Assessment of the Association of Vitamin D Level With SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity Among Working-Age Adults
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11634, May 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Cohort study of 18,148 patients in the USA showing low vitamin D associated with COVID-19 PCR+ status before adjustments but not after.
Authors state that "low vitamin D levels were not independently associated with the
risk of seropositivity", however there is significant correlation between some adjustment variables and vitamin D levels in the logistic regression that prevent drawing this conclusion1. Details of the logistic regression in the matched sample set are not provided.
risk of seropositivity", however there is significant correlation between some adjustment variables and vitamin D levels in the logistic regression that prevent drawing this conclusion1. Details of the logistic regression in the matched sample set are not provided.
Authors analyze only 20ng/mL and 30ng/mL cutoff points, other studies use 10ng/mL (or 12), where more significant differences are typically seen.
This is the 65th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments2.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
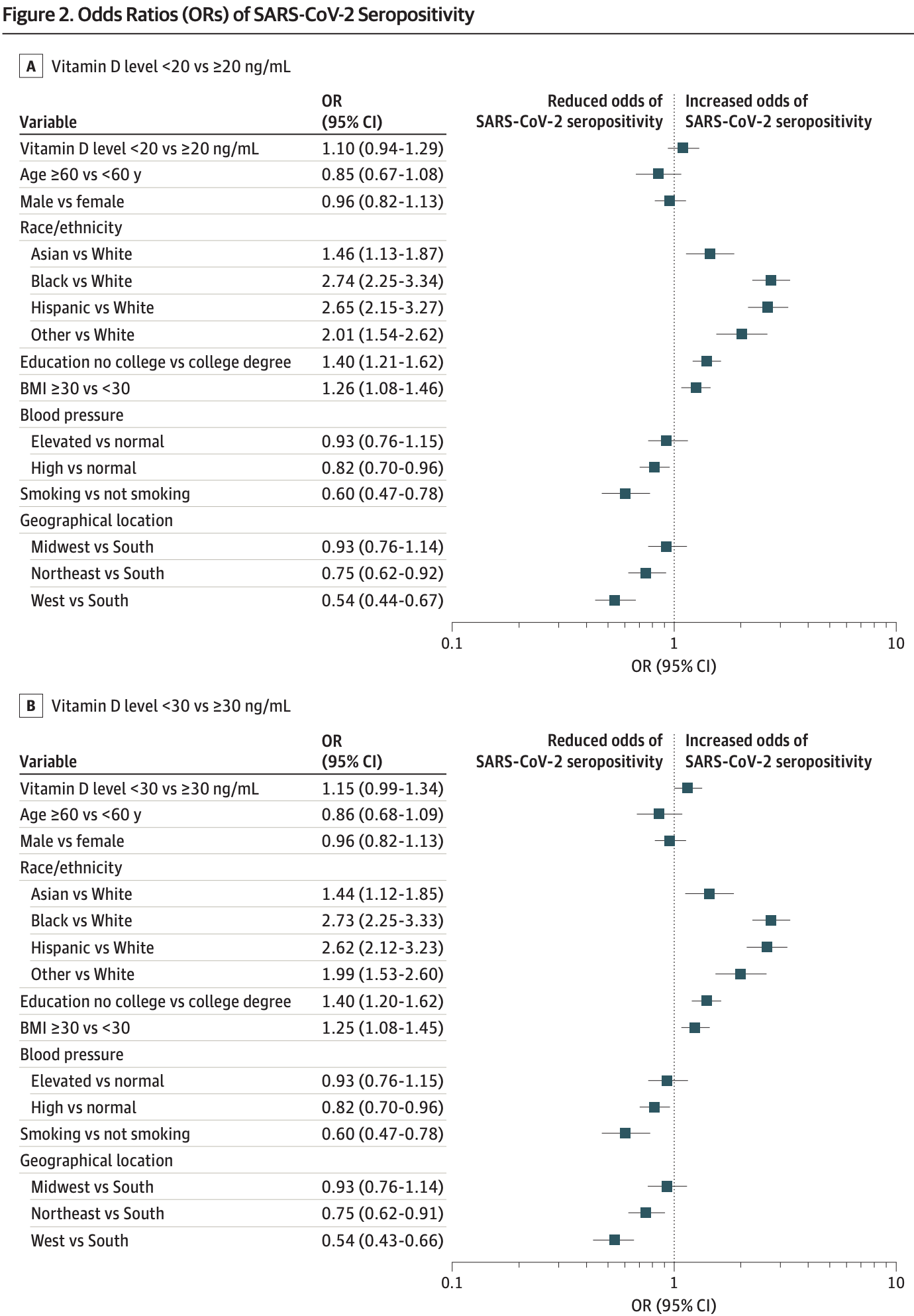
risk of case, 8.6% lower, RR 0.91, p = 0.24, high D levels 610 of 13,650 (4.5%), low D levels 290 of 4,498 (6.4%), adjusted per study, inverted to make RR<1 favor high D levels, odds ratio converted to relative risk, >20ng/mL, Figure 2.
|
|
risk of case, 12.4% lower, RR 0.88, p = 0.07, high D levels 289 of 7,272 (4.0%), low D levels 611 of 10,876 (5.6%), adjusted per study, inverted to make RR<1 favor high D levels, odds ratio converted to relative risk, >30ng/mL, Figure 2.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Li et al., 19 May 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Assessment of the Association of Vitamin D Level With SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity Among Working-Age Adults
JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11634
IMPORTANCE Low vitamin D levels have been reported to be associated with increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Independent, well-powered studies could further our understanding of this association.
OBJECTIVE To examine whether low levels of vitamin D are associated with SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity, an indicator of previous infection. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS This is a cohort study of employees and spouses who elected to be tested for SARS-CoV-2 IgG as part of an annual employer-sponsored health screening program conducted in August to November 2020. This program includes commonly assessed demographic, biometric, and laboratory variables, including total vitamin D measurement. Baseline (prepandemic) levels of vitamin D and potential confounders were obtained from screening results from the previous year (September 2019 to January 2020). Data analysis was performed from December 2020 to March 2021. EXPOSURES Low total serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, defined as either less than 20 ng/mL or less than 30 ng/mL. MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The main outcome was SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity, as determined with US Food and Drug Administration emergency use-authorized assays. The association of SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity with vitamin D levels was assessed by multivariable logistic regression analyses and propensity score analyses.
RESULTS The 18 148 individuals included in this study had test results for SARS-CoV-2 IgG in 2020 and vitamin D levels from the prepandemic and pandemic periods. Their median (interquartile range) age was 47 (37-56) years, 12 170 (67.1%) were women, 900 (5.0%) were seropositive, 4498 (24.8%) had a vitamin D level less than 20 ng/mL, and 10 876 (59.9%) had a vitamin D level less than 30 ng/mL before the pandemic. In multivariable models adjusting for age, sex, race/ethnicity, education, body mass index, blood pressure, smoking status, and geographical location, SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity was not associated with having a vitamin D level less than 20 ng/mL before (odds ratio [OR], 1.04; 95% CI, 0.88-1.22) or during (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.79-1.09) the pandemic; it was also not associated with having a vitamin D level less than 30 ng/mL before (OR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.93-1.27) or during (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.91-1.23) the pandemic. Similar results were observed in propensity score
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None reported. Funding/Support: Quest Diagnostics provided funding for this study.
Role of the Funder/Sponsor: The funder had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, and decision to submit the manuscript for publication. The funder reviewed and approved the manuscript. Additional Contributions: Jeff Radcliff, BS (Director, Global Scientific Publications and Medical Education, Quest Diagnostics), edited the manuscript; Andre A. Arellano, BS (Staff Scientist, Quest Diagnostics), helped with data acquisition; and Charles M. Rowland, MS (Director of Science, Quest Diagnostics), provided statistical advice. No compensation was received beyond usual salary.
References
Cohen, Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051359
Faniyi, Lugg, Faustini, Vitamin D status and seroconversion for COVID-19 in UK healthcare workers, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.04234-2020
Faries, Leon, Haro, Obenchain, Analysis of Observational Health Care Data Using SAS
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Endocrine Society. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
Kaufman, Niles, Kroll, Bi, Holick, SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239252
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA Netw Open, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2021.11634
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Ogedegbe, Ravenell, Adhikari, Assessment of racial/ethnic disparities in hospitalization and mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York City, JAMA Netw Open, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.26881&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2021.11634
Simons, Shahab, Brown, Perski, The association of smoking status with SARS-CoV-2 infection, hospitalization and mortality from COVID-19: a living rapid evidence review with Bayesian meta-analyses (version 7), doi:10.1111/add.15276
Sims, Maine, Childers, COVID-19 seropositivity and asymptomatic rates in healthcare workers are associated with job function and masking, Clin Infect Dis. Published online, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1684
Wadhera, Wadhera, Gaba, Variation in COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths across New York City boroughs, JAMA, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jama.2020.7197&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2021.11634
Yanes-Lane, Winters, Fregonese, Proportion of asymptomatic infection among COVID-19 positive persons and their transmission potential: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0241536
Yetley, Assessing the vitamin D status of the US population, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/88.2.558S
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11634",
"ISSN": [
"2574-3805"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11634",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Quest Diagnostics, San Juan Capistrano, California"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Yonghong",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Quest Diagnostics, San Juan Capistrano, California"
}
],
"family": "Tong",
"given": "Carmen H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Quest Diagnostics, San Juan Capistrano, California"
}
],
"family": "Bare",
"given": "Lance A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Quest Diagnostics, San Juan Capistrano, California"
}
],
"family": "Devlin",
"given": "James J.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Netw Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-19T15:52:01Z",
"timestamp": 1621439521000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-19T15:52:07Z",
"timestamp": 1621439527000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-16T13:06:35Z",
"timestamp": 1710594395688
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 22,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/articlepdf/2779952/li_2021_oi_210346_1620403788.60017.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e2111634",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.26881",
"article-title": "Assessment of racial/ethnic disparities in hospitalization and mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York City.",
"author": "Ogedegbe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "zoi210346r1",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsa2011686",
"article-title": "Hospitalization and mortality among black patients and white patients with Covid-19.",
"author": "Price-Haywood",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2534",
"issue": "26",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi210346r2",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.7197",
"article-title": "Variation in COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths across New York City boroughs.",
"author": "Wadhera",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2192",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "zoi210346r3",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results.",
"author": "Meltzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "zoi210346r4",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239252",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 positivity rates associated with circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels.",
"author": "Kaufman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "zoi210346r5",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.v287.17",
"article-title": "Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study.",
"author": "Merzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3693",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "FEBS J",
"key": "zoi210346r6",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/88.2.558S",
"article-title": "Assessing the vitamin D status of the US population.",
"author": "Yetley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "558S",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "zoi210346r7",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"article-title": "Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline.",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1911",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "zoi210346r8",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"article-title": "25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "D’Avolio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1359",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "zoi210346r11",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and seroconversion for COVID-19 in UK healthcare workers.",
"author": "Faniyi",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "zoi210346r12",
"volume": "2004234",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0241536",
"article-title": "Proportion of asymptomatic infection among COVID-19 positive persons and their transmission potential: a systematic review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Yanes-Lane",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "zoi210346r13",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank.",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "561",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "zoi210346r14",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 seropositivity and asymptomatic rates in healthcare workers are associated with job function and masking.",
"author": "Sims",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "zoi210346r15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The association of smoking status with SARS-CoV-2 infection, hospitalization and mortality from COVID-19: a living rapid evidence review with Bayesian meta-analyses (version 7).",
"author": "Simons",
"journal-title": "Addiction",
"key": "zoi210346r16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Faries",
"key": "zoi210346r9",
"volume-title": "Analysis of Observational Health Care Data Using SAS",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"author": "Cohen",
"edition": "2nd ed",
"key": "zoi210346r10",
"volume-title": "Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences",
"year": "1988"
}
],
"reference-count": 16,
"references-count": 16,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2779952"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Assessment of the Association of Vitamin D Level With SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity Among Working-Age Adults",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "4"
}
