Association between vitamin D status and physical performance in COVID-19 survivors: Results from the Gemelli against COVID-19 post-acute care project
et al., Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, doi:10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684, May 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Analysis of 681 COVID-19 survivors in Italy, showing a high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency. Low vitamin D levels were associated with poor physical performance, and were more common in patients that had been hospitalized.
Galluzzo et al., 13 May 2022, Italy, peer-reviewed, mean age 53.4, 10 authors, study period April 2020 - March 2021.
Contact: riccardo.calvani@policlinicogemelli.it.
Association between vitamin D status and physical performance in COVID-19 survivors: Results from the Gemelli against COVID-19 post-acute care project
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, doi:10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684
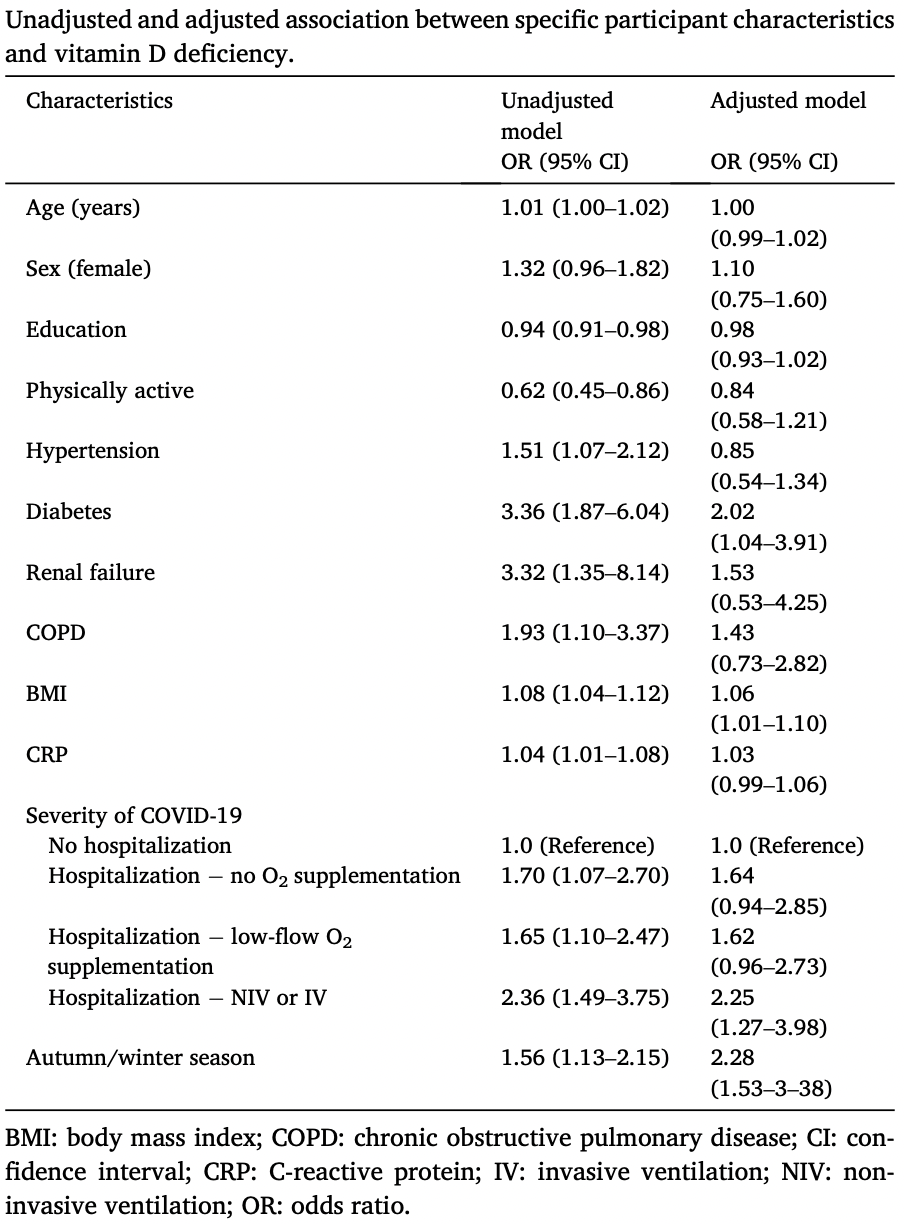
To determine the prevalence and associated factors of vitamin D deficiency in COVID-19 survivors and the relationship between vitamin D status and physical performance. Methods: Vitamin D status was assessed in a sample of patients who had recovered from COVID-19 and were admitted to a post-acute outpatient service at the Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS (Rome, Italy). Participants were offered comprehensive medical assessment, including physical performance and muscle strength tests. Self-rated health was assessed. Vitamin D deficiency was defined as a serum concentration of 25-OH vitamin D < 20 ng/mL. Results: Mean age of 681 participants was 53.4 ± 15.2 years and 49% were women. Vitamin D deficiency was detected in 35.6% of the whole study population, and in 40.2% of those 65 and older. Vitamin D deficiency was associated with diabetes, higher body mass index, and COVID-19 severity, and showed a seasonal pattern with a peak in autumn/winter. Participants with vitamin D deficiency performed poorer on the six-minute walking test, with the lowest performance observed in those 65 and older. No significant associations with any other parameters were found. Conclusion: Our findings indicate that vitamin D deficiency is frequent in COVID-19 survivors, especially in older adults. Low vitamin D levels are associated with poor physical performance, in particular in old age.
Ethics approval and consent to participate The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore (Rome, Italy).
Consent for publication The author gives consent for publication of this paper.
Competing interests None of the members of the Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post-Acute Care Study Group has any conflict of interest.
References
Aghagoli, Gallo Marin, Katchur, Chaves-Sell, Asaad et al., Neurological involvement in COVID-19 and potential mechanisms: a review, Neurocrit. Care, doi:10.1007/s12028-020-01049-4
Amin, COVID-19 and the liver: overview, Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001808
Amrein, Scherkl, Hoffmann, Neuwersch-Sommeregger, Köstenberger et al., Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide, Eur. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
Annweiler, Henni, Walrand, Montero-Odasso, Duque et al., Vitamin D and walking speed in older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis, Maturitas, doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2017.07.012
Baktash, Hosack, Patel, Shah, Kandiah et al., Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19, Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138712
Bassatne, Basbous, Chakhtoura, El Zein, Rahme et al., The link between COVID-19 and VItamin D (VIVID): a systematic review and meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753
Bohannon, Crouch, 1-minute sit-to-stand test: systematic review of procedures, performance, and clinimetric properties, J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev, doi:10.1097/HCR.0000000000000336
Bouillon, Carmeliet, Lieben, Watanabe, Perino et al., Vitamin D and energy homeostasis: of mice and men, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/nrendo.2013.226
Bouillon, Manousaki, Rosen, Trajanoska, Rivadeneira et al., The health effects of vitamin D supplementation: evidence from human studies, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-021-00593-z
Bouillon, Marcocci, Carmeliet, Bikle, White et al., Skeletal and extraskeletal actions of vitamin D: current evidence and outstanding questions, Endocr. Rev, doi:10.1210/er.2018-00126
Boxer, Dauser, Walsh, Hager, Kenny, The association between vitamin D and inflammation with the 6-minute walk and frailty in patients with heart failure, J. Am. Geriatr. Soc, doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01601.x
Briand, Behal, Chenivesse, Wémeau-Stervinou, Wallaert, The 1-minute sit-to-stand test to detect exercise-induced oxygen desaturation in patients with interstitial lung disease, Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis, doi:10.1177/1753466618793028
Carfì, Bernabei, Landi, Gemelli, Against COVID-19 post-acute care study group, "persistent symptoms in patients after acute COVID-19, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.12603
Cashman, Dowling, Škrabáková, Gonzalez-Gross, Valtueña et al., Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.3390/nu12072097
Cheng, Massaro, Fox, Larson, Keyes et al., Adiposity, cardiometabolic risk, and vitamin D status: the Framingham heart study, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/db09-1011
De Boer, Van Lanschot, Stalmeier, Van Sandick, Hulscher et al., Is a single-item visual analogue scale as valid, reliable and responsive as multi-item scales in measuring quality of life?, Qual. Life Res, doi:10.1023/B:QURE.0000018499.64574.1f
De Smet, De Smet, Herroelen, Gryspeerdt, Martens, Serum 25 (OH)D level on hospital admission associated with COVID-19 stage and mortality, Am. J. Clin. Pathol, doi:10.1093/ajcp/aqaa252
Drincic, Armas, Van Diest, Heaney, Volumetric dilution, rather than sequestration best explains the low vitamin D status of obesity, Obesity, doi:10.1038/oby.2011.404
Gardner, Chen, Glenn, Vitamin D and the heart, Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00322.2013
Geirsdottir, Ramel, Chang, Briem, Jonsson et al., Vitamin D and associations with walking ability in community-dwelling elderly adults, J. Food Nutr. Disord, doi:10.4172/2324-9323.1000192
Gemelli, Post-COVID-19 global health strategies: the need for an interdisciplinary approach, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01616-x
Glaser, Kiecolt-Glaser, Stress-associated depression in cellular immunity: implications for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), Brain Behav. Immun, doi:10.1016/0889-1591(87)90013-4
Guyatt, The 6-minute walk: a new measure of exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure, Can. Med. Assoc. J
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank Diabetes, Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050
Holick, Vitamin D deficiency (Jul.), N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra070553
Kasahara, Singh, Noymer, Vitamin D (25OHD) serum seasonality in the United States, PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065785
Kompaniyets, Pennington, Goodman, Rosenblum, Belay et al., Underlying medical conditions and severe illness among 540,667 adults hospitalized with COVID-19, Prev. Chronic Dis, doi:10.5888/pcd18.210123
Koundourakis, Avgoustinaki, Malliaraki, Margioris, Muscular effects of vitamin D in young athletes and non-athletes and in the elderly, Hormones, doi:10.14310/horm.2002.1705
Landi, Calvani, Martone, Salini, Zazzara et al., Normative values of muscle strength across ages in a 'real world' population: results from the longevity check-up 7+ project, J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, doi:10.1002/jcsm.12610
Li, Tong, Bare, Devlin, Assessment of the association of vitamin D level with SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity among working-age adults, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11634
Lips, Eekhoff, Van Schoor, Oosterwerff, De Jongh et al., Vitamin D and type 2 diabetes, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.11.021
Lombardo, Foppiani, Peretti, Mangiavini, Battezzati et al., Long-term coronavirus disease 2019 complications in inpatients and outpatients: a one-year follow-up cohort study, Open Forum Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab384
Luan, Yin, Yao, Update advances on C-reactive protein in COVID-19 and other viral infections, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.720363
Manios, Moschonis, Lambrinou, Tsoutsoulopoulou, Binou et al., A systematic review of vitamin D status in southern European countries, Eur. J. Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-017-1564-2
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Golan Cohen et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Mohammad, Aziz, Al Mahri, Malik, Haji et al., Obesity and COVID-19: what makes obese host so vulnerable?, Immun. Ageing, doi:10.1186/s12979-020-00212-x
Pereira-Santos, Costa, Assis, Santos, Santos, Obesity and vitamin D deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Obes. Rev, doi:10.1111/obr.12239
Polly, Tan, The role of vitamin D in skeletal and cardiac muscle function, Front. Physiol, doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00145
Remelli, Vitali, Zurlo, Volpato, Vitamin D deficiency and sarcopenia in older persons, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11122861
Rodriguez, Mousa, Ebeling, Scott, De Courten, Effects of vitamin D supplementation on inflammatory markers in heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-018-19708-0
Rubin, Sorting out whether vitamin D deficiency raises COVID-19 risk, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24127
Siddiqui, Manansala, Abdulrahman, Nasrallah, Smatti et al., Immune modulatory effects of vitamin D on viral Infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092879
Sulli, Gotelli, Casabella, Paolino, Pizzorni et al., Vitamin D and lung outcomes in elderly COVID-19 patients, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13030717
Tajbakhsh, Gheibi Hayat, Taghizadeh, Akbari, Inabadi et al., COVID-19 and cardiac injury: clinical manifestations, biomarkers, mechanisms, diagnosis, treatment, and follow up, Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther, doi:10.1080/14787210.2020.1822737
Teshome, Adane, Girma, Mekonnen, The impact of vitamin D level on COVID-19 infection: systematic review and meta-analysis Front, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.624559
Theodoratou, Tzoulaki, Zgaga, Ioannidis, Vitamin D and multiple health outcomes: umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies and randomised trials, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.g2035
Toffanello, Perissinotto, Sergi, Zambon, Musacchio et al., Vitamin D and physical performance in elderly subjects: the Pro.V.A study, PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034950
Townsend, Dyer, Mccluskey, O'brien, Dowds et al., Investigating the relationship between vitamin D and persistent symptoms following SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072430
Wang, Kream, Stefano, Long-term respiratory and neurological sequelae of COVID-19, Med Sci. Monit, doi:10.12659/MSM.928996
Wöbke, Sorg, Steinhilber, Vitamin D in inflammatory diseases, Front. Physiol, doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00244
Zhang, Naughton, Vitamin D in health and disease: current perspectives, Nutr. J, doi:10.1186/1475-2891-9-65
Zhou, Luo, Qin, The association between vitamin D deficiency and community-acquired pneumonia: a meta-analysis of observational studies, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000017252
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684",
"ISSN": [
"0047-6374"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684",
"alternative-id": [
"S0047637422000665"
],
"article-number": "111684",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galluzzo",
"given": "Vincenzo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ciciarello",
"given": "Francesca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tosato",
"given": "Matteo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zazzara",
"given": "Maria Beatrice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pais",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Savera",
"given": "Giulia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Calvani",
"given": "Riccardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Picca",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marzetti",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Landi",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Mechanisms of Ageing and Development",
"container-title-short": "Mechanisms of Ageing and Development",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-11T17:06:56Z",
"timestamp": 1652288816000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-14T01:17:39Z",
"timestamp": 1652491059000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-14T01:43:24Z",
"timestamp": 1652492604337
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656633600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0047637422000665?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0047637422000665?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "111684",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12028-020-01049-4",
"article-title": "Neurological involvement in COVID-19 and potential mechanisms: a review",
"author": "Aghagoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1062",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Neurocrit. Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib1",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MEG.0000000000001808",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and the liver: overview",
"author": "Amin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "309",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib2",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide",
"author": "Amrein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1498",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib3",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.maturitas.2017.07.012",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and walking speed in older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Annweiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Maturitas",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib4",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Baktash",
"first-page": "442",
"issue": "1149",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib5",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753",
"article-title": "The link between COVID-19 and VItamin D (VIVID): a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Bassatne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib6",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/HCR.0000000000000336",
"article-title": "1-minute sit-to-stand test: systematic review of procedures, performance, and clinimetric properties",
"author": "Bohannon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib7",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrendo.2013.226",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and energy homeostasis: of mice and men",
"author": "Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "79",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib8",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2018-00126",
"article-title": "Skeletal and extraskeletal actions of vitamin D: current evidence and outstanding questions",
"author": "Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1109",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib9",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-021-00593-z",
"article-title": "The health effects of vitamin D supplementation: evidence from human studies",
"author": "Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "96",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib10",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01601.x",
"article-title": "The association between vitamin D and inflammation with the 6-minute walk and frailty in patients with heart failure",
"author": "Boxer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "454",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Geriatr. Soc.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib11",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1753466618793028",
"article-title": "The 1-minute sit-to-stand test to detect exercise-induced oxygen desaturation in patients with interstitial lung disease",
"author": "Briand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib12",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12603",
"article-title": "Against COVID-19 post-acute care study group, “persistent symptoms in patients after acute COVID-19",
"author": "Carfì",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "603",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib13",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.115.120873",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in Europe: pandemic?",
"author": "Cashman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib14",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072097",
"article-title": "Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease",
"author": "Charoenngam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib15",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db09-1011",
"article-title": "Adiposity, cardiometabolic risk, and vitamin D status: the Framingham heart study",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "242",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib16",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/oby.2011.404",
"article-title": "Volumetric dilution, rather than sequestration best explains the low vitamin D status of obesity",
"author": "Drincic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1444",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Obesity",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib17",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpregu.00322.2013",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and the heart",
"author": "Gardner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R969",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib18",
"volume": "305",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and associations with walking ability in community- dwelling elderly adults",
"author": "Geirsdottir",
"journal-title": "J. Food Nutr. Disord.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib19",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01616-x",
"article-title": "Post-COVID-19 global health strategies: the need for an interdisciplinary approach",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1613",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib20",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0889-1591(87)90013-4",
"article-title": "Stress-associated depression in cellular immunity: implications for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)",
"author": "Glaser",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav. Immun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib21",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"article-title": "The 6-minute walk: a new measure of exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure",
"author": "Guyatt",
"first-page": "919",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Can. Med. Assoc. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib22",
"volume": "132",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank Diabetes",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib23",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra070553",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "266",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib24",
"volume": "357",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0065785",
"article-title": "Vitamin D (25OHD) serum seasonality in the United States",
"author": "Kasahara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "PLOS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib25",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5888/pcd18.210123",
"article-title": "Underlying medical conditions and severe illness among 540,667 adults hospitalized with COVID-19, March 2020-March 2021",
"author": "Kompaniyets",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Prev. Chronic Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib26",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14310/horm.2002.1705",
"article-title": "Muscular effects of vitamin D in young athletes and non-athletes and in the elderly",
"author": "Koundourakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "471",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Hormones",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib27",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcsm.12610",
"article-title": "Normative values of muscle strength across ages in a ‘real world’ population: results from the longevity check-up 7+ project",
"author": "Landi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib28",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11634",
"article-title": "Assessment of the association of vitamin D level with SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity among working-age adults",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib29",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.11.021",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Lips",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "280",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib30",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab384",
"article-title": "Long-term coronavirus disease 2019 complications in inpatients and outpatients: a one-year follow-up cohort study",
"author": "Lombardo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "384",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib31",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.720363",
"article-title": "Update advances on C-reactive protein in COVID-19 and other viral infections",
"author": "Luan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-017-1564-2",
"article-title": "A systematic review of vitamin D status in southern European countries",
"author": "Manios",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2001",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib33",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib34",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"article-title": "Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study",
"author": "Merzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3693",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib35",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12979-020-00212-x",
"article-title": "Obesity and COVID-19: what makes obese host so vulnerable?",
"author": "Mohammad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Immun. Ageing",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib36",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/obr.12239",
"article-title": "Obesity and vitamin D deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pereira-Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "341",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Obes. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib37",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2014.00145",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in skeletal and cardiac muscle function",
"author": "Polly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Front. Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib38",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11122861",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and sarcopenia in older persons",
"author": "Remelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib39",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-018-19708-0",
"article-title": "Effects of vitamin D supplementation on inflammatory markers in heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Rodriguez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1169",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib40",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.24127",
"article-title": "Sorting out whether vitamin D deficiency raises COVID-19 risk",
"author": "Rubin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "329",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib41",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092879",
"article-title": "Immune modulatory effects of vitamin D on viral Infections",
"author": "Siddiqui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib42",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/B:QURE.0000018499.64574.1f",
"article-title": "Is a single-item visual analogue scale as valid, reliable and responsive as multi-item scales in measuring quality of life?",
"author": "de Boer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "311",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Qual. Life Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib43",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcp/aqaa252",
"article-title": "Serum 25(OH)D level on hospital admission associated with COVID-19 stage and mortality",
"author": "de Smet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "381",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Pathol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib44",
"volume": "155",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13030717",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and lung outcomes in elderly COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Sulli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib45",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2020.1822737",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and cardiac injury: clinical manifestations, biomarkers, mechanisms, diagnosis, treatment, and follow up",
"author": "Tajbakhsh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "345",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib46",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.624559",
"article-title": "The impact of vitamin D level on COVID-19 infection: systematic review and meta-analysis Front",
"author": "Teshome",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib47",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.g2035",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and multiple health outcomes: umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies and randomised trials",
"author": "Theodoratou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib48",
"volume": "348",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0034950",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and physical performance in elderly subjects: the Pro.V.A study",
"author": "Toffanello",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "PLOS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib49",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072430",
"article-title": "Investigating the relationship between vitamin D and persistent symptoms following SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Townsend",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib50",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Long-term respiratory and neurological sequelae of COVID-19",
"author": "Wang",
"journal-title": "Med Sci. Monit.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib51",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D in inflammatory diseases",
"author": "Wöbke",
"journal-title": "Front. Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib52",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1475-2891-9-65",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in health and disease: current perspectives",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Nutr. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib53",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000017252",
"article-title": "The association between vitamin D deficiency and community-acquired pneumonia: a meta-analysis of observational studies",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "38",
"journal-title": "Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib54",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.mad.2022.111684_bib55",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization, 2020. Criteria for releasing COVID-19 patients from isolation. https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/criteria-for-releasing-covid-19-patients-from-isolation. Accessed on 5 January 2022."
}
],
"reference-count": 55,
"references-count": 55,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0047637422000665"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Developmental Biology",
"Aging"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Association between vitamin D status and physical performance in COVID-19 survivors: Results from the Gemelli against COVID-19 post-acute care project",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "205"
}
