Optimal dose and safety of molnupiravir in patients with early SARS-CoV-2: a Phase I, open-label, dose-escalating, randomized controlled study
et al., Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dkab318, NCT04746183, Aug 2021
Dose and safety study of molnupiravir with 18 participants, finding no serious adverse events in short-term followup. There was no significant difference in clinical outcomes. NCT04746183 (history).
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the United Kingdom, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments25.
The United Kingdom focused on expensive high-profit treatments, approving only one low-cost early treatment, which required a prescription and had limited adoption. The high-cost prescription treatment strategy reduces the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminates complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
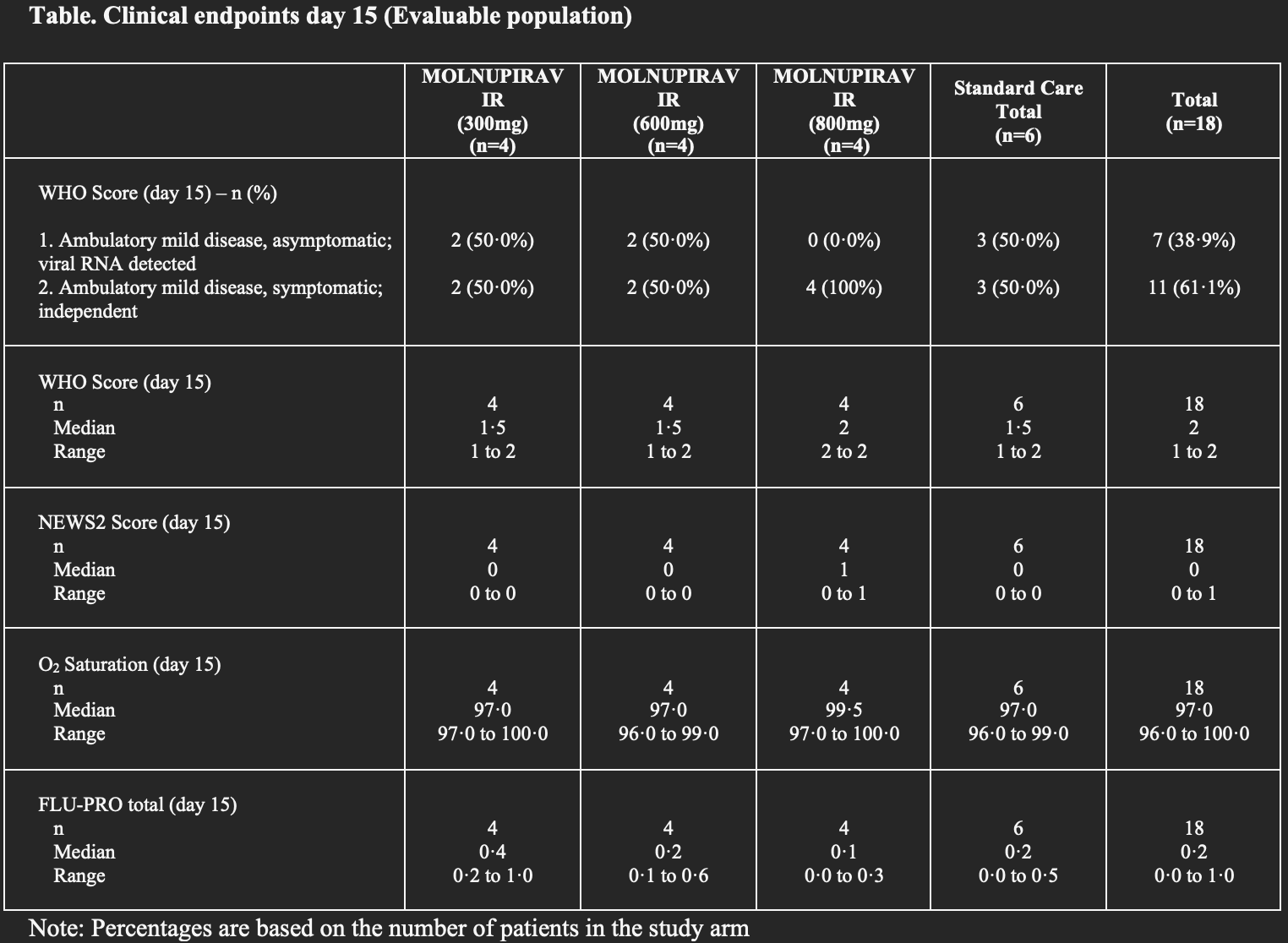
risk of no recovery, 33.3% higher, RR 1.33, p = 0.63, treatment 8 of 12 (66.7%), control 3 of 6 (50.0%), all dosages, symptomatic at day 15.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 100% higher, RR 2.00, p = 0.61, treatment 4 of 12 (33.3%), control 1 of 6 (16.7%), all dosages, symptomatic at day 29.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 100% higher, RR 2.00, p = 0.20, treatment 4 of 4 (100.0%), control 3 of 6 (50.0%), 800mg, symptomatic at day 15.
|
|
risk of no recovery, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 4 (50.0%), control 3 of 6 (50.0%), 600mg, symptomatic at day 15.
|
|
risk of no recovery, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 4 (50.0%), control 3 of 6 (50.0%), 300mg, symptomatic at day 15.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 50.0% higher, RR 1.50, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 4 (25.0%), control 1 of 6 (16.7%), 800mg, symptomatic at day 29.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 200.0% higher, RR 3.00, p = 0.50, treatment 2 of 4 (50.0%), control 1 of 6 (16.7%), 600mg, symptomatic at day 29.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 50.0% higher, RR 1.50, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 4 (25.0%), control 1 of 6 (16.7%), 300mg, symptomatic at day 29.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
23.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Khoo et al., 27 Aug 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, United Kingdom, peer-reviewed, 38 authors, study period 17 July, 2020 - 30 October, 2020, average treatment delay 4.0 days, trial NCT04746183 (history).
Optimal dose and safety of molnupiravir in patients with early SARS-CoV-2: a Phase I, open-label, dose-escalating, randomized controlled study
Objectives: AGILE is a Phase Ib/IIa platform for rapidly evaluating COVID-19 treatments. In this trial (NCT04746183) we evaluated the safety and optimal dose of molnupiravir in participants with early symptomatic infection.
Methods: We undertook a dose-escalating, open-label, randomized-controlled (standard-of-care) Bayesian adaptive Phase I trial at the Royal Liverpool and Broadgreen Clinical Research Facility. Participants (adult outpatients with PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection within 5 days of symptom onset) were randomized 2:1 in groups of 6 participants to 300, 600 and 800 mg doses of molnupiravir orally, twice daily for 5 days or control. A dose was judged unsafe if the probability of 30% or greater dose-limiting toxicity (the primary outcome) over controls was 25% or greater. Secondary outcomes included safety, clinical progression, pharmacokinetics and virological responses. Results: Of 103 participants screened, 18 participants were enrolled between 17 July and 30 October 2020. Molnupiravir was well tolerated at 300, 600 and 800 mg doses with no serious or severe adverse events. Overall, 4 of 4 (100%), 4 of 4 (100%) and 1 of 4 (25%) of the participants receiving 300, 600 and 800 mg molnupiravir, respectively, and 5 of 6 (83%) controls, had at least one adverse event, all of which were mild ( grade 2). The probability of !30% excess toxicity over controls at 800 mg was estimated at 0.9%. Conclusions: Molnupiravir was safe and well tolerated; a dose of 800 mg twice daily for 5 days was recommended for Phase II evaluation.
Author contributions S.H.K., G.G., T.J., S.E., R.F. and P.M. contributed to study design. S.H.K., G.G., T.J., S.E., G.S., K.T., P.M. and H.P. contributed to data analysis and interpretation. R.F. led clinical conduct as the principal investigator of the clinical site. T.F., L.W., R.L. and M.D.B. participated in clinical assessment and data collection. K.F. participated in the management of pharmacovigilance. S.C., E.W., M.R. and L.J. contributed to the digital data collection and data management of the trial. M.R. led set-up of the randomization system. W.G., T.F., V.S., E.A., K.B. and C.H. contributed to study bioanalysis. A.C., N.D., E.M., O.T.-H., S.Y., H.R., J.C., R.L., C.W., J.L.G., A.O., M.J. and D.G.L. contributed to study management and execution. K.M. contributed to monitoring activities. W.P. and W.H. contributed preclinical and safety data on molnupiravir. S.H.K., G.G., M.J., A.O. and D.G.L. were involved in primary manuscript writing. All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript. The statisticians S.E., G.S. and K.T. had full access to all the data in the study and S.H.K. and G.G. had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Disclaimer The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care.
Supplementary data Supplement S1 and Supplement S2 are available as Supplementary data at JAC Online.
References
Cevik, Tate, Lloyd, SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV viral load dynamics, duration of viral shedding, and infectiousness: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Microbe
Cox, Wolf, Plemper, Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets, Nat Microbiol
Griffiths, Fitzgerald, Jaki, AGILE-ACCORD: a randomized, multicentre, seamless, adaptive phase I/II platform study to determine the optimal dose, safety and efficacy of multiple candidate agents for the treatment of COVID-19: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised platform trial, Trials
Mozgunov, Jaki, Paoletti, Randomized dose-escalation designs for drug combination cancer trials with immunotherapy, J Biopharm Stat
Painter, Holman, Bush, Human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of a novel broad-spectrum oral antiviral compound, molnupiravir, with activity against SARS-CoV-2, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Painter, Sheahan, Baric, Reduction in infectious SARS-CoV-2 in treatment study of COVID-19 with molnupiravir
Rosenke, Hansen, Schwarz, Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model, Nat Commun
Wahl, Gralinski, Johnson, SARS-CoV-2 infection is effectively treated and prevented by EIDD-2801, Nature
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkab318",
"ISSN": [
"0305-7453",
"1460-2091"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkab318",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objectives</jats:title>\n <jats:p>AGILE is a Phase Ib/IIa platform for rapidly evaluating COVID-19 treatments. In this trial (NCT04746183) we evaluated the safety and optimal dose of molnupiravir in participants with early symptomatic infection.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We undertook a dose-escalating, open-label, randomized-controlled (standard-of-care) Bayesian adaptive Phase I trial at the Royal Liverpool and Broadgreen Clinical Research Facility. Participants (adult outpatients with PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection within 5 days of symptom onset) were randomized 2:1 in groups of 6 participants to 300, 600 and 800 mg doses of molnupiravir orally, twice daily for 5 days or control. A dose was judged unsafe if the probability of 30% or greater dose-limiting toxicity (the primary outcome) over controls was 25% or greater. Secondary outcomes included safety, clinical progression, pharmacokinetics and virological responses.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Of 103 participants screened, 18 participants were enrolled between 17 July and 30 October 2020. Molnupiravir was well tolerated at 300, 600 and 800 mg doses with no serious or severe adverse events. Overall, 4 of 4 (100%), 4 of 4 (100%) and 1 of 4 (25%) of the participants receiving 300, 600 and 800 mg molnupiravir, respectively, and 5 of 6 (83%) controls, had at least one adverse event, all of which were mild (≤grade 2). The probability of ≥30% excess toxicity over controls at 800 mg was estimated at 0.9%.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Molnupiravir was safe and well tolerated; a dose of 800 mg twice daily for 5 days was recommended for Phase II evaluation.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2769-0967",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool, 70 Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
},
{
"name": "Liverpool University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Prescot Road, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Khoo",
"given": "Saye H",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Liverpool University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Prescot Road, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Fitzgerald",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Liverpool University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Prescot Road, Liverpool, UK"
},
{
"name": "Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Fletcher",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Ewings",
"given": "Sean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Lancaster, Bailrigg, Lancaster, UK"
},
{
"name": "MRC Biostatistics Unit, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK"
}
],
"family": "Jaki",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Liverpool University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Prescot Road, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Lyon",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Downs",
"given": "Nichola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool, 70 Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
},
{
"name": "Liverpool University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Prescot Road, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Tansley-Hancock",
"given": "Olana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool, 70 Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Greenhalf",
"given": "William",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Liverpool University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Prescot Road, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Woods",
"given": "Christie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool, 70 Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Reynolds",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Marwood",
"given": "Ellice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Lancaster, Bailrigg, Lancaster, UK"
}
],
"family": "Mozgunov",
"given": "Pavel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool, 70 Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Bullock",
"given": "Katie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ridgeback Biotherapeutics, 3480 Main Highway, Miami, FL, USA"
}
],
"family": "Holman",
"given": "Wayne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Bula",
"given": "Marcin D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Liverpool University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Prescot Road, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Gibney",
"given": "Jennifer L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Saunders",
"given": "Geoffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Corkhill",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Liverpool University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Prescot Road, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Hale",
"given": "Colin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Thorne",
"given": "Kerensa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool, 70 Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Chiong",
"given": "Justin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Condie",
"given": "Susannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool, 70 Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Pertinez",
"given": "Henry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ridgeback Biotherapeutics, 3480 Main Highway, Miami, FL, USA"
}
],
"family": "Painter",
"given": "Wendy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Wrixon",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "Lucy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Yeats",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Mallard",
"given": "Kim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Radford",
"given": "Mike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Fines",
"given": "Keira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool, 70 Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Liverpool, 70 Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Owen",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK"
}
],
"family": "Lalloo",
"given": "David G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust, Pond Street, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Jacobs",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit, University of Southampton, Tremona Road, Southampton, UK"
}
],
"family": "Griffiths",
"given": "Gareth",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-18T19:15:16Z",
"timestamp": 1629314116000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-21T20:26:06Z",
"timestamp": 1640118366000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Ridgeback Biotherapeutics"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000265",
"award": [
"MR/V028391/1"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Medical Research Council"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100010269",
"award": [
"221590/Z/20/Z"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Wellcome Trust"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000272",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institute for Health Research"
},
{
"name": "Liverpool Clinical Research Facility"
},
{
"name": "Southampton Clinical Trials Unit"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100018956",
"award": [
"BRC-1215–20014"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "NIHR Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000265",
"award": [
"MC_UU_00002/14"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Medical Research Council"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T21:11:55Z",
"timestamp": 1712265115680
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 80,
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
27
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1630022400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jac/article-pdf/76/12/3286/41850133/dkab318.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jac/article-pdf/76/12/3286/41850133/dkab318.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3286-3295",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
27
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30172-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV viral load dynamics, duration of viral shedding, and infectiousness: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cevik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe",
"key": "2021122120254100500_dkab318-B1",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04473-1",
"article-title": "AGILE-ACCORD: a randomized, multicentre, seamless, adaptive phase I/II platform study to determine the optimal dose, safety and efficacy of multiple candidate agents for the treatment of COVID-19: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised platform trial",
"author": "Griffiths",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "544",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "2021122120254100500_dkab318-B2",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03312-w",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection is effectively treated and prevented by EIDD-2801",
"author": "Wahl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2021122120254100500_dkab318-B3",
"volume": "591",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model",
"author": "Rosenke",
"first-page": "2295",
"key": "2021122120254100500_dkab318-B4",
"volume-title": "Nat Commun",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-00835-2",
"article-title": "Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets",
"author": "Cox",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "2021122120254100500_dkab318-B5",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02428-20",
"article-title": "Human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of a novel broad-spectrum oral antiviral compound, molnupiravir, with activity against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Painter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e02428-20",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "2021122120254100500_dkab318-B6",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Painter",
"key": "2021122120254100500_dkab318-B7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10543406.2018.1535503",
"article-title": "Randomized dose-escalation designs for drug combination cancer trials with immunotherapy",
"author": "Mozgunov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "J Biopharm Stat",
"key": "2021122120254100500_dkab318-B8",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 8,
"references-count": 8,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2021.05.03.21256309",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jac/article/76/12/3286/6358705"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmacology",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Optimal dose and safety of molnupiravir in patients with early SARS-CoV-2: a Phase I, open-label, dose-escalating, randomized controlled study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "76"
}