Probiotics in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19: Current Perspective and Future Prospects
et al., Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002, Mar 2021
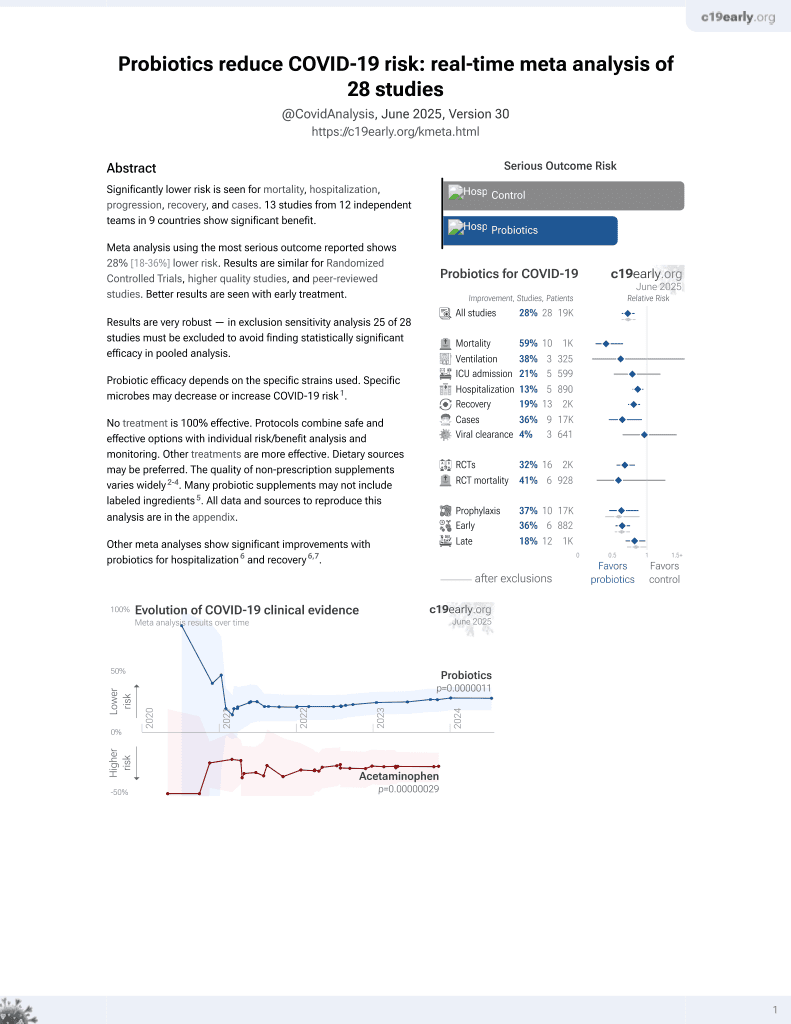
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
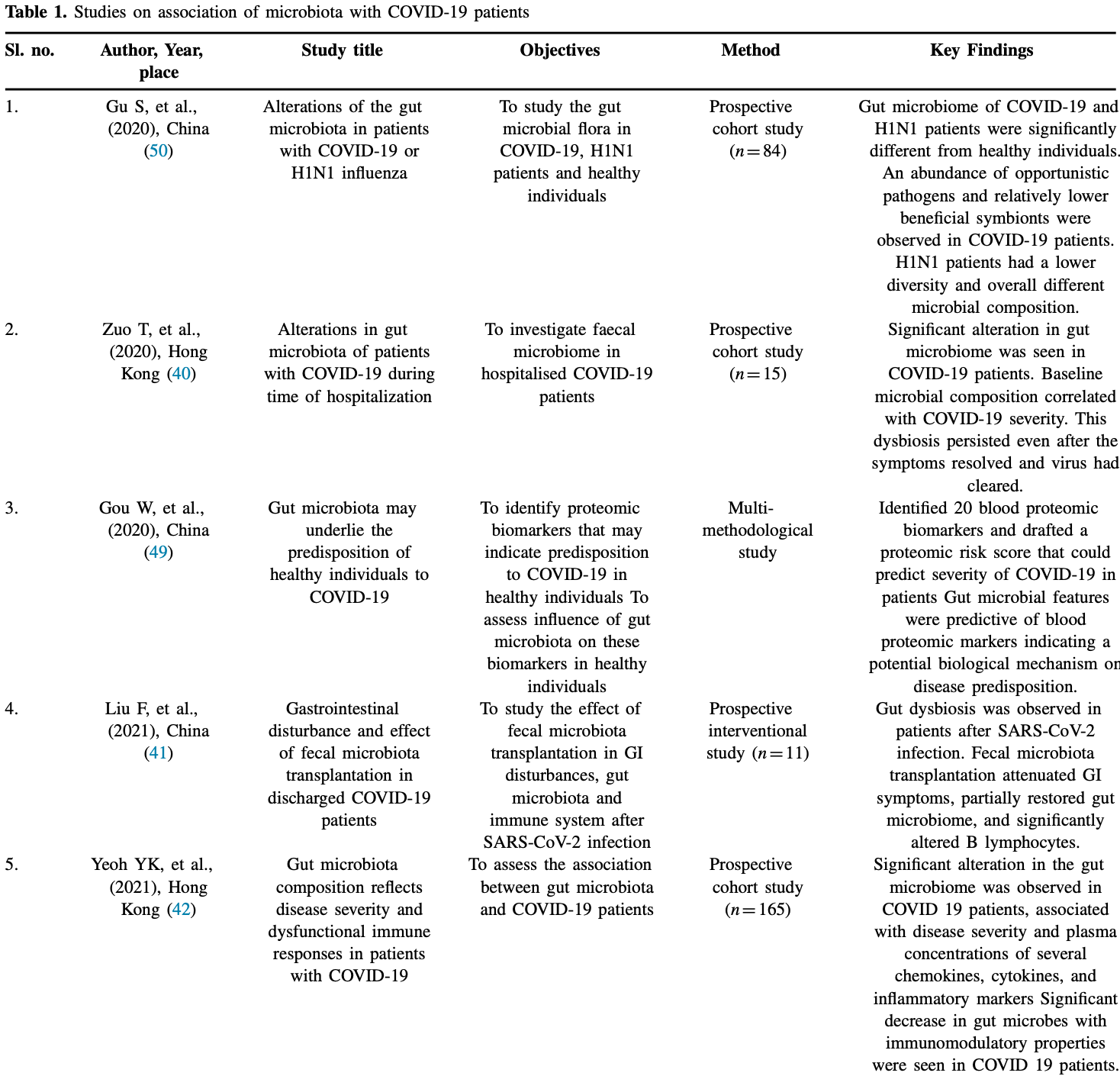
Review of probiotics role in regulating the immune system and use in viral infections, and studies on the association of microbiota with COVID-19 patients. Authors suggest that probiotics supplementation could reduce COVID-19 morbidity and mortality, and they note that probiotics may suppress the inflammatory cytokine response.
1.
Chau et al., Effectiveness of probiotics on COVID-19 prevention and treatment against mild COVID-19 in outpatient care: A systematic review, Nutrition and Health, doi:10.1177/02601060251378200.
2.
Bajić et al., Immunity's core reset: Synbiotics and gut microbiota in the COVID-19 era, Innate Immunity, doi:10.1177/17534259251362023.
3.
Bigman et al., A Comprehensive Scoping Review on Diet and Nutrition in Relation to Long COVID-19 Symptoms and Recovery, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17111802.
4.
Fazli et al., Possible Link between Gut Microbiota, Diet, and COVID-19 Infection, Journal of Medical Bacteriology, 12:4, jmb.tums.ac.ir/index.php/jmb/article/view/525.
5.
Santa et al., Comparative analysis of COVID-19 responses in Japan and Africa: diet, phytochemicals, vitamin D, and gut microbiota in reducing mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1465324.
6.
Kaushal, A., Nutraceuticals and pharmacological to balance the transitional microbiome to extend immunity during COVID-19 and other viral infections, Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05587-9.
7.
Mu et al., Anti-inflammatory and Nutritional Interventions Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Journal of Agriculture and Food Research, doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101422.
8.
Taufer et al., Lactobacilli in COVID-19: A Systematic Review Based on Next-Generation Sequencing Studies, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms12020284.
9.
Righi et al., Gut Microbiome Disruption Following SARS-CoV-2: A Review, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms12010131.
10.
Petrariu et al., Role of probiotics in managing various human diseases, from oral pathology to cancer and gastrointestinal diseases, Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1296447.
11.
Taufer (B) et al., The Role of Bifidobacterium in COVID-19: A Systematic Review, Life, doi:10.3390/life13091847.
12.
Di Pierro, F., A possible probiotic (S. salivarius K12) approach to improve oral and lung microbiotas and raise defenses against SARS-CoV-2, Minerva Medica, doi:10.23736/S0026-4806.20.06570-2.
13.
Kurian et al., Probiotics in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19: Current Perspective and Future Prospects, Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002.
14.
Singh et al., Probiotics: A potential immunomodulator in COVID-19 infection management, Nutrition Research, doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2020.12.014.
15.
Stavropoulou et al., Probiotics as a Weapon in the Fight Against COVID-19, Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2020.614986.
Kurian et al., 19 Mar 2021, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Probiotics in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19: Current Perspective and Future Prospects
Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre -including this research content -immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
Source of Financial Support
None
Competing Interests The authors report no conflicts of interest
Authors' Contribution Dr.Shilia Jacob Kurian and Dr.Sonal Sekhar Miraj conducted the literature search and wrote the manuscript. Dr. B Shrikar Reddy drew the figure I. Dr. Mazhuvancheny Kesavan Unnikrishnan, Dr. Debasis Bagchi, Dr. Mithu Banerjce. Dr. Gabriel Sunil Rodrigues, Dr. Mohan K Manu, Dr. Kavitha Saravu, Dr. Chiranjay Mukhopadhyay and Dr. Mahadev Rao critically evaluated the manuscript. All the authors participated in literature collection and review. All the authors approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Supplementary Materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2021. 03.002.
References
Adnan, Dewi, Potential effects immunomodulators on probiotics in COVID-19 preventing infection in the future. A narrative review, Int J Med Stud, doi:10.5195/ijms.2020.486
Appel-Da-Silva, Narvaez, Perez, Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii fungemia following probiotic treatment, Med Mycol Case Rep
Azad, Sarker, Immunomodulatory effects of probiotics on cytokine profiles, Biomed Res Int
Becker, COVID-19 update: Covid-19-associated coagulopathy, J Thromb Thrombolysis
Bermudez-Brito, Plaza-Díaz, Muñoz-Quezada, Probiotic mechanisms of action, Ann Nutr Metab
Briguglio, Pregliasco, Lombardi, The malnutritional status of the host as a virulence factor for new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Front Med
Budden, Gellatly, Wood, Emerging pathogenic links between microbiota and the gut-lung axis, Nat Rev Microbiol
Carabotti, Scirocco, Maselli, The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems, Ann Gastroenterol
Chai, Burwinkel, Wang, Antiviral effects of a probiotic Enterococcus faecium strain against transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus, Arch Virol
Chen, Zuo, Xue, Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of Lactobacillus helveticus strains from traditional fermented dairy foods and antihypertensive effect of fermented milk of strain H9, J Dairy Sci
Cheung, Hung, Chan, Gastrointestinal manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection and virus load in fecal samples from a Hong Kong cohort: systematic review and meta-analysis, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.065
Dabke, Hendrick, Devkota, The gut microbiome and metabolic syndrome, J Clin Invest
Dai, Wang, Wang, Potential beneficial effects of probiotics on human migraine headache: A literature review, Pain Physician
Daneshkhah, Agrawal, Eshein, The possible role of vitamin D in suppressing cytokine storm and associated mortality in COVID-19 patients, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.08.20058578v4
Dhar, Mohanty, Gut microbiota and covid-19-possible link and implications, Virus Res
Dickson, Arbor, The microbiome and critical illness, Lancet Respir Med
Dinan, Quigley, Ahmed, Hypothalamic-pituitary gut axis dysregulation in irritable bowel syndrome: plasma cytokines as a potential biomarker?, Gastroenterology
Dumas, Bernard, Poquet, The role of the lung microbiota and the gut-lung axis in respiratory infectious diseases, Cell Microbiol
Eguchi, Fujitani, Nakagawa, Prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection with probiotic lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055, Sci Rep
Ellul, Benjamin, Singh, Neurological associations of COVID-19, Lancet Neurol, doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30221-0
Enaud, Prevel, Ciarlo, The gut-lung axis in health and respiratory diseases: a place for inter-organ and inter-kingdom crosstalks, Front Cell Infect Microbiol
Evrard, Coudeyras, Dosgilbert, Dose-dependent immunomodulation of human dendritic cells by the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lcr35, PLoS One
Feng, Wang, Qi, The small intestine, an underestimated site of SARS-CoV-2 infection: from red queen effect to probiotics, doi:10.20944/preprints202003.0161.v1
Fornell, Kawasaki-like inflammatory disease affects children with COVID-19
Foster, Neufeld, Gut-brain axis: how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression, Trends Neurosci
Fujii, Ohtsuka, Lee, Bifidobacterium breve enhances transforming growth factor beta1 signaling by regulating Smad7 expression in preterm infants, J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr
Garcia-Crespo, Chan, Gabryszewski, Lactobacillus priming of the respiratory tract: heterologous immunity and protection against lethal pneumovirus infection, Antiviral Res
Gargar, Divinagracia, When good things go bad: a case series of bacteremia from probiotics, Chest
Gill, Enhancement of immunity in the elderly by dietary supplementation with the probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis HN019, Am J Clin Nutr
Gou, Fu, Yue, Gut microbiota may underlie the predisposition of healthy individuals to COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.22.20076091v1
Gu, Chen, Wu, Alterations of the gut microbiota in patients with COVID-19 or H1N1 influenza, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa709
Guan, Liang, Zhao, Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis, Eur Respir J
Gurung, Li, You, Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology, EBioMedicine
Hanada, Pirzadeh, Carver, Respiratory viral infection-induced microbiome alterations and secondary bacterial pneumonia, Front Immunol
Harata, He, Hiruta, Intranasal administration of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protects mice from H1N1 influenza virus infection by regulating respiratory immune responses, Lett Appl Microbiol
Hill, Guarner, Reid, Expert consensus document. The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol
Horby, Landray, Low-cost dexamethasone reduces death by up to one third in hospitalised patients with severe respiratory complications of COVID-19 (RECOVERY Trial)
Jayawardena, Sooriyaarachchi, Chourdakis, Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: a review, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Jiang, Li, Huang, The gut microbiota and Alzheimer's disease, J Alzheimers Dis
Jones, Martoni, Prakash, Oral supplementation with probiotic L. reuteri NCIMB 30242 increases mean circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D: a post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Jung, Lee, Ngo, Heat-killed Lactobacillus casei confers broad protection against influenza A virus primary infection and develops heterosubtypic immunity against future secondary infection, Sci Rep
Kang, Kim, Hwang, The effect of probiotics on prevention of common cold: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial studies, Korean J Fam Med
Kang, Lee, Ha, Antiviral effects of Lactobacillus ruminis SPM0211 and Bifidobacterium longum SPM1205 and SPM1206 on rotavirus-infected Caco-2 cells and a neonatal mouse model, J Microbiol
Kennedy, King, Baldridge, Mouse microbiota models: comparing germ-free mice and antibiotics treatment as tools for modifying gut bacteria, Front Physiol
Kishino, Takemura, Masaki, Dietary lactosucrose suppresses influenza A (H1N1) virus infection in mice, Biosci Microbiota Food Health
Konieczna, Groeger, Ziegler, Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 administration induces Foxp3 T regulatory cells in human peripheral blood: potential role for myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells, Gut
Kumova, Fike, Thayer, Lung transcriptional unresponsiveness and loss of early influenza virus control in infected neonates is prevented by intranasal Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, PLoS Pathog
Lake, What we know so far: COVID-19 current clinical knowledge and research, Clin Med Lond (Lond), doi:10.7861/clinmed.2019-coron
Lee, Kang, Shin, Antiviral activity of Bifidobacterium adolescentis SPM0212 against hepatitis B virus, Arch Pharm Res
Li, Zhao, Wang, Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides from fermented bovine milk started by Lactobacillus helveticus KLDS.31 and Lactobacillus casei KLDS.105: purification, identification, and interaction mechanisms, Front Microbiol
Liang, Feng, Rao, Diarrhoea may be underestimated: a missing link in 2019 novel coronavirus, Gut
Liu, Katovich, ACE2 and Microbiota: emerging targets for cardiopulmonary disease therapy, J Cardiovasc Pharmacol
Liu, Ye, Zhu, Gastrointestinal disturbance and effect of fecal microbiota transplantation in discharged COVID-19 patients, J Med Case Rep
Locke, UK COVID-19 Update: Dexamethasone praise & scepticism -Medscape
Mak, Chan, Ng, Probiotics and COVID-19: one size does not fit all, Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol
Mammen, Sethi, COPD and the microbiome, Respirology
Meijnikman, Gerdes, Nieuwdorp, Herrema, Evaluating causality of gut microbiota in obesity and diabetes in humans, Endocr Rev
Messaoudi, Lalonde, Violle, Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects, Br J Nutr
Minato, Nirasawa, Sato, B38-CAP is a bacteria-derived ACE2-like enzyme that suppresses hypertension and cardiac dysfunction, Nat Commun
Morshedi, Hashemi, Moazzen, Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review, J Neuroinflammation
Nagpal, Mainali, Ahmadi, Gut microbiome, and aging: physiological and mechanistic insights, Nutr Healthy Aging
Namasivayam, Sher, Glickman, Wipperman, The microbiome and tuberculosis: early evidence for cross talk, mBio
Negi, Das, Pahari, Potential role of gut microbiota in induction and regulation of innate immune memory, Front Immunol
Nishida, Inoue, Inatomi, Gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease, Clin J Gastroenterol
Ostaff, Stange, Wehkamp, Antimicrobial peptides and gut microbiota in homeostasis and pathology, EMBO Mol Med
Park, Ngo, Kwon, Lactobacillus plantarum DK119 as a probiotic confers protection against influenza virus by modulating innate immunity, PLoS One
Plaza-Diaz, Ruiz-Ojeda, Gil-Campos, Mechanisms of action of probiotics, Adv Nutr
Pourhossein, Moravejolahkami, Probiotics in viral infections, with a focus on COVID-19: a systematic review, Prepints, doi:10.22541/au.158938616.61042433
Pradhan, Guha, Naik, and B. clausii modulate gut microbiota in Th1-and Th2-biased mice to ameliorate Salmonella typhimurium-induced diarrhea, Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins
Rai, Sanjukta, Jeyaram, Production of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory (ACE-I) peptides during milk fermentation and their role in reducing hypertension, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr
Renzo, Merra, Esposito, Are probiotics effective adjuvant therapeutic choice in patients with COVID-19?, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, doi:10.26355/eurrev_202004_20977
Rooks, Garrett, Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri.2016.42
Shang, Sun, Vitamin D/VDR, probiotics, and gastrointestinal diseases, Curr Med Chem
Shivakumar, Smibert, Trubiano, Immunosuppression for COVID-19: repurposing medicines in a pandemic, Aust. Prescr, doi:10.18773/austprescr.2020.037
Su, Jia, Li, Probiotics for the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Respir Care
Tang, Kitai, Hazen, Gut microbiota in cardiovascular health and disease, Circ Res
Thaiss, Zmora, Levy, The microbiome and innate immunity, Nature
Thushara, Gangadaran, Solati, Cardiovascular benefits of probiotics: a review of experimental and clinical studies, Food Funct
Tian, Rong, Nian, Review article: gastrointestinal features in COVID-19 and the possibility of faecal transmission, Aliment Pharmacol Ther
Tillisch, Labus, Kilpatrick, Consumption of fermented milk product with probiotic modulates brain activity, Gastroenterology
Umbrello, Esposito, Microbiota and neurologic diseases: potential effects of probiotics, J Transl Med
Undela, Gudi, Assumptions for disparities in case-fatality rates of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) across the globe, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Varatharaj, Thomas, Ellul, Neurological and neuropsychiatric complications of COVID-19 in 153 patients: a UKwide surveillance study, Lancet Psychiatry, doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30287-X
Ver Heul, Planer, Kau, The human microbiota and asthma, Clin Rev Allergy Immunol
Waki, Matsumoto, Fukui, Effects of probiotic Lactobacillus brevis KB290 on incidence of influenza infection among schoolchildren: an open-label pilot study, Lett Appl Microbiol
Wang, Wu, Wang, Antioxidant properties of probiotic bacteria, Nutrients
Wang, Zhu, Qin, Gut microbiota modulation on intestinal mucosal adaptive immunity, J Immunol Res
Weiss, Rasmussen, Zeuthen, Lactobacillus acidophilus induces virus immune defence genes in murine dendritic cells by a Toll-like receptor-2-dependent mechanism, Immunology
West, Jenmalm, Prescott, The gut microbiota and its role in the development of allergic disease: a wider perspective, Clin Exp Allergy
Wu, Liu, Yang, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 Ameliorates Escherichia coli-induced inflammation and cell damage via attenuation of ASC-independent NLRP3 inflammasome activation, Appl Environ Microbiol
Wu, Yoon, Zhang, Vitamin D receptor pathway is required for probiotic protection in colitis, Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol
Xie, Nie, Yu, Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression and regulates Th17/Treg cell immune responses in mice, J Agric Food Chem
Xu, Cai, Shen, Management of corona virus disease-19 (COVID-19): the Zhejiang experience, Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, doi:10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2020.02.02
Yan, Zhang, Li, Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2, Science
Yeoh, Zuo, Lui, Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19, Gut
Yoon, Wu, Zhang, Probiotic regulation of vitamin D receptor in intestinal inflammation, Gastroenterology
Yoon, Zhang, Lu, Probiotic regulation of vitamin D receptor in intestinal inflammation, Gastroenterology
Zelaya, Villena, Lopez, Modulation of the inflammation-coagulation interaction during pneumococcal pneumonia by immunobiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL1505: role of Toll-like receptor 2, Microbiol Immunol
Zeng, Shen, Bo, Cutting edge: probiotics and fecal microbiota transplantation in immunomodulation, J Immunol Res
Zhang, Kang, Gong, The digestive system is a potential route of 2019-nCov infection: a bioinformatics analysis based on single-cell transcriptomes, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.01.30.927806v1
Zhao, Zhang, Li, Incidence, clinical characteristics, and prognostic factor of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.03.17.20037572v1
Zhou, Chi, Lv, Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3377
Zuo, Zhang, Lui, Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002",
"ISSN": [
"0188-4409"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002",
"alternative-id": [
"S0188440921000473"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Probiotics in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19: Current Perspective and Future Prospects"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Archives of Medical Research"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (IMSS). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kurian",
"given": "Shilia Jacob",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Unnikrishnan",
"given": "Mazhuvancherry Kesavan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miraj",
"given": "Sonal Sekhar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bagchi",
"given": "Debasis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Banerjee",
"given": "Mithu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Reddy",
"given": "B. Shrikar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rodrigues",
"given": "Gabriel Sunil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9481-3189",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Manu",
"given": "Mohan K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6399-1129",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Saravu",
"given": "Kavitha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mukhopadhyay",
"given": "Chiranjay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rao",
"given": "Mahadev",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Archives of Medical Research",
"container-title-short": "Archives of Medical Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-20T00:55:56Z",
"timestamp": 1616201756000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-22T01:18:19Z",
"timestamp": 1671671899000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-09T18:30:10Z",
"timestamp": 1715279410806
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 44,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1627776000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0188440921000473?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0188440921000473?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "582-594",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0001",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Rolling updates on coronavirus disease (COVID-19). [updated 31st July 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as-they-happen (Accesed Aug 12, 2020)."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0002",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University. [updated 12th August 2020]. Available from: https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594740fd40299423467b48e9ecf6. (Accessed Aug 12, 2020)."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0003",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. [updated 12th August 2020]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/. (Accessed Aug 12, 2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.08.20058578",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0004",
"unstructured": "Daneshkhah A, Agrawal V, Eshein A, et al.. The possible role of vitamin D in suppressing cytokine storm and associated mortality in COVID-19 patients. MedRxiv 2020.04.08.20058578; Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.08.20058578v4. (Accessed Aug 10, 2020)."
},
{
"article-title": "Assumptions for disparities in case-fatality rates of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) across the globe",
"author": "Undela",
"first-page": "5180",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0005",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0006",
"unstructured": "Zhao X, Zhang B, Li P, et al. Incidence, clinical characteristics, and prognostic factor of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. MedRxiv 2020.03.17.20037572; Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.17.20037572v1. (Accessed Aug 10, 2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18773/austprescr.2020.037",
"article-title": "Immunosuppression for COVID‑19: repurposing medicines in a pandemic",
"author": "Shivakumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106",
"journal-title": "Aust. Prescr",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0007",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Horby",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0008",
"series-title": "Low-cost dexamethasone reduces death by up to one third in hospitalised patients with severe respiratory complications of COVID-19 (RECOVERY Trial)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0009",
"unstructured": "Tim Locke. UK COVID-19 Update: Dexamethasone praise & scepticism - Medscape. Available from: https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/932477 (Accessed Aug 12, 2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/8063647",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory effects of probiotics on cytokine profiles",
"author": "Azad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomed Res Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0010",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12974-019-1611-4",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review",
"author": "Morshedi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "231",
"journal-title": "J Neuroinflammation",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0011",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9050521",
"article-title": "Antioxidant properties of probiotic bacteria",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "521",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0012",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-39602-7",
"article-title": "Prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection with probiotic lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055",
"author": "Eguchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4812",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0013",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cmi.12966",
"article-title": "The role of the lung microbiota and the gut-lung axis in respiratory infectious diseases",
"author": "Dumas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e12966",
"journal-title": "Cell Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0014",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2018.01534",
"article-title": "Mouse microbiota models: comparing germ-free mice and antibiotics treatment as tools for modifying gut bacteria",
"author": "Kennedy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1534",
"journal-title": "Front Physiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0015",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI129194",
"article-title": "The gut microbiome and metabolic syndrome",
"author": "Dabke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4050",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0016",
"volume": "129",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12328-017-0813-5",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease",
"author": "Nishida",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin J Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0017",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2017-00192",
"article-title": "Evaluating causality of gut microbiota in obesity and diabetes in humans",
"author": "Meijnikman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Endocr Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0018",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.051",
"article-title": "Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology",
"author": "Gurung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0019",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.309715",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota in cardiovascular health and disease",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1183",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0020",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/JAD-161141",
"article-title": "The gut microbiota and Alzheimer's disease",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Alzheimers Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0021",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tins.2013.01.005",
"article-title": "Gut-brain axis: how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression",
"author": "Foster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "305",
"journal-title": "Trends Neurosci",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0022",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.00009",
"article-title": "The gut-lung axis in health and respiratory diseases: a place for inter-organ and inter-kingdom crosstalks",
"author": "Enaud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0023",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12016-018-8719-7",
"article-title": "The human microbiota and asthma",
"author": "Ver Heul",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "350",
"journal-title": "Clin Rev Allergy Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0024",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/resp.12732",
"article-title": "COPD and the microbiome",
"author": "Mammen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "590",
"journal-title": "Respirology",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0025",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.01420-18",
"article-title": "The microbiome and tuberculosis: early evidence for cross talk",
"author": "Namasivayam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01418",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0026",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro.2016.142",
"article-title": "Emerging pathogenic links between microbiota and the gut-lung axis",
"author": "Budden",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0027",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems",
"author": "Carabotti",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Ann Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0028",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00427-0",
"article-title": "The microbiome and critical illness",
"author": "Dickson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0029",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/NHA-170030",
"article-title": "Gut microbiome, and aging: physiological and mechanistic insights",
"author": "Nagpal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "267",
"journal-title": "Nutr Healthy Aging",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0030",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature18847",
"article-title": "The microbiome and innate immunity",
"author": "Thaiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0031",
"volume": "535",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2019/4735040",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota modulation on intestinal mucosal adaptive immunity",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Immunol Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0032",
"volume": "2019",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/emmm.201201773",
"article-title": "Antimicrobial peptides and gut microbiota in homeostasis and pathology",
"author": "Ostaff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1465",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0033",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198018",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota and covid-19- possible link and implications",
"author": "Dhar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0034",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.02441",
"article-title": "Potential role of gut microbiota in induction and regulation of innate immune memory",
"author": "Negi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2441",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0035",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12938/bmfh.2015-005",
"article-title": "Dietary lactosucrose suppresses influenza A (H1N1) virus infection in mice",
"author": "Kishino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"journal-title": "Biosci Microbiota Food Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0036",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri.2016.42",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity",
"author": "Rooks",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "341",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0037",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/74.6.833",
"article-title": "Enhancement of immunity in the elderly by dietary supplementation with the probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis HN019",
"author": "Gill",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "833",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0038",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.02640",
"article-title": "Respiratory viral infection-induced microbiome alterations and secondary bacterial pneumonia",
"author": "Hanada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2640",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0039",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048",
"article-title": "Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization",
"author": "Zuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "944",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0040",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13256-020-02583-7",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal disturbance and effect of fecal microbiota transplantation in discharged COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Med Case Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0041",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Yeoh",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0042",
"volume": "0",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.065",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection and virus load in fecal samples from a Hong Kong cohort: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cheung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0043",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15731",
"article-title": "Review article: gastrointestinal features in COVID-19 and the possibility of faecal transmission",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "843",
"journal-title": "Aliment Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0044",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"article-title": "Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1444",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0045",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0046",
"unstructured": "Zhang H, Kang Z, Gong H, et al. The digestive system is a potential route of 2019-nCov infection: a bioinformatics analysis based on single-cell transcriptomes. bioRxiv 2020.01.30.927806; Available from: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.30.927806v1. (Accessed Aug 11, 2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/FJC.0000000000000307",
"article-title": "ACE2 and Microbiota: emerging targets for cardiopulmonary disease therapy",
"author": "Cole-Jeffrey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "540",
"journal-title": "J Cardiovasc Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0047",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2019-coron",
"article-title": "What we know so far: COVID-19 current clinical knowledge and research",
"author": "Lake",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "124",
"journal-title": "Clin Med Lond (Lond)",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0048",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.22.20076091",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0049",
"unstructured": "Gou W, Fu Y, Yue L, et al. Gut microbiota may underlie the predisposition of healthy individuals to COVID-19. medRxiv 2020.04.22.20076091; Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.22.20076091v1. (Accessed Aug 11, 2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa709",
"article-title": "Alterations of the gut microbiota in patients with COVID-19 or H1N1 influenza",
"author": "Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2669",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0050",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66",
"article-title": "Expert consensus document. The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic",
"author": "Hill",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "506",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0051",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2019/1603758",
"article-title": "Cutting edge: probiotics and fecal microbiota transplantation in immunomodulation",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Immunol Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0052",
"volume": "2019",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000342079",
"article-title": "Probiotic mechanisms of action",
"author": "Bermudez-Brito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "160",
"journal-title": "Ann Nutr Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0053",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmy063",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of action of probiotics",
"author": "Plaza-Diaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S49",
"issue": "suppl_1",
"journal-title": "Adv Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0054",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929867323666161202150008",
"article-title": "Vitamin D/VDR, probiotics, and gastrointestinal diseases",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "876",
"journal-title": "Curr Med Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0055",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300936",
"article-title": "Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 administration induces Foxp3 T regulatory cells in human peripheral blood: potential role for myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells",
"author": "Konieczna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "354",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0056",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.mpg.0000228100.04702.f8",
"article-title": "Bifidobacterium breve enhances transforming growth factor beta1 signaling by regulating Smad7 expression in preterm infants",
"author": "Fujii",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0057",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jafc.5b06177",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression and regulates Th17/Treg cell immune responses in mice",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1291",
"journal-title": "J Agric Food Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0058",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AEM.03044-15",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 Ameliorates Escherichia coli-induced inflammation and cell damage via attenuation of ASC-independent NLRP3 inflammasome activation",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1173",
"journal-title": "Appl Environ Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0059",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cea.12332",
"article-title": "The gut microbiota and its role in the development of allergic disease: a wider perspective",
"author": "West",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "43",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Allergy",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0060",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015",
"article-title": "Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: a review",
"author": "Jayawardena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "367",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0061",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2012-4262",
"article-title": "Oral supplementation with probiotic L. reuteri NCIMB 30242 increases mean circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D: a post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Jones",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2944",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0062",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Probiotic regulation of vitamin D receptor in intestinal inflammation",
"author": "Sonia Yoon",
"first-page": "S",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0063",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpgi.00105.2015",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor pathway is required for probiotic protection in colitis",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "G341",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0064",
"volume": "309",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-012-1543-0",
"article-title": "Antiviral effects of a probiotic Enterococcus faecium strain against transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus",
"author": "Chai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "799",
"journal-title": "Arch Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0065",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2019.02643",
"article-title": "Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides from fermented bovine milk started by Lactobacillus helveticus KLDS.31 and Lactobacillus casei KLDS.105: purification, identification, and interaction mechanisms",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2643",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0066",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2015.1068736",
"article-title": "Production of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory (ACE-I) peptides during milk fermentation and their role in reducing hypertension",
"author": "Rai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2789",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0067",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3168/jds.2014-7962",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of Lactobacillus helveticus strains from traditional fermented dairy foods and antihypertensive effect of fermented milk of strain H9",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6680",
"journal-title": "J Dairy Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0068",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.12.022",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus priming of the respiratory tract: heterologous immunity and protection against lethal pneumovirus infection",
"author": "Garcia-Crespo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0069",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1008072",
"article-title": "Lung transcriptional unresponsiveness and loss of early influenza virus control in infected neonates is prevented by intranasal Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG",
"author": "Kumova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0070",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1472-765X.2010.02844.x",
"article-title": "Intranasal administration of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protects mice from H1N1 influenza virus infection by regulating respiratory immune responses",
"author": "Harata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "597",
"journal-title": "Lett Appl Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0071",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-017-17487-8",
"article-title": "Heat-killed Lactobacillus casei confers broad protection against influenza A virus primary infection and develops heterosubtypic immunity against future secondary infection",
"author": "Jung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17360",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0072",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0075368",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus plantarum DK119 as a probiotic confers protection against influenza virus by modulating innate immunity",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e75368",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0073",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0018735",
"article-title": "Dose-dependent immunomodulation of human dendritic cells by the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lcr35",
"author": "Evrard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e18735",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0074",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03301.x",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus acidophilus induces virus immune defence genes in murine dendritic cells by a Toll-like receptor-2-dependent mechanism",
"author": "Weiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "268",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0075",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/lam.12340",
"article-title": "Effects of probiotic Lactobacillus brevis KB290 on incidence of influenza infection among schoolchildren: an open-label pilot study",
"author": "Waki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Lett Appl Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0076",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12272-013-0141-3",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of Bifidobacterium adolescentis SPM0212 against hepatitis B virus",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1525",
"journal-title": "Arch Pharm Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0077",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12275-015-5302-2",
"article-title": "Antiviral effects of Lactobacillus ruminis SPM0211 and Bifidobacterium longum SPM1205 and SPM1206 on rotavirus-infected Caco-2 cells and a neonatal mouse model",
"author": "Kang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "796",
"journal-title": "J Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0078",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22541/au.158938616.61042433",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0079",
"unstructured": "Pourhossein M, Moravejolahkami AR. Probiotics in viral infections, with a focus on COVID-19: a systematic review. Prepints 2020. doi:10.22541/au.158938616.61042433."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5195/ijms.2020.486",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0080",
"unstructured": "Adnan ML, Dewi MD. Potential effects immunomodulators on probiotics in COVID-19 preventing infection in the future. A narrative review. Int J Med Stud 2020. doi:10.5195/ijms.2020.486."
},
{
"article-title": "Management of corona virus disease-19 (COVID-19): the Zhejiang experience",
"author": "Xu",
"first-page": "147",
"journal-title": "Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0081",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4082/kjfm.2013.34.1.2",
"article-title": "The effect of probiotics on prevention of common cold: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial studies",
"author": "Kang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "Korean J Fam Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0082",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4187/respcare.07097",
"article-title": "Probiotics for the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "673",
"journal-title": "Respir Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0083",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0084",
"unstructured": "Fornell D. Kawasaki-like inflammatory disease affects children with COVID-19. Diagnostic and Interventional Cardiology. Available from: https://www.dicardiology.com/article/kawasaki-inflammatory-disease-affects-children-covid-19. (Accessed May 30, 2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00547-2020",
"article-title": "Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0085",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3377",
"article-title": "Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3377",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0086",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00146",
"article-title": "The malnutritional status of the host as a virulence factor for new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Briguglio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0087",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C5FO01190F",
"article-title": "Cardiovascular benefits of probiotics: a review of experimental and clinical studies",
"author": "Thushara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "632",
"journal-title": "Food Funct",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0088",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-14867-z",
"article-title": "B38-CAP is a bacteria-derived ACE2-like enzyme that suppresses hypertension and cardiac dysfunction",
"author": "Minato",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1058",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0089",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11239-020-02134-3",
"article-title": "COVID-19 update: Covid-19-associated coagulopathy",
"author": "Becker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "54",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Thrombolysis",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0090",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1348-0421.12163",
"article-title": "Modulation of the inflammation-coagulation interaction during pneumococcal pneumonia by immunobiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL1505: role of Toll-like receptor 2",
"author": "Zelaya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "416",
"journal-title": "Microbiol Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0091",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Are probiotics effective adjuvant therapeutic choice in patients with COVID-19?",
"author": "Di Renzo",
"first-page": "4062",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0092",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30221-0",
"article-title": "Neurological associations of COVID-19",
"author": "Ellul",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "767",
"journal-title": "Lancet Neurol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0093",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30287-X",
"article-title": "Neurological and neuropsychiatric complications of COVID-19 in 153 patients: a UK-wide surveillance study",
"author": "Varatharaj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "875",
"journal-title": "Lancet Psychiatry",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0094",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-016-1058-7",
"article-title": "Microbiota and neurologic diseases: potential effects of probiotics",
"author": "Umbrello",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "298",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0095",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114510004319",
"article-title": "Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects",
"author": "Messaoudi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "755",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0096",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.043",
"article-title": "Consumption of fermented milk product with probiotic modulates brain activity",
"author": "Tillisch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1394",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0097",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2005.11.033",
"article-title": "Hypothalamic-pituitary gut axis dysregulation in irritable bowel syndrome: plasma cytokines as a potential biomarker?",
"author": "Dinan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "304",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0098",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"article-title": "Potential beneficial effects of probiotics on human migraine headache: A literature review",
"author": "Dai",
"first-page": "E251",
"journal-title": "Pain Physician",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0099",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0100",
"unstructured": "International Scientific Association for probiotics and prebiotics (ISAPP). Probiotics Available from: https://isappscience.org/for-scientists/resources/probiotics/ (Accessed Aug 12, 2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202003.0161.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0101",
"unstructured": "Feng Z, Wang Y, Qi W. The small intestine, an underestimated site of SARS-CoV-2 infection: from red queen effect to probiotics. Preprints.org 2020. doi: 10.20944/preprints202003.0161.v1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320832",
"article-title": "Diarrhoea may be underestimated: a missing link in 2019 novel coronavirus",
"author": "Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1141",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0102",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12602-018-9436-5",
"article-title": "Probiotics L. acidophilus and B. clausii modulate gut microbiota in Th1- and Th2- biased mice to ameliorate Salmonella typhimurium-induced diarrhea",
"author": "Pradhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "887",
"journal-title": "Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0103",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mmcr.2017.07.007",
"article-title": "Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii fungemia following probiotic treatment",
"author": "Appel-da-Silva",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Med Mycol Case Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0104",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2019.02.091",
"article-title": "When good things go bad: a case series of bacteremia from probiotics",
"author": "Gargar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "92A",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0105",
"volume": "155",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0016-5085(11)60075-9",
"article-title": "Probiotic regulation of vitamin D receptor in intestinal inflammation",
"author": "Yoon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0106",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30122-9",
"article-title": "Probiotics and COVID-19: one size does not fit all",
"author": "Mak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "644",
"journal-title": "Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002_bib0107",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 107,
"references-count": 107,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0188440921000473"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Probiotics in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19: Current Perspective and Future Prospects",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "52"
}