatrelvir resistance in the United States after the authorization of nirmatrelvir.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi241054-10\"><jats:title>Conclusions and Relevance</jats:title><jats:p>In this cohort study of 156 participants, treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations were commonly detected, especially in individuals who were immunosuppressed. However, these mutations were generally present at low frequencies and were transient in nature, suggesting a low risk for the spread of nirmatrelvir resistance in the community with the current variants and drug usage patterns.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Tamura",
"given": "Trevor J.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Choudhary",
"given": "Manish C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Deo",
"given": "Rinki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Yousuf",
"given": "Fizah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Gomez",
"given": "Anadela Navarrete",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Edelstein",
"given": "Gregory E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ragon Institute of Massachusetts General Hospital, MIT and Harvard, Cambridge"
}
],
"family": "Boucau",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ragon Institute of Massachusetts General Hospital, MIT and Harvard, Cambridge"
}
],
"family": "Glover",
"given": "Owen T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Barry",
"given": "Mamadou",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Gilbert",
"given": "Rebecca F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Reynolds",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
},
{
"name": "University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Yijia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Tien",
"given": "Dessie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Vyas",
"given": "Tammy D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Passell",
"given": "Eliza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Su",
"given": "Karry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Drapkin",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Abar",
"given": "Emory G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Kawano",
"given": "Yumeko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Sparks",
"given": "Jeffrey A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Wallace",
"given": "Zachary S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
},
{
"name": "Broad Institute, Cambridge, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Vyas",
"given": "Jatin M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, California"
}
],
"family": "Shafer",
"given": "Robert W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Siedner",
"given": "Mark J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Ragon Institute of Massachusetts General Hospital, MIT and Harvard, Cambridge"
},
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Barczak",
"given": "Amy K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
},
{
"name": "Broad Institute, Cambridge, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Lemieux",
"given": "Jacob E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts"
},
{
"name": "Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jonathan Z.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "POSITIVES Study Team",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Netw Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-25T21:40:20Z",
"timestamp": 1727300420000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-25T21:40:23Z",
"timestamp": 1727300423000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-26T04:30:10Z",
"timestamp": 1727325010481
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
25
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/articlepdf/2824050/tamura_2024_oi_241054_1726669148.41936.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e2435431",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
25
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
25
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19.",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi241054r2",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05514-2",
"article-title": "Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir.",
"author": "Iketani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "558",
"issue": "7944",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "zoi241054r4",
"volume": "613",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2023.103004",
"article-title": "Structural basis of nirmatrelvir and ensitrelvir activity against naturally occurring polymorphisms of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease.",
"author": "Noske",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "zoi241054r5",
"volume": "299",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128629",
"article-title": "Main protease mutants of SARS-CoV-2 variants remain susceptible to nirmatrelvir.",
"author": "Ullrich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Bioorg Med Chem Lett",
"key": "zoi241054r6",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00075",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the inhibition potency of nirmatrelvir against main protease mutants of SARS-CoV-2 variants.",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2055",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Biochemistry",
"key": "zoi241054r7",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101972",
"article-title": "Structural basis for the in vitro efficacy of nirmatrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 variants.",
"author": "Greasley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "zoi241054r9",
"volume": "298",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1011231",
"article-title": "Increased flexibility of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-binding site causes resistance to remdesivir.",
"author": "Torii",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "zoi241054r10",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abo0718",
"article-title": "Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase confer resistance to remdesivir by distinct mechanisms.",
"author": "Stevens",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "656",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "zoi241054r11",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac512",
"article-title": "Characterization of virologic rebound following nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).",
"author": "Boucau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e526",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "zoi241054r12",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M23-1756",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy: an observational study.",
"author": "Edelstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1577",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "zoi241054r13",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2206449",
"article-title": "Rebound of SARS-CoV-2 infection after nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment.",
"author": "Charness",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1045",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi241054r14",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-022-01254-1",
"article-title": "Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations during Bamlanivimab therapy in a phase II randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Choudhary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1906",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "zoi241054r15",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19057-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality.",
"author": "Fajnzylber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5493",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "zoi241054r16",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0261045",
"article-title": "Coronavirus Resistance Database (CoV-RDB): SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies, convalescent plasma, and plasma from vaccinated persons.",
"author": "Tzou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "zoi241054r17",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkab062",
"article-title": "Impact of pre-existing drug resistance on risk of virological failure in South Africa.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1558",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "zoi241054r19",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.46234/ccdcw2021.255",
"article-title": "GISAID’s role in pandemic response.",
"author": "Khare",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1049",
"issue": "49",
"journal-title": "China CDC Wkly",
"key": "zoi241054r22",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.adk1599",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance and evolution varies by type and severity of immunodeficiency.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "731",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "zoi241054r23",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad494",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir resistance-de novo E166V/L50V mutations in an immunocompromised patient treated with prolonged nirmatrelvir/ritonavir monotherapy leading to clinical and virological treatment failure—a case report.",
"author": "Zuckerman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "352",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "zoi241054r24",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medj.2023.08.001",
"article-title": "Multidrug-resistant mutations to antiviral and antibody therapy in an immunocompromised patient infected with SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "Hirotsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "813",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Med",
"key": "zoi241054r25",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.166485",
"article-title": "Combined molnupiravir-nirmatrelvir treatment improves the inhibitory effect on SARS-CoV-2 in macaques.",
"author": "Rosenke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "zoi241054r26",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.add7197",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system.",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "51",
"journal-title": "Sci Adv",
"key": "zoi241054r27",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad696",
"article-title": "Symptoms, viral loads, and rebound among COVID-19 outpatients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir compared to propensity score-matched untreated individuals.",
"author": "Smith-Jeffcoat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "zoi241054r28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00171-3",
"article-title": "The persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in tissues and its association with long COVID symptoms: a cross-sectional cohort study in China.",
"author": "Zuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "845",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "zoi241054r29",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-023-01661-4",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral persistence in lung alveolar macrophages is controlled by IFN-? and NK cells.",
"author": "Huot",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2068",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "zoi241054r30",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-023-01601-2",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 reservoir in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC).",
"author": "Proal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1616",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "zoi241054r31",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "zoi241054r1",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for Paxlovid. Accessed August 21, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download"
},
{
"key": "zoi241054r3",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. Highlights of prescribing information: Veklury. Accessed August 21, 2024. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/214787Orig1s000lbl.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.09.22.558628",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "zoi241054r8",
"unstructured": "Costacurta? F, . A comprehensive study of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M(pro)) inhibitor-resistant mutants selected in a VSV-based system.? bioRxiv. Preprint posted online October 4, 2023. doi:10.1101/2023.09.22.558628"
},
{
"key": "zoi241054r18",
"unstructured": "Github. FASTQ-to-CodFreq pipeline for HIV-1 and SARS-CoV-2. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://github.com/hivdb/codfreq"
},
{
"key": "zoi241054r20",
"unstructured": "Stanford University Coronavirus Antiviral & Resistance Database. SARS-CoV-2 resistance mutations—3CLpro inhibitors. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://covdb.stanford.edu/drms/3clpro/"
},
{
"key": "zoi241054r21",
"unstructured": "Stanford University Coronavirus Antiviral & Resistance Database. SARS-CoV-2 resistance mutations—RdRP inhibitors. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://covdb.stanford.edu/drms/rdrp/"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2824050"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Resistance After Antiviral Treatment",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "7"
}