Combining L-Arginine with Vitamin C Improves Long-COVID Symptoms: The Nationwide Multicenter LINCOLN Study
et al., Pharmacological Research, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360, LINCOLN, Jul 2022
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
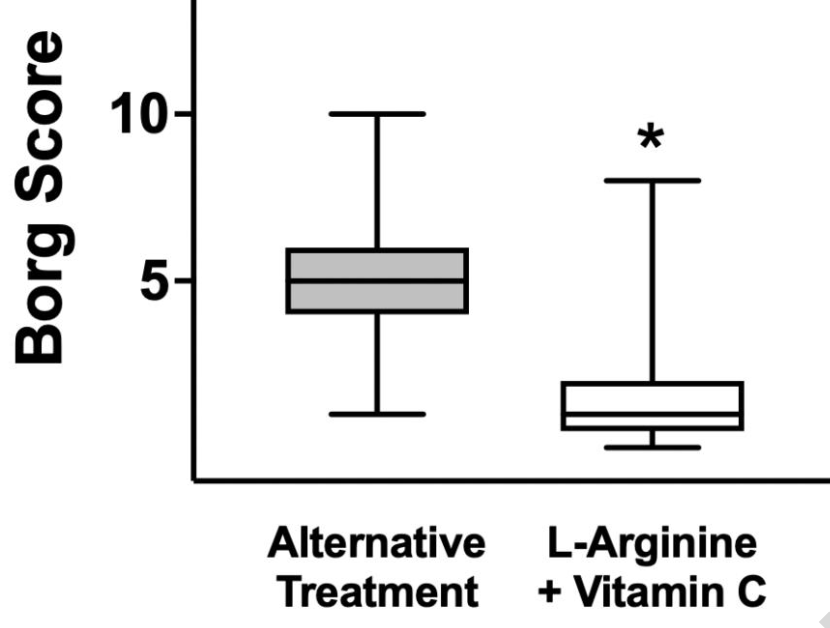
Long COVID trial comparing L-arginine + vitamin C with multivitamin treatment (vitamin B1, B2, B6, B12, nicotinamide, folic acid, pantothenic acid), showing significant improvement in symptoms with L-arginine + vitamin C treatment.
This is the 49th of 74 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000068.
21 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0012.
|
relative recovery, 41.4% better, RR 0.59, p < 0.001, treatment mean 8.15 (±1.3) n=869, control mean 13.9 (±2.3) n=521, relative symptom score.
|
|
relative recovery, 67.5% better, RR 0.33, p < 0.001, treatment 869, control 521, relative Borg score.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Izzo et al., 19 Jul 2022, prospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 21 authors, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with L-arginine) - results of individual treatments may vary, LINCOLN trial.
Combining L-Arginine with vitamin C improves long-COVID symptoms: The LINCOLN Survey
Pharmacological Research, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Flow chart of the study. J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
References
Accili, Can COVID-19 cause diabetes?, Nat Metab, doi:10.1038/s42255-020-00339-7
Adebayo, l-Arginine and COVID-19: An Update, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13113951
Ahmetaj-Shala, Cardiorenal Tissues Express SARS-CoV-2 Entry Genes and Basigin (BSG/CD147) Increases With Age in Endothelial Cells, JACC Basic Transl Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jacbts.2020.09.010
Ambrosino, Endothelial Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Unifying Mechanism and a Potential Therapeutic Target, J Pharmacol Exp Ther, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10040812
Amraei, Extracellular vimentin is an attachment factor that facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry into human endothelial cells, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2113874119
Andrew, Mayer, Enzymatic function of nitric oxide synthases, Cardiovasc Res, doi:10.1016/s0008-6363(99)00115-7
Azizi, Azizi, Neurological injuries in COVID-19 patients: direct viral invasion or a bystander injury after infection of epithelial/endothelial cells, J Neurovirol, doi:10.1007/s13365-020-00903-7
Blann, Circulating endothelial cells. Biomarker of vascular disease, Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1160/TH04-09-0578
Boggiano, Update on and Future Directions for Use of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies: National Institutes of Health Summit on Treatment and Prevention of COVID-19, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M21-3669
Bronte, Zanovello, Regulation of immune responses by L-arginine metabolism, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri1668
Brosnan, Brosnan, Renal arginine metabolism, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/134.10.2791S
Budinger, Misharin, Ridge, Singer, Wunderink, Distinctive features of severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI149412
Burkhard-Koren, Higher prevalence of pulmonary macrothrombi in SARS-CoV-2 than in influenza A: autopsy results from 'Spanish flu' 1918/1919 in Switzerland to Coronavirus disease 2019, J Pathol Clin Res, doi:10.1002/cjp2.189
Bustin, Nolan, RT-qPCR Testing of SARS-CoV-2: A Primer, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms21083004
Carr, Rowe, The Emerging Role of Vitamin C in the Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113286
Ceriello, Combined effect of metformin with ascorbic acid versus acetyl salicylic acid on diabetes-related cardiovascular complication; a 12-month single blind multicenter randomized control trial, Cardiovasc Diabetol, doi:10.2337/dc13-0750
Charfeddine, Long COVID 19 Syndrome: Is It Related to Microcirculation and Endothelial Dysfunction? Insights From TUN-EndCOV Study, Front Cardiovasc Med, doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.745758
Chavarria, Antioxidants and pentoxifylline as coadjuvant measures to standard therapy to improve prognosis of patients with pneumonia by COVID-19, Comput Struct Biotechnol J, doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2021.02.009
Chioh, Convalescent COVID-19 patients are susceptible to endothelial dysfunction due to persistent immune activation, Elife, doi:10.7554/eLife.64909
Cinar, Iyer, Kunos, Dual inhibition of CB1 receptors and iNOS, as a potential novel approach to the pharmacological management of acute and long COVID-19
Crook, Raza, Nowell, Young, Edison, Long covid-mechanisms, risk factors, and management, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n1648
Dean, Transcriptome and Functions of Granulocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Determine their Association with Disease Severity of COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.26.21254441
Denson, Metabolic Syndrome and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.40568
Desai, Lavelle, Boursiquot, Wan, Collins et al., Long-term complications of COVID-19, doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00375.2021
Fauci, Lane, Redfield, Covid-19 -Navigating the Uncharted, The New England journal of medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMe2002387
Feldman, COVID-19 and Diabetes: A Collision and Collusion of Two Diseases, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/dbi20-0032
Fiorentino, Effects of adding L-arginine orally to standard therapy in patients with COVID-19: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Results of J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f the first interim analysis, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101125
Fogarty, Persistent endotheliopathy in the pathogenesis of long COVID syndrome, J Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.15490
Gachter, Huber, Meier, A shot for the US economy, Financ Res Lett, doi:10.1016/j.frl.2021.102638
Gaffney, The Long COVID Conundrum, Am J Med, doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2021.07.037
Gambardella, Arginine and Endothelial Function, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines8080277
Gambardella, Role of Endothelial G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 in Angioedema, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15130
Gambardella, Role of endothelial miR-24 in COVID-19 cerebrovascular events, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03731-1
Gambardella, Santulli, What is linking COVID-19 and endothelial dysfunction? Updates on nanomedicine and bioengineering from the 2020 AHA Scientific Sessions, European Heart Journal (Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy)
Garcia, Immune Response, Inflammation, and the Clinical Spectrum of COVID-19
Gelzo, Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS): Why a Different Production in COVID-19 Patients of the Two Waves?, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14030534
Gu, Thrombocytopathy and endotheliopathy: crucial contributors to COVID-19 thromboinflammation, Nat Rev Cardiol, doi:10.1038/s41569-020-00469-1
Guervilly, Circulating Endothelial Cells as a Marker of Endothelial Injury in Severe COVID -19, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa528
Gupta, Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3
Hoehl, Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Returning Travelers from Wuhan, China, The New England journal of medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2001899
Isidori, Targeting the NO-cGMP-PDE5 pathway in COVID-19 infection. The DEDALO project, Andrology, doi:10.1111/andr.12837
Izcovich, Prognostic factors for severity and mortality in patients infected with COVID-19: A systematic review, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0241955
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F Castanares-Zapatero, Neuropathology and virus in brain of SARS-CoV-2 infected non-human primates, Nat Commun, doi:10.1080/07853890.2022.2076901
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F Datta, Talwar, Lee, A Proposed Framework and Timeline of the Spectrum of Disease Due to SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Illness Beyond Acute Infection and Public Health Implications, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22717
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F Dormanns, Brown, David, The role of nitric oxide in neurovascular coupling, J Theor Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2016.01.009
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F Fauci, The story behind COVID-19 vaccines, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abi8397
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F Kaur, Tripathi, Yadav, The Enigma of Endothelium in COVID-19, Front Physiol, doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.00989
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F Perea Polak, Complement-mediated thrombogenic vasculopathy in COVID-19, Int J Dermatol, doi:10.1111/ijd.15267
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F Raveendran, Jayadevan, Sashidharan, Long COVID: An overview, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.04.007
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F Srivastava, Garg, Hembrom, Kumar, Assessment of nitric oxide (NO) potential to mitigate COVID-19 severity, Virusdisease, doi:10.1007/s13337-021-00702-6
J O U R N A L P R E -P R O O F Varzideh, Sortilin drives hypertension by modulating sphingolipid/ceramide homeostasis and by triggering oxidative stress, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI156624
J O U R, n a l P r e -p r o o f COVID-19?, Cleve Clin J Med, doi:10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc046
Johansson, The effect of prostacyclin (Iloprost) infusion at a dose of 1 ng/kg/min for 72 hours compared to placebo in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04696-2
Jorens, Vermeire, Herman, L-arginine-dependent nitric oxide synthase: a new metabolic pathway in the lung and airways, Eur Respir J
Kelliher, Non-severe COVID-19 is associated with endothelial damage and hypercoagulability despite pharmacological thromboprophylaxis, J Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.15660
Kuck, Effects of L-arginine on cerebral blood flow, microvascular permeability, number of perfused capillaries, and brain water content in the traumatized mouse brain, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.058
Lavine, Bjornstad, Antia, Arginase 1: an unexpected mediator of pulmonary capillary barrier dysfunction in models of acute lung injury, Front Immunol, doi:10.1126/science.abe6522
Leucker, Effect of Crizanlizumab, a P-Selectin Inhibitor, in COVID-19: A Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Trial, JACC Basic Transl Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jacbts.2021.09.013
Libby, Luscher, COVID-19 is, in the end, an endothelial disease, Eur Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa623
Liu, Zhu, Zhang, Li, Peng, Intravenous high-dose vitamin C for the treatment of severe COVID-19: study protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039519
Ma, Yang, Huang, Lui, Endothelial contribution to COVID-19: an update on mechanisms and therapeutic implications, J Mol Cell Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.11.010
Manson, COVID-19-associated hyperinflammation and escalation of patient care: a retrospective longitudinal cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30275-7
Martinez-Salazar, COVID-19 and the Vasculature: Current Aspects and Long-Term Consequences, Front Cell Dev Biol, doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.824851
Matarese, Gambardella, Sardu, Santulli, miR-98 Regulates TMPRSS2 Expression in Human Endothelial Cells: Key Implications for COVID-19, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines8110462
May, Qu, Maggini, Nitric oxide mediates tightening of the endothelial barrier by ascorbic acid, Vitamin C and Immune Function, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.046
Mesquida, Peripheral microcirculatory alterations are associated with the severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19 patients admitted to intermediate respiratory and intensive care units, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03803-2
Mone, L-Arginine Enhances the Effects of Cardiac Rehabilitation on Physical Performance: New Insights for Managing Cardiovascular Patients During the COVID-19
Mone, miR-24 Targets the Transmembrane Glycoprotein Neuropilin-1 in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells, Front Cardiovasc Med, doi:10.3390/ncrna7010009
Montefusco, Acute and long-term disruption of glycometabolic control after SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat Metab, doi:10.1038/s42255-021-00407-6
Morelli, Gambardella, Castellanos, Trimarco, Santulli, Vitamin C and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox9121227
Morens, Taubenberger, Fauci, Universal Coronavirus Vaccines -An Urgent Need, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMp2118468
Nagashima, Endothelial Dysfunction and Thrombosis in Patients With COVID-19-Brief Report, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314860
Nalbandian, Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z
Oikonomou, Endothelial dysfunction in acute and long standing COVID-19: A prospective cohort study, Vascul Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.vph.2022.106975
Ortiz, The ApoA-I mimetic peptide 4F attenuates in vitro replication of SARS-CoV-2, associated apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation in epithelial cells, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102976
Otifi, Adiga, Endothelial Dysfunction in Covid-19, Am J Med Sci, doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2021.12.010
Page, Trends in characteristics and outcomes among US adults hospitalised with COVID-19 throughout 2020: an observational cohort study, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055137
Paules, Fauci, COVID-19: The therapeutic landscape, Med (N Y), doi:10.1016/j.medj.2021.04.015
Prasannan, Impaired exercise capacity in post-COVID syndrome: the role of VWF-ADAMTS13 axis, Blood Adv, doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006944
Qin, Endothelial cell infection and dysfunction, immune activation in severe COVID-19, Theranostics, doi:10.7150/thno.61810
Rath, Muller, Kropf, Closs, Munder, Metabolism via Arginase or Nitric Oxide Synthase: Two Competing Arginine Pathways in Macrophages, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00532
Raveendran, Misra, Post COVID-19 Syndrome ("Long COVID") and Diabetes: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102235
Reizine, SARS-CoV-2-Induced ARDS Associates with MDSC Expansion, Lymphocyte Dysfunction, and Arginine Shortage, J Clin Immunol, doi:10.1007/s10875-020-00920-5
Sacchi, Expansion of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Contributes to Platelet Activation by L-Arginine Deprivation during SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells10082111
Santulli, Morelli, Gambardella, Is Endothelial Dysfunction the Concealed Cornerstone of COVID-19?, BMJ
Sardu, Thrombosis, Kidney Failure, and Diabetes: Is COVID-19 an Endothelial Disease? A Comprehensive Evaluation of Clinical and Basic Evidence, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9051417
Sardu, Thrombosis, Kidney Failure, and Diabetes: Is COVID-19 an Endothelial Disease? A Comprehensive Evaluation of Clinical and Basic Evidence, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9051417
Sathish, Anton, Sivakumar, New-onset diabetes in "long COVID, J Diabetes, doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13187
Schmaier, Tie2 activation protects against prothrombotic endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.151527
Seitz, Ong, Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: A potential predictor of long-COVID?, Int J Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.11.051
Sharma, A randomized open-label trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of triple therapy with aspirin, atorvastatin, and nicorandil in hospitalised patients with SARS Cov-2 infection: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05361-y
Sheahan, Frieman, The continued epidemic threat of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for the future of global public health, Curr Opin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2020.05.010
Siegelman, Reflections of a COVID-19 Long Hauler, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22130
Sievers, Antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 infection or mRNA vaccines have reduced neutralizing activity against Beta and Omicron pseudoviruses, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abn7842
Soto, Guarner-Lans, Soria-Castro, Manzano Pech, Perez-Torres et al., Is Antioxidant Therapy a Useful Complementary Measure for Covid-19 Treatment? An Algorithm for Its Application, Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina56080386
Stephenson, Levin, Spector, Lis, Phase I clinical trial to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of high-dose intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with advanced cancer, Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s00280-013-2179-9
Stokes, COVID-19 and excess mortality in the United States: A county-level analysis, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003571
Ströhle, Von Bibra, Hahn, L-Arginine and vascular health
Sudre, Attributes and predictors of long COVID, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01292-y
Suh, Intravenous vitamin C administration reduces fatigue in office workers: a double-blind randomized controlled trial, Nutr J, doi:10.1186/1475-2891-11-7
Taboada, Caruezo, Naveira, Atanassoff, Corticosteroids and the hyperinflammatory phase of the COVID-19 disease, J Clin Anesth, doi:10.1016/j.jclinane.2020.109926
Tay, Poh, Renia, Macary, Ng, The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
Teuwen, Geldhof, Pasut, Carmeliet, COVID-19: the vasculature unleashed, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0343-0
Tousoulis, Kampoli, Tentolouris, Papageorgiou, Stefanadis, The role of nitric oxide on endothelial function, Curr Vasc Pharmacol, doi:10.2174/157016112798829760
Vollenberg, Indications of Persistent Glycocalyx Damage in Convalescent COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Multicenter Study and Hypothesis, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13112324
Wang, Ascorbate recycling in human neutrophils: induction by bacteria, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.94.25.13816
Wang, Long COVID: The Nature of Thrombotic Sequelae Determines the Necessity of Early Anticoagulation, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.861703
Wijnands, Castermans, Hommen, Meesters, Poeze, Arginine and citrulline and the immune response in sepsis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7031426
Wu, Meininger, Mcneal, Bazer, Rhoads, Role of L-Arginine in Nitric Oxide Synthesis and Health in Humans, Adv Exp Med Biol, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-74180-8_10
Yan, Tie, Messina, Tetrahydrobiopterin, L-arginine and vitamin C act synergistically to decrease oxidative stress, increase nitricoxide and improve blood flow after induction of hindlimbischemia in the rat, Mol Med, doi:10.2119/molmed.2011.00103
Zhang, Deep Vein Thrombosis in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Outcome, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046702
Zimmermann, Pittet, Curtis, Long covid in children and adolescents, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.o143
Zou, SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of Infected Patients, The New England journal of medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2001737
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360",
"ISSN": [
"1043-6618"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360",
"alternative-id": [
"S104366182200305X"
],
"article-number": "106360",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Combining L-Arginine with Vitamin C Improves Long-COVID Symptoms: The Nationwide Multicenter LINCOLN Study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Pharmacological Research"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Izzo",
"given": "Raffaele",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trimarco",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mone",
"given": "Pasquale",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aloè",
"given": "Teresita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marzani",
"given": "Massimo Capra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diana",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fazio",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mallardo",
"given": "Mario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maniscalco",
"given": "Mauro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marazzi",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Messina",
"given": "Nunzia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mininni",
"given": "Simone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mussi",
"given": "Chiara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pelaia",
"given": "Girolamo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pennisi",
"given": "Alfio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santus",
"given": "Pierachille",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scarpelli",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tursi",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zanforlin",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Santulli",
"given": "Gaetano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trimarco",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pharmacological Research",
"container-title-short": "Pharmacological Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-19T21:36:56Z",
"timestamp": 1658266616000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-19T21:38:26Z",
"timestamp": 1658266706000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-19T22:11:19Z",
"timestamp": 1658268679401
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656633600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S104366182200305X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S104366182200305X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "106360",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055137",
"article-title": "Trends in characteristics and outcomes among US adults hospitalised with COVID-19 throughout 2020: an observational cohort study",
"author": "Page",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "A shot for the US economy",
"author": "Gachter",
"journal-title": "Financ Res Lett",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib2",
"volume": "102638",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M21-3669",
"article-title": "Update on and Future Directions for Use of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies: National Institutes of Health Summit on Treatment and Prevention of COVID-19",
"author": "Boggiano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib3",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMp2118468",
"article-title": "Universal Coronavirus Vaccines - An Urgent Need",
"author": "Morens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "297",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib4",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abn7842",
"article-title": "Antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 infection or mRNA vaccines have reduced neutralizing activity against Beta and Omicron pseudoviruses",
"author": "Sievers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med, eabn7842",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abi8397",
"article-title": "The story behind COVID-19 vaccines",
"author": "Fauci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib6",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpcell.00375.2021",
"article-title": "Long-term complications of COVID-19",
"author": "Desai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "C1",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Cell Physiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib7",
"volume": "322",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.19719",
"article-title": "Long-term Health Consequences of COVID-19",
"author": "Del Rio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2021.07.037",
"article-title": "The Long COVID Conundrum",
"author": "Gaffney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "Am J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib9",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102235",
"article-title": "Post COVID-19 Syndrome (\"Long COVID\") and Diabetes: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management",
"author": "Raveendran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib10",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.o143",
"article-title": "Long covid in children and adolescents",
"author": "Zimmermann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "o143",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib11",
"volume": "376",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z",
"article-title": "Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome",
"author": "Nalbandian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "601",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib12",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22130",
"article-title": "Reflections of a COVID-19 Long Hauler",
"author": "Siegelman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2031",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib13",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dbi20-0032",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Diabetes: A Collision and Collusion of Two Diseases",
"author": "Feldman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2549",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib14",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.04.007",
"article-title": "Long COVID: An overview",
"author": "Raveendran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "869",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib15",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003571",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and excess mortality in the United States: A county-level analysis",
"author": "Stokes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib16",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1753-0407.13187",
"article-title": "New-onset diabetes in \"long COVID\"",
"author": "Sathish",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib17",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-021-00407-6",
"article-title": "Acute and long-term disruption of glycometabolic control after SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Montefusco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nat Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2002387",
"article-title": "Covid-19 - Navigating the Uncharted",
"author": "Fauci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1268",
"journal-title": "The New England journal of medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib19",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19: The therapeutic landscape",
"author": "Paules",
"first-page": "493",
"journal-title": "Med (N Y)",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib20",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2001899",
"article-title": "Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Returning Travelers from Wuhan, China",
"author": "Hoehl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1278",
"journal-title": "The New England journal of medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib21",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2001737",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of Infected Patients",
"author": "Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1177",
"journal-title": "The New England journal of medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib22",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coviro.2020.05.010",
"article-title": "The continued epidemic threat of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for the future of global public health",
"author": "Sheahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib23",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"article-title": "Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib24",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-020-00339-7",
"article-title": "Can COVID-19 cause diabetes",
"author": "Accili",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "Nat Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib25",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.40568",
"article-title": "Metabolic Syndrome and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19",
"author": "Denson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib26",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3",
"article-title": "Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1017",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib27",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9051417",
"article-title": "Hypertension, Thrombosis, Kidney Failure, and Diabetes: Is COVID-19 an Endothelial Disease? A Comprehensive Evaluation of Clinical and Basic Evidence",
"author": "Sardu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1417",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib28",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Is Endothelial Dysfunction the Concealed Cornerstone of COVID-19?",
"author": "Santulli",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib29",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/thno.61810",
"article-title": "Endothelial cell infection and dysfunction, immune activation in severe COVID-19",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8076",
"journal-title": "Theranostics",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib30",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa623",
"article-title": "COVID-19 is, in the end, an endothelial disease",
"author": "Libby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3038",
"journal-title": "Eur Heart J",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib31",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Thrombocytopathy and endotheliopathy: crucial contributors to COVID-19 thromboinflammation",
"author": "Gu",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Complement-mediated thrombogenic vasculopathy in COVID-19",
"author": "Perea Polak",
"journal-title": "Int J Dermatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0343-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: the vasculature unleashed",
"author": "Teuwen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "389",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib34",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03803-2",
"article-title": "Peripheral microcirculatory alterations are associated with the severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19 patients admitted to intermediate respiratory and intensive care units",
"author": "Mesquida",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "381",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib35",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.151527",
"article-title": "Tie2 activation protects against prothrombotic endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19",
"author": "Schmaier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib36",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjms.2021.12.010",
"article-title": "Endothelial Dysfunction in Covid-19",
"author": "Otifi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Am J Med Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.15660",
"article-title": "Non-severe COVID-19 is associated with endothelial damage and hypercoagulability despite pharmacological thromboprophylaxis",
"author": "Kelliher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Haemost",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2113874119",
"article-title": "Extracellular vimentin is an attachment factor that facilitates SARS-CoV-2 entry into human endothelial cells",
"author": "Amraei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib39",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa145",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib40",
"unstructured": "Gambardella, J. & Santulli, G. What is linking COVID-19 and endothelial dysfunction? Updates on nanomedicine and bioengineering from the 2020 AHA Scientific Sessions. European Heart Journal (Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy), In press (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2020.00989",
"article-title": "The Enigma of Endothelium in COVID-19",
"author": "Kaur",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "989",
"journal-title": "Front Physiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib41",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines8110462",
"article-title": "miR-98 Regulates TMPRSS2 Expression in Human Endothelial Cells: Key Implications for COVID-19",
"author": "Matarese",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib42",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacbts.2020.09.010",
"article-title": "Cardiorenal Tissues Express SARS-CoV-2 Entry Genes and Basigin (BSG/CD147) Increases With Age in Endothelial Cells",
"author": "Ahmetaj-Shala",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1111",
"journal-title": "JACC Basic Transl Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib43",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "miR-24 Targets the Transmembrane Glycoprotein Neuropilin-1 in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells",
"author": "Mone",
"journal-title": "Noncoding RNA",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib44",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2020.598400",
"article-title": "Vascular Manifestations of COVID-19 - Thromboembolism and Microvascular Dysfunction",
"author": "Roberts",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Cardiovasc Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib45",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102976",
"article-title": "Heterogeneous expression of the SARS-Coronavirus-2 receptor ACE2 in the human respiratory tract",
"author": "Ortiz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib46",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/21505594.2021.1964329",
"article-title": "The ApoA-I mimetic peptide 4F attenuates in vitro replication of SARS-CoV-2, associated apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation in epithelial cells",
"author": "Kelesidis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2214",
"journal-title": "Virulence",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib47",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI156624",
"article-title": "Sortilin drives hypertension by modulating sphingolipid/ceramide homeostasis and by triggering oxidative stress",
"author": "Varzideh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib48",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15130",
"article-title": "Role of Endothelial G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 in Angioedema",
"author": "Gambardella",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1625",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib49",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313237",
"article-title": "Emerging Roles of Vascular Endothelium in Metabolic Homeostasis",
"author": "Pi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "477",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib50",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046702",
"article-title": "Deep Vein Thrombosis in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Outcome",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib51",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314860",
"article-title": "Endothelial Dysfunction and Thrombosis in Patients With COVID-19-Brief Report",
"author": "Nagashima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2404",
"journal-title": "Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib52",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Higher prevalence of pulmonary macrothrombi in SARS-CoV-2 than in influenza A: autopsy results from 'Spanish flu' 1918/1919 in Switzerland to Coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Burkhard-Koren",
"journal-title": "J Pathol Clin Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0241955",
"article-title": "Prognostic factors for severity and mortality in patients infected with COVID-19: A systematic review",
"author": "Izcovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib54",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101125",
"article-title": "Effects of adding L-arginine orally to standard therapy in patients with COVID-19: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Results of the first interim analysis",
"author": "Fiorentino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib55",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04696-2",
"article-title": "The effect of prostacyclin (Iloprost) infusion at a dose of 1 ng/kg/min for 72 hours compared to placebo in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Johansson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "746",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib56",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Intravenous high-dose vitamin C for the treatment of severe COVID-19: study protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Liu",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib57",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13113951",
"article-title": "l-Arginine and COVID-19: An Update",
"author": "Adebayo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib58",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacbts.2021.09.013",
"article-title": "Effect of Crizanlizumab, a P-Selectin Inhibitor, in COVID-19: A Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Trial",
"author": "Leucker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "935",
"journal-title": "JACC Basic Transl Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib59",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.11.010",
"article-title": "Endothelial contribution to COVID-19: an update on mechanisms and therapeutic implications",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "J Mol Cell Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib60",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-021-05361-y",
"article-title": "A randomized open-label trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of triple therapy with aspirin, atorvastatin, and nicorandil in hospitalised patients with SARS Cov-2 infection: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib61",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13337-021-00702-6",
"article-title": "Assessment of nitric oxide (NO) potential to mitigate COVID-19 severity",
"author": "Srivastava",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "589",
"journal-title": "Virusdisease",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib62",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/andr.12837",
"article-title": "Targeting the NO-cGMP-PDE5 pathway in COVID-19 infection. The DEDALO project",
"author": "Isidori",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Andrology",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib63",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Renal arginine metabolism",
"author": "Brosnan",
"first-page": "2796S",
"issue": "2791S-2795S",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib64",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-74180-8_10",
"article-title": "Role of L-Arginine in Nitric Oxide Synthesis and Health in Humans",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Adv Exp Med Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib65",
"volume": "1332",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2014.00532",
"article-title": "Metabolism via Arginase or Nitric Oxide Synthase: Two Competing Arginine Pathways in Macrophages",
"author": "Rath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "532",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib66",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines8080277",
"article-title": "Arginine and Endothelial Function",
"author": "Gambardella",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib67",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0008-6363(99)00115-7",
"article-title": "Enzymatic function of nitric oxide synthases",
"author": "Andrew",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "521",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib68",
"volume": "43",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"article-title": "L-arginine-dependent nitric oxide synthase: a new metabolic pathway in the lung and airways",
"author": "Jorens",
"first-page": "258",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib69",
"volume": "6",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/157016112798829760",
"article-title": "The role of nitric oxide on endothelial function",
"author": "Tousoulis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Curr Vasc Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib70",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtbi.2016.01.009",
"article-title": "The role of nitric oxide in neurovascular coupling",
"author": "Dormanns",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Theor Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib71",
"volume": "394",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "[L-Arginine and vascular health]",
"author": "Ströhle",
"first-page": "515",
"journal-title": "Med Monatsschr Pharm",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib72",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri1668",
"article-title": "Regulation of immune responses by L-arginine metabolism",
"author": "Bronte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "641",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib73",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7031426",
"article-title": "Arginine and citrulline and the immune response in sepsis",
"author": "Wijnands",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1426",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib74",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin C and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update",
"author": "Morelli",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib75",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Is Antioxidant Therapy a Useful Complementary Measure for Covid-19 Treatment? An Algorithm for Its Application",
"author": "Soto",
"journal-title": "Medicina (Kaunas) 56, doi:10.3390/medicina56080386",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.042",
"article-title": "Erythrocyte Glut1 triggers dehydroascorbic acid uptake in mammals unable to synthesize vitamin C",
"author": "Montel-Hagen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1039",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib77",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.94.25.13816",
"article-title": "Ascorbate recycling in human neutrophils: induction by bacteria",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13816",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib78",
"volume": "94",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc046",
"article-title": "What is the role of supplementation with ascorbic acid, zinc, vitamin D, or N-acetylcysteine for prevention or treatment of COVID-19?",
"author": "Bauer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cleve Clin J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib79",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.csbj.2021.02.009",
"article-title": "Antioxidants and pentoxifylline as coadjuvant measures to standard therapy to improve prognosis of patients with pneumonia by COVID-19",
"author": "Chavarria",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1379",
"journal-title": "Comput Struct Biotechnol J",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib80",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113286",
"article-title": "The Emerging Role of Vitamin C in the Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib81",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2119/molmed.2011.00103",
"article-title": "Tetrahydrobiopterin, L-arginine and vitamin C act synergistically to decrease oxidative stress, increase nitricoxide and improve blood flow after induction of hindlimbischemia in the rat",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "676",
"journal-title": "Mol Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib82",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.058",
"article-title": "Ascorbic acid attenuates endothelial permeability triggered by cell-free hemoglobin",
"author": "Kuck",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "433",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib83",
"volume": "495",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mvr.2007.03.001",
"article-title": "Effects of L-arginine on cerebral blood flow, microvascular permeability, number of perfused capillaries, and brain water content in the traumatized mouse brain",
"author": "Lundblad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Microvasc Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib84",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.046",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide mediates tightening of the endothelial barrier by ascorbic acid",
"author": "May",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "701",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib85",
"volume": "404",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9111211",
"article-title": "Vitamin C and Immune Function",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib86",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Long COVID: The Nature of Thrombotic Sequelae Determines the Necessity of Early Anticoagulation",
"author": "Wang",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib87",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2022.824851",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and the Vasculature: Current Aspects and Long-Term Consequences",
"author": "Martinez-Salazar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Dev Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib88",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01292-y",
"article-title": "Attributes and predictors of long COVID",
"author": "Sudre",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "626",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib89",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/jpet.122.001149",
"article-title": "L-Arginine Enhances the Effects of Cardiac Rehabilitation on Physical Performance: New Insights for Managing Cardiovascular Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "Mone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Pharmacol Exp Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib90",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21083004",
"article-title": "RT-qPCR Testing of SARS-CoV-2: A Primer",
"author": "Bustin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib91",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9051417",
"article-title": "Hypertension, Thrombosis, Kidney Failure, and Diabetes: Is COVID-19 an Endothelial Disease? A Comprehensive Evaluation of Clinical and Basic Evidence",
"author": "Sardu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib92",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03731-1",
"article-title": "Role of endothelial miR-24 in COVID-19 cerebrovascular events",
"author": "Gambardella",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "306",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib93",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10040812",
"article-title": "Endothelial Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Unifying Mechanism and a Potential Therapeutic Target",
"author": "Ambrosino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomedicines",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib94",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/jpet.122.001209",
"article-title": "Exosomal miR-145 and miR-885 regulate thrombosis in COVID-19",
"author": "Gambardella",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Pharmacol Exp Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib95",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.11.051",
"article-title": "Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: A potential predictor of long-COVID",
"author": "Seitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Int J Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib96",
"volume": "349",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vph.2022.106975",
"article-title": "Endothelial dysfunction in acute and long standing COVID-19: A prospective cohort study",
"author": "Oikonomou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Vascul Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib97",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Circulating endothelial cells",
"author": "Blann",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "Biomarker of vascular disease. Thromb Haemost",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib98",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa528",
"article-title": "Circulating Endothelial Cells as a Marker of Endothelial Injury in Severe COVID -19",
"author": "Guervilly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1789",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib99",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.64909",
"article-title": "Convalescent COVID-19 patients are susceptible to endothelial dysfunction due to persistent immune activation",
"author": "Chioh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib100",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13112324",
"article-title": "Indications of Persistent Glycocalyx Damage in Convalescent COVID-19 Patients: A Prospective Multicenter Study and Hypothesis",
"author": "Vollenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib101",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.15490",
"article-title": "Persistent endotheliopathy in the pathogenesis of long COVID syndrome",
"author": "Fogarty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2546",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Haemost",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib102",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2021.745758",
"article-title": "Long COVID 19 Syndrome: Is It Related to Microcirculation and Endothelial Dysfunction? Insights From TUN-EndCOV Study",
"author": "Charfeddine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Cardiovasc Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib103",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22717",
"article-title": "A Proposed Framework and Timeline of the Spectrum of Disease Due to SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Illness Beyond Acute Infection and Public Health Implications",
"author": "Datta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2251",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib104",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinane.2020.109926",
"article-title": "Corticosteroids and the hyper-inflammatory phase of the COVID-19 disease",
"author": "Taboada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Anesth",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib105",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01441",
"article-title": "Immune Response, Inflammation, and the Clinical Spectrum of COVID-19",
"author": "Garcia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1441",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib106",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30275-7",
"article-title": "COVID-19-associated hyperinflammation and escalation of patient care: a retrospective longitudinal cohort study",
"author": "Manson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e594",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib107",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"article-title": "The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib108",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI149412",
"article-title": "Distinctive features of severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia",
"author": "Budinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib109",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe6522",
"article-title": "Immunological characteristics govern the transition of COVID-19 to endemicity",
"author": "Lavine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "741",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib110",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2013.00228",
"article-title": "Arginase 1: an unexpected mediator of pulmonary capillary barrier dysfunction in models of acute lung injury",
"author": "Lucas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib111",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10875-020-00920-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-Induced ARDS Associates with MDSC Expansion, Lymphocyte Dysfunction, and Arginine Shortage",
"author": "Reizine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "515",
"journal-title": "J Clin Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib112",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Transcriptome and Functions of Granulocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Determine their Association with Disease Severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Dean",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib113",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10082111",
"article-title": "Expansion of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Contributes to Platelet Activation by L-Arginine Deprivation during SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Sacchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib114",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14030534",
"article-title": "Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS): Why a Different Production in COVID-19 Patients of the Two Waves",
"author": "Gelzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib115",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15461",
"article-title": "Dual inhibition of CB1 receptors and iNOS, as a potential novel approach to the pharmacological management of acute and long COVID-19",
"author": "Cinar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2121",
"journal-title": "Br J Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib116",
"volume": "179",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n1648",
"article-title": "Long covid-mechanisms, risk factors, and management",
"author": "Crook",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "n1648",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib117",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13365-020-00903-7",
"article-title": "Neurological injuries in COVID-19 patients: direct viral invasion or a bystander injury after infection of epithelial/endothelial cells",
"author": "Azizi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "631",
"journal-title": "J Neurovirol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib118",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07853890.2022.2076901",
"article-title": "Pathophysiology and mechanism of long COVID: a comprehensive review",
"author": "Castanares-Zapatero",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1473",
"journal-title": "Ann Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib119",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-29440-z",
"article-title": "Neuropathology and virus in brain of SARS-CoV-2 infected non-human primates",
"author": "Rutkai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1745",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib120",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006944",
"article-title": "Impaired exercise capacity in post-COVID syndrome: the role of VWF-ADAMTS13 axis",
"author": "Prasannan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Blood Adv",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib121",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1475-2891-11-7",
"article-title": "Intravenous vitamin C administration reduces fatigue in office workers: a double-blind randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Suh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Nutr J",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib122",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00280-013-2179-9",
"article-title": "Phase I clinical trial to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of high-dose intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with advanced cancer",
"author": "Stephenson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Cancer Chemother Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib123",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc13-0750",
"article-title": "Vitamin C further improves the protective effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 on acute hypoglycemia-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in type 1 diabetes",
"author": "Ceriello",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4104",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib124",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12933-017-0584-9",
"article-title": "Combined effect of metformin with ascorbic acid versus acetyl salicylic acid on diabetes-related cardiovascular complication; a 12-month single blind multicenter randomized control trial",
"author": "Gillani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Diabetol",
"key": "10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106360_bib125",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
}
],
"reference-count": 125,
"references-count": 125,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S104366182200305X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Combining L-Arginine with Vitamin C Improves Long-COVID Symptoms: The Nationwide Multicenter LINCOLN Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
