Effects of l-Arginine Plus Vitamin C Supplementation on Physical Performance, Endothelial Function, and Persistent Fatigue in Adults with Long COVID: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14234984, NCT04947488, Nov 2022
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
46 patient RCT in Italy showing improved recovery from long COVID symptoms using combined treatment with L-arginine and vitamin C. See also Calvani et al.
Tosato et al., 23 Nov 2022, Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Italy, peer-reviewed, 21 authors, trial NCT04947488 (history).
Contact: riccardo.calvani@policlinicogemelli.it (corresponding author).
Effects of l-Arginine Plus Vitamin C Supplementation on Physical Performance, Endothelial Function, and Persistent Fatigue in Adults with Long COVID: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14234984
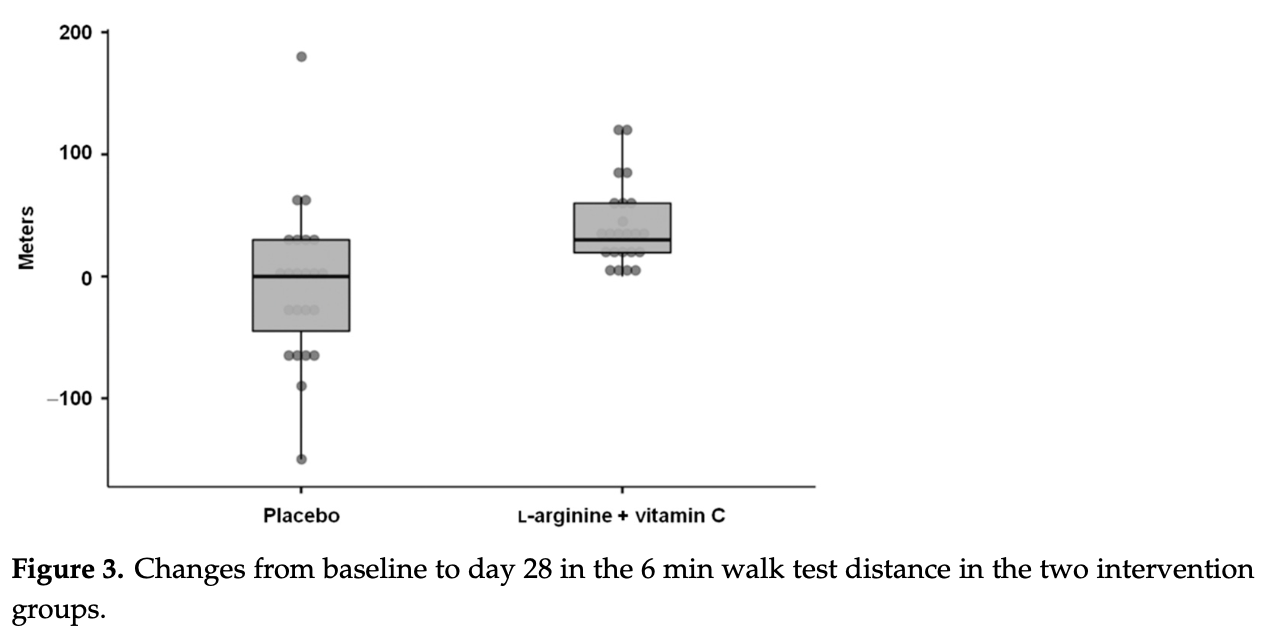
Long COVID, a condition characterized by symptom and/or sign persistence following an acute COVID-19 episode, is associated with reduced physical performance and endothelial dysfunction. Supplementation of L-arginine may improve endothelial and muscle function by stimulating nitric oxide synthesis. A single-blind randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted in adults aged between 20 and 60 years with persistent fatigue attending a post-acute COVID-19 outpatient clinic. Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive twice-daily orally either a combination of 1.66 g L-arginine plus 500 mg liposomal vitamin C or a placebo for 28 days. The primary outcome was the distance walked on the 6 min walk test. Secondary outcomes were handgrip strength, flow-mediated dilation, and fatigue persistence. Fifty participants were randomized to receive either L-arginine plus vitamin C or a placebo. Forty-six participants (median (interquartile range) age 51 (14), 30 [65%] women), 23 per group, received the intervention to which they were allocated and completed the study. At 28 days, L-arginine plus vitamin C increased the 6 min walk distance (+30 (40.5) m; placebo: +0 (75) m, p = 0.001) and induced a greater improvement in handgrip strength (+3.4 (7.5) kg) compared with the placebo (+1 (6.6) kg, p = 0.03). The flow-mediated dilation was greater in the active group than in the placebo (14.3% (7.3) vs. 9.4% (5.8), p = 0.03). At 28 days, fatigue was reported by two participants in the active group (8.7%) and 21 in the placebo group (80.1%; p < 0.0001). L-arginine plus vitamin C supplementation improved walking performance, muscle strength, endothelial function, and fatigue in adults with long COVID. This supplement may, therefore, be considered to restore physical performance and relieve persistent symptoms in this patient population.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. The L-arginine plus vitamin C supplement and placebo were donated by Farmaceutici Damor, Naples, Italy. The supplier had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
Abel, Knechtle, Perret, Eser, Von Arx et al., Influence of chronic supplementation of arginine aspartate in endurance athletes on performance and substrate metabolism − a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, Int. J. Sports Med, doi:10.1055/s-2004-821111
Adebayo, Varzideh, Wilson, Gambardella, Eacobacci et al., l-Arginine and COVID-19: An Update, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13113951
Alvares, Conte-Junior, Silva, Paschoalin, L-arginine does not improve biochemical and hormonal response in trained runners after 4 weeks of supplementation, Nutr. Res, doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2013.10.006
Bai, Sun, Yang, Sun, Chen et al., Increase in fasting vascular endothelial function after short-term oral L-arginine is effective when baseline flow-mediated dilation is low: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.2008.26544
Bednarz, Jaxa-Chamiec, Gebalska, Herbaczy Ńska-Cedro, Ceremuzy Ński et al., L-arginine supplementation prolongs exercise capacity in congestive heart failure, Kardiol. Pol
Belli, Balbi, Prince, Cattaneo, Masocco et al., Low physical functioning and impaired performance of activities of daily life in COVID-19 patients who survived hospitalisation, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.02096-2020
Bescós, Sureda, Tur, Pons, The effect of nitric-oxide-related supplements on human performance, Sports Med, doi:10.2165/11596860-000000000-00000
Bohannon, Crouch, Minimal clinically important difference for change in 6-minute walk test distance of adults with pathology: A systematic review, J. Eval. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1111/jep.12629
Brown, Kempf, Collins, Long, Owens et al., A prescribed walking regimen plus arginine supplementation improves function and quality of life for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A pilot study, Pulm. Circ, doi:10.1177/2045893217743966
Calvani, Miccheli, Landi, Bossola, Cesari et al., Current nutritional recommendations and novel dietary strategies to manage sarcopenia, J. Frailty Aging, doi:10.14283/jfa.2013.7
Carfì, Bernabei, Landi, Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.12603
Chetta, Zanini, Pisi, Aiello, Tzani et al., Reference values for the 6-min walk test in healthy subjects 20-50 years old, Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2006.01.001
Cheval, Sieber, Maltagliati, Millet, Formánek et al., Muscle strength is associated with COVID-19 hospitalization in adults 50 years of age or older, J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, doi:10.1002/jcsm.12738
Corretti, Anderson, Benjamin, Celermajer, Charbonneau et al., Guidelines for the ultrasound assessment of endothelial-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery: A report of the international brachial artery reactivity task force, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol
Davis, Assaf, Mccorkell, Wei, Low et al., Characterizing long COVID in an international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101019
Deanfield, Donald, Ferri, Giannattasio, Halcox et al., Endothelial function and dysfunction. Part I: Methodological issues for assessment in the different vascular beds: A statement by the Working Group on Endothelin and Endothelial Factors of the European Society of Hypertension, J. Hypertens
Doutreleau, Mettauer, Piquard, Rouyer, Schaefer et al., Chronic L-arginine supplementation enhances endurance exercise tolerance in heart failure patients, Int. J. Sports Med, doi:10.1055/s-2005-865847
Doutreleau, Rouyer, Di Marco, Lonsdorfer, Richard et al., L-arginine supplementation improves exercise capacity after a heart transplant, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.27881
Durante, Targeting Arginine in COVID-19-Induced Immunopathology and Vasculopathy, Metabolites, doi:10.3390/metabo12030240
Ferioli, Prediletto, Bensai, Betti, Daniele et al., The role of 6MWT in Covid-19 follow up, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.congress-2021.OA4046
Fiorentino, Coppola, Izzo, Annunziata, Bernardo et al., Effects of adding L-arginine orally to standard therapy in patients with COVID-19: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Results of the first interim analysis, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101125
Fried, Tangen, Walston, Newman, Hirsch et al., Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype, J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci, doi:10.1093/gerona/56.3.M146
Gale, Martyn, Cooper, Sayer, Grip strength, body composition, and mortality, Int. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/ije/dyl224
Galluzzo, Ciciarello, Tosato, Zazzara, Pais et al., Association between vitamin D status and physical performance in COVID-19 survivors: Results from the Gemelli against COVID-19 post-acute care project, Mech. Ageing Dev, doi:10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684
Gambardella, Khondkar, Morelli, Wang, Santulli et al., Arginine and Endothelial Function, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines8080277
Gao, Zhou, Huang, Liu, Bi et al., Persistent Endothelial Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease-2019 Survivors Late After Recovery, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.809033
Green, Dawson, Groenewoud, Jones, Thijssen, Is flow-mediated dilation nitric oxide mediated?: A meta-analysis, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02044
Groff, Sun, Ssentongo, Ba, Parsons et al., Short-term and Long-term Rates of Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Systematic Review, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28568
Guyatt, Sullivan, Thompson, Fallen, Pugsley et al., The 6-minute walk: A new measure of exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure, Can. Med. Assoc. J
Haffke, Freitag, Rudolf, Seifert, Doehner et al., Endothelial dysfunction and altered endothelial biomarkers in patients with post-COVID-19 syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), J. Transl. Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-022-03346-2
Hickson, Nutritional interventions in sarcopenia: A critical review, Proc. Nutr. Soc, doi:10.1017/S0029665115002049
Huang, Yao, Gu, Wang, Ren et al., 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: A longitudinal cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01755-4
Izzo, Trimarco, Mone, Aloè, Capra Marzani et al., Combining L-Arginine with vitamin C improves long-COVID symptoms: The LINCOLN Survey, Pharmacol. Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360
Kara, Kara, Akın, Özçakar, Grip strength as a predictor of disease severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Heart Lung, doi:10.1016/j.hrtlng.2021.06.005
Komaroff, Inflammation correlates with symptoms in chronic fatigue syndrome, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1712475114
Landi, Calvani, Martone, Salini, Zazzara et al., Normative values of muscle strength across ages in a "real world" population: Results from the longevity check-up 7+ project, J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, doi:10.1002/jcsm.12610
Landi, Gremese, Bernabei, Fantoni, Gasbarrini et al., Post-COVID-19 global health strategies: The need for an interdisciplinary approach, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01616-x
Lundberg, Weitzberg, Nitric oxide signaling in health and disease, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.010
Martone, Tosato, Ciciarello, Galluzzo, Zazzara et al., Sarcopenia as potential biological substrate of long COVID-19 syndrome: Prevalence, clinical features, and risk factors, J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, doi:10.1002/jcsm.12931
Martí I Líndez, Reith, Arginine-dependent immune responses, Cell. Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-021-03828-4
Mehandru, Merad, Pathological sequelae of long-haul COVID, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-021-01104-y
Merad, Blish, Sallusto, Iwasaki, The immunology and immunopathology of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abm8108
Michielsen, De Vries, Van Heck, Psychometric qualities of a brief self-rated fatigue measure: The Fatigue Assessment Scale, J. Psychosom. Res, doi:10.1016/S0022-3999(02)00392-6
Morelli, Gambardella, Castellanos, Trimarco, Santulli, Vitamin C and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox9121227
Nagaya, Uematsu, Oya, Sato, Sakamaki et al., Short-term oral administration of L-arginine improves hemodynamics and exercise capacity in patients with precapillary pulmonary hypertension, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/ajrccm.163.4.2007116
Nalbandian, Sehgal, Gupta, Madhavan, Mcgroder et al., Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z
Oikonomou, Souvaliotis, Lampsas, Siasos, Poulakou et al., Endothelial dysfunction in acute and long standing COVID-19: A prospective cohort study, Vascul. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.vph.2022.106975
Ortega, Silventoinen, Tynelius, Rasmussen, Muscular strength in male adolescents and premature death: Cohort study of one million participants, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.e7279
Patrizio, Calvani, Marzetti, Cesari, Physical Functional Assessment in Older Adults, J. Frailty Aging, doi:10.14283/jfa.2020.61
Pernow, Jung, Arginase as a potential target in the treatment of cardiovascular disease: Reversal of arginine steal?, Cardiovasc. Res, doi:10.1093/cvr/cvt036
Pucci, D'abbondanza, Curcio, Alcidi, Campanella et al., Handgrip strength is associated with adverse outcomes in patients hospitalized for COVID-19-associated pneumonia, Intern. Emerg. Med, doi:10.1007/s11739-022-03060-3
Radloff, The CES-D Scale: A Self-Report Depression Scale for Research in the General Population, Appl. Psychol. Meas, doi:10.1177/014662167700100306
Rantanen, Harris, Leveille, Visser, Foley et al., Muscle strength and body mass index as long-term predictors of mortality in initially healthy men, J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci, doi:10.1093/gerona/55.3.M168
Rees, Rostad, Mantus, Anderson, Chahroudi et al., Altered amino acid profile in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2101708118
Reizine, Lesouhaitier, Gregoire, Pinceaux, Gacouin et al., SARS-CoV-2-Induced ARDS Associates with MDSC Expansion, Lymphocyte Dysfunction, and Arginine Shortage, J. Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1007/s10875-020-00920-5
Sacchi, Grassi, Notari, Gili, Bordoni et al., Expansion of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Contributes to Platelet Activation by L-Arginine Deprivation during SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells10082111
Santoro, Falsetti, Zaccone, Nesci, Tosato et al., Impaired Endothelial Function in Convalescent Phase of COVID-19: A 3 Month Follow Up Observational Prospective Study, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm11071774
Santucci, Lomuscio, Canu, Primiano, Persichilli et al., A rapid method for determination of underivatized arginine-related metabolites in human plasma using LC-MS/MS
Sardu, Gambardella, Morelli, Wang, Marfella et al., Thrombosis, Kidney Failure, and Diabetes: Is COVID-19 an Endothelial Disease? A Comprehensive Evaluation of Clinical and Basic Evidence, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9051417
Sayer, Kirkwood, Grip strength and mortality: A biomarker of ageing?, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62349-7
Scott, Maarsingh, Holguin, Grasemann, Arginine Therapy for Lung Diseases, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.627503
Sirayder, Inal-Ince, Kepenek-Varol, Acik, Long-Term Characteristics of Severe COVID-19: Respiratory Function, Functional Capacity, and Quality of Life, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph19106304
Ståhle, Wold, Partial least squares analysis with cross-validation for the two-class problem: A Monte Carlo study, J. Chemom, doi:10.1002/cem.1180010306
Subramanian, Nirantharakumar, Hughes, Myles, Williams et al., Symptoms and risk factors for long COVID in non-hospitalized adults, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-022-01909-w
Szyma Ńska, Saccenti, Smilde, Westerhuis, Double-check: Validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies, Metabolomics, doi:10.1007/s11306-011-0330-3
Thijssen, Black, Pyke, Padilla, Atkinson et al., Assessment of flow-mediated dilation in humans: A methodological and physiological guideline, Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00471.2010
Tosato, Carfì, Martis, Pais, Ciciarello et al., Prevalence and Predictors of Persistence of COVID-19 Symptoms in Older Adults: A Single-Center Study, J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2021.07.003
Tosato, Ciciarello, Zazzara, Pais, Savera et al., Nutraceuticals and Dietary Supplements for Older Adults with Long COVID-19, Clin. Geriatr. Med, doi:10.1016/j.cger.2022.04.004
Viribay, Burgos, Fernández-Landa, Seco-Calvo, Mielgo-Ayuso, Effects of Arginine Supplementation on Athletic Performance Based on Energy Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051300
Zazzara, Bellieni, Calvani, Coelho-Junior, Picca et al., Inflammaging at the Time of COVID-19, Clin. Geriatr. Med, doi:10.1016/j.cger.2022.03.003
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14234984",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu14234984",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Long COVID, a condition characterized by symptom and/or sign persistence following an acute COVID-19 episode, is associated with reduced physical performance and endothelial dysfunction. Supplementation of l-arginine may improve endothelial and muscle function by stimulating nitric oxide synthesis. A single-blind randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted in adults aged between 20 and 60 years with persistent fatigue attending a post-acute COVID-19 outpatient clinic. Participants were randomized 1:1 to receive twice-daily orally either a combination of 1.66 g l-arginine plus 500 mg liposomal vitamin C or a placebo for 28 days. The primary outcome was the distance walked on the 6 min walk test. Secondary outcomes were handgrip strength, flow-mediated dilation, and fatigue persistence. Fifty participants were randomized to receive either l-arginine plus vitamin C or a placebo. Forty-six participants (median (interquartile range) age 51 (14), 30 [65%] women), 23 per group, received the intervention to which they were allocated and completed the study. At 28 days, l-arginine plus vitamin C increased the 6 min walk distance (+30 (40.5) m; placebo: +0 (75) m, p = 0.001) and induced a greater improvement in handgrip strength (+3.4 (7.5) kg) compared with the placebo (+1 (6.6) kg, p = 0.03). The flow-mediated dilation was greater in the active group than in the placebo (14.3% (7.3) vs. 9.4% (5.8), p = 0.03). At 28 days, fatigue was reported by two participants in the active group (8.7%) and 21 in the placebo group (80.1%; p < 0.0001). l-arginine plus vitamin C supplementation improved walking performance, muscle strength, endothelial function, and fatigue in adults with long COVID. This supplement may, therefore, be considered to restore physical performance and relieve persistent symptoms in this patient population.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu14234984"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5750-9746",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tosato",
"given": "Matteo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5472-2365",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Calvani",
"given": "Riccardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7032-3487",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Picca",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ciciarello",
"given": "Francesca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4620-5979",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Galluzzo",
"given": "Vincenzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7482-9514",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Coelho-Júnior",
"given": "Hélio José",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Di Giorgio",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Di Mario",
"given": "Clara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3600-392X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gervasoni",
"given": "Jacopo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gremese",
"given": "Elisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7868-8410",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Leone",
"given": "Paolo Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nesci",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paglionico",
"given": "Anna Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santoliquido",
"given": "Angelo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3614-7314",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Santoro",
"given": "Luca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7448-0604",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Santucci",
"given": "Lavinia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tolusso",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Urbani",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8266-1117",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Marini",
"given": "Federico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9567-6983",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Marzetti",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Landi",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-24T07:54:05Z",
"timestamp": 1669276445000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-25T08:47:30Z",
"timestamp": 1669366050000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-26T06:04:22Z",
"timestamp": 1669442662857
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "23",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "23",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1669161600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/23/4984/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "4984",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z",
"article-title": "Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "601",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jamda.2021.07.003",
"article-title": "Prevalence and Predictors of Persistence of COVID-19 Symptoms in Older Adults: A Single-Center Study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1840",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28568",
"article-title": "Short-term and Long-term Rates of Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Systematic Review",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2128568",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01909-w",
"article-title": "Symptoms and risk factors for long COVID in non-hospitalized adults",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1706",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.02096-2020",
"article-title": "Low physical functioning and impaired performance of activities of daily life in COVID-19 patients who survived hospitalisation",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2002096",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101019",
"article-title": "Characterizing long COVID in an international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101019",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-021-01104-y",
"article-title": "Pathological sequelae of long-haul COVID",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "194",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abm8108",
"article-title": "The immunology and immunopathology of COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1122",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cger.2022.04.004",
"article-title": "Nutraceuticals and Dietary Supplements for Older Adults with Long COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Clin. Geriatr. Med.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13113951",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "Adebayo, A., Varzideh, F., Wilson, S., Gambardella, J., Eacobacci, M., Jankauskas, S.S., Donkor, K., Kansakar, U., Trimarco, V., and Mone, P. (2021). l-Arginine and COVID-19: An Update. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/metabo12030240",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_11",
"unstructured": "Durante, W. (2022). Targeting Arginine in COVID-19-Induced Immunopathology and Vasculopathy. Metabolites, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.010",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide signaling in health and disease",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2853",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-021-03828-4",
"article-title": "Arginine-dependent immune responses",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5303",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvt036",
"article-title": "Arginase as a potential target in the treatment of cardiovascular disease: Reversal of arginine steal?",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "334",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc. Res.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2101708118",
"article-title": "Altered amino acid profile in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2101708118",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10082111",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Sacchi, A., Grassi, G., Notari, S., Gili, S., Bordoni, V., Tartaglia, E., Casetti, R., Cimini, E., Mariotti, D., and Garotto, G. (2021). Expansion of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Contributes to Platelet Activation by L-Arginine Deprivation during SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cells, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10875-020-00920-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-Induced ARDS Associates with MDSC Expansion, Lymphocyte Dysfunction, and Arginine Shortage",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "515",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines8080277",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Gambardella, J., Khondkar, W., Morelli, M.B., Wang, X., Santulli, G., and Trimarco, V. (2020). Arginine and Endothelial Function. Biomedicines, 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox9121227",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "Morelli, M.B., Gambardella, J., Castellanos, V., Trimarco, V., and Santulli, G. (2020). Vitamin C and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update. Antioxidants, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101125",
"article-title": "Effects of adding L-arginine orally to standard therapy in patients with COVID-19: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Results of the first interim analysis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101125",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360",
"article-title": "Combining L-Arginine with vitamin C improves long-COVID symptoms: The LINCOLN Survey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106360",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Res.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.627503",
"article-title": "Arginine Therapy for Lung Diseases",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "627503",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-2005-865847",
"article-title": "Chronic L-arginine supplementation enhances endurance exercise tolerance in heart failure patients",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "567",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Sports Med.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.2009.27881",
"article-title": "L-arginine supplementation improves exercise capacity after a heart transplant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1261",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051300",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Viribay, A., Burgos, J., Fernández-Landa, J., Seco-Calvo, J., and Mielgo-Ayuso, J. (2020). Effects of Arginine Supplementation on Athletic Performance Based on Energy Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/11596860-000000000-00000",
"article-title": "The effect of nitric-oxide-related supplements on human performance",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "Sports Med.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-2004-821111",
"article-title": "Influence of chronic supplementation of arginine aspartate in endurance athletes on performance and substrate metabolism − a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "344",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Sports Med.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2013.10.006",
"article-title": "L-arginine does not improve biochemical and hormonal response in trained runners after 4 weeks of supplementation",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Res.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01616-x",
"article-title": "Post-COVID-19 global health strategies: The need for an interdisciplinary approach",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1613",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_30",
"unstructured": "(2022, September 08). A Clinical Case Definition of Post COVID-19 Condition by a Delphi Consensus, 6 October 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Post_COVID-19_condition-Clinical_case_definition-2021.1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/014662167700100306",
"article-title": "The CES-D Scale: A Self-Report Depression Scale for Research in the General Population",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "385",
"journal-title": "Appl. Psychol. Meas.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1977"
},
{
"key": "ref_32",
"unstructured": "Santucci, L., Lomuscio, S., Canu, F., Primiano, A., Persichilli, S., Urbani, A., and Gervasoni, J. (2022, January 5–7). A rapid method for determination of underivatized arginine-related metabolites in human plasma using LC-MS/MS. Proceedings of the 54° National Conference of Società Italiana di Biochimica Clinica e Biologia Molecolare Clinica (SIBioC), Genoa, Italy. Available online: https://bc.sibioc.it/bc/numero/bcnum/206."
},
{
"article-title": "The 6-minute walk: A new measure of exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure",
"first-page": "919",
"journal-title": "Can. Med. Assoc. J.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "132",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of 6MWT in Covid-19 follow up",
"first-page": "OA4046",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684",
"article-title": "Association between vitamin D status and physical performance in COVID-19 survivors: Results from the Gemelli against COVID-19 post-acute care project",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111684",
"journal-title": "Mech. Ageing Dev.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "205",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Physical Functional Assessment in Older Adults",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "J. Frailty Aging",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcsm.12610",
"article-title": "Normative values of muscle strength across ages in a “real world” population: Results from the longevity check-up 7+ project",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"journal-title": "J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00004872-200501000-00004",
"article-title": "Endothelial function and dysfunction. Part I: Methodological issues for assessment in the different vascular beds: A statement by the Working Group on Endothelin and Endothelial Factors of the European Society of Hypertension",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "J. Hypertens.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0735-1097(01)01746-6",
"article-title": "Guidelines for the ultrasound assessment of endothelial-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery: A report of the international brachial artery reactivity task force",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "257",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11071774",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Santoro, L., Falsetti, L., Zaccone, V., Nesci, A., Tosato, M., Giupponi, B., Savastano, M.C., Moroncini, G., Gasbarrini, A., and Landi, F. (2022). Impaired Endothelial Function in Convalescent Phase of COVID-19: A 3 Month Follow Up Observational Prospective Study. J. Clin. Med., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/56.3.M146",
"article-title": "Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "M146",
"journal-title": "J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0022-3999(02)00392-6",
"article-title": "Psychometric qualities of a brief self-rated fatigue measure: The Fatigue Assessment Scale",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "345",
"journal-title": "J. Psychosom. Res.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2006.01.001",
"article-title": "Reference values for the 6-min walk test in healthy subjects 20-50 years old",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1573",
"journal-title": "Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jep.12629",
"article-title": "Minimal clinically important difference for change in 6-minute walk test distance of adults with pathology: A systematic review",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "377",
"journal-title": "J. Eval. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cem.1180010306",
"article-title": "Partial least squares analysis with cross-validation for the two-class problem: A Monte Carlo study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "185",
"journal-title": "J. Chemom.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11306-011-0330-3",
"article-title": "Double-check: Validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Metabolomics",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01755-4",
"article-title": "1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: A longitudinal cohort study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "747",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "398",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.163.4.2007116",
"article-title": "Short-term oral administration of L-arginine improves hemodynamics and exercise capacity in patients with precapillary pulmonary hypertension",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "887",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"article-title": "A prescribed walking regimen plus arginine supplementation improves function and quality of life for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A pilot study",
"first-page": "2045893217743966",
"journal-title": "Pulm. Circ.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "L-arginine supplementation prolongs exercise capacity in congestive heart failure",
"first-page": "348",
"journal-title": "Kardiol. Pol.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62349-7",
"article-title": "Grip strength and mortality: A biomarker of ageing?",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "226",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ije/dyl224",
"article-title": "Grip strength, body composition, and mortality",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Epidemiol.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/55.3.M168",
"article-title": "Muscle strength and body mass index as long-term predictors of mortality in initially healthy men",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "M168",
"journal-title": "J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.e7279",
"article-title": "Muscular strength in male adolescents and premature death: Cohort study of one million participants",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e7279",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "345",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcsm.12738",
"article-title": "Muscle strength is associated with COVID-19 hospitalization in adults 50 years of age or older",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1136",
"journal-title": "J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hrtlng.2021.06.005",
"article-title": "Grip strength as a predictor of disease severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "743",
"journal-title": "Heart Lung",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-022-03060-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_57",
"unstructured": "Pucci, G., D’Abbondanza, M., Curcio, R., Alcidi, R., Campanella, T., Chiatti, L., Gandolfo, V., Veca, V., Casarola, G., and Leone, M.C. (2022). Handgrip strength is associated with adverse outcomes in patients hospitalized for COVID-19-associated pneumonia. Intern. Emerg. Med., Online ahead of print."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph19106304",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_58",
"unstructured": "Sirayder, U., Inal-Ince, D., Kepenek-Varol, B., and Acik, C. (2022). Long-Term Characteristics of Severe COVID-19: Respiratory Function, Functional Capacity, and Quality of Life. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcsm.12931",
"article-title": "Sarcopenia as potential biological substrate of long COVID-19 syndrome: Prevalence, clinical features, and risk factors",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1974",
"journal-title": "J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Current nutritional recommendations and novel dietary strategies to manage sarcopenia",
"first-page": "38",
"journal-title": "J. Frailty Aging",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665115002049",
"article-title": "Nutritional interventions in sarcopenia: A critical review",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "378",
"journal-title": "Proc. Nutr. Soc.",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpheart.00471.2010",
"article-title": "Assessment of flow-mediated dilation in humans: A methodological and physiological guideline",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "H2",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "300",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vph.2022.106975",
"article-title": "Endothelial dysfunction in acute and long standing COVID-19: A prospective cohort study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106975",
"journal-title": "Vascul. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.809033",
"article-title": "Persistent Endothelial Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease-2019 Survivors Late After Recovery",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "809033",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202004.0204.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_65",
"unstructured": "Sardu, C., Gambardella, J., Morelli, M.B., Wang, X., Marfella, R., and Santulli, G. (2020). Hypertension, Thrombosis, Kidney Failure, and Diabetes: Is COVID-19 an Endothelial Disease? A Comprehensive Evaluation of Clinical and Basic Evidence. J. Clin. Med., 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02044",
"article-title": "Is flow-mediated dilation nitric oxide mediated?: A meta-analysis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "376",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.2008.26544",
"article-title": "Increase in fasting vascular endothelial function after short-term oral L-arginine is effective when baseline flow-mediated dilation is low: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12603",
"article-title": "Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1712475114",
"article-title": "Inflammation correlates with symptoms in chronic fatigue syndrome",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8914",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-022-03346-2",
"article-title": "Endothelial dysfunction and altered endothelial biomarkers in patients with post-COVID-19 syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS)",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "138",
"journal-title": "J. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cger.2022.03.003",
"article-title": "Inflammaging at the Time of COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "473",
"journal-title": "Clin. Geriatr. Med.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 71,
"references-count": 71,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/23/4984"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effects of l-Arginine Plus Vitamin C Supplementation on Physical Performance, Endothelial Function, and Persistent Fatigue in Adults with Long COVID: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}
