Liver injury in non-severe COVID-19 with various pandemic phases: a real-world study
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3484296/v1, Oct 2023
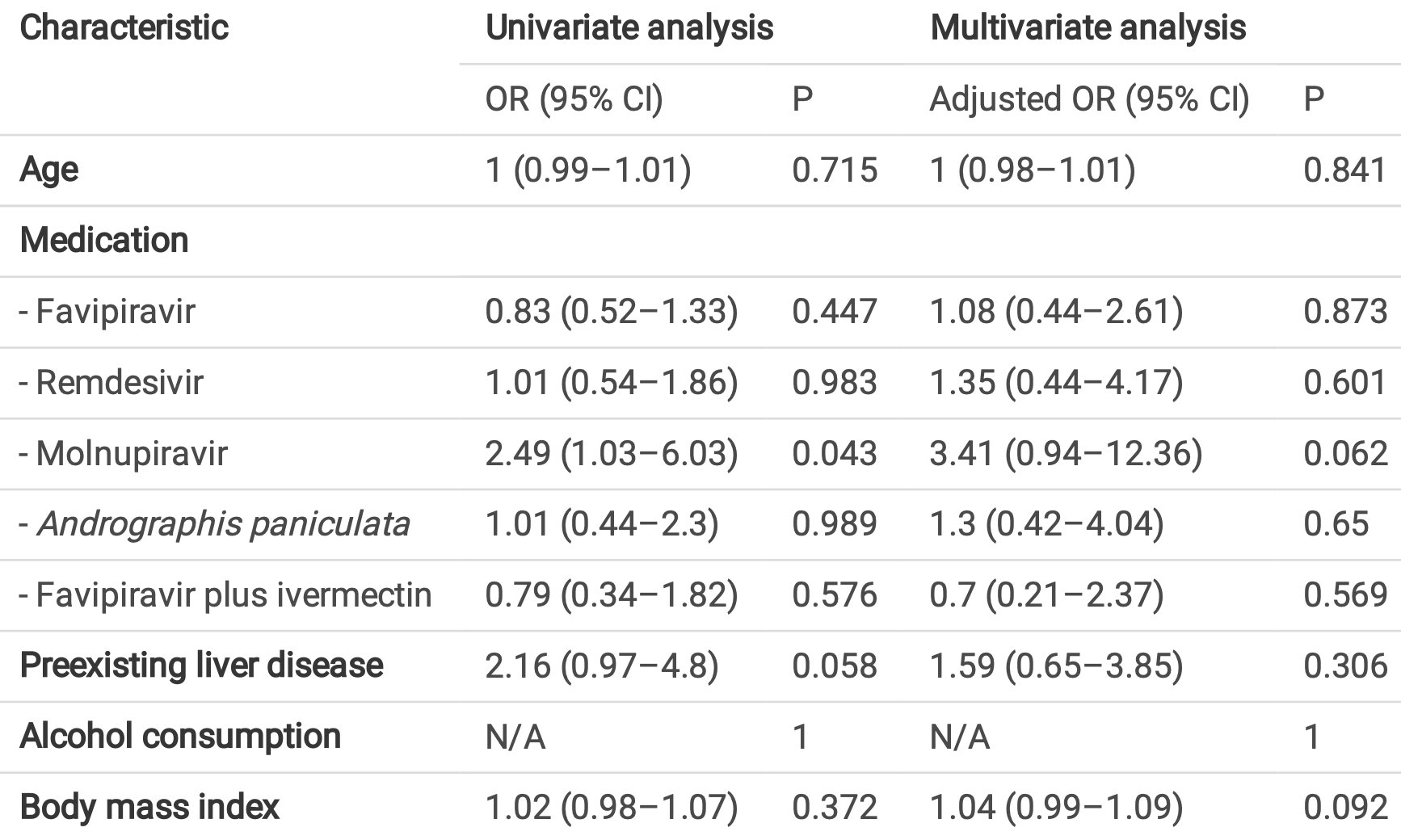
Prospective study of 300 patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 in Thailand, showing the highest risk of liver injury with molnupiravir treatment, OR 3.4 (p = 0.06).
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
|
liver injury, 241.0% higher, OR 3.41, p = 0.06, treatment 22, control 278, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
Winyupakorn et al., 31 Oct 2023, prospective, Thailand, preprint, 4 authors, study period September 2021 - October 2022.
Contact: supatsri@nmu.ac.th.
Liver injury in non-severe COVID-19 with various pandemic phases: a real-world study
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3484296/v1
The using of a variety of anti-COVID-19 medicines connected to the degree of liver impairment in the short term was intriguing. To evaluate the dynamic course of liver injury in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 within 10 days of admission. This was a prospective cohort study of 300 patients who were newly proven mild to moderate COVID-19 between September 2021 and October 2022. There were 188 patients in hospitel/ eld hospital (n = 188) and cohort wards (n = 112). One hundred and fteen patients (38.3%) suffered from liver injury (LI). The majority of Group LI participants (n = 104) received medication to treat the COVID-19 infection, including favipiravir (45%), remdesivir (17.4%), molnupiravir (11.3%), Andrographis paniculata (ADG) (8.7%), and favipiravir in combination with ivermectin (7.7%). When compared to no LI, molnupiravir medication was linked with the largest proportion of transaminase < 2 and 2-5 times the ULN [11.3% vs. 4.9%, p = 0.038; 15.2% vs. 4.9%, p = 0.013]. After 10 days, the majority of patients exhibited a transaminase decline. A less-than-critical level of liver damage was reported in mild to moderate COVID-19 that allows clinicians to administer a variety of standard medications during short periods of hospital stay.
We emphasized the real-world dynamics of LI in mild to moderate COVID-19, the less-than-critical state of liver impairment that enables physicians to give a variety of common drugs over the course of the entire hospitalization period.
Declarations Data availability The data used in this work are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Asselah, Durantel, Pasmant, Lau, Schinazi, COVID-19: Discovery, diagnostics and drug development, J Hepatol
Cai, Huang, Yu, Zhu, Xia et al., COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests, J Hepatol
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Fan, Chen, Li, Cheng, Yang et al., Clinical Features of COVID-19-Related Liver Functional Abnormality, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Hundt, Deng, Ciarleglio, Nathanson, Lim, Abnormal Liver Tests in COVID-19: A Retrospective Observational Cohort Study of 1,827 Patients in a Major U, S. Hospital Network. Hepatology
Ji, Qin, Xu, Zhang, Cheng et al., Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective study, J Hepatol
Kaewdech, Nawalerspanya, Assawasuwannakit, Chamroonkul, Jandee et al., The use of Andrographis paniculata and its effects on liver biochemistry of patients with gastrointestinal problems in Thailand during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross sectional study, Sci Rep
Kaneko, Kurosaki, Nagata, Taki, Ueda et al., Liver injury with COVID-19 based on gastrointestinal symptoms and pneumonia severity, PLoS One
Kulkarni, Kumar, Tevethia, Premkumar, Arab et al., Systematic review with meta-analysis: liver manifestations and outcomes in COVID-19, Aliment Pharmacol Ther
Li, Moore, Vasilieva, Sui, Wong et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus, Nature
Ortiz, Lenhart, Becker, Schwambach, Tovo et al., Drug-induced liver injury and COVID-19: A review for clinical practice, World J Hepatol
Phipps, Barraza, Lasota, Sobieszczyk, Pereira et al., Acute Liver Injury in COVID-19: Prevalence and Association with Clinical Outcomes in a Large U, Hepatology
Pontolillo, Ucciferri, Borrelli, Nicola, Vecchiet et al., Molnupiravir as an Early Treatment for COVID-19: A Real Life Study, Pathogens
Singh, Khan, Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Among Patients With Preexisting Liver Disease in the United States: A Multicenter Research Network Study, Gastroenterology
Sodei An, Seyedalhosseini, Kian, Eftekhari, Najari et al., Drug-Induced Liver Injury in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review, Front Med
Songvut, Suriyo, Panomvana, Rangkadilok, Satayavivad, A comprehensive review on disposition kinetics and dosage of oral administration of Andrographis paniculata, an alternative herbal medicine, in co-treatment of coronavirus disease, Front Pharmacol
Vespa, Pugliese, Piovani, Capogreco, Danese et al., Liver tests abnormalities in COVID-19: trick or treat?, J Hepatol
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, Jama
Wijarnpreecha, Ungprasert, Panjawatanan, Harnois, Zaver et al., COVID-19 and liver injury: a meta-analysis, Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Bacon, Bates et al., Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY, Nature
Yu, Du, Yan, Guo, He et al., Liver injury in COVID-19: clinical features and treatment management, Virol J
Zhang, Shi, Wang, Liver injury in COVID-19: management and challenges, Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-3484296/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3484296/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The using of a variety of anti-COVID-19 medicines connected to the degree of liver impairment in the short term was intriguing. To evaluate the dynamic course of liver injury in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 within 10 days of admission. This was a prospective cohort study of 300 patients who were newly proven mild to moderate COVID-19 between September 2021 and October 2022. There were 188 patients in hospitel/field hospital (n = 188) and cohort wards (n = 112). One hundred and fifteen patients (38.3%) suffered from liver injury (LI). The majority of Group LI participants (n = 104) received medication to treat the COVID-19 infection, including favipiravir (45%), remdesivir (17.4%), molnupiravir (11.3%), Andrographis paniculata (ADG) (8.7%), and favipiravir in combination with ivermectin (7.7%). When compared to no LI, molnupiravir medication was linked with the largest proportion of transaminase < 2 and 2–5 times the ULN [11.3% vs. 4.9%, p = 0.038; 15.2% vs. 4.9%, p = 0.013]. After 10 days, the majority of patients exhibited a transaminase decline. A less-than-critical level of liver damage was reported in mild to moderate COVID-19 that allows clinicians to administer a variety of standard medications during short periods of hospital stay.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
24
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vajira Hospital, Navamindradhiraj University"
}
],
"family": "Winyupakorn",
"given": "Jirayuth",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vajira Hospital, Navamindradhiraj University"
}
],
"family": "Sangketchon",
"given": "Chunlanee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vajira Hospital, Navamindradhiraj University"
}
],
"family": "Ayutthaya",
"given": "Watcharaporn Devakul Na",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vajira Hospital, Navamindradhiraj University"
}
],
"family": "Sethasine",
"given": "Supatsri",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-31T20:51:28Z",
"timestamp": 1698785488000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-31T20:51:52Z",
"timestamp": 1698785512000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-01T07:04:38Z",
"timestamp": 1698822278273
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1698710400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-3484296/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-3484296/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.09.031",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Discovery, diagnostics and drug development",
"author": "Asselah T",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Asselah T, Durantel D, Pasmant E, Lau G, Schinazi RF. COVID-19: Discovery, diagnostics and drug development. J Hepatol. 2021;74(1):168–84.",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature02145",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus",
"author": "Li W",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "450",
"issue": "6965",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Li W, Moore MJ, Vasilieva N, Sui J, Wong SK, Berne MA, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature. 2003;426(6965):450–4.",
"volume": "426",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-021-01593-1",
"article-title": "Liver injury in COVID-19: clinical features and treatment management",
"author": "Yu D",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "121",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Virol J",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Yu D, Du Q, Yan S, Guo XG, He Y, Zhu G, et al. Liver injury in COVID-19: clinical features and treatment management. Virol J. 2021;18(1):121.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study",
"author": "Chen N",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):507–13.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang D",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. Jama. 2020;323(11):1061–9.",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan WJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1708–20.",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.006",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests",
"author": "Cai Q",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "566",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Cai Q, Huang D, Yu H, Zhu Z, Xia Z, Su Y, et al. COVID-19: Abnormal liver function tests. J Hepatol. 2020;73(3):566–74.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0241663",
"article-title": "Liver injury with COVID-19 based on gastrointestinal symptoms and pneumonia severity",
"author": "Kaneko S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0241663",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Kaneko S, Kurosaki M, Nagata K, Taki R, Ueda K, Hanada S, et al. Liver injury with COVID-19 based on gastrointestinal symptoms and pneumonia severity. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):e0241663.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15916",
"article-title": "Systematic review with meta-analysis: liver manifestations and outcomes in COVID-19",
"author": "Kulkarni AV",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "584",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Aliment Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Kulkarni AV, Kumar P, Tevethia HV, Premkumar M, Arab JP, Candia R, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: liver manifestations and outcomes in COVID-19. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;52(4):584–99.",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.31404",
"article-title": "Acute Liver Injury in COVID-19: Prevalence and Association with Clinical Outcomes in a Large U.S. Cohort",
"author": "Phipps MM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "807",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Phipps MM, Barraza LH, LaSota ED, Sobieszczyk ME, Pereira MR, Zheng EX, et al. Acute Liver Injury in COVID-19: Prevalence and Association with Clinical Outcomes in a Large U.S. Cohort. Hepatology. 2020;72(3):807–17.",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.002",
"article-title": "Clinical Features of COVID-19-Related Liver Functional Abnormality",
"author": "Fan Z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1561",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Fan Z, Chen L, Li J, Cheng X, Yang J, Tian C, et al. Clinical Features of COVID-19-Related Liver Functional Abnormality. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(7):1561–6.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.044",
"article-title": "Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective study",
"author": "Ji D",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Ji D, Qin E, Xu J, Zhang D, Cheng G, Wang Y, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective study. J Hepatol. 2020;73(2):451–3.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.033",
"article-title": "Liver tests abnormalities in COVID-19: trick or treat?",
"author": "Vespa E",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1275",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Vespa E, Pugliese N, Piovani D, Capogreco A, Danese S, Aghemo A. Liver tests abnormalities in COVID-19: trick or treat? J Hepatol. 2020;73(5):1275–6.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.31487",
"article-title": "Abnormal Liver Tests in COVID-19: A Retrospective Observational Cohort Study of 1,827 Patients in a Major U.S. Hospital Network",
"author": "Hundt MA",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1169",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Hundt MA, Deng Y, Ciarleglio MM, Nathanson MH, Lim JK. Abnormal Liver Tests in COVID-19: A Retrospective Observational Cohort Study of 1,827 Patients in a Major U.S. Hospital Network. Hepatology. 2020;72(4):1169–76.",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-23189-7",
"article-title": "The use of Andrographis paniculata and its effects on liver biochemistry of patients with gastrointestinal problems in Thailand during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross sectional study",
"author": "Kaewdech A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18213",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Kaewdech A, Nawalerspanya S, Assawasuwannakit S, Chamroonkul N, Jandee S, Sripongpun P. The use of Andrographis paniculata and its effects on liver biochemistry of patients with gastrointestinal problems in Thailand during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross sectional study. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):18213.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.952660",
"article-title": "A comprehensive review on disposition kinetics and dosage of oral administration of Andrographis paniculata, an alternative herbal medicine, in co-treatment of coronavirus disease",
"author": "Songvut P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "952660",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Songvut P, Suriyo T, Panomvana D, Rangkadilok N, Satayavivad J. A comprehensive review on disposition kinetics and dosage of oral administration of Andrographis paniculata, an alternative herbal medicine, in co-treatment of coronavirus disease. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:952660.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.1143",
"article-title": "Drug-induced liver injury and COVID-19: A review for clinical practice",
"author": "Ortiz GX",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1143",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "World J Hepatol",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Ortiz GX, Lenhart G, Becker MW, Schwambach KH, Tovo CV, Blatt CR. Drug-induced liver injury and COVID-19: A review for clinical practice. World J Hepatol. 2021;13(9):1143–53.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.731436",
"article-title": "Drug-Induced Liver Injury in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Sodeifian F",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "731436",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Sodeifian F, Seyedalhosseini ZS, Kian N, Eftekhari M, Najari S, Mirsaeidi M, et al. Drug-Induced Liver Injury in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:731436.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens11101121",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir as an Early Treatment for COVID-19: A Real Life Study",
"author": "Pontolillo M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Pathogens",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Pontolillo M, Ucciferri C, Borrelli P, Di Nicola M, Vecchiet J, Falasca K. Molnupiravir as an Early Treatment for COVID-19: A Real Life Study. Pathogens. 2022;11(10).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MEG.0000000000001817",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and liver injury: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Wijarnpreecha K",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "990",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Wijarnpreecha K, Ungprasert P, Panjawatanan P, Harnois DM, Zaver HB, Ahmed A, et al. COVID-19 and liver injury: a meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;33(7):990–5.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30057-1",
"article-title": "Liver injury in COVID-19: management and challenges",
"author": "Zhang C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "428",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Zhang C, Shi L, Wang FS. Liver injury in COVID-19: management and challenges. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(5):428–30.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.04.064",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Among Patients With Preexisting Liver Disease in the United States: A Multicenter Research Network Study",
"author": "Singh S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "768",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Singh S, Khan A. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Among Patients With Preexisting Liver Disease in the United States: A Multicenter Research Network Study. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(2):768 – 71.e3.",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"article-title": "Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY",
"author": "Williamson EJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"issue": "7821",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Williamson EJ, Walker AJ, Bhaskaran K, Bacon S, Bates C, Morton CE, et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature. 2020;584(7821):430–6.",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-3484296/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Liver injury in non-severe COVID-19 with various pandemic phases: a real-world study",
"type": "posted-content"
}