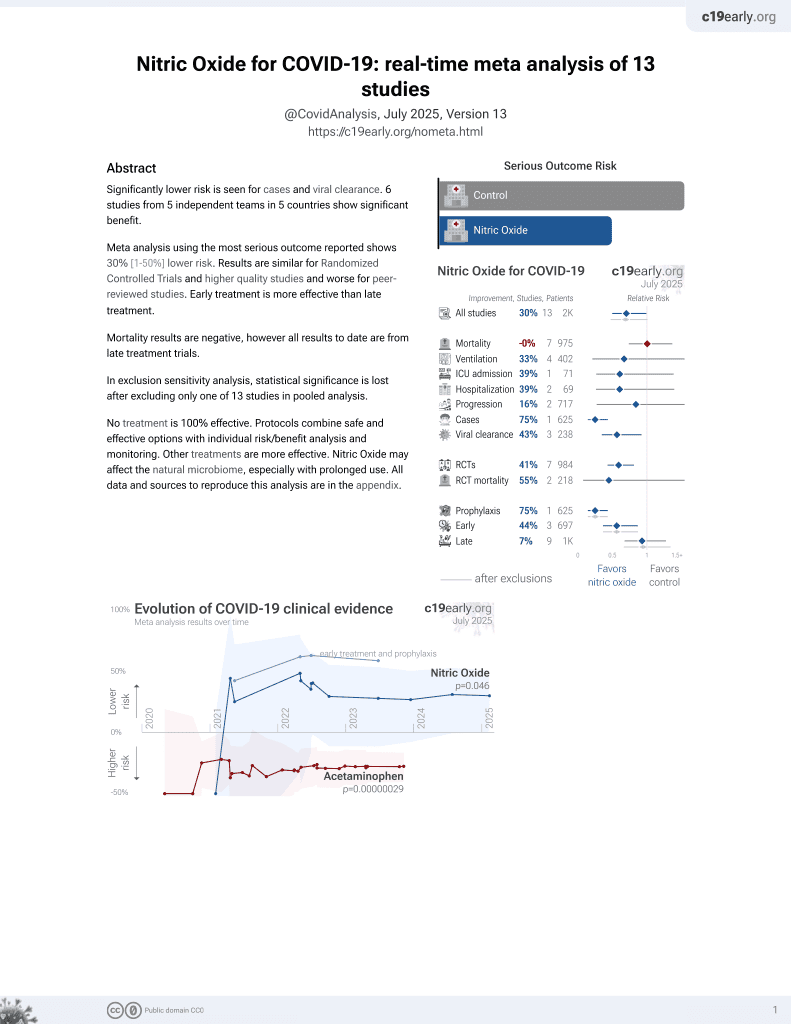
Nitric Oxide in the Treatment of COVID‐19: Nasal Sprays, Inhalants and Nanoparticles
et al., Biochemistry Research International, doi:10.1155/bri/8846903, Oct 2025
43rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2022, now with p = 0.012 from 12 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
Lower risk for cases and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
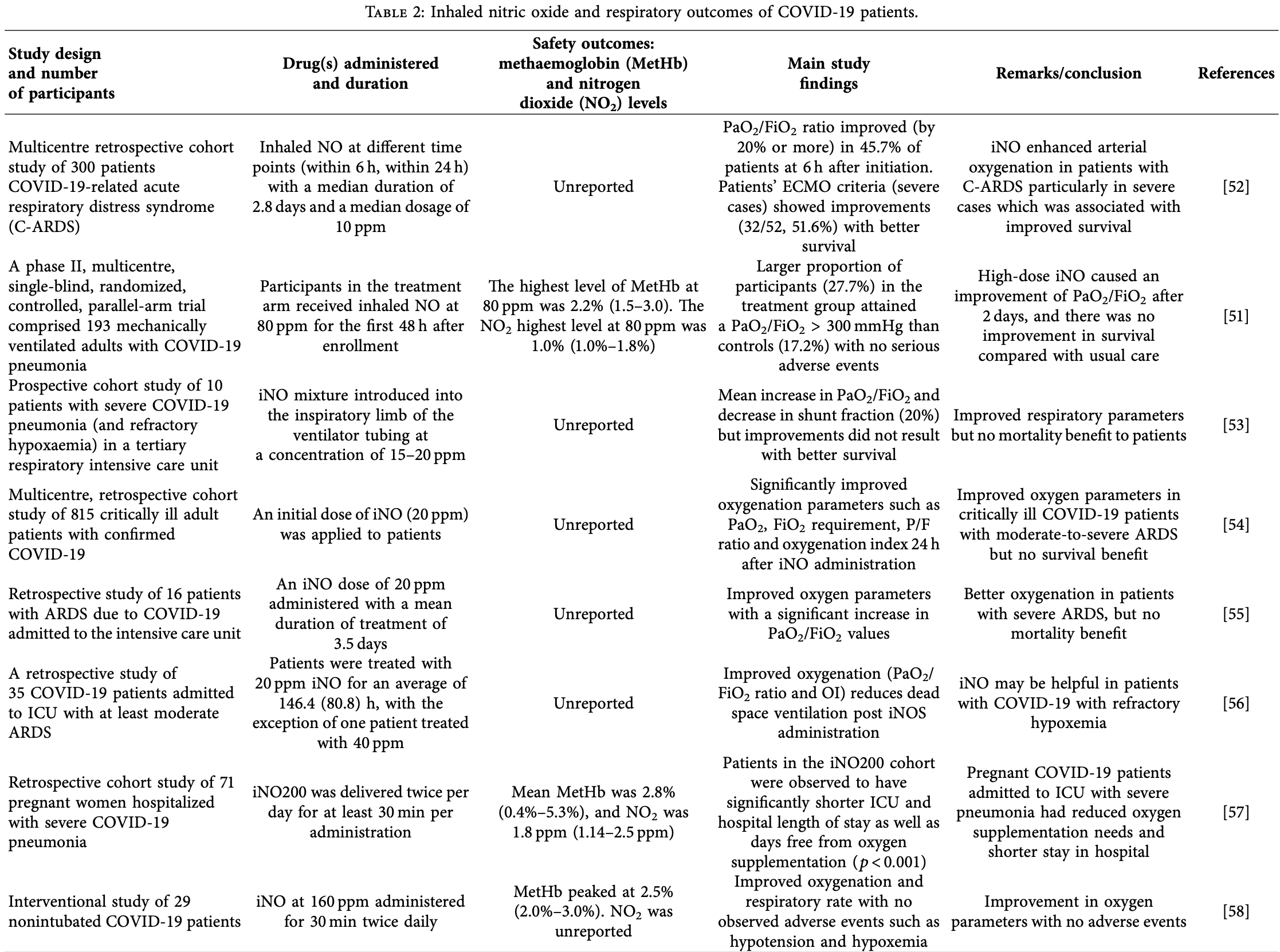
Review of nitric oxide (NO) as a therapeutic for COVID-19, focusing on its administration as a nasal spray, inhalant, or via nanoparticles. Clinical trials on nitric oxide nasal spray (NONS) have shown it to be an effective and safe therapy that significantly reduces SARS-CoV-2 viral load. Authors note that inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) has also been shown to improve oxygenation and respiratory outcomes in COVID-19 patients with varying severity, but with inconsistent survival benefits for severe patients. While iNO carries risks like methaemoglobin and nitrogen dioxide formation, authors found studies showing these levels remained within safe limits. The rationale for NO treatment is based on findings that COVID-19 patients often have decreased NO bioavailability, and NO is believed to inhibit the virus by S-nitrosylation of the host's ACE2 receptor or viral proteases.
1.
Wright et al., Nitric Oxide in the Treatment of COVID‐19: Nasal Sprays, Inhalants and Nanoparticles, Biochemistry Research International, doi:10.1155/bri/8846903.
2.
Zhang et al., Saying No to SARS-CoV-2: the potential of nitric oxide in the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia, Medical Gas Research, doi:10.4103/2045-9912.385414.
3.
Zhao et al., Inhaled nitric oxide: can it serve as a savior for COVID-19 and related respiratory and cardiovascular diseases?, Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1277552.
4.
Yamasaki et al., Pleiotropic Functions of Nitric Oxide Produced by Ascorbate for the Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19: A Revaluation of Pauling’s Vitamin C Therapy, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11020397.
Wright et al., 13 Oct 2025, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: sophia.bryan04@uwimona.edu.jm.
Nitric Oxide in the Treatment of COVID‐19: Nasal Sprays, Inhalants and Nanoparticles
Biochemistry Research International, doi:10.1155/bri/8846903
Although the World Health Organization has declared that the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is not a public health emergency of international concern anymore, it has negatively impacted the world, and efective treatment for this pandemic remains a major priority. Vaccine efectiveness has been a matter of concern given the evolution of variants and subvariants of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Tus, continued protection against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants is still necessary and could work alone or in parallel with vaccinations to treat COVID-19 in the future. Further, fndings from in vitro and in vivo studies have noted the efectiveness of high dosages of nitric oxide (NO) as an antimicrobial agent against respiratory pathogens such as bacteria, viruses and fungi. NO has been previously utilized in the management of SARS-CoV and has shown a similar antiviral efect with SARS-CoV-2 in vivo and in vitro. Efective therapy with NO can be used to target several stages of COVID-19 infection to prevent transmission and progression of the disease. Te unique properties of NO allow this simple, gaseous molecule to be administered in various forms. NO can be used as an inhalant, in the form of NO donor drugs such as Snitrosothiols and more recently as NO-releasing nanoparticles (NO-nps). Tis review summarizes the bioavailability of NO in COVID-19 patients and highlights in vivo and in vitro studies as well as clinical trials with NO administered as a nasal spray, inhalant, or via nanodelivery for therapeutic applications for COVID-19 and other respiratory infections in the future.
Conflicts of Interest Te authors declare no conficts of interest.
References
Abman, Fox, Malik, Real-World Use of Inhaled Nitric Oxide Terapy in Patients With COVID-19 and Mild-to-Moderate Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Drugs in Context, doi:10.7573/dic.2022-1-4
Adebayo, Varzideh, Wilson, L-arginine and COVID-19: An Update, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13113951
Afzal, Altamimi, Nadeem, Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery: From History to Terapeutic Applications, Nanomaterials, doi:10.3390/nano12244494
Akaberi, Krambrich, Ling, Mitigation of the Replication of SARS-CoV-2 by Nitric Oxide in Vitro, Redox Biology, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101734
Al Sulaiman, Korayem, Altebainawi, Evaluation of Inhaled Nitric Oxide (Ino) Treatment for Moderate-to-Severe ARDS in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: a Multicenter Cohort Study, Critical Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-022-04158-y
Almanza-Reyes, Moreno, Plascencia-López, Evaluation of Silver Nanoparticles for the Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Health Workers: In Vitro and In Vivo, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0256401
Alqahtani, Aldhahir, Al Ghamdi, Inhaled Nitric Oxide for Clinical Management of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph191912803
Alvarez, Berra, Gladwin, Home Nitric Oxide Terapy for COVID-19, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.1164/rccm.202005-1906ED
Antosova, Plevkova, Strapkova, Buday, Nitric Oxide-Important Messenger in Human Body, Open Journal of Molecular and Integrative Physiology, doi:10.4236/ojmip.2012.23014
Bicakcioglu, Kalkan, Duzenci, Yalcinsoy, Dogan et al., Inhaled Nitric Oxide as Rescue Terapy in Severe ARDS Cases due to COVID-19 Pneumonia: a Single Center Experience, European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, doi:10.26355/eurrev_202307_33002
Birben, Sahiner, Sackesen, Erzurum, Kalayci, Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense, World Allergy Organization Journal, doi:10.1097/WOX.0b013e3182439613
Chen, Pittman, Popel, Nitric Oxide in the Vasculature: where Does it Come From and Where Does it Go? A Quantitative Perspective, Antioxidants and Redox Signaling, doi:10.1089/ars.2007.1959
Deppisch, Herrmann, Graepler-Mainka, Gaseous Nitric Oxide to Treat Antibiotic Resistant Bacterial and Fungal Lung Infections in Patients With Cystic Fibrosis: A Phase I Clinical Study, Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-016-0879-x
Derakhshani, Hemmat, Asadzadeh, Arginase 1 (Arg1) as an Up-Regulated Gene in COVID-19 Patients: a Promising Marker in COVID-19 Immunopathy, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm10051051
Di Fenza, Shetty, Gianni, High-Dose Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure Due to COVID-19: A Multicenter Phase II Trial, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.1164/rccm.202304-0637OC
Dominic, Ahmad, Bhandari, Decreased Availability of Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfde is a Hallmark of COVID-19, Redox Biology, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2021.101982
Dong, Shamsuddin, Campbell, Teodoratou, Current COVID-19 Treatments: Rapid Review of the Literature, Journal of Global Health, doi:10.7189/jogh.11.10003
Durante, Glutamine Defciency Promotes Immune and Endothelial Cell Dysfunction in COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms24087593
Durante, Targeting Arginine in Covid-19-Induced Immunopathology and Vasculopathy, Metabolites, doi:10.3390/metabo12030240
Fiorentino, Coppola, Izzo, Efects of Adding Larginine Orally to Standard Terapy in Patients with COVID-19: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Trial. Results of the First Interim Analysis, eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101125
Garfeld, Mcfadyen, Briar, Potential for Personalised Application of Inhaled Nitric Oxide in COVID-19 Pneumonia, British Journal of Anaesthesia, doi:10.1016/j.bja.2020.11.006
Gianni, Di Fenza, Araujo Morais, High-Dose Nitric Oxide from Pressurized Cylinders and Nitric Oxide Produced by an Electric Generator from Air, Respiratory Care, doi:10.4187/respcare.09308
Gomes, Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Brazilian Journal of Implantology and Health Sciences
Gorguner, Akgun, Acute Inhalation Injury, Te Eurasian Journal of Medicine, doi:10.5152/eajm.2010.09
Hasöksüz, Kiliç, Saraç, Coronaviruses and SARS-COV-2, Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences, doi:10.3906/sag-2004-127
Ignarro, Buga, Wood, Byrns, Chaudhuri, Endothelium-Derived Relaxing Factor Produced and Released from Artery and Vein is Nitric Oxide, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.84.24.9265
Ignarro, Inhaled NO and COVID-19, British Journal of Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bph.15085
Kamenshchikov, Berra, Carroll, Terapeutic Efects of Inhaled Nitric Oxide Terapy in COVID-19 Patients, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10020369
Kasehagen, Byers, Taylor, COVID-19-associated Deaths After SARS-CoV-2 Infection During Pregnancy-Mississippi, March 1, 2020, MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7047e2
Keyaerts, Vijgen, Chen, Maes, Hedenstierna et al., Inhibition of SARS-Coronavirus Infection in Vitro by S-nitroso-N-Acetylpenicillamine, a Nitric Oxide Donor Compound, International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2004.04.012
Khan, Saeed, Khan, Nanoparticles: Properties, Applications and Toxicities, Arabian Journal of Chemistry, doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011
Krasuski, Warner, Wang, Harrison, Tapson et al., Inhaled Nitric Oxide Selectively Dilates Pulmonary Vasculature in Adult Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension, Irrespective of Etiology, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(00)00994-3
Ludwig, Zarbock, Coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2: A Brief Overview, Anesthesia & Analgesia, doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000004845
Luiking, Engelen, Deutz, Regulation of Nitric Oxide Production in Health and Disease, Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e328332f99d
Ma, Zhang, Chen, Delivery of Nitric Oxide in the Cardiovascular System: Implications for Clinical Diagnosis and Terapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms222212166
Mekontso Dessap, Papazian, Schaller, Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Caused by COVID-19: Treatment Modalities, Clinical Response, and Outcomes, Annals of Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s13613-023-01150-9
Merad, Blish, Sallusto, Iwasaki, Te Immunology and Immunopathology of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abm8108
Meulmeester, Luo, Martens, Mills, Van Heemst et al., Antioxidant Supplementation in Oxidative Stress-Related Diseases: What Have we Learned From Studies on alpha-tocopherol?, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11122322
Michaelsen, Ribeiro, Brambate, A Novel Pre-Clinical Strategy to Deliver Antimicrobial Doses of Inhaled Nitric Oxide, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258368
Mitchell, Berlinski, Canisius, Urgent Appeal From International Society for Aerosols in Medicine (ISAM) During COVID-19: Clinical Decision Makers and Governmental Agencies Should Consider the Inhaled Route of Administration: A Statement From the ISAM Regulatory and Standardization Issues Networking Group, Journal of Aerosol Medicine and Pulmonary Drug Delivery, doi:10.1089/jamp.2020.1622
Montiel, Lobysheva, Gérard, Oxidative Stress-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction and Decreased Vascular Nitric Oxide in COVID-19 Patients, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103893
Ntyonga-Pono, COVID-19 Infection and Oxidative Stress: an Under-Explored Approach for Prevention and Treatment?, Te Pan African medical journal, doi:10.11604/pamj.2020.35.2.22877
Oh, Nakamura, Beutler, Targeted Protein S-Nitrosylation of ACE2 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Nature Chemical Biology, doi:10.1038/s41589-022-01149-6
Ozdemir, Yazici, Could the Decrease in the Endothelial Nitric Oxide (NO) Production and NO Bioavailability be the Crucial Cause of COVID-19 Related Deaths?, Medical Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109970
Petit, Fine, Vásquez, Gamero, Slaughter et al., Te Pathophysiology of Nitrogen Dioxide During Inhaled Nitric Oxide Terapy, ASAIO Journal, doi:10.1097/MAT.0000000000000425
Pieretti, Rubilar, Weller, Tortella, Seabra, Nitric Oxide (NO) and Nanoparticles-Potential Small Tools for the War Against COVID-19 and Other Human Coronavirus Infections, Virus Research, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198202
Rabaan, Al-Ahmed, Haque, SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-COV: A Comparative Overview, Infezioni in Medicina
Rajendran, Chathambath, Al-Sehemi, Critical Role of Nitric Oxide in Impeding COVID-19 Transmission and Prevention: a Promising Possibility, Environmental Science and Pollution Research, doi:10.1007/s11356-022-19148-4
Rana, Polymer-Based nano-therapies to Combat COVID-19 Related Respiratory Injury: Progress, Prospects, and Challenges, Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition, doi:10.1080/09205063.2021.1909412
Raut, Maheshwari, Inhaled Nitric Oxide, Methemoglobinemia, and Route of Delivery, Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, doi:10.4103/sja.SJA_82_17
Rees, Rostad, Mantus, Altered Amino Acid Profle in Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, doi:10.1073/pnas.2101708118
Rehman, Methemoglobinemia, Western Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1136/ewjm.175.3.193
Roberts, Polaner, Lang, Zapol, Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn, Lancet, doi:10.1016/0140-6736(92)92686-a
Rousseaud, Prot, Loriere, Katz, Ramirez-Gil et al., Gaseous Nitric Oxide Failed to Inhibit the Replication Cycle of SARS-CoV-2 in Vitro, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2023.01.004
Safaee Fakhr, Wiegand, Pinciroli, High Concentrations of Nitric Oxide Inhalation Terapy in Pregnant Patients With Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Obstetrics & Gynecology, doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004128
Schairer, Martinez, Blecher, Nitric Oxide Nanoparticles: Pre-Clinical Utility as a Terapeutic for Intramuscular Abscesses, Virulence, doi:10.4161/viru.3.1.18816
Shurbaji, El-Sherbiny, Alser, Nitric Oxide Releasing Hydrogel Nanoparticles Decreases Epithelial Cell Injuries Associated With Airway Reopening, Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, doi:10.3389/fbioe.2020.579788
Six, Guillaume, Jacob, Te Endothelium and COVID-19: An Increasingly Clear Link Brief Title: Endotheliopathy in COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23116196
Sodano, Cavanagh, Pearce, Enhancing Doxorubicin Anticancer Activity With a Novel Polymeric Platform Photoreleasing Nitric Oxide, Biomaterials Science, doi:10.1039/c9bm01644a
Sorbo, Michaelsen, Ali, Wang, Ribeiro et al., High Doses of Inhaled Nitric Oxide as an Innovative Antimicrobial Strategy for Lung Infections, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10071525
Tandon, Wu, Moore, SARS-CoV-2 Accelerated Clearance Using a Novel Nitric Oxide Nasal Spray (NONS) Treatment: A Randomized Trial, Te Lancet Regional Health-Southeast Asia, doi:10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036
Tang, Li, Wang, Huang, Fan et al., In Situ Noninvasive Observation of Nitric Oxide Fluctuation in SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Vivo by Organic Near-Infrared-II Fluorescent Molecular Nanoprobes, ACS Nano, doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c05410
Taylor, Christian, Patel, Churchwell, Wiley Online Library for rules of use; OA articles are governed by the applicable Creative Commons License Terapy, Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.1097/00130478-200101000-00019
Tosato, Calvani, Picca, Efects of L-arginine plus Vitamin C Supplementation on Physical Performance, Endothelial Function, and Persistent Fatigue in Adults With Long COVID: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14234984
Valsecchi, Winterton, Fakhr, High-Dose Inhaled Nitric Oxide for the Treatment of Spontaneously Breathing Pregnant Patients with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia, Obstetrics & Gynecology, doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004847
Van Zyl, Allwood, Koegelenberg, Lalla, Retief, Te Efect of Inhaled Nitric Oxide on Shunt Fraction in Mechanically Ventilated Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia, African Journal of Toracic and Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.7196/AJTCCM.2023.v29i2.279
Vassiliou, Zacharis, Keskinidou, Soluble Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) is Upregulated and Soluble Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) is Downregulated in COVID-19-induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph14070695
Wang, Jin, Yang, Huang, Advanced Nitric Oxide Generating Nanomedicine for Terapeutic Applications, ACS Nano, doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c02303
Wiegand, Safaee Fakhr, Carroll, Zapol, Kacmarek et al., Rescue Treatment With High-Dose Gaseous Nitric Oxide in Spontaneously Breathing Patients With Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019, Critical Care Explorations, doi:10.1097/CCE.0000000000000277
Wieler, Vittos, Mukherjee, Sarkar, Reduction in the COVID-19 Pneumonia Case Fatality Rate by Silver Nanoparticles: a Randomized Case Study, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14419
Williams, Muller, Govender, Control of Systemic Infammation Trough Early Nitric Oxide Supplementation With Nitric Oxide Releasing Nanoparticles, Free Radical Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.09.025
Winchester, John, Jabbar, John, Clinical Effcacy of Nitric Oxide Nasal Spray (NONS) for the Treatment of Mild COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.05.009
Yamasaki, Imai, Tanaka, Otaki, Pleiotropic Functions of Nitric Oxide Produced by Ascorbate for the Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19: A Revaluation of Pauling's Vitamin C Terapy, Microorganisms
Yu, Ichinose, Bloch, Zapol, Inhaled Nitric Oxide, British Journal of Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bph.14512
Zambrano, Ellington, Strid, Update: Characteristics of Symptomatic Women of Reproductive Age with laboratory-confrmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Pregnancy Status-United States, January 22-October 3, 2020, MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6944e3
Åkerström, Gunalan, Keng, Tan, Mirazimi, Dual Efect of Nitric Oxide on SARS-CoV Replication: Viral RNA Production and Palmitoylation of the S Protein are Afected, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007
Åkerström, Mousavi-Jazi, Klingström, Leijon, Lundkvist et al., Nitric Oxide Inhibits the Replication Cycle of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, Journal of Virology, doi:10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1155/bri/8846903",
"ISSN": [
"2090-2247",
"2090-2255"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/bri/8846903",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Although the World Health Organization has declared that the coronavirus disease (COVID‐19) is not a public health emergency of international concern anymore, it has negatively impacted the world, and effective treatment for this pandemic remains a major priority. Vaccine effectiveness has been a matter of concern given the evolution of variants and subvariants of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2). Thus, continued protection against SARS‐CoV‐2 and its variants is still necessary and could work alone or in parallel with vaccinations to treat COVID‐19 in the future. Further, findings from in vitro and in vivo studies have noted the effectiveness of high dosages of nitric oxide (NO) as an antimicrobial agent against respiratory pathogens such as bacteria, viruses and fungi. NO has been previously utilized in the management of SARS‐CoV and has shown a similar antiviral effect with SARS‐CoV‐2 in vivo and in vitro. Effective therapy with NO can be used to target several stages of COVID‐19 infection to prevent transmission and progression of the disease. The unique properties of NO allow this simple, gaseous molecule to be administered in various forms. NO can be used as an inhalant, in the form of NO donor drugs such as S‐nitrosothiols and more recently as NO‐releasing nanoparticles (NO‐nps). This review summarizes the bioavailability of NO in COVID‐19 patients and highlights in vivo and in vitro studies as well as clinical trials with NO administered as a nasal spray, inhalant, or via nanodelivery for therapeutic applications for COVID‐19 and other respiratory infections in the future.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1155/bri/8846903"
],
"article-number": "8846903",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-05-28"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2025-08-11"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-10-13"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6392-4783",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wright",
"given": "Amarley",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8018-7722",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "McGrowder",
"given": "Donovan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4266-7781",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bryan",
"given": "Sophia",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Biochemistry Research International",
"container-title-short": "Biochemistry Research International",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-13T12:34:19Z",
"timestamp": 1760358859000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-13T12:34:32Z",
"timestamp": 1760358872000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khatra",
"given": "Harleen",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-13T13:12:34Z",
"timestamp": 1760361154213,
"version": "build-2065373602"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 285,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1760313600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1155/bri/8846903",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1155",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
13
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Gomes C.",
"journal-title": "Brazilian Journal of Implantology and Health Sciences",
"key": "e_1_2_13_1_2",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abm8108",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_2_2"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-COV: A Comparative Overview",
"author": "Rabaan A. A.",
"first-page": "174",
"journal-title": "Infezioni in Medicina, Le",
"key": "e_1_2_13_3_2",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3906/sag-2004-127",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11356-022-19148-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_5_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1213/ANE.0000000000004845",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_6_2"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "e_1_2_13_7_2",
"volume-title": "Covid-19 Cases",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "e_1_2_13_8_2",
"volume-title": "Covid-19 Deaths",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.84.24.9265",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCO.0b013e328332f99d",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2007.1959",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4236/ojmip.2012.23014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10071525",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-016-0879-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_14_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109970",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2021.101982",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103893",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23116196",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/WOX.0b013e3182439613",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_19_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11122322",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.11604/pamj.2020.35.2.22877",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms11020397",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph14070695",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_23_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/metabo12030240",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_24_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24087593",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10051051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_26_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2101708118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_27_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13113951",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101125",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14234984",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsnano.3c05410",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0258368",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_32_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2004.04.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_33_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101734",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2023.01.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_37_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c9bm01644a",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_38_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41589-022-01149-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_39_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsnano.3c02303",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7189/jogh.11.10003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jamp.2020.1622",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.05.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_43_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_44_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0735-1097(00)00994-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_45_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0140-6736(92)92686-a",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_46_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph191912803",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_47_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15085",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_48_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.14512",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_49_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10020369",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_50_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202304-0637OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_51_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-023-01150-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_52_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26355/eurrev_202307_33002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_53_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-022-04158-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_54_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7196/AJTCCM.2023.v29i2.279",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_55_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bja.2020.11.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_56_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/AOG.0000000000004847",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_57_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/AOG.0000000000004128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_58_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7573/dic.2022-1-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_59_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6944e3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_60_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7047e2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_61_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202005-1906ED",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_62_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms222212166",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_63_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/sja.SJA_82_17",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_64_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00130478-200101000-00019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_65_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/ewjm.175.3.193",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_66_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MAT.0000000000000425",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_67_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5152/eajm.2010.09",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_68_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_13_69_2",
"unstructured": "Occupational Safety and Health Administration Nitric Oxide 2025 https://www.osha.gov/chemicaldata/21."
},
{
"article-title": "Nitrogen Dioxide-IDLH",
"author": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention",
"journal-title": "The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health",
"key": "e_1_2_13_70_2",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4187/respcare.09308",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_71_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCE.0000000000000277",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_72_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_73_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nano12244494",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_74_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/viru.3.1.18816",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_75_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198202",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_76_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.09.025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_77_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fbioe.2020.579788",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_78_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14419",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_79_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0256401",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_80_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09205063.2021.1909412",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_13_81_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 81,
"references-count": 81,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/bri/8846903"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nitric Oxide in the Treatment of COVID‐19: Nasal Sprays, Inhalants and Nanoparticles",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "2025"
}