Pyrimidine inhibitors synergize with nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2
et al., Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04482-x, Feb 2022
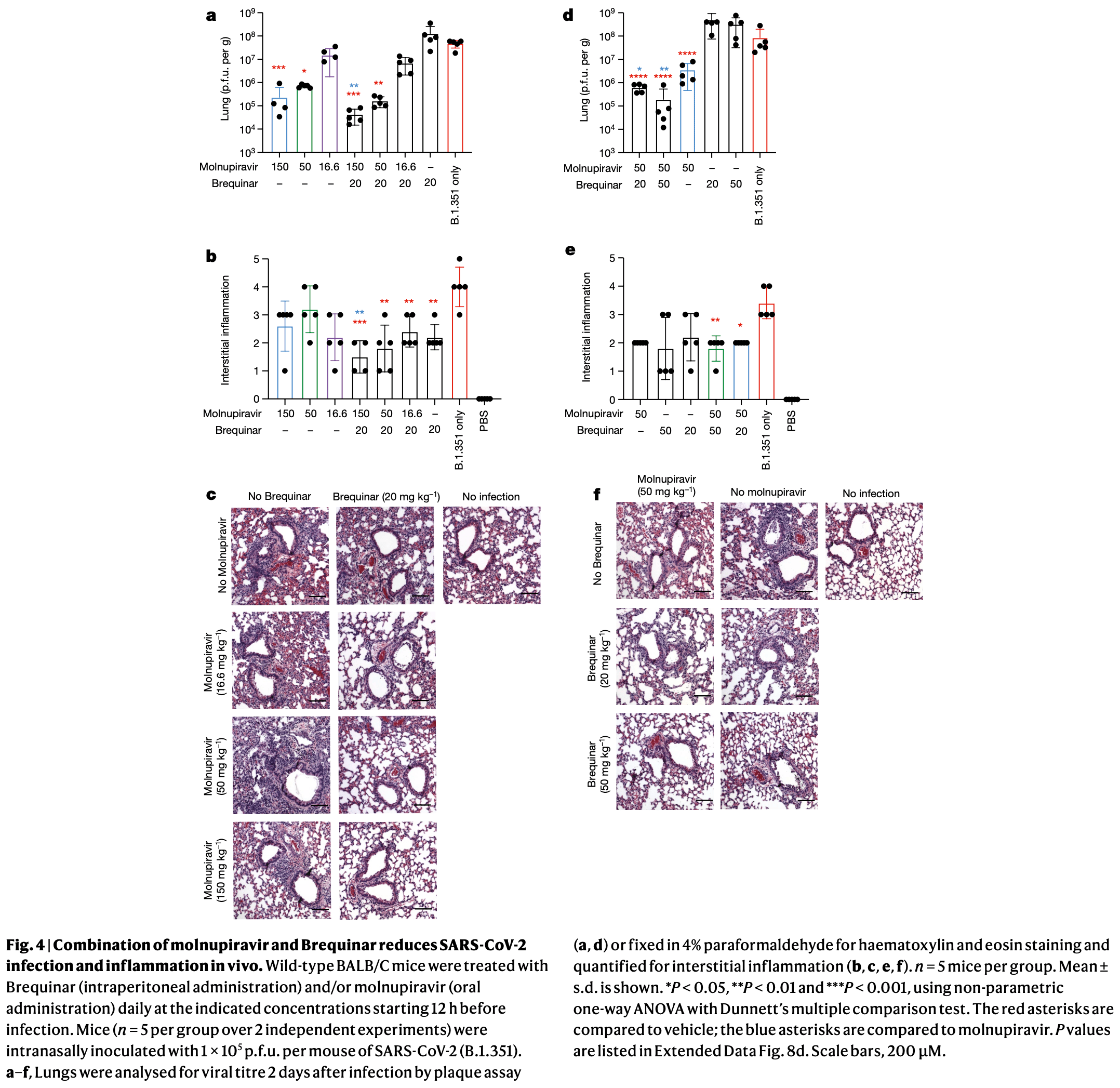
In vitro and mouse study showing synergistic antiviral effects when combining pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitors with antiviral nucleoside analogues against SARS-CoV-2. Authors screened 18 thousand drugs and validated 122 with antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in human respiratory cells, including remdesivir, molnupiravir, camostat, nafamostat, and artesunate. Pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitors such as brequinar and BAY-2402234 (DHODH inhibitors) showed modest antiviral activity alone but demonstrated strong synergy when combined with molnupiravir or remdesivir. In mouse models infected with the SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant, the combination of molnupiravir with brequinar showed significantly reduced viral titers (up to 4-log reduction) and decreased lung inflammation compared to either drug alone. The synergistic effect was observed in multiple cell types and was effective against multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Schultz et al., 7 Feb 2022, USA, peer-reviewed, 22 authors.
Contact: dschultz@pennmedicine.upenn.edu, mfrieman@som.umaryland.edu, cherrys@pennmedicine.upenn.edu.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Abstract: Article
Pyrimidine inhibitors synergize with
nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04482-x
Received: 22 October 2021
Accepted: 26 January 2022
Published online: 7 February 2022
David C. Schultz1 ✉, Robert M. Johnson2,8, Kasirajan Ayyanathan3,8, Jesse Miller3,8,
Kanupriya Whig1, Brinda Kamalia1, Mark Dittmar3, Stuart Weston2, Holly L. Hammond2,
Carly Dillen2, Jeremy Ardanuy2, Louis Taylor2, Jae Seung Lee3, Minghua Li3, Emily Lee4,
Clarissa Shoffler5, Christopher Petucci5, Samuel Constant6, Marc Ferrer4,
Christoph A. Thaiss7, Matthew B. Frieman2 ✉ & Sara Cherry1,3,7 ✉
Check for updates
The SARS-CoV-2 virus has infected more than 261 million people and has led to more
than 5 million deaths in the past year and a half1 (https://www.who.org/). Individuals
with SARS-CoV-2 infection typically develop mild-to-severe flu-like symptoms,
whereas infection of a subset of individuals leads to severe-to-fatal clinical outcomes2.
Although vaccines have been rapidly developed to combat SARS-CoV-2, there has
been a dearth of antiviral therapeutics. There is an urgent need for therapeutics,
which has been amplified by the emerging threats of variants that may evade vaccines.
Large-scale efforts are underway to identify antiviral drugs. Here we screened
approximately 18,000 drugs for antiviral activity using live virus infection in human
respiratory cells and validated 122 drugs with antiviral activity and selectivity against
SARS-CoV-2. Among these candidates are 16 nucleoside analogues, the largest
category of clinically used antivirals. This included the antivirals remdesivir and
molnupiravir, which have been approved for use in COVID-19. RNA viruses rely on a
high supply of nucleoside triphosphates from the host to efficiently replicate, and we
identified a panel of host nucleoside biosynthesis inhibitors as antiviral. Moreover, we
found that combining pyrimidine biosynthesis inhibitors with antiviral nucleoside
analogues synergistically inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro and in vivo against
emerging strains of SARS-CoV-2, suggesting a clinical path forward.
SARS-CoV-2 is a coronavirus, which is a family of single-stranded
positive-sense RNA viruses, at least seven of which infect humans.
RNA viruses including coronaviruses replicate using a virally encoded
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), and nucleoside analogues,
which are incorporated by the RdRp into the growing viral RNA chain,
are a large class of approved direct-acting antivirals3. Depending on
the analogue, incorporation can lead to chain termination or mutagenesis, ultimately inhibiting viral replication4. RdRps have conserved
structures, and thus nucleoside analogues can show broad activity
across related and unrelated viruses5,6. Therefore, repurposing efforts
have identified nucleoside analogues that are active against newly
emerging viruses, and such efforts have discovered that the nucleoside
analogue remdesivir inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication, becoming the
first approved antiviral therapeutic against this novel coronavirus7,8.
As all viruses, including SARS-CoV-2, are dependent on diverse
cellular factors and metabolic products for their replication, the
identification of host-directed antivirals also shows promise. In particular, host nucleoside biogenesis is required for viral replication as
RNA viruses require high levels of nucleoside triphosphates for their
growth. Widespread efforts are underway to identify essential..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04482-x",
"ISSN": [
"0028-0836",
"1476-4687"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04482-x",
"alternative-id": [
"4482"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "22 October 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "26 January 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "7 February 2022"
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7890-8815",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schultz",
"given": "David C.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1976-7688",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "Robert M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ayyanathan",
"given": "Kasirajan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7990-4912",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Jesse",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9114-4365",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Whig",
"given": "Kanupriya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kamalia",
"given": "Brinda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2884-5630",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dittmar",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weston",
"given": "Stuart",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hammond",
"given": "Holly L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dillen",
"given": "Carly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ardanuy",
"given": "Jeremy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "Louis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Jae Seung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Minghua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9064-2378",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Shoffler",
"given": "Clarissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Petucci",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Constant",
"given": "Samuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferrer",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8226-7718",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Thaiss",
"given": "Christoph A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0107-0775",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Frieman",
"given": "Matthew B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3956-6610",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cherry",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Nature"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-07T11:15:53Z",
"timestamp": 1644232553000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-07T12:01:04Z",
"timestamp": 1644235264000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-07T12:42:44Z",
"timestamp": 1644237764036
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0028-0836"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1476-4687"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1644192000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1644192000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04482-x.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04482-x",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04482-x.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Nature"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Pyrimidine inhibitors synergize with nucleoside analogues to block SARS-CoV-2"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}
schultz