Effect of Cyproheptadine on Ventilatory Support-free Days in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: An Open-label, Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24482, NCT04979221, Jun 2023
RCT 40 critically ill COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in outcomes with cyproheptadine.
Cyproheptadine is a serotonin (5-HT) receptor antagonist, particularly at 5-HT2 receptors. Its effects may depend heavily on disease stage. In early disease it may reduce platelet hyperactivation: excessive platelet activation, platelet reactivity, and platelet-leukocyte aggregates are recognized as a pathogenic feature of COVID-19. Among the mediators released from activated platelet granules, serotonin is unique in that its clearance relies heavily on a healthy pulmonary endothelium, which is known to be injured in COVID-19. Cyproheptadine may also prevents serotonin accumulation: early blockade prevents the cycle of platelet activation → serotonin release → endothelial injury → more inflammation. Additionally, cyproheptadine has anti-inflammatory effects.
However in late stage disease, anticholinergic adverse events may cause significant harm. Cyproheptadine may also cause vasomotor disruption: blocking 5-HT2 receptors could worsen ventilation-perfusion matching; and loss of compensatory mechanisms: serotonin plays complex roles in vascular tone regulation that may be compensatory in severe lung injury. Once severe endothelial injury and thromboinflammation are established, blocking serotonin receptors alone cannot reverse the damage.
|
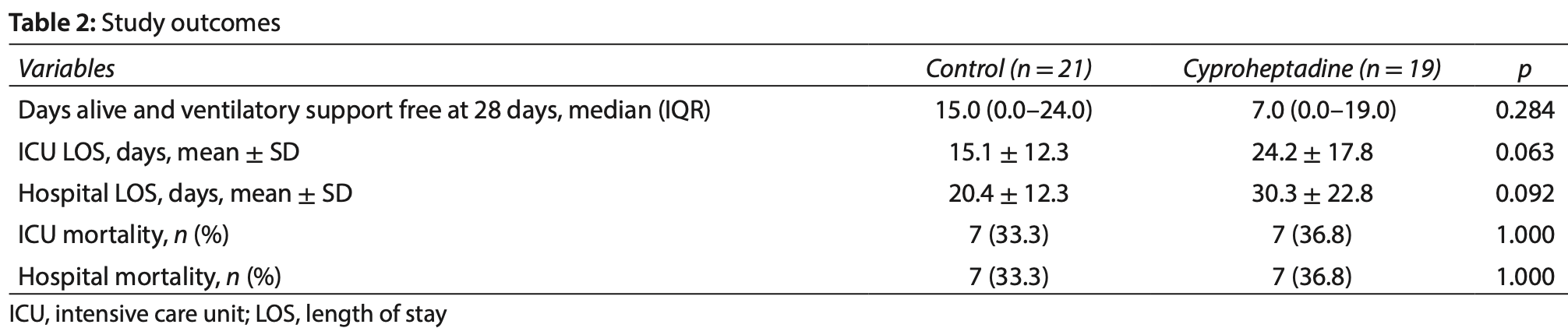
risk of death, 10.5% higher, RR 1.11, p = 1.00, treatment 7 of 19 (36.8%), control 7 of 21 (33.3%).
|
|
hospitalization time, 48.5% higher, relative time 1.49, p = 0.09, treatment mean 30.3 (±22.8) n=19, control mean 20.4 (±12.3) n=21.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Boniatti et al., 30 Jun 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period July 2021 - December 2021, average treatment delay 9.32 days, trial NCT04979221 (history).
Effect of Cyproheptadine on Ventilatory Support-free Days in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: An Open-label, Randomized Clinical Trial
Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24482
Background: Serotonin is a mediator of pulmonary hypoxic vasoconstriction. Experimental studies have shown that serotonin-mediated pulmonary vasoconstriction can be inhibited by cyproheptadine. The aim of this study is to assess whether treatment with cyproheptadine compared to usual care increases ventilatory support-free days during the first 28 days in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) requiring ventilatory support. Materials and methods: This randomized, single-center, open-label clinical trial included patients who were admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) requiring ventilatory support due to COVID-19. Patients allocated to the intervention group received cyproheptadine for 10 days. The primary outcome was ventilator-free days during the first 28 days. Results: Nineteen patients were randomized to receive cyproheptadine and 21 to the control group. The number of ventilatory support-free days during the first 28 days was not different between the two groups (15.0; 95% CI, 0.0-24.0 days in the control group vs 7.0; 95% CI, 0.0-19.0 days in the intervention group; p = 0.284).
Conclusion: In patients with COVID-19 and in need of ventilatory support, the use of cyproheptadine plus usual care, compared with usual care alone, did not increase the number of ventilatory support-free days in 28 days.
AutHors' contributions Márcio MB, Wagner LN, Marcos FR, Patricia S, Edino P, Miriane MSM and Thiago CL have made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the study and to acquisition of data; Márcio MB and Thiago CL performed the analysis and the interpretation of data; all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
References
Carsana, Sonzogni, Nasr, Rossi, Pellegrinelli et al., Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a series of COVID-19 cases from northern Italy: A two-centre descriptive study, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30434-5
Comer, Cullivan, Szklanna, Weiss, Cullen et al., COVID-19 induces a hyperactive phenotype in circulating platelets, bioRxiv medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.07.24.20156240.
Daicoff, Chavez, Anton, Swenson, Serotonin-induced pulmonary venous hypertension in pulmonary embolism, J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg
Facente, Reiersen, Lenze, Boulware, Klausner, Fluvoxamine for the early treatment of sars-cov-2 infection: A review of current evidence, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-021-01636-5
Hashimoto, Suzuki, Hashimoto, Old drug fluvoxamine, new hope for COVID-19, Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, doi:10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z
Hottz, Azevedo-Quintanilha, Palhinha, Teixeira, Barreto et al., Platelet activation and platelet-monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.2020007252
Ishima, Fujita, Hashimoto, Interaction of new antidepressants with sigma-1 receptor chaperones and their potentiation of neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.064
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
Maatman, Jalali, Feizpour, Douglas A 2nd, Mcguire et al., Routine venous thromboembolism prophylaxis may be inadequate in the hypercoagulable state of severe Coronavirus disease 2019, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000004466
Manne, Denorme, Middleton, Portier, Rowley et al., Platelet gene expression and function in patients with COVID-19, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.2020007214
Mcgoon, Vanhoutte, Aggregating platelets contract isolated canine pulmonary arteries by releasing 5-hydroxytryptamine, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI111499
Menga, Cese, Bongiovanni, Lombardi, Michi et al., High failure rate of noninvasive oxygenation strategies in critically ill subjects with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure due to COVID-19, Respir Care, doi:10.4187/respcare.08622
Moll, Zon, Sylvester, Chen, Cheng et al., VTE in ICU Patients With COVID-19, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.07.031
Reis, Santos Moreira-Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: The TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
Skurikhin, Andreeva, Khmelevskaya, Ermolaeva, Pershina et al., Effect of antiserotonin drug on the development of lung fibrosis and blood system reactions after intratracheal administration of bleomycin, Bull Exp Biol Med, doi:10.1007/s10517-012-1567-1
Zaid, Guessous, Puhm, Elhamdani, Chentoufi et al., Platelet reactivity to thrombin differs between patients with COVID-19 and those with ARDS unrelated to COVID-19, Blood Adv, doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003513
Zaid, Puhm, Allaeys, Naya, Oudghiri et al., Platelets Can Associate with SARS-Cov-2 RNA and Are Hyperactivated in COVID-19, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317703
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24482",
"ISSN": [
"0972-5229",
"1998-359X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24482",
"alternative-id": [
"10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24482"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moretti",
"given": "Miriane Melo Silveira",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boniatti",
"given": "Márcio Manozzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nedel",
"given": "Wagner Luis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rihl",
"given": "Marcos Frata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schwarz",
"given": "Patricia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parolo",
"given": "Edino",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lisboa",
"given": "Thiago Costa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-30T11:10:12Z",
"timestamp": 1688123412000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-19T12:10:50Z",
"timestamp": 1689768650000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-19T12:40:42Z",
"timestamp": 1689770442895
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.ijccm.org/doi/pdf/10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24482",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2914",
"original-title": [],
"page": "517-521",
"prefix": "10.5005",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishing",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref=1",
"unstructured": "1. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. Available from: www.covid19.who.int."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30434-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=2",
"unstructured": "2. Carsana L, Sonzogni A, Nasr A, Rossi RS, Pellegrinelli A, Zerbi P, et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a series of COVID-19 cases from northern Italy: A two-centre descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis 2020;20(10):1135–1140. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30434-5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020007214",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=3",
"unstructured": "3. Manne BK, Denorme F, Middleton EA, Portier I, Rowley JW, Stubben C, et al. Platelet gene expression and function in patients with COVID-19. Blood 2020;136(11):1317–1329. DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020007214."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020007252",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=4",
"unstructured": "4. Hottz ED, Azevedo-Quintanilha IG, Palhinha L, Teixeira L, Barreto EA, Pão CRR, et al. Platelet activation and platelet-monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19. Blood 2020;136(11):1330–1341. DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020007252."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317703",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=5",
"unstructured": "5. Zaid Y, Puhm F, Allaeys I, Naya A, Oudghiri M, Khalki L, et al. Platelets Can Associate with SARS-Cov-2 RNA and Are Hyperactivated in COVID-19. Circ Res 2020;127(11):1404–1418. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317703."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003513",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=6",
"unstructured": "6. Zaid Y, Guessous F, Puhm F, Elhamdani W, Chentoufi L, Morris AC, et al. Platelet reactivity to thrombin differs between patients with COVID-19 and those with ARDS unrelated to COVID-19. Blood Adv 2021;5(3):635–639. DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003513."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0022-5223(19)42776-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=7",
"unstructured": "7. Daicoff GR, Chavez FR, Anton AH, Swenson EW. Serotonin-induced pulmonary venous hypertension in pulmonary embolism. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1968;56(6):810–816. PMID: 5722112."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI111499",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=8",
"unstructured": "8. McGoon MD, Vanhoutte PM. Aggregating platelets contract isolated canine pulmonary arteries by releasing 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Clin Invest 1984;74(3):828–833. DOI: 10.1172/JCI111499."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10517-012-1567-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=9",
"unstructured": "9. Skurikhin EG, Andreeva TV, Khmelevskaya ES, Ermolaeva LA, Pershina OV, Krupin VA, et al. Effect of antiserotonin drug on the development of lung fibrosis and blood system reactions after intratracheal administration of bleomycin. Bull Exp Biol Med 2012;152(4):519–523. DOI: 10.1007/s10517-012-1567-1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=10",
"unstructured": "10. Lenze EJ, Mattar C, Zorumski CF, Stevens A, Schweiger J, Nicol GE, et al. Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2020;324(22):2292–2300. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.22760."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=11",
"unstructured": "11. Reis G, Dos Santos Moreira-Silva EA, Silva DCM, Thabane L, Milagres AC, Ferreira TS, et al. Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: The TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial. Lancet Glob Health 2022;10(1):e42–e51. DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-021-01636-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=12",
"unstructured": "12. Facente SN, Reiersen AM, Lenze EJ, Boulware DR, Klausner JD. Fluvoxamine for the early treatment of sars-cov-2 infection: A review of current evidence. Drugs 2021;81(18):2081–2089. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-021-01636-5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=13",
"unstructured": "13. Hashimoto Y, Suzuki T, Hashimoto K. Old drug fluvoxamine, new hope for COVID-19. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2022;272(1):161–163. DOI: 10.1007/s00406-021-01326-z."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4187/respcare.08622",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=14",
"unstructured": "14. Menga LS, Cese LD, Bongiovanni F, Lombardi G, Michi T, Luciani F, et al. High failure rate of noninvasive oxygenation strategies in critically ill subjects with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure due to COVID-19. Respir Care 2021;66(5):705–714. DOI: 10.4187/respcare.08622."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.24.20156240",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=15",
"unstructured": "15. Comer SP, Cullivan S, Szklanna PB, Weiss L, Cullen S, Kelliher S, et al. COVID-19 induces a hyperactive phenotype in circulating platelets. bioRxiv medRxiv 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.24.20156240."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.07.031",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=16",
"unstructured": "16. Moll M, Zon RL, Sylvester KW, Chen EC, Cheng V, Connell NT, et al. VTE in ICU Patients With COVID-19. Chest 2020;158(5):2130–2135. DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.07.031."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000004466",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=17",
"unstructured": "17. Maatman TK, Jalali F, Feizpour C, Douglas A 2nd, McGuire SP, Kinnaman G, et al. Routine venous thromboembolism prophylaxis may be inadequate in the hypercoagulable state of severe Coronavirus disease 2019. Crit Care Med 2020;48(9):e783–e790. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004466."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.064",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref=18",
"unstructured": "18. Ishima T, Fujita Y, Hashimoto K. Interaction of new antidepressants with sigma-1 receptor chaperones and their potentiation of neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 2014;727:167–173. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.064."
}
],
"reference-count": 18,
"references-count": 18,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ijccm.org/doi/10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24482"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of Cyproheptadine on Ventilatory Support-free Days in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: An Open-label, Randomized Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "27"
}