Real-world data concerning the efficacy of molnupiravir in patients vaccinated against COVID-19 during the Omicron surge in Japan
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2451986/v1, Jan 2023
Retrospective 294 consecutive patients in Japan, showing higher risk of hospitalization/death with molnupiravir, without statistical significance.
Potential risks of molnupiravir include the creation of dangerous variants, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity1-15. Multiple analyses have identified variants potentially created by molnupiravir16-20. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury21, cardiovascular toxocity22, and neurological symptoms21. Treatment may increase viral rebound23,24.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
Japan, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments25.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 58.3% lower, RR 0.42, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 84 (0.0%), control 1 of 210 (0.5%), NNT 210, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of death/hospitalization, 127.0% higher, RR 2.27, p = 0.22, treatment 5 of 84 (6.0%), control 8 of 210 (3.8%), odds ratio converted to relative risk, day 28.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 127.0% higher, RR 2.27, p = 0.22, treatment 5 of 84 (6.0%), control 8 of 210 (3.8%), odds ratio converted to relative risk, day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Swanstrom et al., Lethal mutagenesis as an antiviral strategy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abn0048.
2.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
3.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
4.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
5.
Huntsman, M., An assessment of the reproductive toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using stem cell-based embryo models, Master's Thesis, scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/items/cd11342c-b4dc-44c0-8b44-ce6e3369c40b.
6.
Huntsman (B) et al., Detection of developmental toxicity of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir using gastruloid-based in vitro assays, Toxicological Sciences, doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfaf093.
7.
Zibat et al., N4-hydroxycytidine, the active compound of Molnupiravir, promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis and escape from a neutralizing nanobody, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107786.
8.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
9.
Gruber et al., Molnupiravir increases SARS‐CoV‐2 genome diversity and complexity: A case‐control cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.29642.
10.
Marikawa et al., An active metabolite of the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir impairs mouse preimplantation embryos at clinically relevant concentrations, Reproductive Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2023.108475.
11.
Rahman, M., Elucidation of the DNA repair mechanisms involved in the repair of DNA damage caused by the Arabinosides and Anti-COVID-19 drugs, tokyo-metro-u.repo.nii.ac.jp/records/2000972.
12.
Zhou et al., β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab247.
13.
Chamod et al., Molnupiravir Metabolite--N4-hydroxycytidine Causes Cytotoxicity and DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells in vitro: N4-hydroxycytidine Induced Cytotoxicity DNA Damage, Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine, 23:3, asianmedjam.com/index.php/amjam/article/view/1448.
14.
Standing et al., Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0.
15.
Mori et al., Reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxic and DNA-damaging mechanism of N4-hydroxycytidine, a metabolite of the COVID-19 therapeutic drug molnupiravir, Free Radical Research, doi:10.1080/10715762.2025.2469738.
16.
Focosi et al., The fitness of molnupiravir-signed SARS-CoV-2 variants: imputation analysis based on prescription counts and GISAID analyses by country, Intervirology, doi:10.1159/000540282.
17.
Sanderson et al., A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6.
18.
Fountain-Jones et al., Effect of molnupiravir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients: a retrospective observational study, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00393-2.
19.
Kosakovsky Pond et al., Anti-COVID drug accelerates viral evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-023-03248-3.
21.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
22.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
23.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Inaba et al., 15 Jan 2023, retrospective, Japan, preprint, 9 authors.
Real-world data concerning the efficacy of molnupiravir in patients vaccinated against COVID-19 during the Omicron surge in Japan
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-2451986/v1
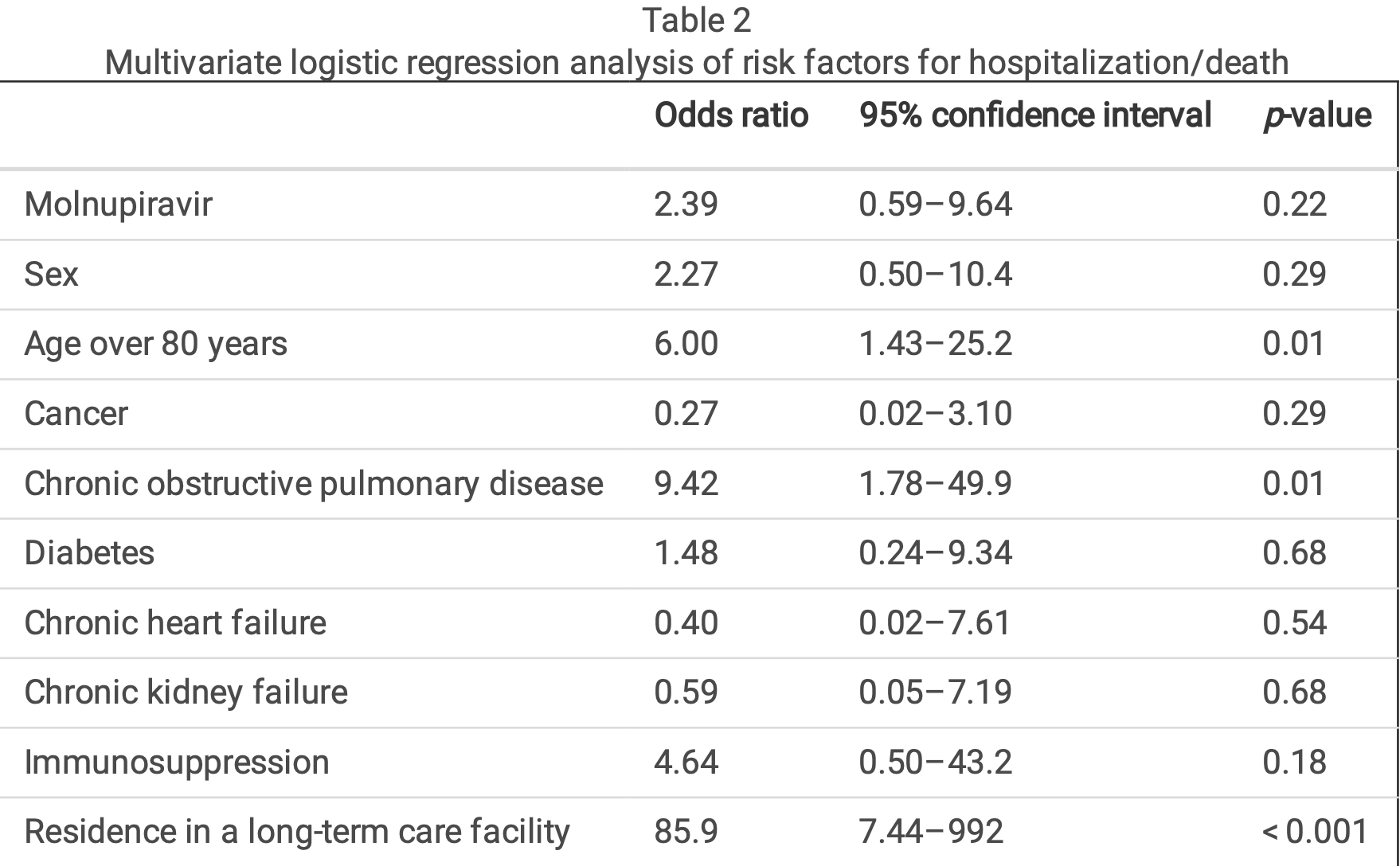
Molnupiravir is among the antiviral agents used to treat COVID-19; however, reported data on the e cacy of this drug are based on results from unvaccinated patients. As such, the e cacy of molnupiravir among vaccinated patients during the B1.1.529 (Omicron) variant outbreak remains unknown. To address this issue, this study retrospectively analyzed data from 294 vaccinated patients with COVID-19 who had at least one risk factor, between May and October 2022. Patients were divided into the molnupiravir group and the control group to investigate the correlations of molnupiravir and other factors with rates of hospitalization and death (hospitalization/death) within 28 days of admission. Potential risk factors were also examined. The study ndings indicated that molnupiravir was not associated with the rate of hospitalization/death, while age ≥ 80 years, residence in a long-term care facility, and presence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease were signi cantly associated with the rate of hospitalization/death. Although the current results suggest that the effect of vaccination in preventing severe illness against the Omicron variant is well maintained, additional studies on risk factors and outcomes are required to validate this study's ndings.
Author Contributions: NN and ND made substantial contributions to the conception of the work. HO, KN, YH, TH, and KO made signi cant contributions to the data analysis and interpretation. SI drafted the original manuscript. NN and other authors substantially contributed to the revision of the manuscript drafts. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Local Ethical Committee of Fukuchiyama City Hospital (Code number 4-26 and date of approval: September 28, 2022).
Informed Consent Statement: Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective design and the ethical guidelines.
Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
References
Abdelnabi, Molnupiravir inhibits replication of the emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in a hamster infection model, J. Infect. Dis
Agostini, Small-molecule antiviral β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine inhibits a proofreading-intact coronavirus with a high genetic barrier to resistance, J. Virol
Andrews, Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against the omicron (B.1.1.529) variant, N. Engl. J. Med
Beigel, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 -Final report, N. Engl. J. Med
Bernal, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N. Engl. J. Med
Butler, Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): An open-label, platformadaptive randomised controlled trial, Lancet
Cox, Wolf, Plemper, Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets, Nat. Microbiol
De, Vito, Safety and e cacy of molnupiravir in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients: A real-life experience, J. Med. Virol
Fan, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Recent progress and future perspectives, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther
Gerayeli, COPD and the risk of poor outcomes in COVID-19: A systematic review and metaanalysis, EClinicalmedicine
Hammond, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
He, Hong, Pan, Lu, Wei, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Characteristics and prevention, Med
Iacobucci, Covid-19: Runny nose, headache, and fatigue are commonest symptoms of omicron, early data show, BMJ
Johansen, Increased SARS-CoV-2 infection, protease, and in ammatory responses in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease primary bronchial epithelial cells de ned with single-cell RNA sequencing, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med
Kamal, Ramadan, Farraj, Bahig, Ezzat, The pill of recovery; Molnupiravir for treatment of COVID-19 patients; a systematic review, Saudi Pharm. J
Kanda, Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software 'EZR' for medical statistics, Bone Marrow Transplant
Lauring, Clinical severity and mRNA vaccine effectiveness for omicron, delta, and alpha SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States: A prospective observational study
Lee, Hsieh, Ko, Molnupiravir-A novel oral anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent, Antibiotics
Nealon, Cowling, Omicron severity: Milder but not mild, Lancet
Nyberg, Comparative analysis of the risks of hospitalisation and death associated with SARS-CoV-2 omicron, Lancet
Pontolillo, Molnupiravir as an early treatment for COVID-19: A real life study, Pathogens
Sheahan, An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice, Sci. Transl. Med
Takashita, E cacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against Covid-19 omicron variant, N. Engl. J. Med
Tenforde, Association between mRNA vaccination and COVID-19 hospitalization and disease severity, JAMA
Thompson, Effectiveness of a third dose of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19-associated emergency department and urgent care encounters and hospitalizations among adults during periods of Delta and omicron variant predominance -VISION network, 10 states, MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep
Ulloa, Buchan, Daneman, Brown, Estimates of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant severity in Ontario, Canada, JAMA
Wahl, SARS-CoV-2 infection is effectively treated and prevented by EIDD-2801, Nature
Wen, E cacy and safety of three new oral antiviral treatment (molnupiravir, uvoxamine and Paxlovid) for COVID-19: a meta-analysis, Ann. Med
Wong, Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong's omicron BA.2 wave: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet Infect. Dis
Yoon, Orally e cacious broad-spectrum ribonucleoside analog inhibitor of in uenza and respiratory syncytial viruses, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother
Zhao, The impact of COPD and smoking history on the severity of COVID-19: A systemic review and meta-analysis, J. Med. Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2451986/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2451986/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Molnupiravir is among the antiviral agents used to treat COVID-19; however, reported data on the efficacy of this drug are based on results from unvaccinated patients. As such, the efficacy of molnupiravir among vaccinated patients during the B1.1.529 (Omicron) variant outbreak remains unknown. To address this issue, this study retrospectively analyzed data from 294 vaccinated patients with COVID-19 who had at least one risk factor, between May and October 2022. Patients were divided into the molnupiravir group and the control group to investigate the correlations of molnupiravir and other factors with rates of hospitalization and death (hospitalization/death) within 28 days of admission. Potential risk factors were also examined. The study findings indicated that molnupiravir was not associated with the rate of hospitalization/death, while age ≥ 80 years, residence in a long-term care facility, and presence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease were significantly associated with the rate of hospitalization/death. Although the current results suggest that the effect of vaccination in preventing severe illness against the Omicron variant is well maintained, additional studies on risk factors and outcomes are required to validate this study’s findings.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
7
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fukuchiyama City Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Inaba",
"given": "Satoshi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fukuchiyama City Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Nishioka",
"given": "Naoya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fukuchiyama City Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Okumura",
"given": "Hisatoshi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fukuchiyama City Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Nakao",
"given": "Koshi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fukuchiyama City Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Hattori",
"given": "Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fukuchiyama City Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Futamura",
"given": "Shun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fukuchiyama City Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Hattori",
"given": "Tomohito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fukuchiyama City Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Okabe",
"given": "Kengo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fukuchiyama City Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Nishiyama",
"given": "Daichi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-16T14:36:12Z",
"timestamp": 1673879772000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-04T12:16:10Z",
"timestamp": 1680610570000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-05T04:43:20Z",
"timestamp": 1680669800369
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1673827200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2451986/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2451986/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00462-7",
"article-title": "Comparative analysis of the risks of hospitalisation and death associated with SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B.1.1.529) and delta (B.1.617.2) variants in England: A cohort study",
"author": "Nyberg T",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1303",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Nyberg, T. et al. Comparative analysis of the risks of hospitalisation and death associated with SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B.1.1.529) and delta (B.1.617.2) variants in England: A cohort study. Lancet 399, 1303–1312 (2022).",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7104e3",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of a third dose of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19-associated emergency department and urgent care encounters and hospitalizations among adults during periods of Delta and omicron variant predominance - VISION network, 10 states, August 2021–January 2022",
"author": "Thompson MG",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep.",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Thompson, M. G. et al. Effectiveness of a third dose of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19-associated emergency department and urgent care encounters and hospitalizations among adults during periods of Delta and omicron variant predominance - VISION network, 10 states, August 2021–January 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 71, 139–145 (2022).",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Orally efficacious broad-spectrum ribonucleoside analog inhibitor of influenza and respiratory syncytial viruses",
"author": "Yoon JJ",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Yoon, J. J. et al. Orally efficacious broad-spectrum ribonucleoside analog inhibitor of influenza and respiratory syncytial viruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62 (2018).",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-00835-2",
"article-title": "Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets",
"author": "Cox RM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Cox, R. M., Wolf, J. D. & Plemper, R. K. Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets. Nat. Microbiol. 6, 11–18 (2021).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abb5883",
"article-title": "An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice",
"author": "Sheahan TP",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Sheahan, T. P. et al. An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 12 (2020).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03312-w",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection is effectively treated and prevented by EIDD-2801",
"author": "Wahl A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Wahl, A. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection is effectively treated and prevented by EIDD-2801. Nature 591, 451–457 (2021).",
"volume": "591",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab361",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir inhibits replication of the emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in a hamster infection model",
"author": "Abdelnabi R",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "749",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Abdelnabi, R. et al. Molnupiravir inhibits replication of the emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in a hamster infection model. J. Infect. Dis. 224, 749–753 (2021).",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Small-molecule antiviral β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine inhibits a proofreading-intact coronavirus with a high genetic barrier to resistance",
"author": "Agostini ML",
"first-page": "93",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Agostini, M. L. et al. Small-molecule antiviral β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine inhibits a proofreading-intact coronavirus with a high genetic barrier to resistance. J. Virol. 93 (2019).",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Jayk Bernal, A. et al. Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 509–520 (2022).",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - Final report",
"author": "Beigel JH",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Beigel, J. H. et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - Final report. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 1813–1826 (2020).",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2119407",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against Covid-19 omicron variant",
"author": "Takashita E",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "995",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Takashita, E. et al. Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against Covid-19 omicron variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 995–998 (2022).",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Hammond, J. et al. Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 1397–1408 (2022).",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/bmt.2012.244",
"article-title": "Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics",
"author": "Kanda Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "452",
"journal-title": "Bone Marrow Transplant.",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 48, 452–458 (2013).",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Molnupiravir-A novel oral anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent",
"author": "Lee CC",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Antibiotics (Basel)",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Lee, C. C., Hsieh, C. C. & Ko, W. C. Molnupiravir-A novel oral anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent. Antibiotics (Basel) 10 (2021).",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07853890.2022.2034936",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of three new oral antiviral treatment (molnupiravir, fluvoxamine and Paxlovid) for COVID-19: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Wen W",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "516",
"journal-title": "Ann. Med.",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Wen, W. et al. Efficacy and safety of three new oral antiviral treatment (molnupiravir, fluvoxamine and Paxlovid) for COVID-19: a meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 54, 516–523 (2022).",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsps.2022.03.002",
"article-title": "The pill of recovery; Molnupiravir for treatment of COVID-19 patients; a systematic review",
"author": "Kamal L",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "508",
"journal-title": "Saudi Pharm. J.",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Kamal, L., Ramadan, A., Farraj, S., Bahig, L. & Ezzat, S. The pill of recovery; Molnupiravir for treatment of COVID-19 patients; a systematic review. Saudi Pharm. J. 30, 508–518 (2022).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28011",
"article-title": "Safety and efficacy of molnupiravir in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients: A real-life experience",
"author": "Vito A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5582",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "De Vito, A. et al. Safety and efficacy of molnupiravir in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients: A real-life experience. J. Med. Virol. 94, 5582–5588 (2022).",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens11101121",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir as an early treatment for COVID-19: A real life study",
"author": "Pontolillo M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Pathogens",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Pontolillo, M. et al. Molnupiravir as an early treatment for COVID-19: A real life study. Pathogens 11 (2022).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-00997-x",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Recent progress and future perspectives",
"author": "Fan Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Fan, Y. et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Recent progress and future perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7, 141 (2022).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n3103",
"article-title": "Covid-19: Runny nose, headache, and fatigue are commonest symptoms of omicron, early data show",
"author": "Iacobucci G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "n3103",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Iacobucci, G. Covid-19: Runny nose, headache, and fatigue are commonest symptoms of omicron, early data show. BMJ 375, n3103 (2021).",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Characteristics and prevention",
"author": "He X",
"first-page": "838",
"journal-title": "Med.",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "He, X., Hong, W., Pan, X., Lu, G. & Wei, X. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Characteristics and prevention. Med. 2, 838–845 (2021).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00056-3",
"article-title": "Omicron severity: Milder but not mild",
"author": "Nealon J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "412",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Nealon, J. & Cowling, B. J. Omicron severity: Milder but not mild. Lancet 399, 412–413 (2022).",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.2274",
"article-title": "Estimates of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant severity in Ontario, Canada",
"author": "Ulloa AC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1286",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Ulloa, A. C., Buchan, S. A., Daneman, N. & Brown, K. A. Estimates of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant severity in Ontario, Canada. JAMA 327, 1286–1288 (2022).",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.19499",
"article-title": "Association between mRNA vaccination and COVID-19 hospitalization and disease severity",
"author": "Tenforde MW",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2043",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Tenforde, M. W. et al. Association between mRNA vaccination and COVID-19 hospitalization and disease severity. JAMA 326, 2043–2054 (2021).",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2119451",
"article-title": "Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against the omicron (B.1.1.529) variant",
"author": "Andrews N",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1532",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "Andrews, N. et al. Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against the omicron (B.1.1.529) variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 1532–1546 (2022).",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical severity and mRNA vaccine effectiveness for omicron, delta, and alpha SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States: A prospective observational study",
"author": "Lauring AS",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Lauring, A. S. et al. Clinical severity and mRNA vaccine effectiveness for omicron, delta, and alpha SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States: A prospective observational study. medRxiv (2022).",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): An open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Butler CC",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref27",
"unstructured": "Butler, C. C. et al. Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): An open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial. Lancet (2022).",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00507-2",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong’s omicron BA.2 wave: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Wong CKH",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1681",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref28",
"unstructured": "Wong, C. K. H. et al. Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong’s omicron BA.2 wave: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22, 1681–1693 (2022).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25889",
"article-title": "The impact of COPD and smoking history on the severity of COVID-19: A systemic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Zhao Q",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1915",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref29",
"unstructured": "Zhao, Q. et al. The impact of COPD and smoking history on the severity of COVID-19: A systemic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 92, 1915–1921 (2020).",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100789",
"article-title": "COPD and the risk of poor outcomes in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Gerayeli FV",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100789",
"journal-title": "EClinicalmedicine",
"key": "ref30",
"unstructured": "Gerayeli, F. V. et al. COPD and the risk of poor outcomes in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalmedicine 33, 100789 (2021).",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202108-1901OC",
"article-title": "Increased SARS-CoV-2 infection, protease, and inflammatory responses in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease primary bronchial epithelial cells defined with single-cell RNA sequencing",
"author": "Johansen MD",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "712",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref31",
"unstructured": "Johansen, M. D. et al. Increased SARS-CoV-2 infection, protease, and inflammatory responses in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease primary bronchial epithelial cells defined with single-cell RNA sequencing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 206, 712–729 (2022).",
"volume": "206",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2451986/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Real-world data concerning the efficacy of molnupiravir in patients vaccinated against COVID-19 during the Omicron surge in Japan",
"type": "posted-content"
}