SARS-CoV-2 accelerated clearance using a novel nitric oxide nasal spray (NONS) treatment: A randomized trial
et al., The Lancet Regional Health - Southeast Asia, doi:10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036, CTRI/2021/08, Jun 2022
43rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2022, now with p = 0.012 from 12 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
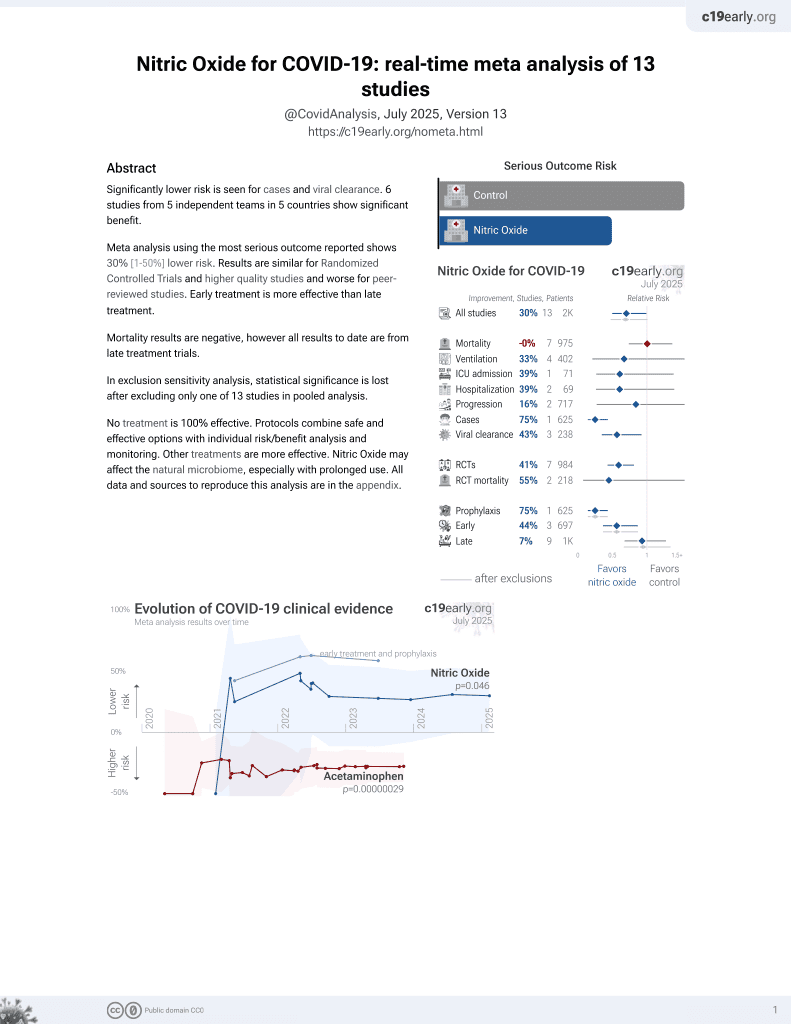
Lower risk for cases and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT with 153 patients treated with a nitric oxide nasal spray, and 153 placebo patients, showing faster viral clearance with treatment. NO generated by a nasal spray (NONS) self-administered six times daily as two sprays per nostril (0.45mL of solution/dose) for seven days.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects.
|
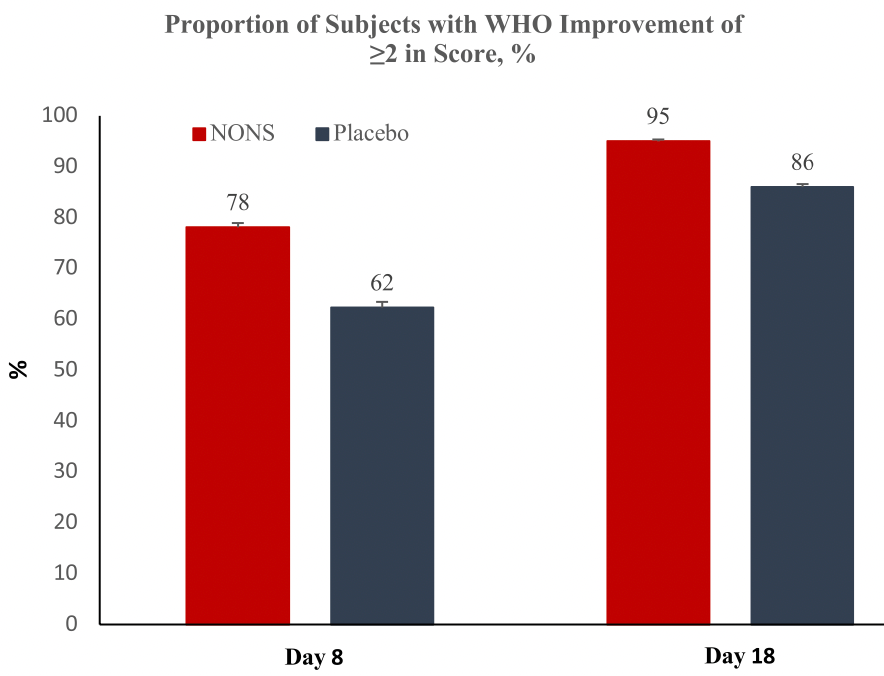
risk of no improvement, 67.7% lower, RR 0.32, p = 0.08, treatment 3 of 64 (4.7%), control 10 of 69 (14.5%), NNT 10, mITT high risk, day 18.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 66.8% lower, RR 0.33, p = 0.04, treatment 4 of 64 (6.2%), control 13 of 69 (18.8%), NNT 7.9, mITT high risk, day 16.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 41.9% lower, RR 0.58, p = 0.06, treatment 14 of 64 (21.9%), control 26 of 69 (37.7%), NNT 6.3, mITT high risk, day 8.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 22.3% lower, RR 0.78, p = 0.63, treatment 8 of 105 (7.6%), control 10 of 102 (9.8%), NNT 46, day 18, modified intention-to-treat.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 17.8% lower, RR 0.82, p = 0.67, treatment 11 of 105 (10.5%), control 13 of 102 (12.7%), NNT 44, day 16, modified intention-to-treat.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 8.9% lower, RR 0.91, p = 0.76, treatment 30 of 105 (28.6%), control 32 of 102 (31.4%), NNT 36, day 8, modified intention-to-treat.
|
|
viral load, 19.8% lower, relative load 0.80, p < 0.001, treatment mean 2.62 (±0.14) n=64, control mean 2.1 (±0.14) n=69, mITT high risk, day 8.
|
|
viral load, 13.5% lower, relative load 0.86, p < 0.001, treatment mean 2.51 (±0.11) n=105, control mean 2.17 (±0.12) n=102, day 8, modified intention-to-treat.
|
|
time to viral-, 26.1% lower, relative time 0.74, p = 0.09, treatment 64, control 69, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, mITT high risk, Kaplan-Meier.
|
|
time to viral-, 6.5% lower, relative time 0.94, p = 0.66, treatment 105, control 102, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, Kaplan-Meier, modified intention-to-treat.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tandon et al., 29 Jun 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, India, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period 10 August, 2021 - 25 January, 2022, trial CTRI/2021/08.
Contact: monika.tandon@glenmarkpharma.com.
SARS-CoV-2 accelerated clearance using a novel nitric oxide nasal spray (NONS) treatment: A randomized trial
The Lancet Regional Health - Southeast Asia, doi:10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036
Background Additional outpatient therapies which are readily accessible will be essential to reduce COVID-19 illness progression in high risk individuals. Especially as the virus continues to mutate with greater transmissibility despite increased global vaccination. Methods A randomized, double-blind, multicentre, parallel group, placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial evaluated the ability of nitric oxide (NO) to rapidly eradicate nasal SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Adults (18À70 years) with mild symptomatic COVID-19 were randomized, confirmed by laboratory SARS-CoV-2 reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) nasal swab. Randomisation was 1:1, NONS (N = 153) vs placebo (N = 153). NO generated by a nasal spray (NONS) was self-administered six times daily as two sprays per nostril (0Á45 mL of solution/dose) for seven days. Patients at high risk of illness progression, defined as unvaccinated, 45 years of age or having comorbidities, were the primary analysis population. Findings Overall, mean SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentrations (6¢96 log10 copies/mL in the NONS group and 7¢16 log10 copies/mL in the placebo group) were comparable at baseline. Primary endpoint mean treatment difference SARS-CoV-2 RNA change from baseline to the end of treatment (EOT) was -0¢52 copies/mL (SE 0¢202, 95% CI -0¢ 92 to -0¢12; p = 0¢010) with NONS compared to placebo. Secondary endpoint assessments demonstrated a greater proportion of patients receiving NONS (82¢8%) cleared SARS-CoV-2 (RT-PCR negative) by EOT compared to placebo (66¢7%, p = 0¢046), with no virus RNA detected a median of four days earlier compared to placebo (three vs seven days; p = 0¢044). Interpretation Use of NONS in patients recently infected with SARS-CoV-2 accelerates nasal virus clearance.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.lan sea.2022.100036.
References
Akaberi, Krambrich, Ling, Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101734
Fang, Perspectives series: host/pathogen interactions. Mechanisms of nitric oxide-related antimicrobial activity, J Clin Invest
Friedland, Tucker, Goodall, In vivo (human) and in vitro inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 with 0.5% povidone-iodine nasal spray, Aust J Otolaryng, doi:10.21037/ajo-21-40
Giarratana, Rajan, Kamala, Mendenhall, Giorgio, A sprayable Acid-Oxidizing solution containing hypochlorous acid (AOS2020) efficiently and safely inactivates SARS-Cov-2: a new potential solution for upper respiratory tract hygiene, Eur Archi Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, doi:10.1007/s00405-021-06644-5
Hirabara, Serdan, Gorjao, SARS-COV-2 variants: differences and potential of immune evasion, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2021.781429
Jin, Yang, Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of COVID-19, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v12040372
Kerstr€ Om S, Gunalan, Keng, Tan, Mirazimi, Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected, Virology
Lisi, Zelikin, Chandrawati, Nitric oxide to fight viral infections, Adv Sci, doi:10.1002/advs.202003895
Mccarthy, Rennick, Nambulli, Recurrent deletions in the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein drive antibody escape, Science
Moncada, Higgs, Endogenous nitric oxide: physiology, pathology, and clinical relevance, Eur J Clin Invest
Motozono, Toyoda, Zahradnik, SARS-CoV-2 spike L452R variant evades cellular immunity and increases infectivity, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2021.06.006
Pajon, Paila, Girard, Initial analysis of viral dynamics and circulating viral variants during the mRNA-1273 Phase 3 COVE trial, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-022-01679-5
Regev-Shoshani, Vimalanathan, Mcmullin, Road, Gay et al., Gaseous nitric oxide reduces influenza infectivity in vitro, Nitric Oxide
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2108163
Winchester, John, Jabbar, Isaac, Clinical efficacy of nitric oxide nasal spray (NONS) for the treatment of mild COVID-19 infection, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.05.009
Yeh, Using trapezoidal rule for the area under a curve calculation
Yu, Sun, Shi, Wang, Zhao et al., SARSCoV-2 viral load in sputum correlates with risk of COVID-19 progression, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-02893-8
Zou, Ruan, Huang, Liang, Huang et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036",
"ISSN": [
"2772-3682"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036",
"alternative-id": [
"S2772368222000464"
],
"article-number": "100036",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tandon",
"given": "Monika",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Wen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "Keith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Winchester",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tu",
"given": "Yuan-Po",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5697-2779",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1701-2115",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kodgule",
"given": "Rahul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6333-7098",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pendse",
"given": "Amol",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rangwala",
"given": "Shabbir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "Shashank",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Regional Health - Southeast Asia",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Regional Health - Southeast Asia",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-29T06:31:35Z",
"timestamp": 1656484295000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-13T06:23:48Z",
"timestamp": 1657693428000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-13T06:41:44Z",
"timestamp": 1657694504651
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1654041600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 24,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656115200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2772368222000464?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2772368222000464?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100036",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0001",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed 1 March 2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.05.009",
"article-title": "Clinical efficacy of nitric oxide nasal spray (NONS) for the treatment of mild COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Winchester",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "237",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0002",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101734",
"article-title": "Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro",
"author": "Akaberi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0003",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2362.1991.tb01383.x",
"article-title": "Endogenous nitric oxide: physiology, pathology, and clinical relevance",
"author": "Moncada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "361",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0004",
"volume": "21",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI119473",
"article-title": "Perspectives series: host/pathogen interactions. Mechanisms of nitric oxide-related antimicrobial activity",
"author": "Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2818",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0005",
"volume": "99",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2013.03.007",
"article-title": "Gaseous nitric oxide reduces influenza infectivity in vitro",
"author": "Regev-Shoshani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0006",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007",
"article-title": "Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected",
"author": "Åkerström",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0007",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0008",
"series-title": "Assessing COVID-19-Related Symptoms in Outpatient Adult and Adolescent Subjects in Clinical Trials of Drugs and Biological Products for COVID-19 Prevention or Treatment Guidance for Industry",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"article-title": "A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e192",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0009",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0010",
"unstructured": "Yeh S Using trapezoidal rule for the area under a curve calculation. SAS Conference Proceedings: SAS User Group International Conference (SUGI) -27, 2002, Paper 229-27.https://support.sas.com/resources/papers/proceedings/proceedings/sugi27/p229-27.pdf. Accessed 21 May 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01679-5",
"article-title": "Initial analysis of viral dynamics and circulating viral variants during the mRNA-1273 Phase 3 COVE trial",
"author": "Pajon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "823",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0011",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abf6950",
"article-title": "Recurrent deletions in the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein drive antibody escape",
"author": "McCarthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1139",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0012",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2021.06.006",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 spike L452R variant evades cellular immunity and increases infectivity",
"author": "Motozono",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1124",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0013",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2021.781429",
"article-title": "SARS-COV-2 variants: differences and potential of immune evasion",
"author": "Hirabara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0014",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2108163",
"article-title": "REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with COVID-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e81",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0015",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0016",
"unstructured": "Pfizer Press Release. Pfizer announces additional phase 2/3 study results confirming robust efficacy of novel COVID-19 oral antiviral treatment candidate in reducing risk of hospitalization or death, 14 December 2021. https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer-announces-additional-phase-23-study-results. Accessed 18 February 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12040372",
"article-title": "Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of COVID-19",
"author": "Jin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "372",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0017",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-021-06644-5",
"article-title": "A sprayable Acid‑Oxidizing solution containing hypochlorous acid (AOS2020) efficiently and safely inactivates SARS‑Cov‑2: a new potential solution for upper respiratory tract hygiene",
"author": "Giarratana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3099",
"journal-title": "Eur Archi Oto-Rhino-Laryngology",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0018",
"volume": "278",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2001737",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients",
"author": "Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1177",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0019",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-02893-8",
"article-title": "SARSCoV-2 viral load in sputum correlates with risk of COVID-19 progression",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "170",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0020",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202003895",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide to fight viral infections",
"author": "Lisi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Adv Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0021",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/ajo-21-40",
"article-title": "In vivo (human) and in vitro inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 with 0.5% povidone-iodine nasal spray",
"author": "Friedland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "Aust J Otolaryng",
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0022",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0023",
"unstructured": "Utah State University Institute for Antiviral Research.Virucidal assay against Influenza A, HRV-14, and RSV. Report 2021-098. June 25, 2021 [data on file]."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0024",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Available at: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Accessed 15 April 2022."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036_bib0025",
"unstructured": "SaNOtize study report - control test of NONS formulation against H1N1 [2021, data on file]."
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2772368222000464"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 accelerated clearance using a novel nitric oxide nasal spray (NONS) treatment: A randomized trial",
"type": "journal-article"
}