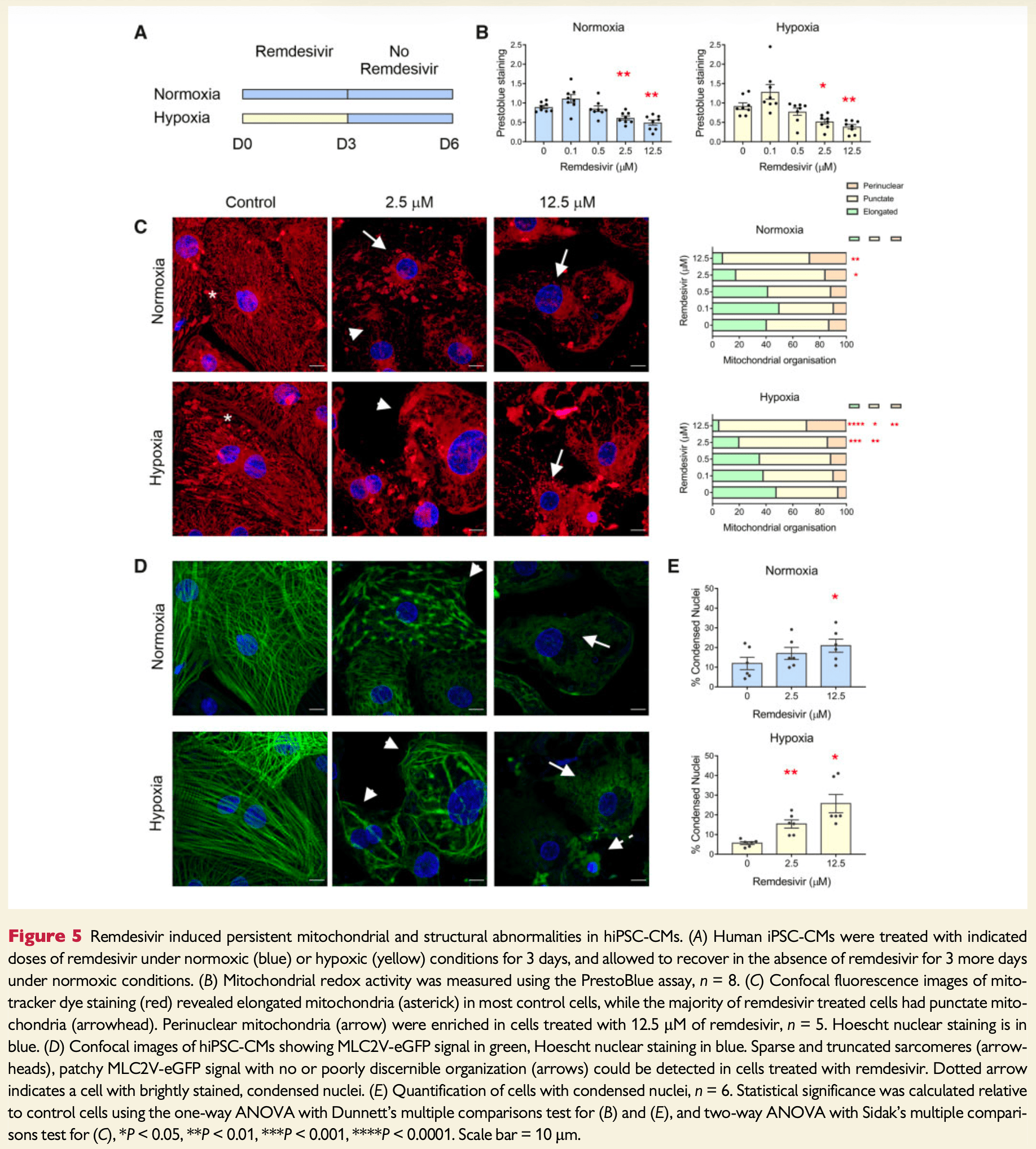
Remdesivir induces persistent mitochondrial and structural damage in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
et al., Cardiovascular Research, doi:10.1093/cvr/cvab311, Oct 2021
In vitro study showing that remdesivir induces persistent cardiotoxicity in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) at clinically relevant concentrations. Authors exposed hiPSC-CMs to remdesivir (0.1-12.5 μM) under normoxic and hypoxic conditions and found dose-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction, including fragmentation, reduced redox potential, and suppressed respiration at concentrations as low as 2.5 μM (below the estimated plasma concentration). Non-mitochondrial damage including electrophysiological alterations and sarcomere disarray were also observed. These changes persisted after cessation of treatment and culminated in increased cell death.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Kwok et al., 5 Oct 2021, China, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
Contact: ellen.poon@cuhk.edu.hk.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Remdesivir induces persistent mitochondrial and structural damage in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
Cardiovascular Research, doi:10.1093/cvr/cvab311
Aims Remdesivir is a prodrug of an adenosine triphosphate analogue and is currently the only drug formally approved for the treatment of hospitalized coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) patients. Nucleoside/nucleotide analogues have been shown to induce mitochondrial damage and cardiotoxicity, and this may be exacerbated by hypoxia, which frequently occurs in severe COVID-19 patients. Although there have been few reports of adverse cardiovascular events associated with remdesivir, clinical data are limited. Here, we investigated whether remdesivir induced cardiotoxicity using an in vitro human cardiac model. .......
Supplementary material Supplementary material is available at Cardiovascular Research online.
Authors' contributions
References
Ahmad, Yin, Saffitz, Pockros, Lalezari et al., Cardiac dysfunction associated with a nucleotide polymerase inhibitor for treatment of hepatitis C, Hepatology
Akinci, Cha, Lin, Yeo, Hamilton et al., Elucidation of remdesivir cytotoxicity pathways through genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening and transcriptomics, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.27.270819
Apostolova, Blas-Garcı ´a, Esplugues, Mitochondrial interference by anti-HIV drugs: mechanisms beyond Pol-gamma inhibition, Trends Pharmacol Sci
Archer, Mitochondrial dynamics-mitochondrial fission and fusion in human diseases, N Engl J Med
Bansal, Cardiovascular disease and COVID-19, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Boheler, Poon, Cell surface markers for immunophenotyping human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Pflugers Arch
Bojkova, Wagner, Shumliakivska, Aslan, Saleem et al., SARS-CoV-2 infects and induces cytotoxic effects in human cardiomyocytes, Cardiovasc Res
Bose, Mccarthy, Direct SARS-CoV-2 infection of the heart potentiates the cardiovascular sequelae of COVID-19, Drug Discov Today
Cassidy-Stone, Chipuk, Ingerman, Song, Yoo et al., Chemical inhibition of the mitochondrial division dynamin reveals its role in Bax/Bak-dependent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, Dev Cell
Choi, Shin, Park, Park, Lee et al., Antiviral activity and safety of remdesivir against SARS-CoV-2 infection in human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, Antiviral Res
Consortium, Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Preziosi et al., Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19-Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results, N Engl J Med
Feng, Xu, Barauskas, Perry, Ahmadyar et al., Role of mitochondrial RNA polymerase in the toxicity of nucleotide inhibitors of hepatitis C virus, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Gao, Mukhopadhyay, Mohanraj, Wang, Horvath et al., Resveratrol attenuates azidothymidine-induced cardiotoxicity by decreasing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation in human cardiomyocytes, Mol Med Rep
Gharanei, Hussain, Janneh, Maddock, Attenuation of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by mdivi-1: a mitochondrial division/mitophagy inhibitor, PLoS One
Gintant, Burridge, Gepstein, Harding, Herron et al., Use of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in preclinical cancer drug cardiotoxicity testing: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association, Circ Res
Givvimani, Munjal, Tyagi, Sen, Metreveli et al., Mitochondrial division/ mitophagy inhibitor (Mdivi) ameliorates pressure overload induced heart failure, PLoS One
Goldman, Lye, Hui, Marks, Bruno et al., Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Gopal, Marinelli, Alcorn, Immune mechanisms in cardiovascular diseases associated with viral infection, Front Immunol
Ishikita, Matoba, Ikeda, Koga, Mao et al., Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of mitochondrial division inhibitor 1 to the myocardium protects the heart from ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of mitochondria outer membrane permeabilization: a new therapeutic modality for acute myocardial infarction, J Am Heart Assoc
Jorgensen, Kebriaei, Dresser, Remdesivir: review of pharmacology, pre-clinical data, and emerging clinical experience for COVID-19, Pharmacotherapy
Lewis, Simpson, Meyer, Cardiac mitochondrial DNA polymerase-gamma is inhibited competitively and noncompetitively by phosphorylated zidovudine, Circ Res
Lund, Wallace, Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent phosphoregulation of mitochondrial complex I is inhibited by nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, Toxicol Appl Pharmacol
Madjid, Safavi-Naeini, Solomon, Vardeny, Potential effects of coronaviruses on the cardiovascular system: a review, JAMA Cardiol
Magadum, Kishore, Cardiovascular manifestations of COVID-19 infection, Cells
Magdy, Schuldt, Wu, Bernstein, Burridge, Human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived cells to assess drug cardiotoxicity: opportunities and problems, Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol
Maneechote, Palee, Kerdphoo, Jaiwongkam, Chattipakorn et al., Differential temporal inhibition of mitochondrial fission by Mdivi-1 exerts effective cardioprotection in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury, Clin Sci
Musunuru, Sheikh, Gupta, Houser, Maher et al., Induced pluripotent stem cells for cardiovascular disease modeling and precision medicine: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association, Circ Genom Precis Med
Ni, Williams, Ding, Mitochondrial dynamics and mitochondrial quality control, Redox Biol
Paik, Chandy, Wu, Patient and disease-specific induced pluripotent stem cells for discovery of personalized cardiovascular drugs and therapeutics, Pharmacol Rev
Pallotto, Suardi, Gabbuti, Esperti, Mecocci et al., Potential remdesivirrelated transient bradycardia in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), J Med Virol
Poon, Hao, Guan, Li, Lu et al., Integrated transcriptomic and regulatory network analyses identify microRNA-200c as a novel repressor of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte differentiation and maturation, Cardiovasc Res
Poon, Keung, Liang, Ramalingam, Yan et al., Proteomic analysis of human pluripotent stem cell-derived, fetal, and adult ventricular cardiomyocytes reveals pathways crucial for cardiac metabolism and maturation, Circ Cardiovasc Genet
Poon, Luo, Webb, Yan, Zhao et al., The cell surface marker CD36 selectively identifies matured, mitochondria-rich hPSC-cardiomyocytes, Cell Res
Poon, Yan, Zhang, Rushing, Keung et al., Transcriptome-guided functional analyses reveal novel biological properties and regulatory hierarchy of human embryonic stem cellderived ventricular cardiomyocytes crucial for maturation, PLoS One
Pruijssers, George, Schafer, Leist, Gralinksi et al., Remdesivir inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung cells and chimeric SARS-CoV expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase in mice, Cell Rep
Sahakijpijarn, Moon, Koleng, Christensen, Williams, experiments in in vivo animal models, investigations of cardioprotective strategies, and closer patient monitoring such that treatment-induced cardiotoxicity does not contribute to the long-term sequelae of COVID-19 patients
Saleh, Oraii, Soleimani, Hadadi, Shajari et al., The association between cardiac injury and outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Intern Emerg Med
Sharma, Garcia, Jr, Wang, Plummer et al., Human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Cell Rep Med
Sheahan, Sims, Graham, Menachery, Gralinski et al., Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses, Sci Transl Med
Shi, Qin, Shen, Cai, Liu et al., Association of cardiac injury with mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, JAMA Cardiol
Smirnova, Griparic, Shurland, Van Der Bliek, Dynamin-related protein Drp1 is required for mitochondrial division in mammalian cells, Mol Biol Cell
Spinner, Gottlieb, Criner, Lopez, Cattelan et al., Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Tchesnokov, Feng, Porter, Gotte, Mechanism of inhibition of Ebola virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by remdesivir, Viruses
Tobin, Laghi, Jubran, Why COVID-19 silent hypoxemia is baffling to physicians, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Touafchia, Bagheri, Durrieu, Sommet, Chouchana et al., Serious bradycardia and remdesivir for coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19): a new safety concerns, Clin Microbiol Infect
Vo, Carerj, Wieters, Fahim, Arendt et al., Outcomes of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in patients recently recovered from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), JAMA Cardiol
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Yang, Liu et al., Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet
Weber, Schwanke, Greten, Wendland, Iorga et al., Stiff matrix induces switch to pure betacardiac myosin heavy chain expression in human ESC-derived cardiomyocytes, Basic Res Cardiol
Wichmann, Sperhake, Lu ¨tgehetmann, Steurer, Edler et al., Autopsy findings and venous thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study, Ann Intern Med
Williamson, Feldmann, Schwarz, Meade-White, Porter et al., Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2, Nature
Wong, Luk, Lai, Lau, Zhang et al., Human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes platform to study SARS-CoV-2 related myocardial injury, Circ J
Wu, Dasgupta, Chen, Neuber-Hess, Patel et al., Identification of novel dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) GTPase inhibitors: therapeutic potential of Drpitor1 and Drpitor1a in cancer and cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury, FASEB J
Xie, Covassin, Fan, Singh, Gao et al., Association between hypoxemia and mortality in patients with COVID-19, Mayo Clin Proc
Xu, Barauskas, Kim, Babusis, Murakami et al., Off-target in vitro profiling demonstrates that remdesivir is a highly selective antiviral agent, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Yang, Han, Nilsson-Payant, Gupta, Wang et al., A human pluripotent stem cell-based platform to study SARS-CoV-2 tropism and model virus infection in human cells and organoids, Cell Stem Cell
Yang, Rodriguez, Leonard, Sun, Fischer et al., Fatty acids enhance the maturation of cardiomyocytes derived from human pluripotent stem cells, Stem Cell Reports
Yin, Mao, Luan, Shen, Shen et al., Structural basis for inhibition of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir, Science
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvab311",
"ISSN": [
"0008-6363",
"1755-3245"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvab311",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Aims</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Remdesivir is a prodrug of an adenosine triphosphate analogue and is currently the only drug formally approved for the treatment of hospitalized coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) patients. Nucleoside/nucleotide analogues have been shown to induce mitochondrial damage and cardiotoxicity, and this may be exacerbated by hypoxia, which frequently occurs in severe COVID-19 patients. Although there have been few reports of adverse cardiovascular events associated with remdesivir, clinical data are limited. Here, we investigated whether remdesivir induced cardiotoxicity using an in vitro human cardiac model.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods and results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) were exposed to remdesivir under normoxic and hypoxic conditions to simulate mild and severe COVID-19, respectively. Remdesivir induced mitochondrial fragmentation, reduced redox potential, and suppressed mitochondrial respiration at levels below the estimated plasma concentration under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Non-mitochondrial damage such as electrophysiological alterations and sarcomere disarray were also observed. Importantly, some of these changes persisted after the cessation of treatment, culminating in increased cell death. Mechanistically, we found that inhibition of DRP1, a regulator of mitochondrial fission, ameliorated the cardiotoxic effects of remdesivir, showing that remdesivir-induced cardiotoxicity was preventable and excessive mitochondrial fission might contribute to this phenotype.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Using an in vitro model, we demonstrated that remdesivir can induce cardiotoxicity in hiPSC-CMs at clinically relevant concentrations. These results reveal previously unknown potential side-effects of remdesivir and highlight the importance of further investigations with in vivo animal models and active clinical monitoring to prevent lasting cardiac damage to patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5920-9341",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Hong Kong Hub of Paediatric Excellence (HK HOPE), The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kwok",
"given": "Maxwell",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hong Kong Hub of Paediatric Excellence (HK HOPE), The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Centre for Cardiovascular Genomics and Medicine, Lui Che Woo Institute of Innovative Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Carrie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hong Kong Hub of Paediatric Excellence (HK HOPE), The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Centre for Cardiovascular Genomics and Medicine, Lui Che Woo Institute of Innovative Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Paediatrics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Hung Sing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hong Kong Hub of Paediatric Excellence (HK HOPE), The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Centre for Cardiovascular Genomics and Medicine, Lui Che Woo Institute of Innovative Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
}
],
"family": "Deng",
"given": "Ruixia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0528-9977",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hong Kong Hub of Paediatric Excellence (HK HOPE), The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Centre for Cardiovascular Genomics and Medicine, Lui Che Woo Institute of Innovative Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tsoi",
"given": "Chantelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Life Sciences, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
}
],
"family": "Ding",
"given": "Qianqian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9992-5454",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Life Sciences, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agrobiotechnology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory for Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Institute for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tsang",
"given": "Suk Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hong Kong Hub of Paediatric Excellence (HK HOPE), The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Paediatrics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
}
],
"family": "Leung",
"given": "Kam Tong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0430-5752",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Heart and Vascular Institute, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Bryan P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9280-3681",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Hong Kong Hub of Paediatric Excellence (HK HOPE), The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
},
{
"name": "Centre for Cardiovascular Genomics and Medicine, Lui Che Woo Institute of Innovative Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) , Hong Kong SAR , China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Poon",
"given": "Ellen N",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cardiovascular Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-30T20:45:30Z",
"timestamp": 1633034730000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-21T20:28:20Z",
"timestamp": 1663792100000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"4930915"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"4930915"
]
}
],
"name": "Improvement on competitiveness in hiring new faculties"
},
{
"award": [
"4054538",
"4054609"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"4054538",
"4054609"
]
}
],
"name": "Direct grant for research"
},
{
"name": "Chinese University of Hong Kong to E.N.P."
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
11,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2025-11-20T18:51:19Z",
"timestamp": 1763664679734,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 29,
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
20
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633392000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cardiovascres/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cvr/cvab311/41089935/cvab311.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cardiovascres/article-pdf/118/12/2652/45955229/cvab311.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cardiovascres/article-pdf/118/12/2652/45955229/cvab311.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2652-2664",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
5
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1286",
"article-title": "Potential effects of coronaviruses on the cardiovascular system: a review",
"author": "Madjid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "831",
"journal-title": "JAMA Cardiol",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2423-5",
"article-title": "Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B2",
"volume": "585",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B3",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107940",
"article-title": "Remdesivir inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung cells and chimeric SARS-CoV expressing the SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase in mice",
"author": "Pruijssers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107940",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B4",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B5",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1569",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B6",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"article-title": "Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19—Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results",
"author": "Consortium WHOST",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B7",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc1560",
"article-title": "Structural basis for inhibition of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir",
"author": "Yin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1499",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B8",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tips.2011.07.007",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial interference by anti-HIV drugs: mechanisms beyond Pol-gamma inhibition",
"author": "Apostolova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "715",
"journal-title": "Trends Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B9",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.27488",
"article-title": "Cardiac dysfunction associated with a nucleotide polymerase inhibitor for treatment of hepatitis C",
"author": "Ahmad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B10",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.RES.74.2.344",
"article-title": "Cardiac mitochondrial DNA polymerase-gamma is inhibited competitively and noncompetitively by phosphorylated zidovudine",
"author": "Lewis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "344",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B11",
"volume": "74",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01922-15",
"article-title": "Role of mitochondrial RNA polymerase in the toxicity of nucleotide inhibitors of hepatitis C virus",
"author": "Feng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "806",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B12",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.taap.2007.08.015",
"article-title": "Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent phosphoregulation of mitochondrial complex I is inhibited by nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors",
"author": "Lund",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "94",
"journal-title": "Toxicol Appl Pharmacol",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B13",
"volume": "226",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"article-title": "Resveratrol attenuates azidothymidine-induced cardiotoxicity by decreasing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation in human cardiomyocytes",
"author": "Gao",
"first-page": "151",
"journal-title": "Mol Med Rep",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B14",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.03.013",
"article-title": "Cardiovascular disease and COVID-19",
"author": "Bansal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "247",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B15",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B16",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0950",
"article-title": "Association of cardiac injury with mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "802",
"journal-title": "JAMA Cardiol",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B17",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100052",
"article-title": "Human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100052",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep Med",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B18",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2020.06.015",
"article-title": "A human pluripotent stem cell-based platform to study SARS-CoV-2 tropism and model virus infection in human cells and organoids",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B19",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-2003",
"article-title": "Autopsy findings and venous thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Wichmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "268",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B20",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drudis.2020.06.021",
"article-title": "Direct SARS-CoV-2 infection of the heart potentiates the cardiovascular sequelae of COVID-19",
"author": "Bose",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1559",
"journal-title": "Drug Discov Today",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B21",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvaa267",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infects and induces cytotoxic effects in human cardiomyocytes",
"author": "Bojkova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2207",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Res",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B22",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.570681",
"article-title": "Immune mechanisms in cardiovascular diseases associated with viral infection",
"author": "Gopal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "570681",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B23",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells9112508",
"article-title": "Cardiovascular manifestations of COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Magadum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2508",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B24",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.04.006",
"article-title": "Association between hypoxemia and mortality in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1138",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B25",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-020-02466-1",
"article-title": "The association between cardiac injury and outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Karbalai Saleh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1415",
"journal-title": "Intern Emerg Med",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B26",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Induced pluripotent stem cells for cardiovascular disease modeling and precision medicine: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association",
"author": "Musunuru",
"first-page": "e000043",
"journal-title": "Circ Genom Precis Med",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B27",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/RES.0000000000000291",
"article-title": "Use of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in preclinical cancer drug cardiotoxicity testing: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association",
"author": "Gintant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e75",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B28",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010617-053110",
"article-title": "Human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived cells to assess drug cardiotoxicity: opportunities and problems",
"author": "Magdy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B29",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/pr.116.013003",
"article-title": "Patient and disease-specific induced pluripotent stem cells for discovery of personalized cardiovascular drugs and therapeutics",
"author": "Paik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "320",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rev",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B30",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0292-y",
"article-title": "The cell surface marker CD36 selectively identifies matured, mitochondria-rich hPSC-cardiomyocytes",
"author": "Poon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "626",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B31",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104955",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity and safety of remdesivir against SARS-CoV-2 infection in human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104955",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B32",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1253/circj.CJ-20-0881",
"article-title": "Human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes platform to study SARS-CoV-2 related myocardial injury",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2027",
"journal-title": "Circ J",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B33",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.08.013",
"article-title": "Fatty acids enhance the maturation of cardiomyocytes derived from human pluripotent stem cells",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "657",
"journal-title": "Stem Cell Reports",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B34",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00395-016-0587-9",
"article-title": "Stiff matrix induces switch to pure beta-cardiac myosin heavy chain expression in human ESC-derived cardiomyocytes",
"author": "Weber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "68",
"journal-title": "Basic Res Cardiol",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B35",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/phar.2429",
"article-title": "Remdesivir: review of pharmacology, pre-clinical data, and emerging clinical experience for COVID-19",
"author": "Jorgensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "659",
"journal-title": "Pharmacotherapy",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B36",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2014.11.006",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial dynamics and mitochondrial quality control",
"author": "Ni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B37",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra1215233",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial dynamics–mitochondrial fission and fusion in human diseases",
"author": "Archer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2236",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B38",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.12.8.2245",
"article-title": "Dynamin-related protein Drp1 is required for mitochondrial division in mammalian cells",
"author": "Smirnova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2245",
"journal-title": "Mol Biol Cell",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B39",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.devcel.2007.11.019",
"article-title": "Chemical inhibition of the mitochondrial division dynamin reveals its role in Bax/Bak-dependent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization",
"author": "Cassidy-Stone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "193",
"journal-title": "Dev Cell",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B40",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.201901467R",
"article-title": "Identification of novel dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) GTPase inhibitors: therapeutic potential of Drpitor1 and Drpitor1a in cancer and cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1447",
"journal-title": "FASEB J",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B41",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653",
"article-title": "Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses",
"author": "Sheahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B42",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.27.270819",
"article-title": "Elucidation of remdesivir cytotoxicity pathways through genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening and transcriptomics",
"author": "Akinci",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B43",
"volume-title": "bioRxiv",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02237-20",
"article-title": "Off-target in vitro profiling demonstrates that remdesivir is a highly selective antiviral agent",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e02237",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B44",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11040326",
"article-title": "Mechanism of inhibition of Ebola virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by remdesivir",
"author": "Tchesnokov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "326",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B45",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0077713",
"article-title": "Attenuation of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by mdivi-1: a mitochondrial division/mitophagy inhibitor",
"author": "Gharanei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e77713",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B46",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/JAHA.116.003872",
"article-title": "Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of mitochondrial division inhibitor 1 to the myocardium protects the heart from ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of mitochondria outer membrane permeabilization: a new therapeutic modality for acute myocardial infarction",
"author": "Ishikita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Am Heart Assoc",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B47",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20180510",
"article-title": "Differential temporal inhibition of mitochondrial fission by Mdivi-1 exerts effective cardioprotection in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury",
"author": "Maneechote",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1669",
"journal-title": "Clin Sci",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B48",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0032388",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial division/mitophagy inhibitor (Mdivi) ameliorates pressure overload induced heart failure",
"author": "Givvimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e32388",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B49",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202006-2157CP",
"article-title": "Why COVID-19 silent hypoxemia is baffling to physicians",
"author": "Tobin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "356",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B50",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.02.013",
"article-title": "Serious bradycardia and remdesivir for coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19): a new safety concerns",
"author": "Touafchia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "791.e5",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B51",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26898",
"article-title": "Potential remdesivir-related transient bradycardia in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Pallotto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2631",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B52",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.16349",
"article-title": "Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Spinner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1048",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B53",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015301",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid-19",
"author": "Goldman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1827",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B54",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.114.000918",
"article-title": "Proteomic analysis of human pluripotent stem cell-derived, fetal, and adult ventricular cardiomyocytes reveals pathways crucial for cardiac metabolism and maturation",
"author": "Poon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "427",
"journal-title": "Circ Cardiovasc Genet",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B55",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0077784",
"article-title": "Transcriptome-guided functional analyses reveal novel biological properties and regulatory hierarchy of human embryonic stem cell-derived ventricular cardiomyocytes crucial for maturation",
"author": "Poon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e77784",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B56",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvy019",
"article-title": "Integrated transcriptomic and regulatory network analyses identify microRNA-200c as a novel repressor of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte differentiation and maturation",
"author": "Poon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "894",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Res",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B57",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00424-021-02549-8",
"article-title": "Cell surface markers for immunophenotyping human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes",
"author": "Boheler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1023",
"journal-title": "Pflugers Arch",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B58",
"volume": "473",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamacardio.2020.3557",
"article-title": "Outcomes of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in patients recently recovered from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Puntmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1265",
"journal-title": "JAMA Cardiol",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B59",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics12111002",
"article-title": "Development of remdesivir as a dry powder for inhalation by thin film freezing",
"author": "Sahakijpijarn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1002",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceutics",
"key": "2022092120252987000_cvab311-B60",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 60,
"references-count": 60,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cardiovascres/article/118/12/2652/6381566"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Remdesivir induces persistent mitochondrial and structural damage in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "118"
}