Safety and Effectiveness of SA58 Nasal Spray against SARS-CoV-2 family transmission: an exploratory single-arm trial
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.03.19.23287462, NCT05667714, Mar 2023
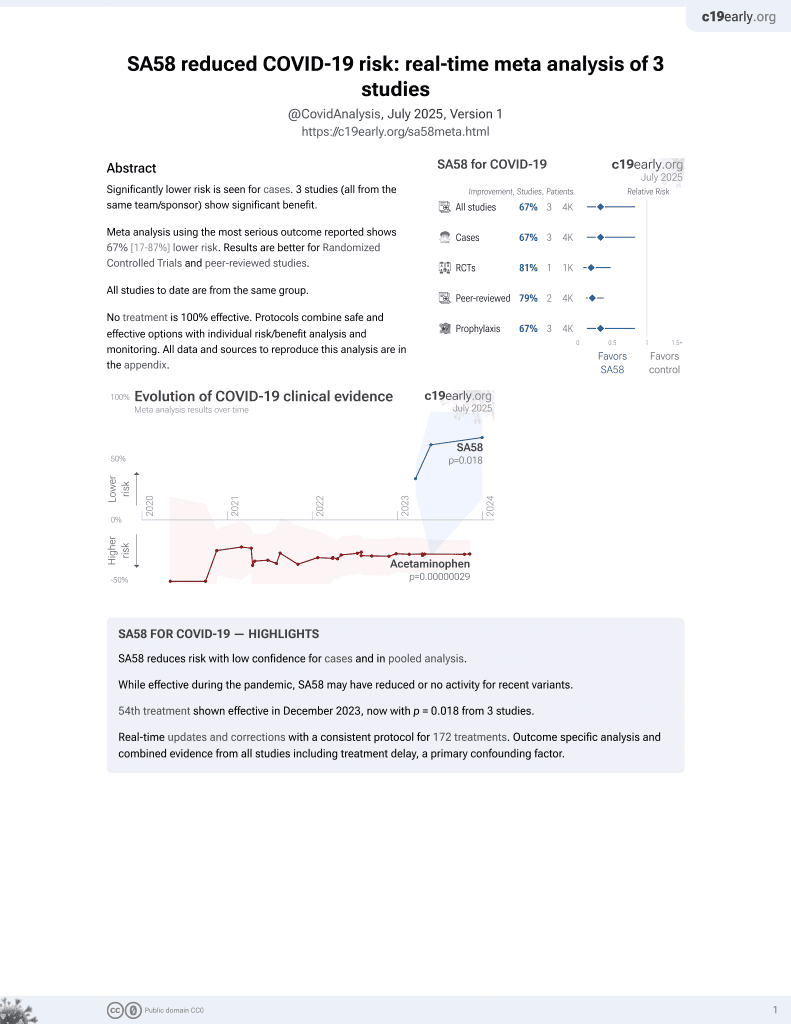
SA58 for COVID-19
55th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2023, now with p = 0.018 from 3 studies.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
Lower risk for cases.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
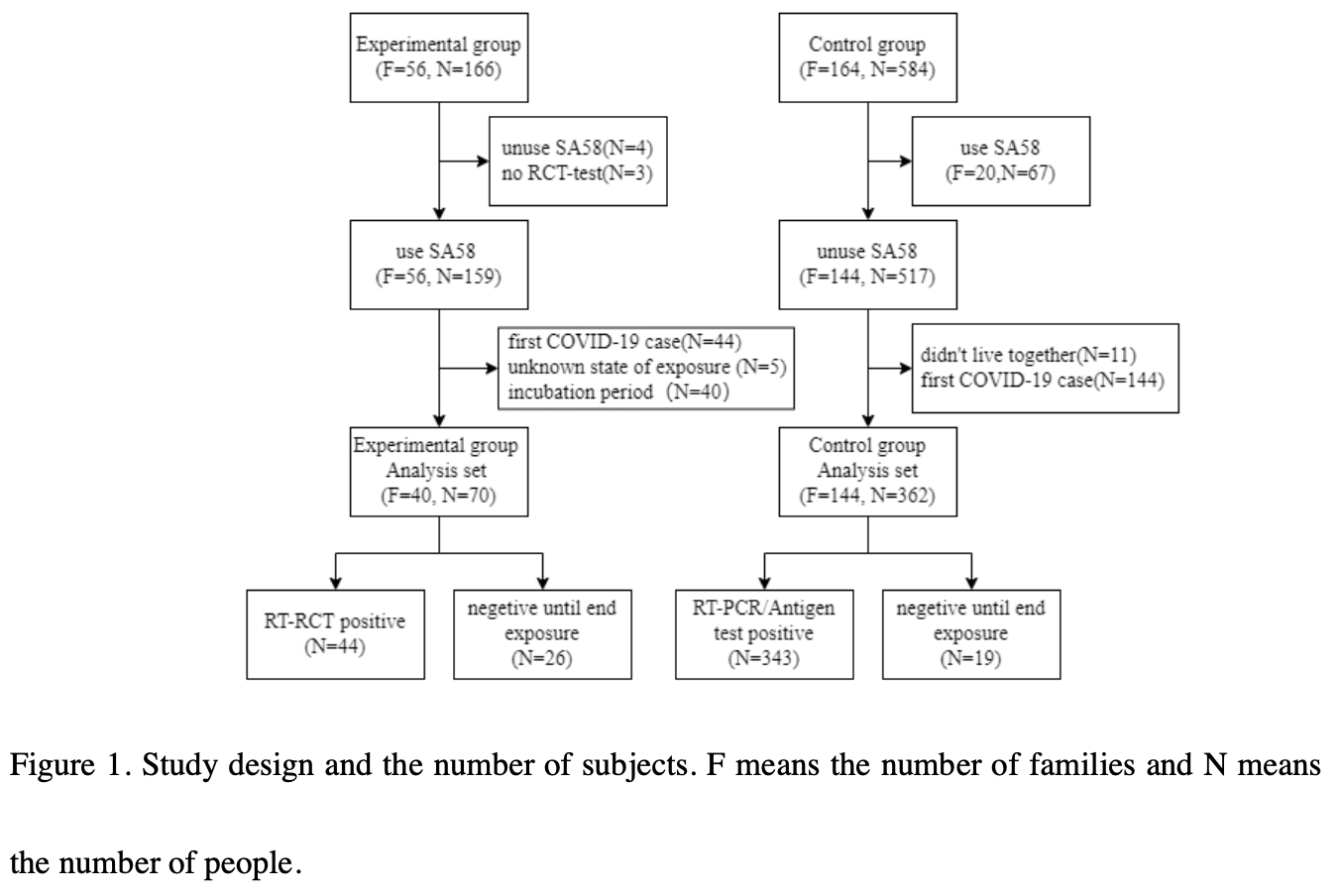
Exploratory single-arm trial of 70 family contacts showing a protective effect of SA58 nasal spray against household SARS-CoV-2 transmission. The incidence of infection was 62.9% in the experimental group versus 94.8% in a contemporaneous control group (n=362), suggesting that SA58 nasal spray reduced transmission risk by 33.8% overall. Using SA58 at least three times daily showed better protection than once a day.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments4.
|
risk of case, 33.7% lower, RR 0.66, p < 0.001, treatment 44 of 70 (62.9%), control 343 of 362 (94.8%), NNT 3.1.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Si et al., Safety and Effectiveness of SA58 Nasal Spray Against COVID-19 Infection in Medical Personnel: An Open-Label, Blank-Controlled Study — Hohhot City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China, 2022, China CDC Weekly, doi:10.46234/ccdcw2023.040.
2.
Song et al., Post-exposure prophylaxis with SA58 (anti-SARS-COV-2 monoclonal antibody) nasal spray for the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19 in healthy adult workers: a randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2023.2212806.
Wang et al., 20 Mar 2023, prospective, China, preprint, 15 authors, study period 9 November, 2022 - 24 November, 2022, trial NCT05667714 (history).
Contact: ronghuajin_youan@126.com, gaoq@sinovac.com.
Safety and Effectiveness of SA58 Nasal Spray against SARS-CoV-2 family transmission: an exploratory single-arm trial
doi:10.1101/2023.03.19.23287462
Background: This study has assessed the protective effect of a new Anti-COVID-19 SA58 Nasal Spray (SA58 Nasal Spray) against SARS-CoV-2 infection under continuous exposure. Methods: This is an exploratory open-label, single-arm trial. To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of SA58 against SARS-CoV-2 family transmission, SA58 was administered to all enrolled family contacts at 3~6-hour intervals. The frequency of administration and adverse events (AEs) were self-reported by online questionnaire, and RT-PCR tests were used to diagnose SARS-CoV-2 infection. The effectiveness was assessed in comparison to a contemporaneous control group whose information was collected through three follow-up visits. Total effectiveness and single-day effectiveness were calculated.
Results: The incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection was 62.9% (44/70) in the experimental group and 94.8% (343/362) in the control group. Using SA58 nasal spray at least three times per day could possibly reduce the risk of household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by 46.7%~56.5%. The incidence of AEs was 41.4% and the severity of all AEs was mild.
Conclusion: Even under the scenario of continuous exposure to SARS-CoV-2, SA58 nasal spray remained effective in blocking viral transmission and was well tolerated.
References
Cao, Jian, Zhang, Rational identification of potent and broad sarbecovirus-neutralizing antibody cocktails from SARS convalescents, Cell reports
Cao, Su, Guo, Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Identified by High-Throughput Single-Cell Sequencing of Convalescent Patients' B Cells, Cell
Cao, Wang, Jian, Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, Nature
Du, Yang, Zhang, Neutralizing antibodies for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, Cellular & molecular immunology
Garcia-Beltran, Lam, Denis, Multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants escape neutralization by vaccine-induced humoral immunity, Cell
Lu, Mok, Chen, Neutralization of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Omicron Variant by Sera From BNT162b2 or CoronaVac Vaccine Recipients, Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America
Nyberg, Ferguson, Nash, Comparative analysis of the risks of hospitalisation and death associated with SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B.1.1.529) and delta (B.1.617.2) variants in England: a cohort study, Lancet
Si, Cao, Safety and Effectiveness of SA58 Nasal Spray against COVID-19 Infection in Medical Personnel:An Open-label, Blank-controlled Study, medRxiv
Song, Zeng, Yu, Post-Exposure Prophylaxis with SA58 (anti-COVID-19 monoclonal antibody) Nasal Spray for the prevention of symptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019 in healthy adult workers: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, medRxiv
Wang, Iketani, Li, Alarming antibody evasion properties of rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB subvariants, Cell
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.03.19.23287462",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.19.23287462",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>This study has assessed the protective effect of a new Anti-COVID-19 SA58 Nasal Spray (SA58 Nasal Spray) against SARS-CoV-2 infection under continuous exposure.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This is an exploratory open-label, single-arm trial. To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of SA58 against SARS-CoV-2 family transmission, SA58 was administered to all enrolled family contacts at 3∼6-hour intervals. The frequency of administration and adverse events (AEs) were self-reported by online questionnaire, and RT-PCR tests were used to diagnose SARS-CoV-2 infection. The effectiveness was assessed in comparison to a contemporaneous control group whose information was collected through three follow-up visits. Total effectiveness and single-day effectiveness were calculated.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>The incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection was 62.9% (44/70) in the experimental group and 94.8% (343/362) in the control group. Using SA58 nasal spray at least three times per day could possibly reduce the risk of household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by 46.7%∼56.5%. The incidence of AEs was 41.4% and the severity of all AEs was mild.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Even under the scenario of continuous exposure to SARS-CoV-2, SA58 nasal spray remained effective in blocking viral transmission and was well tolerated.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
20
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Lianhao",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Rui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Yuansheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeng",
"given": "Gang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Keqiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Jianfeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bao",
"given": "Yafeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Yun’ao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Long",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Can",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pu",
"given": "Junfan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Han",
"given": "Xing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Junlan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jin",
"given": "Ronghua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Qiang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-20T22:55:10Z",
"timestamp": 1679352910000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-23T19:15:24Z",
"timestamp": 1679598924000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-24T04:45:19Z",
"timestamp": 1679633119686
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
20
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2023.03.19.23287462",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
20
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. COVID-19 vaccine tracker and landscape. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-candidate-vaccines/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.013",
"article-title": "Multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants escape neutralization by vaccine-induced humoral immunity",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2372",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.2",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab1041",
"article-title": "Neutralization of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Omicron Variant by Sera From BNT162b2 or CoronaVac Vaccine Recipients",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e822",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America",
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.3",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.4",
"unstructured": "Geneva: World Health Organization. WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Available at: https://covid19.who.int/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00462-7",
"article-title": "Comparative analysis of the risks of hospitalisation and death associated with SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B.1.1.529) and delta (B.1.617.2) variants in England: a cohort study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1303",
"issue": "10332",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London, England)",
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.5",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.6",
"unstructured": "Health CfHPotDo. Provisional Data Analysis on COVID-19 Reported Death Cases."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-021-00752-2",
"article-title": "Neutralizing antibodies for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2293",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Cellular & molecular immunology",
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.7",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3",
"article-title": "Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "657",
"issue": "7898",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.8",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.025",
"article-title": "Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Identified by High-Throughput Single-Cell Sequencing of Convalescent Patients’ B Cells",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.9",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.11.23.517532",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.10",
"unstructured": "Wang Q , Iketani S , Li Z , et al. Alarming antibody evasion properties of rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB subvariants. Cell 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111845",
"article-title": "Rational identification of potent and broad sarbecovirus-neutralizing antibody cocktails from SARS convalescents",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111845",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Cell reports",
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.11",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.12.27.22283698",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.12",
"unstructured": "Si S , Jin C , Cao Y , et al. Safety and Effectiveness of SA58 Nasal Spray against COVID-19 Infection in Medical Personnel:An Open-label, Blank-controlled Study. medRxiv 2022: 2022.12.27.22283698."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.12.28.22283666",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2023032312150806000_2023.03.19.23287462v1.13",
"unstructured": "Song R , Zeng G , Yu J , et al. Post-Exposure Prophylaxis with SA58 (anti-COVID-19 monoclonal antibody) Nasal Spray for the prevention of symptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019 in healthy adult workers: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. medRxiv 2023: 2022.12.28.22283666."
}
],
"reference-count": 13,
"references-count": 13,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2023.03.19.23287462"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Safety and Effectiveness of SA58 Nasal Spray against SARS-CoV-2 family transmission: an exploratory single-arm trial",
"type": "posted-content"
}