Efficacy of Remdesivir and Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies in Monotherapy or Combination Therapy in Reducing the Risk of Disease Progression in Elderly or Immunocompromised Hosts Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Single Center Retrospective Study
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15051199, May 2023
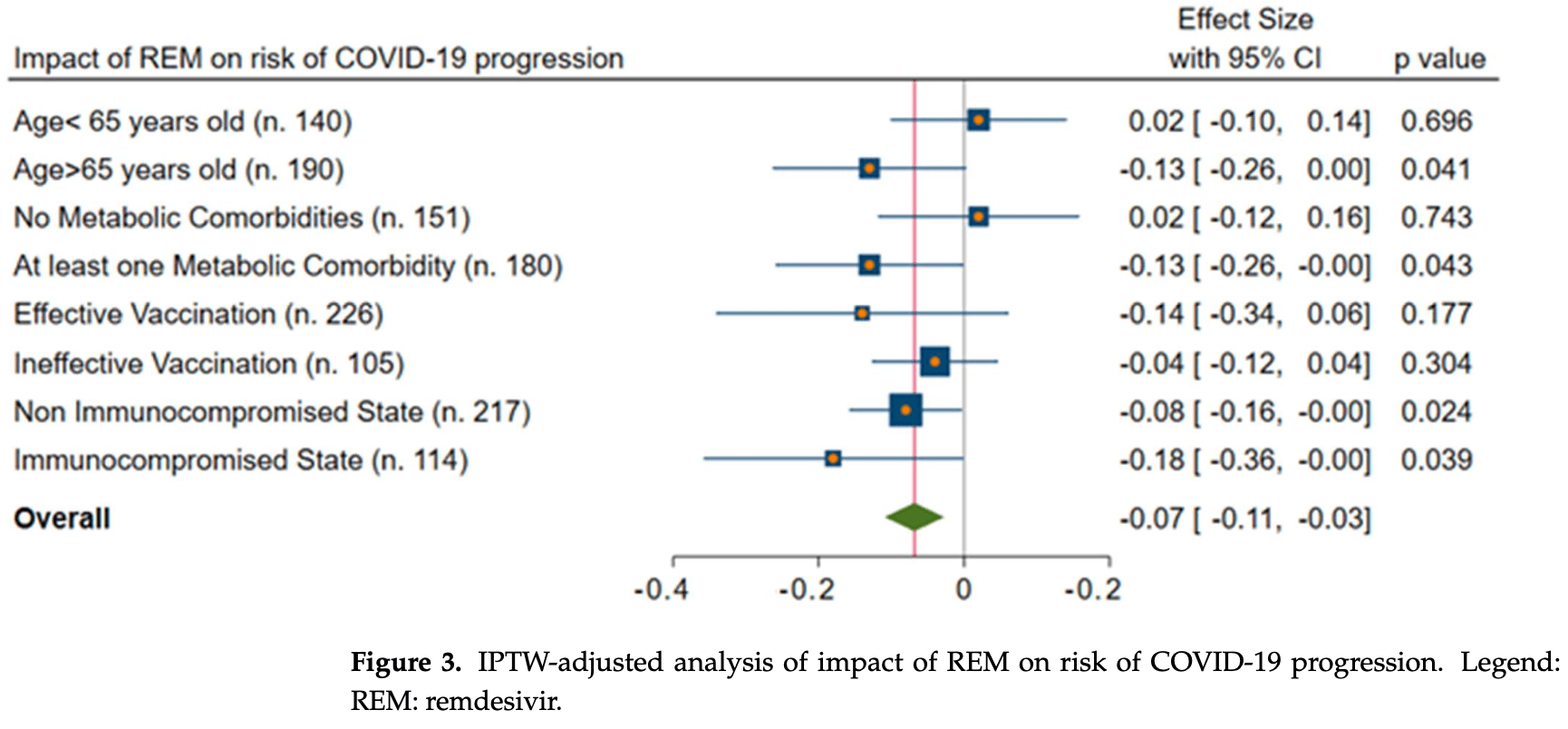
Retrospective 331 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Italy, showing lower progression with remdesivir. Combination therapy with mAbs was more effective, and improved results were seen for immunocompromised patients.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
|
risk of severe case, 7.0% lower, RR 0.93, p < 0.001, treatment 120, control 211, propensity score weighting.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Bavaro et al., 19 May 2023, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, median age 75.0, 27 authors, study period 1 July, 2021 - 15 March, 2022.
Contact: davidebavaro@gmail.com (corresponding author).
Efficacy of Remdesivir and Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies in Monotherapy or Combination Therapy in Reducing the Risk of Disease Progression in Elderly or Immunocompromised Hosts Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Single Center Retrospective Study
Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15051199
Introduction: Remdesivir (REM) and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) could alleviate severe COVID-19 in at-risk outpatients. However, data on their use in hospitalized patients, particularly in elderly or immunocompromised hosts, are lacking. Methods: All consecutive patients hospitalized with COVID-19 at our unit from 1 July 2021 to 15 March 2022 were retrospectively enrolled. The primary outcome was the progression to severe COVID-19 (P/F < 200). Descriptive statistics, a Cox univariate-multivariate model, and an inverse probability treatment-weighted (IPTW) analysis were performed. Results: Overall, 331 subjects were included; their median (q1-q3) age was 71 (51-80) years, and they were males in 52% of the cases. Of them, 78 (23%) developed severe COVID-19. All-cause in-hospital mortality was 14%; it was higher in those with disease progression (36% vs. 7%, p < 0.001). REM and mAbs resulted in a 7% (95%CI = 3-11%) and 14% (95%CI = 3-25%) reduction in the risk of severe COVID-19, respectively, after adjusting the analysis with the IPTW. In addition, by evaluating only immunocompromised hosts, the combination of REM and mAbs was associated with a significantly lower incidence of severe COVID-19 (aHR = 0.06, 95%CI = 0.02-0.77) when compared with monotherapy. Conclusions: REM and mAbs may reduce the risk of COVID-19 progression in hospitalized patients. Importantly, in immunocompromised hosts, the combination of mAbs and REM may be beneficial.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https: //www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v15051199/s1, Table S1 : Standardized differences of variables used to generate the IPTW model.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted with the formal approval of the ethics committee of the University Hospital Policlinico (Bari, Italy) (Study Code: 6357). The study was
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Activ-3/Tico Bamlanivimab, Group; Lundgren, Grund, Barkauskas, Holland et al., Responses to a Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody for Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 According to Baseline Antibody and Antigen Levels: A Randomized Controlled Trial, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/M21-3507
Antonelli, Penfold, Merino, Sudre, Molteni et al., Risk factors and disease profile of post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK users of the COVID Symptom Study app: A prospective, community-based, nested, case-control study, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00460-6
Austin, Stuart, Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies, Stat. Med, doi:10.1002/sim.6607
Balena, Bavaro, Fabrizio, Bottalico, Calamo et al., Tocilizumab and corticosteroids for COVID-19 treatment in elderly patients, J. Gerontol. Geriatr, doi:10.36150/2499-6564-283
Bansal, Goyal, Cusick, Lahan, Dhaliwal et al., Hydroxychloroquine: A comprehensive review and its controversial role in coronavirus disease 2019, Ann. Med
Bartoletti, Azap, Barac, Bussini, Ergonul et al., ESCMID COVID-19 living guidelines: Drug treatment and clinical management, Clin. Microbiol. Infect
Bavaro, Belati, Diella, Poli, Calamo et al., Prompt and Appropriate Antimicrobial Therapy Improves Outcomes of NDM-Producing and KPC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Bloodstream Infections in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Comparative Retrospective Case-Series, Antibiotics, doi:10.3390/antibiotics11111519
Bernal, Gomes Da Silva, Musungaie, Kovalchuk, Gonzalez et al., Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of COVID-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Bharadwaj, El-Kafrawy, Alandijany, Bajrai, Shah et al., Structure-Based Identification of Natural Products as SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Antagonist from Echinacea angustifolia Using Computational Approaches, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13020305
Brookhart, Schneeweiss, Rothman, Glynn, Avorn et al., Variable selection for propensity score models, Am. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/aje/kwj149
Chamlagain, Shah, Sharma Paudel, Dhital, Kandel, Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab in COVID-19: A Systematic Review, Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1155/2021/8903435
Cox, Peacock, Harvey, Hughes, Wright, COVID-19 Genomics UK (COG-UK) Consortium
Damanti, Ramirez, Bozzolo, Da Prat, Di Lucca et al., Frailty as a predictor of mortality in COVID-19 patients receiving CPAP for respiratory insufficiency, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-021-02070-z
Falcone, Suardi, Tiseo, Barbieri, Giusti et al., Early Use of Remdesivir and Risk of Disease Progression in Hospitalized Patients with Mild to Moderate COVID-19, Clin. Ther, doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2022.01.007
Falcone, Suardi, Tiseo, Galfo, Occhineri et al., Superinfections caused by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A multicentre observational study from Italy (CREVID Study), doi:10.1093/jacamr/dlac064
Falcone, Tiseo, Giordano, Leonildi, Menichini et al., Predictors of hospital-acquired bacterial and fungal superinfections in COVID-19: A prospective observational study, J. Antimicrob. Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa530
Ford, Simmons, Karmarkar, Yoke, Braimah et al., Successful treatment of prolonged, severe COVID-19 lower respiratory tract disease in a B-cell ALL patient with an extended course of remdesivir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac868
Gandhi, Klein, Robertson, Peña-Hernández, Lin et al., De novo emergence of a remdesivir resistance mutation during treatment of persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection in an immunocompromised patient: A case report, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29104-y
Gidari, Sabbatini, Schiaroli, Bastianelli, Pierucci et al., The Combination of Molnupiravir with Nirmatrelvir or GC376 Has a Synergic Role in the Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Replication In Vitro, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms10071475
Goletti, Cantini, Baricitinib Therapy in COVID-19 Pneumonia-An Unmet Need Fulfilled, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMe2034982
Gottlieb, Vaca, Paredes, Mera, Webb et al., Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe Covid-19 in Outpatients, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116846
Helleberg, Niemann, Moestrup, Kirk, Lebech et al., Persistent COVID-19 in an Immunocompromised Patient Temporarily Responsive to Two Courses of Remdesivir Therapy, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa446
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Bell et al., Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Hussain Alsayed, Saheb Sharif-Askari, Saheb Sharif-Askari, Hussain, Hamid et al., Early administration of remdesivir to COVID-19 patients associates with higher recovery rate and lower need for ICU admission: A retrospective cohort study, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258643
Komagamine, Yabuki, Yoshihara, Tanaka, The effect of casirivimab with imdevimab on disease progression in nonsevere COVID-19 patients in a single hospital in Japan, J. Gen. Fam. Med, doi:10.1002/jgf2.516
Martinez, Chen, Choi, Hwang, Navarathna et al., Extended Remdesivir Infusion for Persistent Coronavirus Disease, Infection. Open Forum Infect. Dis
Milam, Doan, Childress, Durham, Evaluation of Monoclonal Antibodies in Preventing Hospitalizations, Emergency Department Visits, and Mortality in High-Risk COVID-19 Patients, J. Pharm. Technol, doi:10.1177/87551225221080027
Montazersaheb, Hosseiniyan Khatibi, Hejazi, Tarhriz, Farjami et al., COVID-19 infection: An overview on cytokine storm and related interventions, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/s12985-022-01814-1
Ozer, Goksu, Conception, Ulker, Balderas et al., Effectiveness and safety of Ivermectin in COVID-19 patients: A prospective study at a safety-net hospital, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27469
Pagano, Salmanton-García, Marchesi, Busca, Corradini et al., COVID-19 infection in adult patients with hematological malignancies: A European Hematology Association Survey (EPICOVIDEHA), J. Hematol. Oncol, doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01177-0
Paranjape, Husain, Priestley, Koonjah, Watts et al., Early Use of Remdesivir in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Improves Clinical Outcomes: A Retrospective Observational Study, Infect. Dis. Clin. Pract. 2021, doi:10.1097/IPC.0000000000001023
Patel, Patel, Barvaliya, Saurabh, Bhalla et al., Efficacy and safety of lopinavir-ritonavir in COVID-19: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2021.03.015
Shafran, Shafran, Ben-Zvi, Sofer, Sheena et al., Secondary bacterial infection in COVID-19 patients is a stronger predictor for death compared to influenza patients, Sci. Rep
Takahashi, Wakita, Ishihara, Okazaki, Ito et al., Short-course remdesivir for healthcareassociated COVID-19: Case series from a non-acute care hospital, J. Infect. Chemother, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2022.08.025
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Sakai-Tagawa, Fujisaki et al., Efficacy of Antiviral Agents against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariant BA.2, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2201933
Wada, Nakamori, Maruyama, Shimazu, Saito et al., Novel treatment combining antiviral and neutralizing antibody-based therapies with monitoring of spike-specific antibody and viral load for immunocompromised patients with persistent COVID-19 infection, Exp. Hematol. Oncol, doi:10.1186/s40164-022-00307-9
Wang, Yang, Chinese herbal medicine: Fighting SARS-CoV-2 infection on all fronts, J. Ethnopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.113869
Wang, Yang, Song, Oral GS-441524 derivatives: Next-generation inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1015355
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9
Westblade, Simon, Satlin, Bacterial Coinfections in Coronavirus Disease, Trends Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2021.03.018
Willett, Thomson, Gupta, Peacock, SARS-CoV-2 variant evasion of monoclonal antibodies based on in vitro studies, Nature reviews. Microbiology, doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00809-7
Yang, Wang, Natural Products, Alone or in Combination with FDA-Approved Drugs, to Treat COVID-19 and Lung Cancer, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines9060689
Zazzara, Bellieni, Calvani, Coelho-Junior, Picca et al., Inflammaging at the Time of COVID-19, Clin. Geriatr. Med, doi:10.1016/j.cger.2022.03.003
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15051199",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4915"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v15051199",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Introduction: Remdesivir (REM) and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) could alleviate severe COVID-19 in at-risk outpatients. However, data on their use in hospitalized patients, particularly in elderly or immunocompromised hosts, are lacking. Methods: All consecutive patients hospitalized with COVID-19 at our unit from 1 July 2021 to 15 March 2022 were retrospectively enrolled. The primary outcome was the progression to severe COVID-19 (P/F < 200). Descriptive statistics, a Cox univariate–multivariate model, and an inverse probability treatment-weighted (IPTW) analysis were performed. Results: Overall, 331 subjects were included; their median (q1–q3) age was 71 (51–80) years, and they were males in 52% of the cases. Of them, 78 (23%) developed severe COVID-19. All-cause in-hospital mortality was 14%; it was higher in those with disease progression (36% vs. 7%, p < 0.001). REM and mAbs resulted in a 7% (95%CI = 3–11%) and 14% (95%CI = 3–25%) reduction in the risk of severe COVID-19, respectively, after adjusting the analysis with the IPTW. In addition, by evaluating only immunocompromised hosts, the combination of REM and mAbs was associated with a significantly lower incidence of severe COVID-19 (aHR = 0.06, 95%CI = 0.02–0.77) when compared with monotherapy. Conclusions: REM and mAbs may reduce the risk of COVID-19 progression in hospitalized patients. Importantly, in immunocompromised hosts, the combination of mAbs and REM may be beneficial.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"v15051199"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4833-7118",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bavaro",
"given": "Davide Fiore",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Diella",
"given": "Lucia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Belati",
"given": "Alessandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Metrangolo",
"given": "Giuliana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "De Santis",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Spada",
"given": "Vito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Camporeale",
"given": "Michele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Dargenio",
"given": "Angelo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7163-7437",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Brindicci",
"given": "Gaetano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Balena",
"given": "Flavia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Fiordelisi",
"given": "Deborah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Signorile",
"given": "Fabio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hematology Unit, IRCCS Istituto Tumori “Giovanni Paolo II”, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Loseto",
"given": "Giacomo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hematology Unit, IRCCS Istituto Tumori “Giovanni Paolo II”, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Pasciolla",
"given": "Crescenza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5707-0689",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hematology Unit, IRCCS Istituto Tumori “Giovanni Paolo II”, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Minoia",
"given": "Carla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unit of Hematology and Stem Cell Transplantation, AOUC Policlinic, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Attolico",
"given": "Immacolata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unit of Hematology and Stem Cell Transplantation, AOUC Policlinic, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Perrone",
"given": "Tommasina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Nephrology Dialysis and Transplantation Unit, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Simone",
"given": "Simona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Gastroenterology, Department of Emergency and Organ Transplantation, University of Bari, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Rendina",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital Pharmacy Department, University Hospital of Bari, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Giovine",
"given": "Nicoletta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3453-5647",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Di Gennaro",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3277-6594",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unit of Hematology and Stem Cell Transplantation, AOUC Policlinic, 70124 Bari, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area University of Bari and Unit of Hematology and Stem Cell Transplantation, AOUC Policlinico, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Musto",
"given": "Pellegrino",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hematology Unit, IRCCS Istituto Tumori “Giovanni Paolo II”, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Guarini",
"given": "Attilio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2026-1200",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Section of Gastroenterology, Department of Emergency and Organ Transplantation, University of Bari, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Di Leo",
"given": "Alfredo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4861-0911",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Nephrology Dialysis and Transplantation Unit, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gesualdo",
"given": "Loreto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital Pharmacy Department, University Hospital of Bari, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Dell’Aera",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, Department of Precision and Regenerative Medicine and Ionian Area, University of Bari, Piazza G. Cesare 11, 70124 Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Saracino",
"given": "Annalisa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viruses",
"container-title-short": "Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-19T13:23:10Z",
"timestamp": 1684502590000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-19T13:33:36Z",
"timestamp": 1684503216000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"PE00000007",
"INF-ACT"
],
"name": "Next Generation EU-MUR PNRR Extended Partnership initiative on Emerging Infectious Diseases"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-20T04:44:35Z",
"timestamp": 1684557875721
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1684454400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/15/5/1199/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1199",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group, Horby, P., Lim, W.S., Emberson, J.R., Mafham, M., Bell, J.L., Linsell, L., Staplin, N., Brightling, C., and Ustianowski, A. (2021). Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med., 384, 693–704."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2034982",
"article-title": "Baricitinib Therapy in COVID-19 Pneumonia—An Unmet Need Fulfilled",
"author": "Goletti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "867",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jep.2021.113869",
"article-title": "Chinese herbal medicine: Fighting SARS-CoV-2 infection on all fronts",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113869",
"journal-title": "J. Ethnopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "270",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13020305",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "Bharadwaj, S., El-Kafrawy, S.A., Alandijany, T.A., Bajrai, L.H., Shah, A.A., Dubey, A., Sahoo, A.K., Yadava, U., Kamal, M.A., and Azhar, E.I. (2021). Structure-Based Identification of Natural Products as SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Antagonist from Echinacea angustifolia Using Computational Approaches. Viruses, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.02.11.21249258",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group (2021). Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): A randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet, 397, 1637–1645."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/8903435",
"article-title": "Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab in COVID-19: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Chamlagain",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8903435",
"journal-title": "Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.36150/2499-6564-283",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab and corticosteroids for COVID-19 treatment in elderly patients",
"author": "Balena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "197",
"journal-title": "J. Gerontol. Geriatr.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2021.03.015",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of lopinavir-ritonavir in COVID-19: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Patel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "740",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public Health",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07853890.2020.1839959",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine: A comprehensive review and its controversial role in coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Bansal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117",
"journal-title": "Ann. Med.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27469",
"article-title": "Effectiveness and safety of Ivermectin in COVID-19 patients: A prospective study at a safety-net hospital",
"author": "Ozer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1473",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/87551225221080027",
"article-title": "Evaluation of Monoclonal Antibodies in Preventing Hospitalizations, Emergency Department Visits, and Mortality in High-Risk COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Milam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "169",
"journal-title": "J. Pharm. Technol.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jgf2.516",
"article-title": "The effect of casirivimab with imdevimab on disease progression in nonsevere COVID-19 patients in a single hospital in Japan",
"author": "Komagamine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "158",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Fam. Med.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref_13",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Admninstration (2023, January 11). Facts Sheet for Healthcare Providers: Emergency Use Authorization for Paxlovid, Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1569",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"article-title": "Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe Covid-19 in Outpatients",
"author": "Gottlieb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "305",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of COVID-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients",
"author": "Musungaie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.11.007",
"article-title": "ESCMID COVID-19 living guidelines: Drug treatment and clinical management",
"author": "Bartoletti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Infect.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "(2022). Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines [Internet], National Institutes of Health (US). 21 April 2021–30 September."
},
{
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "(2023, January 12). Veklury: EPAR–Medicine Overview, EMA 666777/2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/overview/veklury-epar-medicine-overview_en.pdf."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40164-022-00307-9",
"article-title": "Novel treatment combining antiviral and neutralizing antibody-based therapies with monitoring of spike-specific antibody and viral load for immunocompromised patients with persistent COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Wada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "Exp. Hematol. Oncol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa446",
"article-title": "Persistent COVID-19 in an Immunocompromised Patient Temporarily Responsive to Two Courses of Remdesivir Therapy",
"author": "Helleberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1103",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-29104-y",
"article-title": "De novo emergence of a remdesivir resistance mutation during treatment of persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection in an immunocompromised patient: A case report",
"author": "Gandhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1547",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.1015355",
"article-title": "Oral GS-441524 derivatives: Next-generation inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1015355",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202206.0272.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Gidari, A., Sabbatini, S., Schiaroli, E., Bastianelli, S., Pierucci, S., Busti, C., Comez, L., Libera, V., Macchiarulo, A., and Paciaroni, A. (2022). The Combination of Molnupiravir with Nirmatrelvir or GC376 Has a Synergic Role in the Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Replication In Vitro. Microorganisms, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwj149",
"article-title": "Variable selection for propensity score models",
"author": "Brookhart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1149",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Epidemiol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.6607",
"article-title": "Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3661",
"journal-title": "Stat. Med.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2023, April 21). COVID Data Tracker, Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cger.2022.03.003",
"article-title": "Inflammaging at the Time of COVID-19",
"author": "Zazzara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "473",
"journal-title": "Clin. Geriatr. Med.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-021-02070-z",
"article-title": "Frailty as a predictor of mortality in COVID-19 patients receiving CPAP for respiratory insufficiency",
"author": "Damanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "945",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13045-021-01177-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19 infection in adult patients with hematological malignancies: A European Hematology Association Survey (EPICOVIDEHA)",
"author": "Pagano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "J. Hematol. Oncol.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac382",
"article-title": "Extended Remdesivir Infusion for Persistent Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection",
"author": "Martinez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofac382",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac868",
"article-title": "Successful treatment of prolonged, severe COVID-19 lower respiratory tract disease in a B-cell ALL patient with an extended course of remdesivir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir",
"author": "Ford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "926",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2201933",
"article-title": "Efficacy of Antiviral Agents against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariant BA.2",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1475",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variant evasion of monoclonal antibodies based on in vitro studies. Nature reviews",
"author": "Cox",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "Microbiology",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2022.01.007",
"article-title": "Early Use of Remdesivir and Risk of Disease Progression in Hospitalized Patients with Mild to Moderate COVID-19",
"author": "Falcone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "364",
"journal-title": "Clin. Ther.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0258643",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_36",
"unstructured": "Hussain Alsayed, H.A., Saheb Sharif-Askari, F., Saheb Sharif-Askari, N., Hussain, A.A.S., Hamid, Q., and Halwani, R. (2021). Early administration of remdesivir to COVID-19 patients associates with higher recovery rate and lower need for ICU admission: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/IPC.0000000000001023",
"article-title": "Early Use of Remdesivir in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Improves Clinical Outcomes: A Retrospective Observational Study",
"author": "Paranjape",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e282",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.08.025",
"article-title": "Short-course remdesivir for healthcare-associated COVID-19: Case series from a non-acute care hospital",
"author": "Takahashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Chemother.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "ref_39",
"unstructured": "ACTIV-3–Therapeutics for Inpatients with COVID-19 (TICO) Study Group (2022). Tixagevimab-cilgavimab for treatment of patients hospitalised with COVID-19: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med., 10, 972–984."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9060689",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Yang, L., and Wang, Z. (2021). Natural Products, Alone or in Combination with FDA-Approved Drugs, to Treat COVID-19 and Lung Cancer. Biomedicines, 9."
},
{
"key": "ref_41",
"unstructured": "ACTIV-3/TICO Bamlanivimab Study Group, Lundgren, J.D., Grund, B., Barkauskas, C.E., Holland, T.L., Gottlieb, R.L., Sandkovsky, U., Brown, S.M., Knowlton, K.U., and Self, W.H. (2022). Responses to a Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody for Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 According to Baseline Antibody and Antigen Levels: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med., 175, 234–243."
},
{
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "ACTIV-3/Therapeutics for Inpatients with COVID-19 (TICO) Study Group (2022). Efficacy and safety of two neutralising monoclonal antibody therapies, sotrovimab and BRII-196 plus BRII-198, for adults hospitalised with COVID-19 (TICO): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect. Dis., 22, 622–635."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-022-01814-1",
"article-title": "COVID-19 infection: An overview on cytokine storm and related interventions",
"author": "Montazersaheb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "92",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00460-6",
"article-title": "Risk factors and disease profile of post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK users of the COVID Symptom Study app: A prospective, community-based, nested, case-control study",
"author": "Antonelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-92220-0",
"article-title": "Secondary bacterial infection in COVID-19 patients is a stronger predictor for death compared to influenza patients",
"author": "Shafran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12703",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antibiotics11111519",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "Bavaro, D.F., Belati, A., Diella, L., Poli, M.A., Calamo, A., De Candia, G., Altamura, M., Spadavecchia, F.A., Brindicci, G., and De Gennaro, N. (2022). Prompt and Appropriate Antimicrobial Therapy Improves Outcomes of NDM-Producing and KPC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Bloodstream Infections in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Comparative Retrospective Case-Series. Antibiotics, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jacamr/dlac064",
"article-title": "Superinfections caused by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A multicentre observational study from Italy (CREVID Study)",
"author": "Falcone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "dlac064",
"journal-title": "JAC-Antimicrob. Resist.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkaa530",
"article-title": "Predictors of hospital-acquired bacterial and fungal superinfections in COVID-19: A prospective observational study",
"author": "Falcone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1078",
"journal-title": "J. Antimicrob. Chemother.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2021.03.018",
"article-title": "Bacterial Coinfections in Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"author": "Westblade",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "930",
"journal-title": "Trends Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref_50",
"unstructured": "(2023, February 15). Ministry of Health, COVID-19 Portal. Available online: https://www.covid19dataportal.it/highlights/highlight47/."
}
],
"reference-count": 50,
"references-count": 50,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/15/5/1199"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Infectious Diseases"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of Remdesivir and Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies in Monotherapy or Combination Therapy in Reducing the Risk of Disease Progression in Elderly or Immunocompromised Hosts Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Single Center Retrospective Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "15"
}