Is There a Crucial Link Between Vitamin D Status and Inflammatory Response in Patients With COVID-19?
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.745713, Jan 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
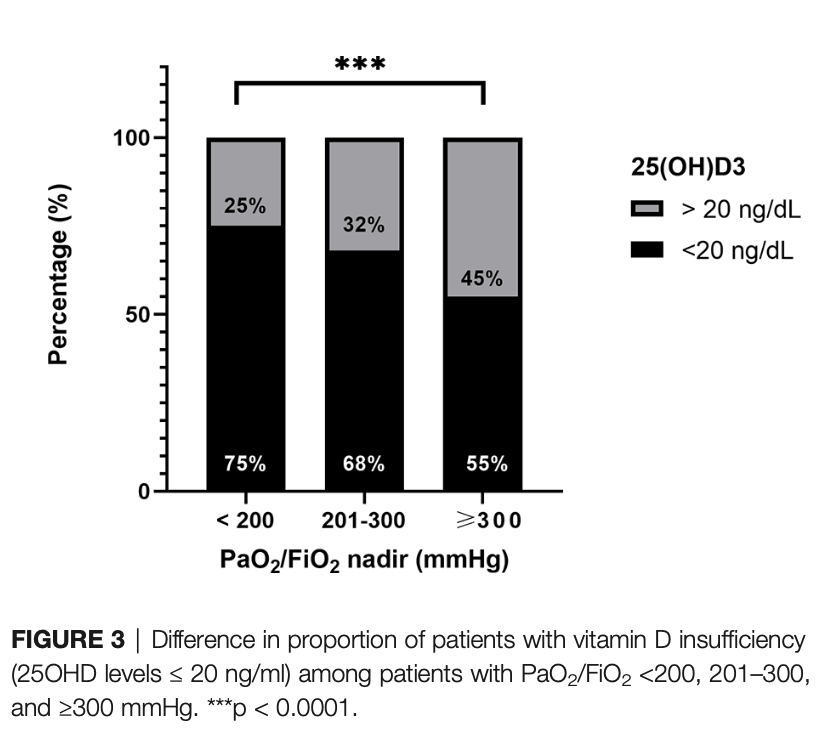
Retrospective 93 COVID-19 pneumonia patients in Italy, showing low vitamin D levels associated with severe ARDS, and significantly lower vitamin D levels for non-survivors.
This is the 114th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of ARDS, 36.5% lower, RR 0.64, p = 0.43, high D levels (≥20ng/ml) 5 of 32 (15.6%), low D levels (<20ng/ml) 15 of 61 (24.6%), NNT 11, severe ARDS.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Saponaro et al., 24 Jan 2022, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 13 authors, study period March 2020 - May 2020.
Is There a Crucial Link Between Vitamin D Status and Inflammatory Response in Patients With COVID-19?
Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.745713
Background: Hypovitaminosis D has been suggested to play a possible role in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection.
Methods: The aim of this study is to analyze the relationship between vitamin D status and a biochemical panel of inflammatory markers in a cohort of patients with COVID-19. A secondary endpoint was to evaluate the correlation between 25OHD levels and the severity of the disease. Ninety-three consecutive patients with COVID-19-related pneumonia were evaluated from March to May 2020 in two hospital units in Pisa, in whom biochemical inflammatory markers, 25OHD levels, P/F ratio at nadir during hospitalization, and complete clinical data were available. Results: Sixty-five percent of patients presented hypovitaminosis D (25OHD ≤ 20 ng/ml) and showed significantly higher IL
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Publisher's Note: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Belderbos, Houben, Wilbrink, Lentjes, Bloemen et al., Cord Blood Vitamin D Deficiency is Associated With Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis, Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.2010-3054
Berry, Hesketh, Power, Hyppönen, Vitamin D Status has a Linear Association With Seasonal Infections and Lung Function in British Adults, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114511001991
Bikle, Patzek, Wang, Physiologic and Pathophysiologic Roles of Extra Renal CYP27b1: Case Report and Review, Bone Rep, doi:10.1016/j.bonr.2018.02.004
Bouillon, Carmeliet, Verlinden, Van Etten, Verstuyf et al., Vitamin D and Human Health: Lessons From Vitamin D Receptor Null Mice, Endocrine Rev, doi:10.1210/er.2008-0004
Buja, Wolf, Zhao, Akkanti, Mcdonald et al., The Emerging Spectrum of Cardiopulmonary Pathology of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Report of 3 Autopsies From Houston, Texas, and Review of Autopsy Findings From Other United States Cities, Cardiovasc Pathol, doi:10.1016/j.carpath.2020.107233
Butler-Laporte, Nakanishi, Mooser, Morrison, Abdullah et al., Vitamin D and COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity in the COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative: A Mendelian Randomization Study, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003605
Campi, Gennari, Merlotti, Mingiano, Frosali et al., Vitamin D and COVID-19 Severity and Related Mortality: A Prospective Study in Italy, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06281-7
Carpagnano, Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D Deficiency as a Predictor of Poor Prognosis in Patients With Acute Respiratory Failure Due to COVID-19, J Endocrinol Invest, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-41173/v1
Carsana, Sonzogni, Nasr, Rossi, Pellegrinelli et al., Pulmonary Post-Mortem Findings in a Series of COVID-19 Cases From Northern Italy: A Two-Centre Descriptive Study, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30434-5
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Alcaládıáz, Miranda et al., Effect of Calcifediol Treatment and Best Available Therapy Versus Best Available Therapy on Intensive Care Unit Admission and Mortality Among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Channappanavar, Perlman, Pathogenic Human Coronavirus Infections: Causes and Consequences of Cytokine Storm and Immunopathology, Semin Immunopathology, doi:10.1007/s00281-017-0629-x
Daneshkhah, Agrawal, Eshein, Subramanian, Roy et al., Evidence for Possible Association of Vitamin D Status With Cytokine Storm and Unregulated Inflammation in COVID-19 Patients, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y
Demir, Demir, Aygun, Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated With COVID-19 Positivity and Severity of the Disease, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26832
Entezari-Maleki, Talasaz, Salarifar, Hadjibabaie, Javadi et al., Plasma Vitamin D Status and Its Correlation With Risk Factors of Thrombosis, P-Selectin and Hs-CRP Level in Patients With Venous Thromboembolism; the First Study of Iranian Population, Iran J Pharm Res
Fakhoury, Kvietys, Shakir, Shams, Grant et al., Lung-Centric Inflammation of Covid-19: Potential Modulation by Vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072216
Federico, Genoni, Puggioni, Saba, Gallo et al., Vitamin D Status, Enterovirus Infection, and Type 1 Diabetes in Italian Children/Adolescents, Pediatr Diabetes, doi:10.1111/pedi.12673
Giannini, Passeri, Tripepi, Sella, Fusaro et al., Effectiveness of in-Hospital Cholecalciferol Use on Clinical Outcomes in Comorbid Covid-19 Patients: A Hypothesis-Generating Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13010219
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence That Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Celis-Morales, Katikireddi et al., Vitamin D Concentrations and COVID-19 Infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050
Hastie, Pell, Sattar, Vitamin D and COVID-19 Infection and Mortality in UK Biobank, Eur J Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-020-02372-4
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical Features of Patients Infected With 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The Role of Vitamin D in the Prevention of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Infante, Buoso, Pieri, Lupisella, Nuccetelli et al., Low Vitamin D Status at Admission as a Risk Factor for Poor Survival in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: An Italian Retrospective Study, J Am Coll Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.2021.1877580
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Singh, Mahor et al., Analysis of Vitamin D Level Among Asymptomatic and Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients and its Correlation With Inflammatory Markers, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z
Kim, Yang, Jang, Jang, Human b-Defensin 2 Plays a Regulatory Role in Innate Antiviral Immunity and Is Capable of Potentiating the Induction of Antigen-Specific Immunity, Virol J, doi:10.1186/s12985-018-1035-2
Kvietys, Fakhoury, Kadan, Yaqinuddin, Al-Mutairy et al., COVID-19: Lung-Centric Immunothrombosis, Front Cell Infection Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2021.679878
Laaksi, Ruohola, Mattila, Auvinen, Ylikomi et al., Vitamin D Supplementation for the Prevention of Acute Respiratory Tract Infection: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Trial Among Young Finnish Men, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1086/654881
Larner, Adams, Hewison, Regulation of Renal and Extrarenal 1a-Hydroxylase
Liu, Li, Liu, Liang, Wang et al., Longitudinal Characteristics of Lymphocyte Responses and Cytokine Profiles in the Peripheral Blood of SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102763
Liu, Stenger, Li, Wenzel, Tan et al., Toll-Like Receptor Triggering of a Vitamin D-Mediated Human Antimicrobial Response, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1123933
Magro, Mulvey, Berlin, Nuovo, Salvatore et al., Complement Associated Microvascular Injury and Thrombosis in the Pathogenesis of Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Report of Five Cases, Transl Res, doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007
Mangalmurti, Hunter, Cytokine Storms: Understanding COVID-19, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.017
Marazuela, Giustina, Puig-Domingo, Endocrine and Metabolic Aspects of the COVID-19 Pandemic, Rev Endocrine Metab Disord, doi:10.1007/s11154-020-09569-2
Martens, Gysemans, Verstuyf, Mathieu, Vitamin D's Effect on Immune Function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051248
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent Acute Respiratory Tract Infections: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Participant Data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Mendy, Apewokin, Wells, Morrow, Factors Associated With Hospitalization and Disease Severity in a Racially and Ethnically Diverse Population of COVID-19 Patients, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.25.20137323
Mohammad, Mishra, Ashraf, Emerging Role of Vitamin D and Its Associated Molecules in Pathways Related to Pathogenesis of Thrombosis, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom9110649
Moore, June, Cytokine Release Syndrome in Severe COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb8925
Munshi, Hussein, Toraih, Elshazli, Jardak et al., Vitamin D Insufficiency as a Potential Culprit in Critical COVID-19 Patients, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26360
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation vs Placebo on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Severe COVID-19: A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.11.16.20232397
Pereira, Damascena, Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da et al., Vitamin D Deficiency Aggravates COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Raisi-Estabragh, Mccracken, Bethell, Cooper, Cooper et al., Greater Risk of Severe COVID-19 in Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic Populations is Not Explained by Cardiometabolic, Socioeconomic or Behavioural Factors, or by 25(OH)-Vitamin D Status: Study of 1326 Cases From the UK Biobank, J Public Heal, doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdaa095
Ranieri, Rubenfeld, Thompson, Ferguson, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition, JAMA -J Am Med Assoc, doi:10.1001/jama.2012.5669
Rastogi, Bhansali, Khare, Suri, Yaddanapudi et al., Short Term, High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation for COVID-19 Disease: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Study (SHADE Study), Postgrad Med J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065
Reijven, Soeters, Vitamin D: A Magic Bullet or a Myth?, Clin Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2019.12.028
Saba, Frascarelli, Campi, The Role of Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Chemistry: Quantification of Steroid Hormones and Vitamin D, Compr Anal Chem
Sabetta, Depetrillo, Cipriani, Smardin, Burns et al., Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and the Incidence of Acute Viral Respiratory Tract Infections in Healthy Adults, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011088
Saponaro, Marcocci, Zucchi, Prontera, Clerico et al., Hypovitaminosis D in Patients With Heart Failure: Effects on Functional Capacity and Patients' Survival, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-017-1282-9
Saponaro, Marcocci, Zucchi, Vitamin D Status and Cardiovascular Outcome, J Endocrinological Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-019-01057-y
Saponaro, Rutigliano, Sestito, Bandini, Storti et al., ACE2 in the Era of SARS-CoV-2: Controversies and Novel Perspectives, Front Mol Biosci, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2020.588618
Saponaro, Saba, Frascarelli, Prontera, Clerico et al., Vitamin D Measurement and Effect on Outcome in a Cohort of Patients With Heart Failure, Endocr Connect, doi:10.1530/EC-18-0207
Saponaro, Saba, Zucchi, An Update on Vitamin D Metabolism, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms21186573
Tan, Huang, Shi, Tan, Ma et al., C-Reactive Protein Correlates With Computed Tomographic Findings and Predicts Severe COVID-19 Early, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25871
Ulivieri, Banfi, Camozzi, Colao, Formenti et al., Vitamin D in the Covid-19 Era: A Review With Recommendations From a G, I.O.S.E.G. Expert Panel. Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-021-02749-3
Waldron, Ashby, Cornes, Bechervaise, Razavi et al., Vitamin D: A Negative Acute Phase Reactant, J Clin Pathol, doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2012-201301
Wang, C-Reactive Protein Levels in the Early Stage of COVID-19, Med Mal Infect, doi:10.1016/j.medmal.2020.03.007
Wu, He, Low Vitamin D Levels Are Associated With the Development of Deep Venous Thromboembolic Events in Patients With Ischemic Stroke, Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, doi:10.1177/1076029618786574
Yisak, Ewunetei, Kefale, Mamuye, Teshome et al., Effects of Vitamin D on Covid-19 Infection and Prognosis: A Systematic Review, Risk Manag Healthc Policy, doi:10.2147/RMHP.S291584
Zhou, Luo, Qin, The Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Community-Acquired Pneumonia, Med, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000017252
Zhou, Wang, Huang, Li, Hu et al., Lower Vitamin D Status is Associated With an Increased Risk of Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10030277
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.745713",
"ISSN": [
"1664-3224"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.745713",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Hypovitaminosis D has been suggested to play a possible role in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>The aim of this study is to analyze the relationship between vitamin D status and a biochemical panel of inflammatory markers in a cohort of patients with COVID-19. A secondary endpoint was to evaluate the correlation between 25OHD levels and the severity of the disease. Ninety-three consecutive patients with COVID-19-related pneumonia were evaluated from March to May 2020 in two hospital units in Pisa, in whom biochemical inflammatory markers, 25OHD levels, P/F ratio at nadir during hospitalization, and complete clinical data were available.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Sixty-five percent of patients presented hypovitaminosis D (25OHD ≤ 20 ng/ml) and showed significantly higher IL-6 [20.8 (10.9–45.6) vs. 12.9 (8.7–21.1) pg/ml, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.02], CRP [10.7 (4.2–19.2) vs. 5.9 (1.6–8.1) mg/dl, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.003], TNF-α [8.9 (6.0–14.8) vs. 4.4 (1.5–10.6) pg/ml, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.01], D-dimer [0.53 (0.25–0.72) vs. 0.22 (0.17–0.35) mg/l, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.002], and IL-10 [3.7 (1.8–6.9) vs. 2.3 (0.5–5.8) pg/ml, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.03]. A significant inverse correlation was found between 25OHD and all these markers, even adjusted for age and sex. Hypovitaminosis D was prevalent in patients with severe ARDS, compared with the other groups (75% vs. 68% vs. 55%, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> &lt; 0.001), and 25OHD levels were lower in non-survivor patients.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>The relationship between 25OHD levels and inflammatory markers suggests that vitamin D status needs to be taken into account in the management of these patients. If vitamin D is a marker of poor prognosis or a possible risk factor with beneficial effects from supplementation, this still needs to be elucidated.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fimmu.2021.745713"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saponaro",
"given": "Federica",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Franzini",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Okoye",
"given": "Chukwuma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Antognoli",
"given": "Rachele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campi",
"given": "Beatrice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scalese",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neri",
"given": "Tommaso",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carrozzi",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Monzani",
"given": "Fabio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zucchi",
"given": "Riccardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Celi",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paolicchi",
"given": "Aldo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saba",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Frontiers in Immunology"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-24T06:12:22Z",
"timestamp": 1643004742000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-24T06:12:25Z",
"timestamp": 1643004745000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-24T06:40:50Z",
"timestamp": 1643006450453
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1664-3224"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
24
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1642982400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.745713/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence That Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "988",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11154-020-09569-2",
"article-title": "Endocrine and Metabolic Aspects of the COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "Marazuela",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "495",
"journal-title": "Rev Endocrine Metab Disord",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/654881",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Supplementation for the Prevention of Acute Respiratory Tract Infection: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Trial Among Young Finnish Men",
"author": "Laaksi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114511001991",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Status has a Linear Association With Seasonal Infections and Lung Function in British Adults",
"author": "Berry",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0011088",
"article-title": "Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and the Incidence of Acute Viral Respiratory Tract Infections in Healthy Adults",
"author": "Sabetta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e11088",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2010-3054",
"article-title": "Cord Blood Vitamin D Deficiency is Associated With Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis",
"author": "Belderbos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000017252",
"article-title": "The Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Community-Acquired Pneumonia",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "94",
"journal-title": "Med (Baltimore)",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent Acute Respiratory Tract Infections: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Participant Data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The Role of Vitamin D in the Prevention of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Deficiency Aggravates COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Pereira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "B10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072216",
"article-title": "Lung-Centric Inflammation of Covid-19: Potential Modulation by Vitamin D",
"author": "Fakhoury",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2216",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2012.5669",
"article-title": "Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition",
"author": "Ranieri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA - J Am Med Assoc",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "307",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/pedi.12673",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Status, Enterovirus Infection, and Type 1 Diabetes in Italian Children/Adolescents",
"author": "Federico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Diabetes",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.coac.2017.06.011",
"article-title": "The Role of Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Chemistry: Quantification of Steroid Hormones and Vitamin D",
"author": "Saba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Compr Anal Chem",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "410",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z",
"article-title": "Analysis of Vitamin D Level Among Asymptomatic and Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients and its Correlation With Inflammatory Markers",
"author": "Jain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medmal.2020.03.007",
"article-title": "C-Reactive Protein Levels in the Early Stage of COVID-19",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Med Mal Infect",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25871",
"article-title": "C-Reactive Protein Correlates With Computed Tomographic Findings and Predicts Severe COVID-19 Early",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y",
"article-title": "Evidence for Possible Association of Vitamin D Status With Cytokine Storm and Unregulated Inflammation in COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Daneshkhah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26832",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated With COVID-19 Positivity and Severity of the Disease",
"author": "Demir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "0",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13010219",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of in-Hospital Cholecalciferol Use on Clinical Outcomes in Comorbid Covid-19 Patients: A Hypothesis-Generating Study",
"author": "Giannini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00281-017-0629-x",
"article-title": "Pathogenic Human Coronavirus Infections: Causes and Consequences of Cytokine Storm and Immunopathology",
"author": "Channappanavar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Semin Immunopathology",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2021.679878",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Lung-Centric Immunothrombosis",
"author": "Kvietys",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infection Microbiol",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.carpath.2020.107233",
"article-title": "The Emerging Spectrum of Cardiopulmonary Pathology of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Report of 3 Autopsies From Houston, Texas, and Review of Autopsy Findings From Other United States Cities",
"author": "Buja",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107233",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Pathol",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30434-5",
"article-title": "Pulmonary Post-Mortem Findings in a Series of COVID-19 Cases From Northern Italy: A Two-Centre Descriptive Study",
"author": "Carsana",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007",
"article-title": "Complement Associated Microvascular Injury and Thrombosis in the Pathogenesis of Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Report of Five Cases",
"author": "Magro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Transl Res",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "220",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.017",
"article-title": "Cytokine Storms: Understanding COVID-19",
"author": "Mangalmurti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical Features of Patients Infected With 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb8925",
"article-title": "Cytokine Release Syndrome in Severe COVID-19",
"author": "Moore",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102763",
"article-title": "Longitudinal Characteristics of Lymphocyte Responses and Cytokine Profiles in the Peripheral Blood of SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102763",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.2021.1877580",
"article-title": "Low Vitamin D Status at Admission as a Risk Factor for Poor Survival in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19: An Italian Retrospective Study",
"author": "Infante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Am Coll Nutr",
"key": "B30",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/jclinpath-2012-201301",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: A Negative Acute Phase Reactant",
"author": "Waldron",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Pathol",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2019.12.028",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: A Magic Bullet or a Myth",
"author": "Reijven",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Concentrations and COVID-19 Infection in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/pubmed/fdaa095",
"article-title": "Greater Risk of Severe COVID-19 in Black, Asian and Minority Ethnic Populations is Not Explained by Cardiometabolic, Socioeconomic or Behavioural Factors, or by 25(OH)-Vitamin D Status: Study of 1326 Cases From the UK Biobank",
"author": "Raisi-Estabragh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Public Heal (United Kingdom)",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-020-02372-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19 Infection and Mortality in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur J Nutr",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06281-7",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19 Severity and Related Mortality: A Prospective Study in Italy",
"author": "Campi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "566",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051248",
"article-title": "Vitamin D’s Effect on Immune Function",
"author": "Martens",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1248",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21186573",
"article-title": "An Update on Vitamin D Metabolism",
"author": "Saponaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bonr.2018.02.004",
"article-title": "Physiologic and Pathophysiologic Roles of Extra Renal CYP27b1: Case Report and Review",
"author": "Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Bone Rep",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-809965-0.00008-2",
"article-title": "Regulation of Renal and Extrarenal 1α-Hydroxylase",
"author": "Larner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "B40",
"volume-title": "Vitamin D: Fourth Edition",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1123933",
"article-title": "Toll-Like Receptor Triggering of a Vitamin D-Mediated Human Antimicrobial Response",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "311",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-018-1035-2",
"article-title": "Human β-Defensin 2 Plays a Regulatory Role in Innate Antiviral Immunity and Is Capable of Potentiating the Induction of Antigen-Specific Immunity",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "124",
"journal-title": "Virol J",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2008-0004",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and Human Health: Lessons From Vitamin D Receptor Null Mice",
"author": "Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocrine Rev",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom9110649",
"article-title": "Emerging Role of Vitamin D and Its Associated Molecules in Pathways Related to Pathogenesis of Thrombosis",
"author": "Mohammad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "649",
"journal-title": "Biomolecules",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-019-01057-y",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Status and Cardiovascular Outcome",
"author": "Saponaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Endocrinological Invest",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EC-18-0207",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Measurement and Effect on Outcome in a Cohort of Patients With Heart Failure",
"author": "Saponaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocr Connect",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Plasma Vitamin D Status and Its Correlation With Risk Factors of Thrombosis, P-Selectin and Hs-CRP Level in Patients With Venous Thromboembolism; the First Study of Iranian Population",
"author": "Entezari-Maleki",
"journal-title": "Iran J Pharm Res",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10030277",
"article-title": "Lower Vitamin D Status is Associated With an Increased Risk of Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "277",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1076029618786574",
"article-title": "Low Vitamin D Levels Are Associated With the Development of Deep Venous Thromboembolic Events in Patients With Ischemic Stroke",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "69S",
"journal-title": "Clin Appl Thromb Hemost",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-017-1282-9",
"article-title": "Hypovitaminosis D in Patients With Heart Failure: Effects on Functional Capacity and Patients’ Survival",
"author": "Saponaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmolb.2020.588618",
"article-title": "ACE2 in the Era of SARS-CoV-2: Controversies and Novel Perspectives",
"author": "Saponaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Mol Biosci",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/RMHP.S291584",
"article-title": "Effects of Vitamin D on Covid-19 Infection and Prognosis: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Yisak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Risk Manag Healthc Policy",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.25.20137323",
"article-title": "Factors Associated With Hospitalization and Disease Severity in a Racially and Ethnically Diverse Population of COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Mendy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "B53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-41173/v1",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Deficiency as a Predictor of Poor Prognosis in Patients With Acute Respiratory Failure Due to COVID-19",
"author": "Carpagnano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Endocrinol Invest",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26360",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Insufficiency as a Potential Culprit in Critical COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Munshi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003605",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity in the COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative: A Mendelian Randomization Study",
"author": "Butler-Laporte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1003605",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.11.16.20232397",
"article-title": "Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation vs Placebo on Hospital Length of Stay in Patients With Severe COVID-19: A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial",
"author": "Murai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "B57",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139065",
"article-title": "Short Term, High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation for COVID-19 Disease: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Study (SHADE Study)",
"author": "Rastogi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Postgrad Med J",
"key": "B58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"article-title": "“Effect of Calcifediol Treatment and Best Available Therapy Versus Best Available Therapy on Intensive Care Unit Admission and Mortality Among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Study”",
"author": "Entrenas Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-021-02749-3",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in the Covid-19 Era: A Review With Recommendations From a G.I.O.S.E.G. Expert Panel",
"author": "Ulivieri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "597",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 60,
"references-count": 60,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Front. Immunol."
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Immunology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Is There a Crucial Link Between Vitamin D Status and Inflammatory Response in Patients With COVID-19?"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "12"
}
